Dec 2, 2014 | Article, Volume 4 - Issue 5
Elizabeth Villares, Kimberly Colvin, John Carey, Linda Webb, Greg Brigman, Karen Harrington
This study examines the convergent validity and divergent validity of the Student Engagement in School Success Skills (SESSS) survey. The SESSS is easy to administer (it takes fewer than 15 minutes to complete) and is used in schools to provide educators with useful information about students’ use of skills and strategies related to school success. A total of 4,342 fifth graders completed the SESSS; the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) Cognitive Strategy Use, Self-Regulation, Self-Efficacy and Test Anxiety subscales; and the Self-Efficacy for Self-Regulated Learning (SESRL). The three subscales of the SESSS (Self-Direction of Learning, Support of Classmates’ Learning and Self-Regulation of Arousal) correlated highly with the MSLQ Cognitive Strategy Use and Self-Regulation subscales, moderately correlated with the Self-Efficacy subscale and the SESRL, and did not correlate with the MSLQ Test Anxiety subscale. Future research is needed to use the SESSS subscales as discriminable dimensions.
Keywords: school success, convergent validity, divergent validity, Student Engagement in School Success Skills survey, educators
For more than a decade, researchers have placed increased emphasis on evidence-based practice and a programmatic approach to school counseling (Carey, 2004; Green & Keys, 2001; Gysbers, 2004; Lapan, 2005; Myrick, 2003; Paisley & Hayes, 2003; Whiston, 2002, 2011). This emphasis from the school counseling profession reflects national initiatives. In 2001, the Institute of Education Sciences, the research arm of the U.S. Department of Education, was established to determine, through rigorous and relevant research, what interventions are effective and ineffective for improving student achievement and education outcomes. The What Works Clearinghouse (WWC), an initiative of the Institute of Education Sciences, was created in 2002 to identify studies that provide credible and reliable evidence of the effectiveness of education interventions. The purpose of WWC is to inform researchers, educators and policymakers of interventions designed to improve student outcomes.
The American School Counselor Association’s (ASCA, 2005) response to emerging national policy and initiatives included a call for school counselor-led interventions that contribute to increased student achievement as part of a comprehensive school counseling program. The need for more research to identify evidence-based interventions tying school counselors to improved student academic performance also surfaced in a school counseling Delphi study, which identified the most pressing research questions in the profession (Dimmitt, Carey, McGannon, & Henningson, 2005). The top priority cited by this Delphi study was the need to determine which school counseling interventions resulted in the greatest student achievement gains. In addition, five major reviews of school counseling research all discussed the need for more research to strengthen the link between school counselor interventions and student achievement (Brown & Trusty, 2005; Dimmitt, Carey, & Hatch, 2007; Whiston & Quinby, 2009; Whiston & Sexton, 1998; Whiston, Tai, Rahardja, & Eder, 2011). However, researchers continue to report limitations in the school counseling outcome research. Among the limitations are conclusions drawn from studies based on nonstandardized outcome assessments. For instance, in a review of school counseling studies, Brown and Trusty (2005) concluded that school counseling research has been limited by the lack of valid and reliable instruments that measure the skills, strategies and personal attributes associated with academic and social/relationship success. More recently, Whiston et al. (2011) completed a meta-analytic examination of school counseling interventions and also determined the dominance of nonstandardized outcome assessments in school counseling research as a significant limitation. These limitations continue to be a hindrance for the school counseling profession, given the goal of establishing evidence-based practices that link school counselor interventions to improved student outcomes. The current WWC’s Procedures and Standards Handbook (WWC, 2011) includes review procedures for evaluating studies that determine a particular intervention to be effective in improving student outcomes. The handbook provides nine reasons why a study under review would fail to meet WWC standards for rigorous research. Among the reasons is a failure to use reliable and valid outcome measures.
While a few valid instruments have recently been developed to measure school counseling outcomes (Scarborough, 2005; Sink & Spencer, 2007; Whiston & Aricak, 2008), they do not measure student changes in knowledge and skills related to academic achievement. The Student Engagement in School Success Skills survey (SESSS; Carey, Brigman, Webb, Villares, & Harrington, 2013) was developed to measure student use of the skills and strategies that were (a) identified as most critical for long-term school success and (b) could be taught by school counselors within the scope of the ASCA National Model, through classroom guidance. The importance of continuing to evaluate the psychometric properties of the SESSS lies in the fact that, for school counselors, there has typically been no standardized way to measure these types of outcomes and tie them directly to school counselor interventions. Previous studies on self-report measures of student metacognition indicate that it is feasible to develop such a measure for elementary-level students (Sperling, Howard, Miller, & Murphy, 2002; Yildiz, Akpinar, Tatar, & Ergin, 2009). The foundational concepts, skills and strategies of metacognition as well as the social skills and self-management skills taught in the Student Success Skills (SSS) program are developmentally appropriate for grades 4–10. The questions for the SESSS were developed to parallel these key strategies and skills taught in the SSS program. The instrument was tested for readability and is appropriate for grade 4 and above.
The SESSS is a self-report measure of students’ use of key skills and strategies that have been identified consistently over several decades as critically important to student success in school, as noted in large reviews of educational research literature (Hattie, Biggs, & Purdie, 1996; Masten & Coatsworth, 1998; Wang, Haertel, & Walberg, 1994a). Three skill sets have emerged from this research literature as common threads in contributing to student academic success and social competence: (a) cognitive and metacognitive skills such as goal setting, progress monitoring and memory skills; (b) social skills such as interpersonal skills, social problem solving, listening and teamwork skills; and (c) self-management skills such as managing attention, motivation and anger (Villares, Frain, Brigman, Webb, & Peluso, 2012). Additional research in support of these skills and strategies continues to weave a coherent research tapestry that is useful in separating successful students from students at risk of academic failure (Durlak, Weissberg, Dymnicki, Taylor, & Schellinger, 2011; Greenberg et al., 2003; Marzano, Pickering, & Pollock, 2001; Zins, Weissberg, Wang, & Walberg, 2004).
Linking school counseling programs and interventions to improved student outcomes has become increasingly important (Carey et al., 2013). One way for school counselors to demonstrate the impact of classroom guidance and small group counseling on achievement is by measuring the impact of their interventions on intermediate variables associated with achievement. These intermediate variables include the previously mentioned skills and strategies involving cognitive, social and self-management. Instruments that measure these critically important fundamental learning skills and strategies are limited.
The present article explores the convergent and divergent validity of the SESSS (Carey et al., 2013). The article builds upon previous research describing the item development of the SESSS and exploratory factor analysis (Carey et al., 2013) and a recently completed confirmatory factor analysis (Brigman et al., 2014). The current findings contribute to the establishment of the SESSS as a valid instrument for measuring the impact of school counselor-led interventions on intermediate variables associated with improved student achievement.
Method
The data collected on the SESSS occurred within the context of a multiyear, large-scale, randomized control trial funded through the U.S. Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences. The purpose of the grant was to investigate the effectiveness of the SSS program (Brigman & Webb, 2010) with fifth graders from two large school districts (Webb, Brigman, Carey, & Villares, 2011). In order to guard against researcher bias, the authors hired data collectors to administer the SESSS, Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) and Self-Efficacy for Self-Regulated Learning (SESRL), and standardized the training and data collection process. The authors selected these particular surveys because they reflected factors known to be related to effective learning in different ways and because they provided a range of measures, some of which were theoretically related to the SESSS and some of which were not.
Procedures
During the 2011–2012 academic year, graduate students who were enrolled in master’s-level Counselor Education programs at two universities were hired and trained in a one-day workshop to administer the SESSS, MSLQ and SESRL and handle data collection materials. At the training, each data collector was assigned to five of the 60 schools across two school districts. After obtaining approvals from the university institutional review board and school district, the research team members notified parents of fifth-grade students of the study via district call-home systems and sent a letter home explaining the study, risks, benefits, voluntary nature of the study and directions on how to decline participation. One month later, data collectors entered their assigned schools and participating classrooms to administer the study instruments. Prior to administering the instruments, each data collector read aloud the student assent. Students who gave their assent were instructed to place a precoded generic label at the top of their instrument, and then each data collector read aloud the directions, along with each item and possible response choice on the SESSS, MSLQ and SESRL. Each assigned data collector was responsible for distributing, collecting and returning all the completed instruments to a district project coordinator once the data collector left the school building according to the Survey Data Collection Manual. In addition, the data collector noted any student absences and/or irregularities, and confirmed that all procedures were followed.
The district project coordinators were responsible for verifying that all materials were returned and secured in a locked cabinet until they were ready to be shipped to a partner university for data analysis. The coordinators gathered demographic information from the district databases and matched it to the participating fifth-grade students and the precoded instrument labels through a generic coding system (district #1–2, school #1–30, classroom #1–6, student #1–25). The coordinators then saved the demographic information in a password-protected and encrypted Excel spreadsheet on an external device and shipped it to a partner university for data analysis.
Participants
A total of 4,342 fifth-grade students in two large school districts completed the SESSS. The following is the demographic profile of the total participants: (a) gender = 2,150 (49.52%) female and 2,192 (50.48%) male; (b) ethnicity = 149 (3.43%) Asian, 1,502 (34.59%) Black, 865 (19.92%) Hispanic, 18 (.42%) Native American, 125 (2.88%) Multiracial, 1,682 (38.74%) White, and 1 (.02%) no response; (c) socioeconomic status = 1,999 (46.04%) noneconomically disadvantaged and 2,343 (53.96%) economically disadvantaged; (d) disability = 3,677 (84.68%) nondisabled and 665 (15.32%) disabled; (e) 504 status = 4,155 (95.70%) non-504 and 187 504 (4.3%); and (f) English language learners (ELL) = 3,999 (92.1%) non-ELL and 343 (7.9%) ELL students. Demographic information for fifth-grade students in each school district is reported in Table 1.
Table 1
Fifth-Grade Student Participant Demographics by School District
|
Demographic Characteristics
|
District 1
(n = 2,162)
|
District 2
(n = 2,180)
|
|
|
|
| Gender |
FemaleMale |
1,080 (49.90%)
1,082 (50.10%)
|
1,070 (49.10%)
1,110 (50.90%)
|
| Ethnicity |
AsianBlack
Hispanic
Native American
Multiracial
White
No response |
89 (04.12%)
899 (41.58%)
165 (07.63%)
7 (00.32%)
64 (02.95%)
938 (43.40%)
—-
|
60 (02.75%)
603 (27.66%)
700 (32.11%)
11 (00.50%)
61 (02.80%)
744 (34.13%)
1 (00.05%)
|
| SES |
Non-economically disadvantagedEconomically disadvantaged |
1,118 (51.71%)
1,044 (48.29%)
|
881 (40.41%)
1,299 (59.59%)
|
| Disability |
NondisabledDisabled |
1,847 (85.43%)
315 (14.57%)
|
1,830 (83.94%)
350 (16.06%)
|
| 504 Status |
Non-504504 |
2,108 (97.50%)
54 (02.50%)
|
2,047 (93.90%)
133 (06.10%)
|
| English language learners |
Non-ELLELL |
1,968 (91.03%)
194 (08.97%)
|
2,031 (93.17%)
149 (06.83%)
|
Note. n = number of students enrolled in the district; SES = socioeconomic status; ELL = English language learners.
Instruments
Student Engagement in School Success Skills. The SESSS (Carey et al., 2013) was developed to measure the extent to which students use the specific strategies that researchers have shown relate to enhanced academic achievement (Hattie et al., 1996; Masten & Coatsworth, 1998; Wang et al., 1994b). Survey items were written to assess students’ cognitive and metacognitive skills (e.g., goal setting, progress monitoring, memory skills), social skills (e.g., communication skills, social problem solving, listening, teamwork skills) and self-management skills (e.g., managing attention, motivation, anger). After the initial pool of items was developed, items were reviewed by an expert panel of elementary educators and school counselors and subjected to a readability analysis using the Lexile Framework for Reading system (MetaMetrics, 2012). At each stage of review, minor changes were made to improve clarity on several items.
Twenty-seven self-report items (plus six additional items used to control for response set) were assembled into a scale with the following directions: “Below is a list of things that some students do to help themselves do better in school. No one does all these things. No one does any of these things all the time. Please think back over the last two weeks and indicate how often you did each of these things in the last two weeks. Please follow along as each statement is read and circle the answer that indicates what you really did. Please do your best to be as accurate as possible. There are no right or wrong answers. We will not share your answers with your parents or teachers. We will not grade your answers.”
The response format included four options that reflected frequency of strategy use in the last two weeks: “I didn’t do this at all,” “I did this once,” “I did this two times” and “I did this three or more times.” This response format was not conducive to writing clear negatively worded items; therefore, six additional items were developed to help control for response set. Three of these additional items reflected strategies that elementary students were unlikely to use (e.g., searching the Internet for additional math problems to complete). Three items reflected strategies that elementary students were likely to use (e.g., asking a friend when homework was due), but they were not covered in the SSS program.
Based on a previous administration of the SESSS to 262 elementary students in the fourth through eighth grades, Carey et al. (2013) reported an overall alpha coefficient for reliability for the 27-item scale to be .91, and coefficient alphas for each grade ranged between .87 (for fifth grade) and .95 (for seventh grade). All items correlated well with the total scale (ranging between .34 and .63). Scores on the total scale were distributed approximately normally: M =65.83, SD = 15.44.
In addition, Carey et al., (2013) found in an exploratory factor analysis of the SESSS scores of 402 fourth through sixth graders that a four-factor solution provided the best model of scale dimensionality, considering both the solution’s clean factor structure and the interpretability of these factors. These four factors reflected students’ Self-Management of Learning, Application of Learning Strategies, Support of Classmates’ Learning and Self-Regulation of Arousal. Regarding the SESSS factors, Self-Management of Learning and Application of Learning Strategies related closely to the categories of cognitive skills, metacognitive skills and the intentional self-regulation of cognitive processes. Support of Classmates’ Learning related closely to social skills that support classroom learning. Self-Regulation of Arousal related to the self-management of arousal and emotion that can interfere with effective learning. While determining the actual associations of SESSS factors with specific, previously established constructs requires empirical study, it is encouraging that the factor structure determined in this research corresponded with previous research.
In a confirmatory factor analysis study (Brigman et al., 2014), using SESSS scores from a diverse sample of almost 4,000 fifth-grade students, who found that while a four-factor model fit the data well, the scales associated with Self-Management of Learning and Application of Learning Strategies correlated so highly (r = .90) as to be indiscriminate. These items associated with the two factors were combined, and the subsequent three-factor model also proved to better fit the data. Brigman et al. (2014) suggested that the SESSS is best thought of as having three underlying factors corresponding to Self-Direction of Learning (which represents the combination of the original Management of Learning and Application of Learning Strategies factors), Support of Classmates’ Learning and Self-Regulation of Arousal.
Based on factor loadings, Brigman et al. (2014) created three SESSS subscales. The Self-Direction of Learning subscale (19 items) reflects the students’ intentional use of cognitive and metacognitive strategies to promote their own learning. Typical items include the following: “After I failed to reach a goal, I told myself to try a new strategy and not to doubt my ability,” and “I tried to keep myself motivated by imagining what it would be like to achieve an important goal.” The Support of Classmates’ Learning subscale (six items) reflects the students’ intentional use of strategies to help classmates learn effectively. Typical items include the following: “I tried to help a classmate learn how to do something that was difficult for them to do,” and “I tried to encourage a classmate who was having a hard time doing something.” Finally, the Self-Regulation of Arousal subscale (three items) reflects students’ intentional use of strategies to control disabling anxiety and cope with stress. Typical items include the following: “I focused on slowing my breathing so I would feel less stressed,” and “I imagined being in a calm place in order to feel less stressed.”
Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. The MSLQ is a 55-item, student self-report instrument with five subscales that measure different aspects of students’ motivation, emotion, effort and strategy use (Pintrich & DeGroot, 1990). The different subscales of the MSLQ are designed to be used singly or in combination to fit the needs of a researcher (Duncan & McKeachie, 2005). Items were adapted from various instruments used to assess student motivation, cognitive strategy use and metacognition (e.g., Eccles, 1983; Harter, 1981; Weinstein, Schulte, & Palmer, 1987). The present study used the following four subscales of the MSLQ: Cognitive Strategy Use, Self-Regulation, Self-Efficacy and Test Anxiety.
The Cognitive Strategy Use subscale is composed of 13 items that reflect the use of different types of cognitive strategies (e.g., rehearsal, elaboration, organizational strategies) to support learning. Typical items include the following: “When I read material for class, I say the words over and over to myself to help me remember,” “When I study, I put important ideas into my own words” and “I outline the chapters in my book to help me study.” Pintrich and DeGroot (1990) reported that the Cognitive Strategy Use subscale is reliable (Cronbach’s alpha = .83).
The Self-Regulation subscale includes nine items that reflect metacognitive and effort management strategies that support learning. Typical items include the following: “I ask myself questions to make sure I know the material I have been studying” and “Even when study materials are boring I keep working until I finish.” Pintrich and DeGroot (1990) reported that the Self-Regulation subscale is reliable (Cronbach’s alpha = .74).
The Self-Efficacy subscale is composed of nine items that reflect students’ ratings of their level of confidence in their ability to do well in classroom work. Typical items include the following: “Compared with others in this class, I think I’m a good student” and “I know that I will be able to learn the material for this class.” Pintrich and DeGroot (1990) reported that the Self-Efficacy subscale is reliable (Cronbach’s alpha = .89).
The Test Anxiety subscale includes four items that reflect students’ ratings of their experience of disabling levels of anxiety associated with classroom tests and examinations. Typical items include the following: “I am so nervous during a test that I cannot remember facts I have learned” and “I worry a great deal about tests.” Pintrich and DeGroot (1990) reported that the Self-Efficacy subscale is reliable (Cronbach’s alpha = .75).
Factor analyses indicated that these MSLQ subscales are related to different latent factors. Scores on the Cognitive Strategy Use subscale have been demonstrated to be related to grades on quizzes and examinations, grades on essays and reports, and overall class grades. Scores on the Self-Regulation subscale have been shown to be related to the above measures plus student performance on classroom seatwork assignments. Scores on the Self-Efficacy subscale have been demonstrated to be related to students’ grades on quizzes and examinations, grades for classroom seatwork assignments, grades on essays and reports, and overall class grades. Scores on the Test Anxiety subscale proved to be associated with lower levels of performance on classroom examinations and quizzes, as well as course grades (Pintrich & DeGroot, 1990).
Duncan and McKeachie (2005) reviewed the extensive research on the psychometric properties and research uses of the MSLQ. They concluded that the subscales are reliable, measure their target constructs and have been successfully used in numerous studies to measure student change after educational interventions targeting these constructs.
Self-Efficacy for Self-Regulated Learning scale. The SESRL was designed to measure students’ confidence in their abilities to perform self-regulatory strategies. It is a seven-item self-report instrument based on the Children’s Self-Efficacy Scale (Bandura, 2006; Usher & Pajares, 2008). Items (e.g., “How well can you motivate yourself to do schoolwork?”) reflect students’ judgments about their abilities to perform self-regulation strategies identified by teachers as being frequently used by students (Pajares & Valiante, 1999). The scale has been used successfully with older elementary students in a self-read format and with fourth graders in a read aloud administration format (Usher & Pajares, 2006). Cronbach’s alpha estimates of reliability have ranged between .78 and .84 (Britner & Pajares, 2006; Pajares & Valiante, 2002; Usher & Pajares, 2008). Factor analysis has suggested that the scale is unidimensional. Concurrent validity studies have indicated that the scale is related to measures of self-efficacy, task orientation and achievement (Usher & Pajares, 2006).
Data Analysis
In the initial analysis of the three SESSS subscales, the present authors used mean imputation to replace missing survey responses, by replacing a missing response with the overall mean for that survey item. For each of the 33 SESSS items, only 8.3%–9.1% of the responses were missing. Mean imputation is appropriate when the percentage of missing data is less than 10% and can be considered to be missing at random (Longford, 2005). In the current study, the students with missing survey data had an average SESSS score equal to that of the students with a complete response set, thus supporting the notion that the data were missing at random. Coefficient alpha, used as a measure of reliability, was calculated for each of the subscales before missing values were replaced.
Both convergent and discriminant evidence is needed in the validation process (Campbell & Fiske, 1959; Messick, 1993). Messick (1993) argued that while convergent evidence is important, it can mask certain problems. For example, if all tests of a construct do not measure a particular facet of that construct, the tests could all correlate highly. Likewise, if all tests of a construct include some particular form of construct-irrelevant variance, then the tests may correlate even more strongly because of that fact. Due to these possible shortcomings of convergent evidence, discriminant evidence is needed to ensure that the test is not correlated with another construct that could account for the misleading convergent evidence.
To determine the validity of the three SESSS subscales, the authors examined the correlations between each of the subscales with five other measures: four subscales of the MSLQ (Self-Efficacy, Cognitive Strategy Use, Self-Regulation and Test Anxiety), and the SESRL. Specifically, the authors considered the strength and direction of the SESSS subscales’ correlations with these other measures.
Results
Descriptive statistics and reliability estimates for the instruments used in this study are contained in Table 2. Coefficient alphas for the three SESSS subscales (Self-Direction of Learning, Support of Classmates’ Learning and Self-Regulation of Arousal), were 0.89, 0.79 and 0.68, respectively, and 0.90 for the SESSS as a whole. These results indicate good internal consistency (i.e., that the items within each instrument measure the same construct).
All correlations between pairs of subscales appear in Table 3. Because of the large sample size in this study, statistical significance by itself could be misleading, so the authors used the magnitude and direction of the correlations for their interpretations. Correlation is an effect size reflecting the degree of association of two variables (Ellis, 2010). The correlations among the three SESSS subscales ranged between .47 and .70, which suggests that the subscales measured related but discriminable dimensions of students’ success skill use. In assessing the concurrent validity of these three subscales, it was helpful to first focus on the scales that correlated most highly with the three SESSS subscales. The three SESSS subscales followed the same pattern with respect to strength of correlation. All three correlated most highly with both the Cognitive Strategy Use and Self-Regulation subscales of the MSLQ. These two subscales measure the students’ reported use of cognitive and metacognitive strategies associated with effort management and effective learning.
Table 2
Descriptive Statistics and Reliability Estimates for the Study Scales
| Scales |
Scales |
M
|
SD
|
Alpha
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SESSS |
Self-Direction of Learning |
48.6
|
10.88
|
0.89
|
|
Support of Classmates’ Learning |
16.6
|
4.28
|
0.79
|
|
Self-Regulation of Arousal |
7.9
|
2.60
|
0.68
|
|
|
|
|
|
| MSLQ |
Self-Efficacy |
28.3
|
4.41
|
0.83
|
|
Cognitive Strategy Use |
48.6
|
8.31
|
0.82
|
|
Self-Regulation |
31.2
|
5.08
|
0.75
|
|
Test Anxiety |
8.8
|
4.03
|
0.79
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SESRL |
Self-Eff. for Self-Reg. Learning |
31.2
|
6.10
|
0.83
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note. SESSS = Student Engagement in School Success Skills; MSLQ = Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire; SESRL = Self-Efficacy for Self-Regulated Learning.
Table 3
Correlations Between Scales
|
SESSS
|
|
MSLQ
|
|
|
SDL
|
SCL
|
SRA
|
|
SE
|
CSU
|
SR
|
TA
|
SESRL
|
| SESSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDL
|
—–
|
0.70*
|
0.58*
|
|
0.28*
|
0.54*
|
0.53*
|
-0.02
|
0.44*
|
|
SCL
|
|
—–
|
0.47*
|
|
0.25*
|
0.39*
|
0.39*
|
-0.02
|
0.35*
|
|
SRA
|
|
|
—–
|
|
0.12*
|
0.32*
|
0.30*
|
0.08*
|
0.24*
|
| MSLQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SE
|
|
|
|
|
—–
|
0.61*
|
0.54*
|
-0.38*
|
0.67*
|
|
CSU
|
|
|
|
|
|
—–
|
0.70*
|
-0.20*
|
0.68*
|
|
SR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—–
|
-0.25*
|
0.70*
|
|
TA
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—–
|
-0.35*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SESRL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—–
|
Note. SESSS = Student Engagement in School Success Skills survey; MSLQ = Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire; SESRL = Self-Efficacy for Self-Regulated Learning scale; SDL = Self-Direction of Learning; SCL = Support of Classmates’ Learning; SRA = Self-Regulation of Arousal; SE = Self-Efficacy; CSU = Cognitive Strategy Use; SR = Self-Regulation; TA = Test Anxiety;
*p < .01
Next, the three SESSS subscales correlated with the SESRL, which measures students’ beliefs in their capability to engage in common effective self-regulation learning strategies. Again, all three SESSS subscales followed the same pattern, and had a considerable drop in magnitude of correlation with the MSLQ Self-Efficacy subscale, which measures students’ reports of general academic self-efficacy. While smaller, the correlations with the Self-Efficacy subscale (which ranged between .12 and .28) were practically different than 0. The Self-Direction of Learning subscale had the strongest correlations with the other measures, followed by the Support of Classmates’ Learning subscale and finally by the Self-Regulation of Arousal subscale. There is evidence that the three SESSS subscales, the Cognitive Strategy Use subscale and the Self-Regulation subscale of the MSLQ, and the SESRL all measure some common dimension of an underlying construct, probably relating to students’ intentional use of strategies to promote effective learning.
The Self-Regulation of Arousal subscale was the only one of the three SESSS subscales to be significantly correlated with the MSLQ Test Anxiety subscale. Conceptually, students’ abilities to self-regulate arousal should be related to their reported levels of test anxiety. However, given the weak relationship (r = 0.08) and the fact that this observed correlation was actually opposite in direction to the relationship that would be expected, this finding should not be given undue weight. The results of this study offer little to no evidence that the three SESSS subscales measure the same construct as the MSLQ Test Anxiety subscale. This weak or nonexistent relationship is discriminant evidence in that the other SESSS subscales did not correlate strongly or at all with the MSLQ Test Anxiety subscale. However, the three other MSLQ subscales and the SESRL all showed moderate, negative correlations with the MSLQ Test Anxiety subscale. These differing patterns of correlation with MSLQ Test Anxiety suggest that the SESSS subscales capture a different dimension than the common dimension of the underlying construct measured by the MSLQ subscales (including the Test Anxiety subscale) and the SESRL.
Discussion
The observed pattern of results is very useful in determining the validity of inferences that currently can be made from SESSS scores. Based on prior factor analytic studies (Brigman et al., 2014; Carey et al., 2013), the present authors made an attempt to create three SESSS subscales based on the items that load most strongly on each of three underlying factors. These three SESSS subscales showed good internal consistency and moderate intercorrelations suggesting that the three subscales most probably measure related but discriminable dimensions of students’ success skill use. However, the three SESSS subscales showed essentially the same pattern of correlation with comparison scales. Similarly, the pattern of results suggests that there is little or no overlap between the construct measured by the three SESSS subscales and the construct measured by the Test Anxiety subscale of the MSLQ.
Unfortunately, these results do not shed much light on any differences among the SESSS subscales. Each subscale showed essentially the same pattern of correlations with the comparison scales even where differences would have been expected. For example, the authors would have expected the SESSS Self-Regulation of Arousal subscale to correlate significantly with the MSLQ Test Anxiety subscale, since individuals who are better able to regulate their levels of emotional arousal would be expected to experience less specific anxiety.
These results suggest that the SESSS as a whole represents a valid measure of students’ intentional use of strategies to promote academic success. While prior factor analytic studies (Brigman et al., 2014; Carey et al., 2013) have suggested that the SESSS has three related dimensions, making inferences based upon the three SESSS subscales related to these dimensions is not warranted. Instead, until evidence can be found that these three subscales measure discriminable dimensions of success skill use, the SESSS should be used as a unitary measure in research and practice. Future research in this area is necessary.
Conclusion
Researchers have thoroughly documented the need for school counselors to demonstrate their impact on student achievement (Brown & Trusty, 2005; Dimmitt et al., 2007; Whiston & Quinby, 2009; Whiston & Sexton, 1998; Whiston et al., 2011). School counselor-led interventions that provide evidence of improving student performance remain at the top of national initiatives and research agendas (ASCA, 2005; Dimmitt et al., 2005). However, there is a limited amount of standardized outcome assessments specifically tied to school counselor interventions available to evaluate changes in student knowledge, skills and attitudes related to academic achievement.
The SESSS is easy to administer (it takes fewer than 15 minutes to complete) and educators use it in schools to gain valuable information about students’ use of skills and strategies related to school success. Results on the SESSS may be used to improve the implementation of school counselor-led interventions and reinforcement of specific skills in school and home settings. Current findings indicate that SESSS results should be interpreted as a whole rather than by subscale. SESSS results can be used to monitor student progress, and identify gaps in learning as well as factors affecting student behavior.
The SESSS may be used as a screening tool to identify students in need of school counseling interventions and to evaluate student growth in the academic and behavioral domains. A review of SESSS student data may reveal gaps between student groups and identify the need for additional education opportunities, as well as lead to decisions about future goals of the school counseling program and discussions with administration and staff about program improvement (Carey et al., 2013). Finally, SESSS student data can be used to demonstrate how school counselors can impact student academic and personal/social development related to classroom learning and achievement. SESSS results can be shared with various stakeholders through a variety of report formats (e.g., Web sites, handouts, newsletters), publications, or presentations at the local, regional or national level to document the school counselor’s ability to affect student outcomes most related to parents, administrators and other staff (Carey et al., 2013).
There is one limitation in the study worth noting. While the sample size for the current analysis is considered large and diverse, all participates represented a single grade level, fifth grade, and two public school districts. Future analyses should include students from various elementary and secondary settings and grade levels.
Future research on the psychometric properties of the SESSS should include studies that address (a) the reliability and intercorrelations of the assessments corresponding to the three SESSS subscales and (b) the predictive validity that establishes the relationships between SESSS subscales and measures of academic success (e.g., achievement test scores, grades, teacher ratings). These additional studies are necessary to firmly establish the utility of the SESSS as a reliable and valid measure of student success skills.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of
interest or funding contributions for
the development of this manuscript.
References
American School Counselor Association. (2005). The ASCA national model: A framework for school counseling programs (2nd ed.). Alexandria, VA: Author.
Bandura, A. (2006). Guide for constructing self-efficacy scales. In F. Pajares & T. Urdan (Eds.), Self-efficacy beliefs of adolescents (pp. 307–337). Greenwich, CT: Information Age.
Brigman, G., & Webb, L. (2010). Student Success Skills: Classroom manual (3rd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: Atlantic Education Consultants.
Brigman, G., Wells, C., Webb, L., Villares, E., Carey, J. C., & Harrington, K. (2014). Psychometric properties and confirmatory factor analysis of the student engagement in school success skills. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development. Advance online publication. doi:10.1177/0748175614544545
Britner, S. L., & Pajares, F. (2006). Sources of science self-efficacy beliefs of middle school
students. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 43, 485–499.
Brown, D., & Trusty, J. (2005). School counselors, comprehensive school counseling programs, and academic achievement: Are school counselors promising more than they can deliver? Professional School Counseling, 9, 1–8.
Campbell, D. T., & Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56, 81–105.
Carey, J. C. (2004). Does implementing a research-based school counseling curriculum enhance student achievement? Amherst, MA: Center for School Counseling Outcome Research. Retrieved from http://www.umass.edu/schoolcounseling/uploads/ResearchBrief2.3.pdf
Carey, J., Brigman, G., Webb, L., Villares, E., & Harrington, K. (2013). Development of an instrument to measure student use of academic success skills: An exploratory factor analysis. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 47, 171–180. doi:10.1177/0748175613505622
Dimmitt, C., Carey, J. C., & Hatch, T. (2007). Evidence-based school counseling: Making a difference with data-driven practices. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Dimmitt, C., Carey, J. C., McGannon, W., & Henningson, I. (2005). Identifying a school counseling research agenda: A delphi study. Counselor Education and Supervision, 44, 214–228. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2005.tb01748.x
Duncan, T. G., & McKeachie, W. J. (2005). The making of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire. Educational Psychologist, 40, 117–128.
Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: A meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82, 405–432. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01564.x
Eccles, J. (1983). Expectancies, values and academic behaviors. In J. T. Spence (Ed.), Achievement and achievement motives: Psychological and sociological approaches (pp. 75–146). San Francisco, CA: W.H. Freeman.
Ellis, P. D. (2010). The essential guide to effect sizes: Statistical power, meta-analysis, and the interpretation of research results. Leiden, Netherlands: Cambridge University Press.
Green, A., & Keys, S. (2001). Expanding the developmental school-counseling paradigm: Meeting the needs of the 21st century student. Professional School Counseling, 5, 84–95.
Greenberg, M. T., Weissberg, R. P., O’Brien, M. U., Zins, J. E., Fredericks, L., Resnik, H., & Elias, M. J. (2003). Enhancing school-based prevention and youth development through coordinated social, emotional, and academic learning. American Psychologist. Special Issue: Prevention that Works for Children and Youth, 58, 466–474.
Gysbers, N. C. (2004). Comprehensive guidance and counseling programs: The evolution of accountability. Professional School Counseling, 8, 1–14.
Harter, S. (1981). A new self-report scale of intrinsic versus extrinsic orientation in the classroom: Motivational and informational components. Developmental Psychology, 17, 300–312.
Hattie, J., Biggs, J., & Purdie, N. (1996). Effects of learning skills interventions on student learning: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 66(2), 99–136. doi:10.3102/00346543066002099
Lapan, R. (2005). Evaluating school counseling programs. In C. A. Sink (Ed.), Contemporary school counseling: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 257–293). Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Longford, N. T. (2005). Missing data and small-area estimation: Modern analytical equipment for the survey statistician. New York, NY: Springer.
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D. & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
Masten, A. S., & Coatsworth, J. D. (1998). The development of competence in favorable and unfavorable environments: Lessons from research on successful children. American Psychologist, 53, 205–220.
Messick, S. (1993). Validity. In R. L. Linn (Ed.), Educational measurement, (3rd ed., pp. 13–100). Phoenix, AZ: American Council on Education/Oryx.
MetaMetrics, Inc. (2012). The Lexile® framework for reading. Retrieved from http://www.lexile.com
Myrick, R. D. (2003). Accountability: Counselors count. Professional School Counseling, 6, 174–179.
Paisley, P. O., & Hayes, R. L. (2003). School counseling in the academic domain: Transformations in preparation and practice. Professional School Counseling, 6, 198–204.
Pajares, F., & Valiante, G. (1999). Grade level and gender differences in the writing self-beliefs of middle school students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 24, 390–405.doi:10.1006/ceps.1998.0995
Pajares, F., & Valiante, G. (2002). Students’ self-efficacy in their self-regulated learning strategies: A developmental perspective. Psychologia, 45, 211–221.
Pintrich, P. R., & De Groot, E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 33–40.
Scarborough, J. L. (2005). The school counselor activity rating scale: An instrument for gathering process data. Professional School Counseling, 8, 274–283.
Sink, C. A., & Spencer, L. R. (2007). Teacher version of the my class inventory-short form: An accountability tool for elementary school counselors. Professional School Counseling, 11, 129–139.
Sperling, R. A., Howard, B. C., Miller, L. A., & Murphy, C. (2002). Measures of children’s knowledge and regulation of cognition. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 27, 51–79. doi:10.1006/ceps.2001.1091
Usher, E. L., & Pajares, F. (2006). Sources of academic and self-regulatory efficacy beliefs of entering middle school students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 31, 125–141. doi:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2005.03.002
Usher, E. L., & Pajares, F. (2008). Self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: A validation study. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 68, 443–463. doi:10.1177/0013164407308475
Villares, E., Frain, M., Brigman, G., Webb, L., & Peluso, P. (2012). The impact of student success skills on standardized test scores: A meta-analysis. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 3, 3–16. doi:10.1177/2150137811434041
Wang, M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg, H. J. (1994a). What helps students learn? Educational Leadership, 51(4), 74–79.
Wang, M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg, H. J. (1994b). Educational resilience in inner cities. In M. C. Wang & E. W. Gordon (Eds.), Educational resilience in inner-city America: Challenges and prospects (pp. 45–72). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Webb, L., Brigman, G., Carey, J., & Villares, E. (2011). A randomized controlled trial of student success skills: A program to improve academic achievement for all students (Education Research Grant 84.305A). Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Unpublished.
Weinstein, C. E., Schulte, A. C., & Palmer, D. R. (1987). LASSI: Learning and study strategies inventory. Clearwater, FL: H & H.
What Works Clearinghouse (2011). Procedures and standards handbook, version 2.1. Washington, DC: Author.
Whiston, S. C. (2002). Response to the past, present, and future of school counseling: Raising some issues. Professional School Counseling, 5, 148–155.
Whiston, S. C. (2011). Vocational counseling and interventions: An exploration of future “big” questions. Journal of Career Assessment, 19, 287–295. doi:10.1177/1069072710395535
Whiston, S. C., & Aricak, O. T. (2008). Development and initial investigation of the school counseling program evaluation scale. Professional School Counseling, 11, 253–261.
Whiston, S. C., & Quinby, R. F. (2009). Review of school counseling outcome research. Psychology in the Schools, 46, 267–272. doi:10.1002/pits.20372
Whiston, S. C., & Sexton, T. L. (1998). A review of school counseling outcome research: Implications for practice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 76, 412–426. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1998.tb02700.x
Whiston, S. C., Tai, W. L., Rahardja, D., & Eder, K. (2011). School counseling outcome: A meta-analytic examination of interventions. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 37–55.
Yildiz, E., Akpinar, E., Tatar, N., & Ergin, O. (2009). Exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis of the metacognition scale for primary school students. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 9, 1591–1604.
Zins, J. E., Weissberg, R. P., Wang, M. C., & Walberg, H. J. (Eds.). (2004). Building academic success on social and emotional learning: What does the research say? New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Elizabeth Villares is an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University. Kimberly Colvin is an assistant professor at the University at Albany, SUNY. John Carey is a professor at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst. Linda Webb is a senior research associate at Florida State University. Greg Brigman, NCC, is a professor at Florida Atlantic University. Karen Harrington is assistant director at the Ronald H. Fredrickson Center for School Counseling Research and Evaluation at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst. Correspondence can be addressed to Elizabeth Villares, 5353 Parkside Drive, EC 202H, Jupiter, FL 33458, evillare@fau.edu.
Oct 15, 2014 | Article, Volume 3 - Issue 1
Jeffrey M. Warren, Edwin R. Gerler, Jr.
Consultation is an indirect service frequently offered as part of comprehensive school counseling programs. This study explored the efficacy of a specific model of consultation, rational emotive-social behavior consultation (RE-SBC). Elementary school teachers participated in face-to-face and online consultation groups aimed at influencing irrational and efficacy beliefs. A modified posttest, quasi-experimental design was utilized. Findings suggested face-to-face RE-SB consultation is useful in directly promoting positive mental health among teachers and indirectly fostering student success. Implications and recommendations for school counselors are presented.
Keywords: school counseling, irrational beliefs, rational emotive behavior therapy, consultation, efficacy beliefs, cognitive behavioral therapy
Professional school counselors are largely responsible for developing and maintaining comprehensive school counseling programs. Comprehensive programming includes collaboration and consultation aimed at supporting teachers and influencing student achievement. The recently released third edition of the ASCA National Model further supports collaboration and consultation to help teachers influence student achievement (ASCA, 2012). Consultation has been defined by Caplan (1970) as “a process of interactions between two professional persons—the consultant, who is a specialist, and the consultee, who invokes a consultant’s help in regard to a current work problem” (p. 19). More recently, Kampwirth and Powers (2012) noted that engaging in collaborative endeavors during the consultation process fosters egalitarian relationships and often yields the greatest degree of change. School counselors engaging in consultation with teachers from a collaborative perspective are typically successful in advancing educational opportunities and fostering student growth (Baker & Gerler, 2008; Schmidt, 2010; Schmidt, 2014; Sink, 2008).
Parsons and Kahn (2005) describe an integrated consultation model in which school counselors are agents of change and students are influenced systemically. In this model, for example, school counselors may provide consultation to a teacher or group of teachers in efforts to identify goals, solutions and resources aimed at meeting the needs of the school. School counselors also may engage in consultation when providing information, instructing or resolving adversities (Purkey, Schmidt, & Novak, 2010; Schmidt, 2010; Schmidt, 2014). Consultation can be conducted using various theoretical paradigms of counseling (see Crothers, Hughes, & Morine, 2008; Henderson, 1987; Jackson & Brown, 1986; Warren, 2010a). Regardless of the process or approach, however, it is important that school counselors consider consultee factors (i.e., training, culture, and emotional and cognitive characteristics) that may hinder or promote the consultation process (Brown, Pryzwansky, & Shulte, 2011).
In a review of the literature, Warren (2010b) suggested rational-emotive behavior consultation (REBC) was a viable means for addressing thoughts and emotions of teachers. REBC is a model of consultation based on rational-emotive behavior therapy (Ellis, 1962). In REBC, school counselors help identify and challenge irrational beliefs that impede teachers’ classroom performance. An irrational belief is considered a strong, unrealistic cognition that leads to self-destructive emotions and behaviors (Dryden, 2009). In a study conducted by Warren and Dowden (2012), relationships between teachers’ irrational beliefs and emotions were confirmed. REBC was effective in addressing irrational beliefs and promoting healthy emotions (Warren, 2010b, 2013a). Teachers who participated in face-to-face and asynchronous, online group consultation across eight weeks reported more flexible and preferential thought patterns as well as decreases in stress.
In addition to finding relationships between irrational beliefs and emotions, Warren and Dowden (2012) also noted that irrational beliefs and efficacy beliefs were strongly correlated. Efficacy beliefs are “beliefs in one’s capacity to organize and execute the courses of action required to produce given attainments” (Bandura, 1997, p. 3). Due to emerging research on irrational beliefs and efficacy beliefs, Warren and Baker (2013) explored the potential for school counselors to incorporate components of social cognitive theory (SCT; Bandura, 1986) in REBC. This integrated model of consultation uses converging aspects of SCT and REBT to comprehensively conceptualize cognitions and responses of teachers and students.
The present study builds on current literature and research related to school counselor consultation with teachers. Based on the work of Brown and Schulte (1987), Bernard and DiGiuseppe (1994), Warren (2010a, 2010b, 2013a), and Warren and Dowden (2012), rational emotive-social behavior consultation (RE-SBC) was employed in elementary schools via face-to-face and online formats. It was hypothesized that both modes of consultation would reduce the irrational beliefs of teachers. It also was hypothesized that efficacy beliefs would increase as a result of the consultation.
Method
Participants
Teacher participation was solicited during weekly staff meetings at three elementary schools in the southeastern United States. Information, including a recruitment letter about the study, was provided to prospective subjects during staff meetings. Across the three schools, 42 out of 67 teachers agreed to participate in the consultation; thirty-five teachers completed the study titled, Performance Enhancing Strategies and Techniques-Teachers (PEST-T). Thirty-two (91%)of the participants were female and three (9%) were male. The median years of teaching experience for the participants was between a range of six and fifteen.
Consultant
A doctoral candidate in counselor education and supervision provided rational emotive-social behavior consultation (RE-SBC) to both PEST-T treatment groups. The consultant’s work history included school counseling and private practice therapy. The primary theoretical orientation of the consultant was cognitive behavior therapy (CBT). The consultant, and author of this paper, completed primary and advanced practica in Rational Emotive-Cognitive Behavior Therapy at the Albert Ellis Institute in New York.
Study Design
A modified posttest, quasi-experimental design was implemented in this study. Participating teachers were grouped according to their school affiliation. The three groups were randomly assigned to one of three treatment conditions (face-to-face, online, or control). All participants completed a pretest. The posttest measures differed from those of the pretest.
Measures
The Irrational Beliefs Inventory (IBI), developed by Koopmans, Sanderman, Timmerman, and Emmelkamp (1994), was used in a preliminary analysis of the treatment groups. The IBI is a 50-item self-report measure used to assess irrational beliefs. The IBI was designed in an attempt to focus solely on irrational cognition, while isolating the construct from emotions (Bridges & Sanderman, 2002). The irrational beliefs measured on the IBI are consistent with those described in REBT (Ellis, 1962). A five-point Likert-type scale, ranging from “1” (strongly disagree) to “5” (strongly agree) is provided for respondents to demonstrate a level of agreement for each item. A sample item reads, “If I can’t keep something from happening, I don’t worry about it.” The IBI is scored by summing all item responses. Low scores reflect a tendency to think rationally, while high scores indicate a propensity to think irrationally. The IBI includes five factors: worrying, rigidity, need for approval, problem avoidance, and emotional irresponsibility. The internal consistency of the subscales of the IBI for American samples ranges from .69 (emotional irresponsibility) to .79 (worrying). When evaluated, the IBI was found more reliable and valid than other measures of irrational beliefs (DuPlessis, Moller, & Steel, 2004)
The General Self Efficacy Scale (GSES; Schwarzer & Jerusalem, 1995) is a measure of self-efficacy designed for use with general populations, but can be used as a measure for specific samples as well. Statements include “I can always manage to solve difficult problems if I try hard enough” and “I am confident that I could deal efficiently with unexpected events.” The ten self-report items are rated on a 4-point scale ranging from “1” (not at all true) to “4” (exactly true). Higher scores on the GSES indicate a greater sense of agency, or the capacity to act. In most samples, the mean score per GSES item was around 2.9. The internal consistency of the GSES is .86. The validity of this measure is well-documented by studies and related literature (Scholz, Dona, Sud, & Schwarzer, 2002).
The Teachers’ Irrational Beliefs Scale (TIBS; Bernard, 1990) is used to measure irrational beliefs of teachers; its 22 self-report items are scored on a 5-point scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). High scores on the TIBS suggest rigidity and irrationality. The irrational beliefs measured are consistent with the theory of REBT and include low frustration tolerance, ‘awfulizing,’ demandingness, and global worth/rating. The TIBS evaluates these irrational beliefs across various teaching-related areas. These areas are represented by four subscales: Self-Downing Attitudes, Low-Frustration Tolerance Attitudes, Attitudes to School Organization, and Authoritarian Attitudes Toward Students. These areas account for 41.5% of the variance, which is similar to other scales of irrationality, thus providing evidence for construct validity (Bora, Bernard, Trip, Decsei-Radu, & Chereji, 2009). Internal consistency for the English version of the TIBS ranges from .70–.85 across the subscales and the total scale score; test-rest reliability is .80.
The Teacher Sense of Efficacy Scale (TSES; Tschannen-Moran & Woolfolk Hoy, 2001) is a measure that captures teachers’ perceived efficacy consisting of 24 items rated on a nine-point scale anchored by “1” (Nothing) to “9” (A Great Deal). The TSES includes three subscales; Efficacy in Student Engagement, Efficacy in Instructional Strategies, and Efficacy in Classroom Management. The mean score for the TSES is 7.1. Higher scores on the TSES and its subscales indicate a greater likelihood for perceived control during the completion of teaching-related tasks. Low scores reflect a poor sense of ability to affect student learning. Reliability estimates for the three sub-scales, Engagement (.87), Instruction (.91), Management (.90), and the total scale (.94) of the TSES are high. Scores on the TSES are positively correlated to scores of other existing validated measures of teacher efficacy providing evidence for construct validity (Tschannen-Moran & Woolfolk Hoy, 2001).
Procedure
Participating teachers from one elementary school met face-to-face with the consultant. All participants from another school met asynchronously, online with the consultant. The participants of the remaining school were designated as the control group. The face-to-face group met in weekly seventy-minute consultation sessions, spanning an eight-week period. The online group consultation consisted of five, asynchronous, yet interactive discussion modules, completed across an eight-week period.
Both formats of the group consultation (PEST-T) were derived from a consultation model implemented by Warren (2010a, 2013a). Decreases in irrational beliefs were noted as a result of providing face-to-face and online consultation to teachers based on rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT; Ellis, 1962). Warren, (2010a) also found a negative relationship exists between irrational beliefs and efficacy beliefs. As a result of this finding and the extrapolation of theoretical nuances of SCT (Bandura, 1986) and REBT (Ellis, 1962), suggested by Warren (2010a, 2010b), participants in this study received group rational emotive-social behavioral consultation (RE-SBC).
During the first consultation session, the face-to-face group was presented with concepts including observational learning, efficacy and reciprocal determinism. Irrational beliefs, emotions, self-defeating behaviors and other principles of REBT were explored throughout the remaining group consultation sessions. Cognitive, emotive, and behavioral strategies and techniques for increasing rational thought and efficacy beliefs were provided and demonstrated throughout the consultation (see Ellis & MacLaren, 2005). Case examples and analogies focused on teaching and classroom situations were used to explain the information presented. Interactive discussions, songs, humor and participation in demonstrations were encouraged throughout the consultation.
Throughout the asynchronous, online group consultation, the consultant provided the participants with select, layperson-oriented articles on REBT and SCT. During each session, participants were asked to read articles provided via the discussion module. The discussion modules focused on ways to increase self-efficacy, the ABC model, benefits of living rationally, and how to dispute irrational beliefs. Participants were responsible for commenting on the readings and responding to other participants’ comments. The consultant moderated the discussion modules. Participants could access and complete the discussion modules at their convenience due to the asynchronous format of the group consultation. Participants were required to dedicate approximately 1.25 hours a week to the group consultation, completing the online discussion modules and applying concepts discussed to daily living. At the conclusion of the study, members of the control group received copies of the articles used during online consultation.
Results
Preliminary Analysis
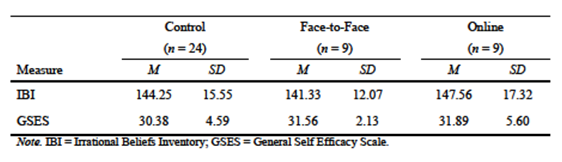
Univariate analyses of variance (ANOVAs) were conducted on scores of the IBI and the GSES compiled from both treatment conditions and the control group. No significant differences were found among the three conditions in terms of irrational beliefs, F(2, 39) = .37, p > .05. Pre-test equivalency also was noted for efficacy beliefs for all conditions F(2, 39) = .48, p > .05. In summation, irrational beliefs and efficacy beliefs held by elementary school teachers in this study were comparable across all groups.
Treatment Efficacy
Means and standard deviations for the face-to-face, on-line and control groups are presented in Table 1. Teachers who received the treatments were expected to respond by maintaining fewer irrational beliefs than the control group. Analysis revealed statistical significance for teachers’ irrational beliefs, F(2, 33) = 8.80, p < .001, which accounted for approximately 35% of the variance among the three groups. Post hoc analyses using Tukey HSD criterion for significance indicated the average level of irrational beliefs was significantly lower in the face-to-face treatment (M = 49.33, SD = 15.57), when compared to the control group (M = 65.95, SD = 9.66). Contrary to the hypothesis, the effect of the on-line treatment on teachers’ irrational beliefs (M = 74.2, SD = 13.41) was not statistically different from the control group.
Table 1
Means and Standard Deviations of Pre-Intervention Measures
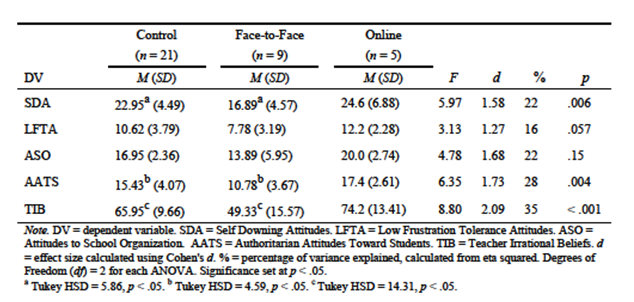
Further analyses on the items from the subscales of the TIBS provided additional insight into the effects of the treatments on specific irrational beliefs. Analysis of the three groups indicated statistical significance for self-downing attitudes (SDA), F(2, 35) = 5.97, p = .006. Post hoc comparisons indicated the mean for the face-to-face group (M = 16.89, SD = 4.57) statistically differed from the control group (M = 22.95, SD = 4.49) in terms of SDA. An omnibus ANOVA indicated that means for low frustration tolerance attitudes (LFTA) were not significantly different across groups, although a slight trend toward significance was present, F(2, 33) = 3.13, p = .057. Another analysis indicated statistical significance across groups for attitudes of school organization (ASO), F(2, 33) = 4.78, p =. 015. However, criterion for significance in a Tukey HSD analysis was not met when comparing the mean of the control group (M = 16.95, SD = 2.36) with the mean of either treatment, face-to-face (M = 13.89, SD = 5.95) or online (M = 20.0, SD = 2.74). Group means for authoritarian attitudes toward students (AATS) also were found to be statistically significant when an ANOVA was conducted, F(2, 33) = 6.35, p = .004. Post hoc comparisons using the Tukey HSD analysis indicated the mean scores of the face-to-face treatment (M = 10.78, SD = 3.67) were significantly different from the control group (M = 15.43, SD = 4.07). However, the effect of the online treatment on AATS (M = 17.4, SD = 2.61) was not statistically different from the control group. The effects of the treatments on the participants’ irrational thoughts are presented in Table 2.
Table 2
Means, Standard Deviations, and Group Comparisons on Measures of Teachers’ Specific and General Irrational Beliefs at Posttest
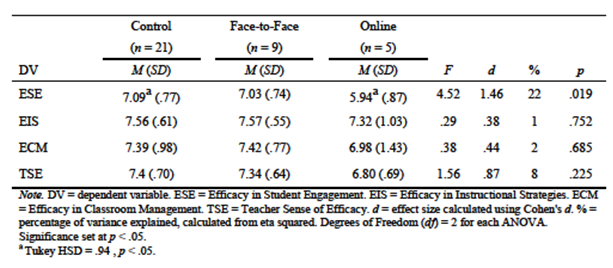
It also was expected that participants receiving the treatments would report higher levels of efficacy than the control group. Results indicated no statistical significance across groups in terms of teacher sense of efficacy (TSE), F(2, 33) = 1.56, p = .225. Additional analyses were conducted on the subscales of the TSES. Analyses measuring the group differences in terms of efficacy in instructional strategies (EIS), F(2, 33) = .29, p = .752, and efficacy in classroom management (ECM), F(2, 33) = .38, p = .685, yielded no significant difference. A statistically significant difference was found on efficacy in student engagement (ESE) when the three groups were compared, F(2, 33) = 4.52, p = .018, accounting for 22% of the variance. A post hoc comparison indicated the mean of the face-to-face treatment (M = 7.03, SD = .74) was not significant in terms of ESE when compared to the control group (M = 7.09, SD = .77). However, the mean of the online group (M = 5.94, SD = .87) was significantly less than the mean of the control group. The effects of the treatments on the participants’ irrational thoughts are presented in Table 3.
Table 3
Means, Standard Deviations, and Group Comparisons on Measure of Specific and General Teacher Efficacy at Posttest
Discussion
The findings of this study contribute to the literature on consultation as an indirect, responsive service school counselors can incorporate in comprehensive programs. In this study, teachers participating in the face-to-face RE-SBC group reported fewer irrational beliefs as compared to the control group. While low frustration tolerance attitudes (LFTA) and attitudes of school organization (ASO) were not statistically different, participants reported significant differences in irrational beliefs related to self-downing attitudes (SDA) and authoritarian attitudes toward students (AATS). The face-to-face RE-SB consultation appeared successful; however, the online consultation was not found to be effective in decreasing teachers’ irrational beliefs. Inconsistent with expectation, the online group consultation appeared to increase irrational beliefs experienced by participants. Therefore, the hypothesis that both modes of consultation would reduce the irrational beliefs of teachers was partially supported.
The apparent impact of the face-to-face RE-SB group consultation on teachers’ irrational beliefs is consistent with previous studies exploring face-to-face REBT group consultation (see Forman & Forman, 1980; Warren, 2010b, 2013a). In each of these studies, group consultation was found to reduce irrational beliefs and promote positive mental health among teachers. In this study, the influence of RE-SB on specific teacher beliefs is particularly noteworthy, given the negative impact of self-downing and authoritarian teaching styles on student success (see Bernard & DiGiuseppe, 1994; Phelan, 2005).
RE-SB face-to-face group consultation did not appear to influence teacher efficacy beliefs. Efficacy beliefs remained relatively unchanged for this consultation group, as compared to the control group. This finding is important to note when considering concurrent lack of change in LFTA among face-to-face group consultation participants. In an explanation of school counselors’ use of cognitive behavioral consultation, Warren and Baker (2013) posited that teacher efficacy beliefs and low frustration tolerance beliefs converge. Teachers with low self-efficacy for engaging students, for example, essentially think student engagement is “too hard” or “unbearable,” signature thoughts of low frustration tolerance. Warren and Dowden (2012) supported this claim in a study exploring the relationships between irrational beliefs and efficacy beliefs of teachers. In short, since low frustration tolerance beliefs were not impacted by the consultation, a lack of change in efficacy beliefs is expected. The findings of this study may further support the relationship between these constructs. However, an alternative explanation for the lack of change in efficacy beliefs and LFTA of teachers participating in the face-to-face group consultation may lie with the presentation of the consultation. It is plausible that the delivery of the consultation, related to these constructs, was slightly flawed. Positive relationships have been noted between teacher efficacy and student achievement (Goddard, Hoy, & Woolfolk Hoy, 2004; Henson, 2001; Pintrich & Schunk, 1996; Ross, 1998). More emphasis on low frustration tolerance and teacher efficacy beliefs may be needed in this consultation model if a goal for school counselors is to indirectly impact student achievement.
Regarding the online group consultation, decreases in efficacy beliefs were found among these participants. The difference in efficacy in student engagement (ESE) was significant for participants in this group as compared to the control group. On-line consultation participants reported decreases in efficacy beliefs. This finding was contrary to the hypotheses that the consultation groups would increase teachers’ efficacy beliefs. Because neither consultation group was deemed to significantly increase efficacy beliefs of teachers, this hypothesis was not supported.
Implications and Recommendations for School Counselor
This study offers promise for school counselors eager to implement responsive services that have the potential to support teachers and effect systemic change. The study is consistent with current literature on school counseling practices suggesting the value of multilevel, responsive interventions that support teachers and students (see ASCA, 2012; Erford, 2011; Lee & Goodnough, 2011). Maximizing the success of students is a crucial role of professional school counselors (Dahir & Stone, 2012; Lapan, Gysbers, & Kayson, 2007). School counselors providing group consultation to teachers systemically influence student success (Parsons & Kahn, 2005). This consultation model, in its face-to-face format, has the potential to offer multilevel support, directly promoting positive mental health of teachers and indirectly influencing the success of students and parents. Teachers who think in rational ways will respond more favorably during encounters with students and parents, thus enhancing the relationship and the potential for educational success.
The findings of this study offer several implications for school counselors. First, school counselors should embrace the consultative role in their comprehensive school counseling programs. This includes intentional demonstrations of leadership, advocacy and collaboration. School counselors must play a leadership role when assessing and conceptualizing the social-emotional needs of teachers and students. Preparing, establishing and implementing systemic services such as group consultation also require leadership (Schmidt, 2014). School counselors providing consultation must possess adequate knowledge of school and classroom settings and how these environments interact with the social-emotional wellness of teachers and students. Advocacy for the success of teachers and students is inherently demonstrated by the leadership displayed when implementing responsive services such as consultation. School counselors should diligently and methodically find productive ways to advocate for students when engaging in RE-SB group consultation with teachers. As suggested by Kampwirth and Powers (2012), school counselors will find consultation with teachers is most effective when a collaborative approach is taken. Collaborating and teaming encourages teachers to be proactive and invest in the goals of the consultation efforts. School counselors can support teachers and students through consultation most readily, and ultimately effect systemic change when demonstrating these necessary roles of comprehensive services.
Next, school counselors will need to have a basic understanding of recent research and assessment procedures in order to determine the overall social-emotional health in their schools. By understanding the social-emotional climate, school counselors can tailor consultation efforts to meet individual and group needs of teachers and students. Based on recent research (Nucci, 2002; Pirtle & Perez, 2003) and data collection at the school level, school counselors may want to target beginning teachers, for example, for participation in RE-SBC. There are several models and approaches of RE-SBC that school counselors can use depending on the needs of the school (Warren & Baker, 2013).
Finally, school counselors must be knowledgeable of and understand how cognitive behavioral theory, specifically REBT, can be applied to the school setting. Some of the core tenets of REBT appear to debunk the typical mindset of teachers and school counselors. For example, teachers usually think that “students should listen and follow directions” or “parents should help their children with homework.” However, these thoughts are desirable, but not mandatory as the word “should” implies. Therefore, teachers may be skeptical, experience cognitive dissonance, or simply reject the content of the trainings altogether. School counselors will need to navigate theoretical concerns carefully, accepting teachers’ positions, yet providing clear alternative perspectives. While advanced training in REBT-CBT may not be required, it is vital that school counselors prepare and equip themselves appropriately for conducting group consultation (Warren, 2013b). Failure to adequately prepare will likely impact the effectiveness of the consultation.
Limitations and Future Research
The current study was limited in several ways. First, based on school affiliation, participants were grouped in either a control, face-to-face or online group. This cluster, convenience sampling may have led to non-equivalent groups. Preliminary analyses were conducted to control for this threat and to determine the level of homogeneity across groups. A two-stage random sample also may have been useful in ensuring randomness and equivalent groups (Ross, 2009).
Second, history is typically a threat to the validity of a study when the design includes only one group (Heppner, Kivlighan, & Wampold, 2008). Aspects of this study may be influenced by history, despite a three-group experimental design. Levels of stress for each group potentially increased toward the conclusion of the consultation due to upcoming end-of-grade testing. If this occurred, the posttest responses may have reflected the influence of the upcoming event, thus negating the true effects of the consultation. It also is important to note other factors that may have influenced the outcomes of this study, such as socio-cultural factors, the mean age of staff members, and the “culture” or “personality” each school assumes as a result of administrative leadership.
Next, experimenter expectancies may have influenced the responses of the participants beyond the effects of the consultation. If this occurred, the scores of the measures may be elevated, implying the training was more effective than it actually was. While the face-to-face group was most vulnerable to this threat due to the format of the consultation, differential attrition (44%) may have influenced the findings of the online group consultation.
Finally, all types of irrational beliefs were decreased, to some degree, for participants of the face-to-face consultation group. Teacher efficacy beliefs were not influenced and remained consistent with mean scores proposed by Tschannen-Moran and Woolfolk Hoy (2001). Due to the size of the sample of the face-to-face group, Type II errors may exist for LFTA and ASO and teacher efficacy beliefs. A significant difference may have existed, although not detected because of the limited number of participants.
Moving forward, this study may lead researchers in several directions. For example, conducting classroom observations or interviews of teachers post-consultation would provide insight into the lasting effects of the training. Ellis (2005) and Dryden (2009) have emphasized that cognitive change occurs most readily when individuals continue to challenge irrational beliefs and practice rational thinking. Replicating this study, while exploring the influence of the addition of homework assignments on irrational beliefs and efficacy beliefs of teachers, would also offer additional insight into the amount of practice required for cognitive change. Additionally, conducting a six-month follow-up may help answer questions related to level of teacher engagement, consultation duration and degree of support needed for teachers to maintain cognitive-behavioral change.
As advancements in technology occur, a redesigned online group RE-SBC model may be warranted. School counselor researchers should explore additional ways to design online RE-SBC models that are supportive and accommodating of teachers. For example, the inclusion of synchronous sessions within an asynchronous online design is worth exploring. Researchers also may want to explore synchronous, online models of consultation using technology such as webinars or three-dimensional, virtual worlds. YouTube, in particular, seems to be a useful online tool for improving online offerings for school counselors and teachers. The Halo Rational Emotive Therapy (2011) video, for example, shows the creative possibilities offered by YouTube. Apps for cell phones and tablet computing devices offer seemingly endless possibilities for convenient, online consultation and collaboration strategies for school counselors. Additionally, a modification of the face-to-face consultation to include online components may be a viable option and worth studying.
Advancements in the preparation of school counselors also may influence and increase the effectiveness of school counselors’ use of technology for RE-SBC. Counselor education programs need to challenge and support graduate students in creative and inventive applications of technology in the practice of school counseling. Gerler’s (1995) early challenge for school counselors to explore the edges of technology, and then later challenges by Hayden, Poynton, and Sabella (2008) for using technology to apply the ASCA National Model offer hope that the preparation of school counselors will improve online and other technological strategies in school counseling, including the use of technology for RE-SB consultation.
School counselor researchers also may want to explore the effects of RE-SB group consultation on various critical school issues. RE-SB group consultation may impact factors that influence student success, including academic achievement, bullying, disciplinary problems, motivation and teacher burnout. Warren and Stewart (2012) also suggested cognitive behavioral approaches to school counselor-teacher consultation may be effective in reducing student dropout rates. Research in these areas will be invaluable as school counselors continue to refine their roles as consultants.
In conclusion, the findings of this study provide direction for school counselors providing consultation. Cognitive behavioral consultation, such as the RE-SBC face-to-face group approach, appears to influence the irrational beliefs of elementary school teachers. Specifically, decreases in self-downing attitudes and authoritarian attitudes toward students were noted. While teacher efficacy beliefs, a predictor of student achievement, were not found, the decrease in irrational beliefs alone is important and potentially a factor in promoting student success. The online group RE-SBC effort was largely ineffective in reducing irrational beliefs or increasing efficacy beliefs. The online model of consultation should be carefully considered before implementation and deemed useless pending a significant redesign. However, both formats of RE-SBC demonstrate leadership, advocacy for the well-being of teachers and students, and collaboration among stakeholders— qualities mandatory for school counselors wishing to effect systemic change. It is hoped that this study will encourage school counselors to become familiar with and implement models of consultation that promote positive mental health of teachers and have the potential to support the educational success of students and parents.
References
American School Counselor Association. (2012). The ASCA national model: A framework for school counseling programs (3rd ed.). Alexandria, VA: Author.
Baker, S. B., & Gerler, E. R. (2008). School counseling for the twenty-first century (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Merrill.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-Efficacy the exercise of control. New York, NY: Freeman.
Bernard, M. E. (1990). Taking the stress out of teaching. Melbourne, Vic: Collins-Dove.
Bernard, M. E., & DiGiuseppe, R. (1994). Rational-emotive consultation in applied settings.Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Bora, C., Bernard, M. E., Trip, S., Decsei-Radu, A., & Chereji, S. (2009). Teacher irrational belief scale—preliminary norms for Romanian population. Journal of Cognitive and Behavioral Psychotherapies, 9, 211–220.
Bridges, K. R., & Sanderman, R. (2002). The Irrational Beliefs Inventory: Cross cultural comparisons between American and Dutch samples. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy, 20, 65–71. doi: 10.1023/A:1015133004916
Brown, D., & Schulte, A. C. (1987). A social learning model of consultation. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 18, 283–287. doi: 10.1037/0735-7028.18.3.283
Brown, D., Pryzwansky, W. B., & Shulte, A. C. (2011). Psychological consultation and collaboration: Introduction to theory and practice (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Caplan, G. (1970). The theory and practice of mental health consultation. New York, NY: Basic.
Crothers, L. M., Hughes, T. L., & Morine, K. A. (2008). Theory and cases in school-based consultation. New York, NY: Routledge.
Dahir, C. A., & Stone, C. B. (2012). The transformed school counselor (2nd ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Dryden, W. (2009). Rational-emotive behaviour therapy: Distinctive features. New York, NY: Routledge.
DuPlessis, M., Moller, A. T., & Steel, H. R. (2004). The Irrational Beliefs Inventory: Cross-cultural comparisons between South African and previously published Dutch and American samples. Psychological Reports, 95, 841–849.
Ellis, A. (1962). Reason and emotion in psychotherapy. Secaucas, NJ: Citadel Press.
Ellis, A. (2005). The myth of self-esteem: How rational emotive behavior therapy can change your life forever. Amherst, NY: Prometheus.
Ellis, A., & MacLaren, C. (2005). Rational emotive behavior therapy: A therapist’s guide (2nd ed.). Atascadero, CA: Impact.
Erford, B. T. (2011). Transforming the school counseling profession (3rd ed.). Columbus, OH: Pearson Merrill Prentice-Hall.
Forman, S. G., & Forman, B. D. (1980). Rational-emotive staff development. Psychology in the Schools, 17, 90–95. doi: 10.1002/1520-6807(198001)17:1<90::AID-PITS2310170116>3.0.CO;2-2
Gerler, E. R. (1995). Counseling on the edge of technology. Elementary School Guidance and Counseling, 30, 2-7.
Goddard, R. D., Hoy, W. K., & Woolfolk Hoy, A. (2004). Collective efficacy beliefs: Theoretical developments, empirical evidence, and future directions. Educational Researcher, 33, 3–13.
Hayden, L., Poynton, T, & Sabella, R.A. (2008). School counselors’ use of technology within the ASCA national model’s delivery system. Journal of Technology in Counseling, 5(1). Retrieved from http://jtc.colstate.edu/Vol5_1/Hayden.htm
Halo Rational Emotive Therapy (2011). Halo rational emotive therapy. Retrieved from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vg FdO3zIDMc
Henderson, A. (1987). The evidence continues to grow: Parent involvement improves student achievement. Columbia, MD: National Committee for Citizens in Education.
Henson, R. K. (2001, January). Teacher self-efficacy: Substantive implications and measurement dilemmas. Invited keynote address at the annual meeting of the Educational Researcher Exchange, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX.
Heppner, P. P., Kivlighan, D. M., Jr., & Wampold, B. E. (2008). Research design in counseling (3rd ed.). Belmont, CA: Thompson.
Jackson, M. D., & Brown, D. (1986). Use of systematic training for effective parenting (STEP) with elementary school parents. School Counselor, 34, 100–104.
Kampwirth, T. J., & Powers, K. M. (2012). Collaborative consultation in the schools (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Koopmans, P. C., Sanderman, R., Timmerman, I., & Emmelkamp, P. M. G. (1994). The Irrational Beliefs Inventory (IBI): Development and psychometric evaluation. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 10, 15–27.
Lapan, R., Gysbers, N. C., & Kayson, M. (2007). Missouri school counselors benefit all students: How implementing comprehensive guidance programs improve academic achievement for all Missouri students. Jefferson City, MO: Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education.
Lee, V. V., & Goodnough, G. E. (2011). Systemic data-driven school counseling practice and programming for equity. In B. T. Erford (Ed.), Transforming the school counseling profession (3rd. ed., pp. 129–153). Columbus, OH: Pearson Merrill Prentice-Hall.
Nucci, C. (2002). The rational teacher: rational-emotive behavior therapy in teacher education. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy, 20, 15–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1015176819937
Parsons, R. D., & Kahn, W. J. (2005). The school counselor as consultant: An integrated model for school-based consultation. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning.
Phelan, T. W. (2005). Teaching style and classroom management. ParentMagic Newsletter, Special Teachers’ Edition. Retrieved from http://www.bridges4kids.org/articles/2005/8-05/Phelan7-05.html
Pintrich, P., & Schunk, D. (1996). Motivation in education: Theory, research & applications. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Pirtle, T. N., & Perez, P. (2003). Survival counseling skills for new teachers. Journal of Border Educational Research, 2, 8–10
Purkey, W. W., Schmidt, J. J., & Novak, J. M. (2010). From conflict to conciliation: How to diffuse difficult situations. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
Ross, J. A. (1998). The antecedents and consequences of teacher efficacy. In J. Brophy (Ed.), Research on teaching (Vol. 7) (pp. 49–74). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Ross, S. M. (2009). Introductory statistics. Burlington, MA: Academic Press.
Schmidt, J. J. (2010). The elementary/middle school counselor’s survival guide (3rd ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Schmidt, J. J. (2014). Counseling in schools: Comprehensive programs of responsive services for all students (6th ed.). Boston, MA:
Pearson.
Scholz, U., Dona, B. G., Sud, S., & Schwarzer, R. (2002). Is general self-efficacy a universal construct? Psychometric findings from 25 countries. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 18, 242-251.
Schwarzer, R., & Jerusalem, M. (1995). Generalized Self-Efficacy Scale. In J. Weinman, S. Wright, & M. Johnston (Eds.), Measures in health psychology: A user’s portfolio. Causal and control beliefs (pp. 35-37). Windsor, UK: NFER-NELSON.
Sink, C. A. (2008). Elementary school counselors and teachers: Collaborators for higher student achievement. Elementary School Journal, 108, 445–458.
Tschannen-Moran, M., & Woolfolk Hoy, A. (2001). Teacher efficacy: Capturing and elusive construct. Teaching and Teacher Education, 17, 783–805.
Warren, J. M. (2010a). School counselor system support using mental health interventions. The New York State School Counseling Association Journal, 7, 30–39.
Warren, J. M. (2010b). The impact of rational emotive behavior therapy on teacher efficacy and student achievement. Journal of School Counseling, 8(11). Retrieved from http://www.jsc.montana.edu/articles/v8n11.pdf
Warren, J. M. (2013a). School counselor consultation: Teachers’ experiences with rational emotive behavior therapy. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 31, 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s10942-011-0139-z
Warren, J. M. (2013b, March). Consultation: Enhancing performance and student success. Paper presented at the 6th Annual Southeast Region of NC Drive-in Workshop for Area Counselors, University of North Carolina at Pembroke, Pembroke, NC.
Warren, J. M., & Baker, S. B. (2013). School counselor consultation: Supporting teachers and students through the application of cognitive-behavioral theories. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Warren, J. M., & Dowden, A. R. (2012). Elementary school teachers’ beliefs and emotions: Implications for school counselors and counselor educators. Journal of School Counseling, 10(19). Retrieved from http://www.jsc.montana.edu/articles/v10n19.pdf
Warren, J. M., & Stewart, J. C. (2012, March). A cognitive behavioral systems approach to drop-out prevention. Paper presented at the North Carolina School Counselor Association, Southeast Region Drive-in Workshop, University of North Carolina at Pembroke, Pembroke, NC.
Jeffrey M. Warren, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of North Carolina at Pembroke. Edwin R. Gerler, Jr. is a Professor at North Carolina State University. Correspondence can be addressed to Jeffrey M. Warren, UNC-Pembroke School of Education, PO Box 1510, Pembroke, NC 28372, jeffrey.warren@uncp.edu.
Oct 15, 2014 | Article, Volume 3 - Issue 1
Angie D. Wilson, Pennie Johnson
The addictions field continues to grow and is expanding beyond the area of substance abuse and substance dependence. Process addictions are now an integral aspect of addictions treatment, diagnosis, and assessment. There is a gap in the literature related to process addictions which impacts counselors and clients due to lack of literature and knowledge on this new area. It also is hypothesized that there is a gap in continued education for incorporating treatment and assessment measure into clinical practice. This initial study was conducted to initiate an understanding of levels of knowledge counselors have in diagnosing, assessing and treating clients suffering with process addictions, indicators of where and how they learned about process addictions, and how they integrate their level of the treatment of process addictions into clinical practice. The authors provide a brief overview of process addictions, a summary of original research, implications of this study, discussion, and recommendations for future research.
Keywords: process addictions, counseling, addiction disorders, compulsive behaviors, behavioral addictions
It is important for counselors and mental health professionals to stay current with information impacting their profession. Staying abreast of new ideas and new information can assist in providing successful and holistic treatment for clients (ACA, 2005). Specifically, the field of addictions has had many transformations over the last few decades. One of the most recent issues impacting the addictions area in counseling is process addictions (PAs) (Grant, Potenza, Weinstein, & Gorelick, 2010; Holden, 2001; Martin & Petry, 2005). For many years, mental health professionals have treated clients with systematic behaviors mimicking the disease of addiction, but many find they haven’t received adequate training in this area to be competent. The terminology of PA sweeps a wide variety of behavioral addictions or compulsive behaviors. PA is defined as any compulsive-like behavior that interferes with normal living and causes significant negative consequences in the person’s family, work and social life. Gambling, Internet addiction, sex addiction, exercise addiction and eating addictions are among those identified as PA (Sussman, Lisha, & Griffiths, 2011).
The neurological changes in the brains of people who engaged in gambling, binge eating, and compulsive sex were similar to those brains of persons who abused substances such as alcohol and marijuana. Treatment observations and prevalence data, coupled with a growing body of literature, suggest the existence of PAs (Smith & Seymour, 2004), also called compulsive behaviors (Inaba & Cohen, 2011) and behavioral addictions (Grant et al., 2010). PAs may be new to some; however, PAs represent neither a new phenomenon nor new disorders. In actuality, PAs have been an area of concern in the addictions field for many years (Grant et al., 2010; Holden, 2001; Martin & Petry, 2005).
There is little evidence that this evolving research on PAs is being translated to those providing services to clients. Due to the gap in the literature related to PAs and the knowledge of counselors, students, and counselor educators related to PA, the International Association for Addictions and Offender Counseling (IAAOC) Process Addictions Committee (a division and committee of the American Counseling Association) conducted a survey of students, post-graduate counselors, and counselor educators with the purpose of understanding the deficiencies clinicians are struggling with in understanding process addiction. The purpose of this article is to provide the results of a survey, which indicated the percentage of post-graduate counselors/clinicians in the study and their understanding of PAs. The information in this manuscript will specifically address the knowledge of counselors who are actively engaged in providing treatment services in community settings.
Review of Relevant Literature
The most recent definition of addiction was the product of research studies, which took place over four years and included over 80 experts from across the country. These research studies were spearheaded by The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM). According to ASAM (2012) an addiction is not merely a behavioral problem involving the consumption or intake of substances, gambling, or sex; an addiction is a chronic brain disorder. Another definition of addiction is the behavior that occurs with continued substance use or involvement in a PA regardless of the negative impact it has on the participant’s life (Shallcross, 2011). What follows is a brief overview of several PAs that have been researched and are referenced in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (4th ed., text rev.; DSM–IV–TR; American Psychiatric Association [APA], 2000), and the new DSM-5 (APA, 2012a).
The diagnostic criteria of the various PAs are similar to those of substance addictions. Due to these negative consequences, PAs continue to disrupt the lives of significant proportions of the U.S. adult population (Sussman et al., 2011). Based upon a literature review of 83 studies, Sussman et al. (2011) estimated prevalence rates for gambling addiction (2%), Internet addiction (2%), sex addiction (3%), exercise addiction (2%), and eating addiction (2%) among the general American population. The growing concern regarding PAs may be due to the increased co-morbidity with mental health concerns and substance addictions (Sussman et al., 2011). Substance abuse co-morbidity rates for gambling addiction were approximated at 20-30%, Internet addiction 10%, love and sex addictions 40%, exercise addiction 15%, and eating addiction 25% (Sussman et al., 2011). According to Carnes (2009) most addicts have more than one addiction, sustained recovery is more successful when all addictions present are addressed in counseling, and addictions do not merely coexist, but actually interact with each other.
The term disorder is often used interchangeably with the term addiction. For example, one of the most widely known and recognizable PA is gambling disorder, which is also called gambling addiction and pathological gambling (Ashley & Boehlke, 2012; Jamieson, Mazmanian, Penney, Black, & Nguyen, 2011). It is believed that gambling disorder will be categorized under Addiction and Related Disorders in the DSM-5 (APA, 2012b), as the diagnosing criteria closely resemble substance use disorder. In order for one to be diagnosed with gambling disorder, the gambling behavior must disrupt the personal or work life of the affected person and cannot be related to a manic episode (APA, 2000). According to Crozier and Sligar (2010), some indicators that one’s social gambling is shifting into a PA include lifestyle changes to accommodate gambling-related activities, extreme mood fluctuations related to gambling, justifications for continued gambling, perceptible excitement when discussing gambling, as well as financial indicators such as hiding debt and frequently borrowing money.
Food addiction, eating addiction, and compulsive eating also are referenced as Binge Eating Disorder (BED) and is another of the PAs that may be revised in the DSM-5, from the category of Other Conditions (APA, 2000) to Feeding and Eating Disorders (APA, 2012c; Wonderlich, Gordon, Mitchell, Crosby, & Engel, 2009). Frequent episodes of uninhibited food consumption beyond the point of fullness, without being followed by purging behaviors (e.g., vomiting or the use of laxatives), are characteristics of BED. According to Karim and Chaudhri (2012), individuals with BED will typically eat without feeling hungry, spend excessive amounts of time thinking about and obtaining food, and may attempt to hide their eating from others. Although some people with BED may be obese or overweight, BED is distinct from other eating disorders, as individuals with this condition are mentally and emotionally different from individuals who are obese or overweight (Wonderlich et al., 2009).
The term exercise addiction was first introduced by Glasser (1976), who studied long-distance runners and found out that most of them had an obsessive-compulsive disorder. Exercise addiction, or sports addiction, is a phenomenon typically found in athletes (McNamara & McCabe, 2012). Exercise addiction has been a growing concern for the counseling field for a number of years (Parastatidou, Doganis, Theodorakis, & Vlachopoulos, 2012). Exercise dependence, obligatory exercise, compulsive exercise, and excessive exercise are other names for exercise addiction or sports addiction (Parastatidou et al., 2012). Training interferes with daily life and is diagnosed with criteria similar to those of substance abuse disorders as well as other PAs.
Another widely recognized addiction is Internet addiction, also called Internet Use Disorder (APA, 2012d), which is not found in the DSM-IV, but is being considered for inclusion in the DSM-5 (APA, 2012d; Ko, Yen, Yen, Chen, & Chen, 2012). The criteria used to define this addiction closely match the criteria for substance dependence. For example, the use of the Internet becomes a preoccupation or begins to monopolize the individual’s time, there is an increased need to obtain positive feelings, social relationships are negatively affected by Internet usage, and a person returns to maladaptive Internet use after a period of abstinence (Smahel, Brown, & Blinka, 2012).
According to Karim and Chaudhri (2012), a disproportionate amount of time spent on planning for and participating in sexual activity, participating in sexual activity to alter one’s mood or as a way to handle stress, inability to control sexual compulsions and sexual fantasies, and engaging in unsafe sexual activity can be called hypersexual disorder (APA, 2012e). Hypersexual disorder (APA, 2012e) also is called sex addiction and compulsive sex. Shifts in emotions and values; compulsive masturbation; inappropriate jokes, personal boundaries, and touching; boasting about sexual conquests; and unplanned sexual encounters are indicators of compulsive sex (Crozier & Sligar, 2010).
Training of Counselors on Process Addictions
The US Department of Health and Human Services, TAP 21 (HHS, 2006) recommends that all counselors should be competent in “understanding of addiction, treatment knowledge, application to practice, and professional readiness” (p. 5). Although this is recommended, it is often difficult for counselors to locate educational training and research related to PAs due to the limited available information. Although licensed counselors graduate from master’s- and doctorate-level universities in counseling programs, researchers (Crozier & Agius, 2012) indicate many counselor educators are not adequately equipped with recent knowledge regarding PAs and, therefore, academic organizations are not properly educating future counselors in this area. Of course, some information regarding addictions is infused into the coursework in most graduate programs, but counselors with specific interest in addictions must seek additional training and education through outside sources such as continuing education and specified certification programs. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of licensed counselors to stay abreast with clinical training and new areas related to treatment, assessment and diagnosis of maladaptive disorders. However, there are concerns regarding the accessibility of training and professional growth seminars on PAs, as many counselor educators who are the primary researchers in the counseling field are not aware of this growing area of PAs (Crozier & Agius, 2012), and many counseling students are not being taught about PAs in their counselor training programs (Nelson, Wilson, & Holman, n.d.). This creates a problem for the counseling profession in that there is continued need for training and research in this area. “The development of effective practice in addiction counseling depends on the presence of attitudes reflecting openness to alternative approaches, appreciation of diversity, and willingness to change” (HHS, 2005, p.5).
Methodology
This pilot study has helped provide structure for a national study being conducted by the IAAOC. An online survey was constructed by members of the IAAOC Committee on PAs who are all active professionals in the field. They followed methodological research guidelines (Dillman, Smyth, & Christian, 2009) to design a valid, mixed-methods design (Onwuegbuzie & Johnson, 2006) comprised of open-ended and closed-ended research questions. Upon approval from the Institutional Review Boards, counselors in NC and TX received an email requesting their participation in this initial study. The survey, statement of anonymity and confidentiality, as well as the informed consent was posted in Zip Survey and participants were prompted to review this information before proceeding with the study. The data also was collected and analyzed within the Zip Survey program. Potential participants later received two separate reminder emails prior to the survey’s closing date asking them to participate in the study.
Participants
The participants were solicited by the investigators through professional listservs, websites of professional organizations, personal communication with counseling professionals and word of mouth. Participants were asked to address the online survey, read the informed consent and begin the survey. Calculating the response rate for the survey was not possible because it was not possible to determine how many counselors actually received the survey. It also is important to note that counselors may have chosen to describe themselves as counselor educators, if they were both counselors and counselor educators. In this case, those counselors’ responses would have been included in the data for counselor educators and not counselors.
The total sample for our study included 37 counselors who were post-graduate clinicians/counselors. The counselors who participated in the study included the following: 59% with a master’s degree in community counseling/mental health counseling, 8 % with a master’s degree in a counseling-related field with a certificate in addiction, 3% with an educational specialist degree in a counseling-related field, and 22% with a doctorate in a counseling-related field. Fifty-eight percent graduated from CACREP-accredited programs with 2009 standards and 3% from CACREP-accredited programs with 2013 standards. Thirty percent graduated from a regionally accredited program that was not CACREP-accredited, and 9% graduated from an academic setting that was not regionally accredited or CACREP-accredited. It must be noted that five participants omitted the question regarding accreditation of their most recent counselor education program.
Instrument
A survey was developed to obtain counselors’ opinions and experiences with assessing, diagnosing and treating PAs. The survey questions were based on a thorough review of the literature and were relevant to the participants’ knowledge of PAs and their experiences as clinicians. The survey questions were developed in accordance to current survey methodological research guidelines (Dillman et al., 2009), and then the questions were sent to all members of the IAAOC Process Addictions Committee to asses for content validity. Finally, they were revised based on the members’ feedback. The survey included both closed- and open-ended questions and was designed to be completed in 10–15 minutes.
A grand tour question is a type of descriptive inquiry that provides information on an experience or phenomenon. According to Spradley (1979), using grand tour questions constitutes an emergent quality of the interview process that results in subsequent questions. One grand tour question was used: “What are your thoughts or feelings about working with clients who present with PA?” In addition to the grand tour question, descriptive survey questions and open-ended text boxes were provided for participants to elaborate on their responses.
Data Collection and Analysis
Zip Survey was used to post the surveys and collect responses as well as to analyze the demographic and quantitative data. Participants received an email with a link to the survey requesting their participation. Upon opening the link, participants read the informed consent and agreed that they understood the nature of the study by continuing with the survey questions. Participants were assured in the informed consent that their responses were anonymous and confidential.
The survey program collected the responses and aggregated them into charts and Excel files. The quantitative results are descriptive data and are reported as such in the results section. Participants also had the opportunity to utilize text boxes within the survey in order to give a rich description of their experiences. The qualitative data obtained from participants who shared their ideas and experiences through the text boxes embedded in the survey also were utilized as data in this study. According to Moustakas (1994), data must be in written form in order to organize qualitative research; the qualitative data was in written form for this study as the Zip Survey collected the written words of participants via typed text. Organizing the text responses and following Moustakas’s (1994) seven steps adapted from Van Kaam’s (1959, 1966) interview analysis process were key steps during the data organization phase of the study. Additionally, both quantitative and qualitative data were compared with one another to achieve triangulation (Onwuegbuzie & Johnson, 2006).
Results
The total sample for this study included 37 counselors. They provided information on their training and clinical experiences related directly to the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of clients with PAs. Specifically, the participants responded to questions regarding their comfort levels working with PAs and assessing, diagnosing, and treating nine different forms of PAs. Approximately 89% of the respondents indicated that learning about PA was very important for clinicians, while 6% noted that it was important and 6% indicated learning about PA was a neutral issue. Less than 13% of the participants understood that PA included compulsive behaviors such as eating disorders, exercise, Internet, gaming, gambling, relationships, sex, work addiction and compulsive spending. Sixty-four percent of the counselors surveyed acknowledged they treated clients with PAs, but where lacking the training to assess and screen for addictions.
Regarding comfort level in assessing, diagnosing and treating PAs, 25% of respondents reported feeling very comfortable, 42% reported feeling comfortable, 22% reported feeling ambivalent, 6% reported not feeling comfortable, and 6% selected not applicable. Counselors reported being trained to assess, diagnose and treat eating disorders more than the other PAs listed on the survey. Eating disorders, relationships and sex were the three PAs that counselors reported having the most learning experiences. Approximately 24% of the respondents had been trained to assess and screen for eating disorders. However, 36% of the participants were trained to diagnose eating disorders and only 19% had been trained to treat eating disorders. From the responses of the participants in this pilot study, it can be gathered that counselors are treating PAs without adequate training and continued education.
On average, a third of the participants had been trained to diagnose eating disorders, but most had little to no training in diagnosing the various other forms of PA. Yet, they knowingly are treating clients with addictions. With this admittance, the 89% of counselors who participated in the survey identified the importance of training counselors to assess, screen, diagnose and treat PAs, and 94% expressed interest in taking a process addictions seminar or course. Regarding theoretical orientation, 69% of the participants identified as cognitive behavioral, 8 % as humanistic, and 6% as psychodynamic.
Participants also were given the opportunity to provide qualitative responses to some questions. Overall, participants shared that they believed learning about PAs was important. Many were not prepared to provide treatment for clients with PAs, and many were not trained to adequately provide therapeutic services for clients with PAs. One participant stated, “I have never considered the term process addiction, and I could easily see myself changing that answer upon further thought and education. I find the ignorance in the counseling world regarding process addictions terrifying.” Another wrote, “I think graduate programs are very deficient in chemical and behavioral education/training. I was never taught anything in graduate school about addictions.” Overall, the majority of participants expressed their opinions about the importance of continued education and knowledge of PAs, shared that they had not been educated on PAs, or shared that their education on addictions was mainly focused on substance abuse treatment.
Discussion
“Counselors practice only within the boundaries of their competence, based on their education, training, supervised experience, state and national professional credentials, and appropriate professional experience” (ACA, 2005, p. 9) is an integral aspect of the counseling profession. By adhering to this section of the ACA Code of Ethics (ACA, 2005), all licensed professionals vow to accept responsibility to ‘do no harm’ to the physical, mental and emotional well-being of self, clients, and associates. Although most counselors intend to do no harm and strictly follow ethical guidelines, it is important to understand that by not providing comprehensive treatment for all addictive or problematic behaviors, some counselors may be unintentionally harming clients. Moreover, when the counselors’ only focus for treatment is the first behavior presented by the client, there is a danger of overlooking co-addictions. “Once the initial neural pathway is laid down, other addictions become overlays using some of the same circuitry” (Carnes, 2009, p.13). These co-addictions are often referred to as addiction interactions. Unfortunately, many factors of co-addictions can be found in PAs, which are often compounded by nature such as eating, sex and exercise, making the need or craving acceptable in society.
PA can be defined as any compulsive-like behavior that interferes with normal living and causes significant negative consequences, and the physiological responses in the brain are similar to chemical dependency (Grant, 2008). As aforementioned, the difficulties in recognizing PAs lie within the realm of society. For example, many of the associated behaviors are socially accepted, such as sex, spending, eating and work, all of which are an intricate part of our hierarchy of basic human needs. When assessing and diagnosing addictions, the focus is typically drug and alcohol dependency behaviors; however, PAs may mimic some of the same characteristics. Such characteristics include loss of control, compulsive behaviors, efforts to stop the compulsive behavior, loss of time, preoccupation, inability to fulfill obligations, continuation of the behavior despite the consequences, withdrawal, escalation and losses (Carnes, 2010). Other potential problems are often experienced by clients who have not been treated for all addictions and problem behaviors. Some of these include personal neglect, compulsive Internet use, isolation and avoidance of people, lost productivity, depression, dissociative states, marital and relationships problems, increased sexual risk behaviors, gambling, and academic failure.
Recommendations and Future Research
The addictions field is emerging with various types of disorders, and counselors are finding themselves to be overwhelmed and incompetent in handling the increasing demands for diagnosis, assessment and treatment of addictions in general and specifically PAs. Although counselors are expected to obtain continuing education to keep abreast of the evolution of counseling in the field, clinicians who participated in this study indicated that they were overall ill-prepared to work with clients who are living with PAs. First, it is recommended that counselor education programs implement courses that include properly assessing, diagnosing and treating PAs.
Second, it is important to reiterate that counselors make a professional vow to practice within their scope and to make referrals for services they are not capable of providing. Based on the information provided by participants in this pilot study, counselors who have no training with treating PAs are not making referrals for their clients, and are making the conscious efforts to continue working with clients who are living with PAs. It is recommended that workshops and continuing education programs specifically focused on PAs be provided for counselors who are active in the field. Staying current with the profession is of utmost importance when working in a field that changes based on available information. Moreover, it is an ethical violation to provide treatment services in an area that is beyond one’s scope of competency (ACA, 2005).
Finally, this pilot study will be replicated on a national level, obtaining further information about counselors’ knowledge and comfort level with assessing, diagnosing and treating PAs. The IAAOC is interested in further researching the knowledge of counselor educators and graduate students in counselor education programs regarding their knowledge of PAs in order to meet the needs of this population and strengthen the knowledge base of PAs within the counseling profession.
References
American Counseling Association. (2005). ACA code of ethics. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/resources/codeofethics/TP/ home/ct2.aspx.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). doi:10.1176/appi. books.9780890423349.
American Psychiatric Association. (2012a). DSM-5 development. Retrieved from http://www.dsm5.org/Pages/Default.aspx.
American Psychiatric Association. (2012b). R 37 gambling disorder. Retrieved from http://www.dsm5.org/proposedrevision/pages/proposedrevision.aspx?rid=210.
American Psychiatric Association. (2012c). DSM-5 development: K 05 binge eating disorder. Retrieved from http://www.dsm5.org/proposedrevision/pages/proposedrevision.aspx?rid=372#.
American Psychiatric Association. (2012d). DSM-5 development: Internet use disorder. Retrieved from http://www.dsm5.org/proposedrevision/Pages/proposedrevision.aspx?rid=573.
American Psychiatric Association. (2012e). Hypersexual disorder. Retrieved from http://www.dsm5.org/proposedrevision/pages/proposedrevision.aspx?rid=415
American Society of Addiction Medicine. (2012). Addiction defined. Retrieved from http://www.asam.org/for-the-public/definition-of-addiction.
Ashley, L. L., & Boehlke, K. K. (2012). Pathological gambling: A general overview. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 44(1), 2737. doi:10.1080/02791072.2012.662078.
Carnes, P. (2010). Facing the shadow (2nd ed.). Carefree, AZ: Gentle Path Press.
Carnes, P. (2009). Recovery zone, volume 1: Making changes that last: The internal tasks. Carefree, AZ: Gentle Path Press.
Crozier, M., & Agius, M. (2012). Counselor educators & process addictions: How we know what we know. NC Perspectives, 7, 32–40.
Crozier, M., & Sligar, S. (2010). Behavioral addictions screening during the vocational evaluation process. Vocational Evaluation & Work Adjustment Association Journal, 37, 45–57.
Dillman, D., Smyth, J., & Christian, L. (2009). Internet, mail, and mixed-mode surveys: The tailored design method (3rd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley.
Glasser, W. (1976). Positive addiction. New York, NY: Harper & Row.
Grant, J. (2008). Impulse control disorders: A clinician’s guide to understanding and treating behavioral addictions. New York, NY: W.W. Norton.
Grant, J. E., Potenza, M. N., Weinstein, A., & Gorelick, D. A. (2010). Introduction to behavioral addictions. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 36(5), 233–241. doi:10.3109/00952990.2010.491884
Holden C. (2001). ‘Behavioral’ addictions: Do they exist? Science, 294, 980–982.
Inaba, D., & Cohen, W. (2011). Uppers, downers, all arounders: Physical and mental effects of psychoactive drugs (7th ed.). Medford, OR: CNS Productions.
Jamieson, J., Mazmanian, D., Penney, A., Black, N., & Nguyen, A. (2011). When problem gambling is the primary reason for seeking addiction treatment. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 9(2), 180–192. doi:10.1007/s11469-009-9268-3
Karim, R., & Chaudhri, P. (2012). Behavioral addictions: An overview. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 44(1), 5–17. doi:10.1080/027910722012.662859
Ko, C., Yen, J., Yen, C., Chen, C., & Chen, C. (2012). The association between Internet addiction and psychiatric disorder: A review of the literature. European Psychiatry, 27(1), 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.04.011
Martin, P. R., & Petry, N. M. (2005). Are non-substance-related addictions really addictions? The American Journal on Addictions, 14(1), 1–7. doi: 10.1080/10550490590899808
McNamara, J., & McCabe, M. P. (2012). Striving for success or addiction? Exercise dependence among elite Australian athletes. Journal of Sports Sciences, 30, 755–766. doi:10.1080/02640414.2012.667879
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Nelson, J., Wilson, A., & Holman, L. (n.d.). Training students in counselor education programs on process addictions. Unpublished manuscript.
Onwuegbuzie, A. J., & Johnson, B. (2006). The validity issue in mixed research. Research in Schools, 13, 48–63.
Parastatidou, I. S., Doganis, G., Theodorakis, Y., & Vlachopoulos, S. P. (2012). Addicted to exercise: Psychometric properties of the Exercise Dependence Scale-Revised in a sample of Greek exercise participants. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 28(1), 3–10. doi:10.1027/1015-5759/a000084
Shallcross, L. (June, 2011). Don’t turn away. Counseling Today, 53(12), 30–38.
Smahel, D., Brown, B., & Blinka, L. (2012). Associations between online friendship and Internet addiction among adolescents and emerging adults. Developmental Psychology, 48(2), 381–388. doi:10.1037/a0027025
Smith, D., & Seymour, R. (2004). The nature of addiction. In R. Coombs (Ed.), Handbook of addictive disorders: A practical guide to diagnosis and treatment (pp. 3–30). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Spradley, J. P. (1979). The Ethnographic Interview. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning.
Sussman, S., Lisha, N., & Griffiths, M. (2011). Prevalence of the addictions: A problem of the majority or the minority? Evaluation & the Health Professions, 34(1), 3–56. doi: 10.1177/0163278710380124
US Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Substance Abuse Treatment (2006). Addiction counseling competencies: The knowledge, skills, and attitudes of professional practice, TAP 21, Technical Assistance Publication Series [DHHS Publication No. SMA 06-4171]. Retrieved from http://www.kap.samhsa.gov/ products/manuals/pdfs/tap21_08r.pdf.
Van Kaam, A. (1959). Phenomenal analysis. Exemplified by a study of the experience of “really feeling understood.” Journal of Individual Psychology, 15, 66-72.
Van Kaam, A. (1966). Existential foundations of psychology. Lanham, MD: University Press of America.
Wonderlich, S. A., Gordon, K. H., Mitchell, J. E., Crosby, R. D., & Engel, S. G. (2009). The validity and clinical utility of binge eating disorder. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 42(8), 687–705. doi:10.1002/eat.20719
Angie D. Wilson is an Assistant Professor at Texas A&M University-Commerce. Pennie Johnson is the Vice President for Project Management at the International Institute for Trauma and Addiction Professionals (IITAP) and a doctoral student at Walden University in the Department of Counselor Education and Supervision. Correspondence can be addressed to Angie D. Wilson, 1700 Hwy 24, Department of Psychology, Counseling, and Special Education (Binnion Hall), Texas A&M University-Commerce, Commerce, TX 75429, angie.wilson@tamuc.edu.
Oct 15, 2014 | Article, Volume 3 - Issue 1
Ryan F. Reese, J. Scott Young, Gerald A. Hutchinson
To date, few scholars in counselor education have attended to the processes and impacts of introducing business-related concepts within counseling curricula. The authors describe the development, implementation and evaluation of a graduate-level course titled Entrepreneurship in Clinical Settings wherein students were tasked with producing a business plan for their ideal clinical practice. Implications and recommendations are explored.
Keywords: entrepreneurship, private practice, problem-based learning, clinical settings, counselor education
Recent attention in mainstream professional counseling has brought to light the complexities of establishing and maintaining a successful clinical practice (Shallcross, 2011). Developing and sustaining a caseload through a referral base, deciding whether to buy or rent office space, and identifying a marketable niche are just a few of the many challenges practitioners face in establishing a counseling practice. Despite the complex nature of counseling practice that requires a competent understanding of foundational business concepts, limited literature exists within counselor education to address the importance of preparing counselors to succeed in private practice (Reynolds, 2010). A search for business failure rates for 2012 revealed that only 47.6% of services business, of which a counseling practice is one type, survive for five years (Shane, 2012), meaning that less that one of two counselors who begins a clinical practice will be in business five years hence. Relatedly, researchers within the field have noted that mental health practitioners have been economically naive and must expand conceptualizations of potential applications of psychological treatment, stressing the need for counselors to become more entrepreneurial (Cummings, Cummings, & O’Donohue, 2009). The development of scholarly writing around business-related concepts in counselor education might help counselor educators better prepare counselors to develop competencies related to successfully developing and running a clinical practice. Although there is a dearth of such writing at present in counselor education literature, scholars within related professions (e.g., social work; Green, Baskind, Mustian, Reed, & Taylor, 2007) have highlighted the lack of preparation that students in their fields receive in developing and managing a clinical practice and are taking steps to increase training in business-related practices. In a survey study (N=261) conducted by Green and colleagues with social work graduate stakeholders (e.g., graduate students, graduate-level deans, private and agency-level social workers), nearly 66% of graduate students intended to enter private practice, yet none of the graduate schools surveyed taught content associated with the establishment and management of a clinical practice. A similar lack of literature regarding entrepreneurship in counselor education settings would suggest that a quandary exists in programs preparing counselors for professional private practice enterprises.
Current educational standards within programs accredited by the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) do not require that students complete coursework in the business-related aspects of professional counseling. However, counselor educators who would like to provide students with practice management training cite the CACREP (2009) standards to support the infusion of business-related concepts into current courses or even in the development of a new graduate course. For example, the standards state that upon graduation from a CACREP-accredited program, a student pursuing a clinical mental health counseling track “understands the roles and functions of clinical mental health counselors in various practice settings” (CACREP, 2009, Code A.3; p. 30). That is, students will understand how to function in clinical settings, which includes private practice. In addition, the standards state that a student “understands the management of mental health services and programs, including areas such as administration, finance, and accountability” for their roles in counseling settings (CACREP, 2009, Code A.8; p. 30). Thus, the standards encourage students to gain an understanding of the technical aspects of professional counseling that can include an understanding of developing and maintaining a successful counseling practice. Offering students opportunities to gain practice management skills and competencies within counselor education programs might better prepare them to one day develop their own counseling practices.
Without an exhaustive survey, it is not known how many counselor education programs cover any of the business-related skills of clinical practice. What is certain is that in the United States nearly 20% of all small businesses do not survive past their first year and only 44% of small businesses survive to see their four-year anniversary (Knaup & Piazza, 2007). As of August 1, 2011, of the 42,926 American Counseling Association (ACA) members reporting their work settings, 10.45% described their full-time work setting as private practice and 4.1% described their part-time work setting as private practice. In sum, 14.5% of current ACA members who reported their work setting described themselves as working in private practice (C. Neiman, personal communication, August 15, 2011). Given the high failure rates for small businesses in the service sector and the fact that nearly one in seven counselors describe themselves as conducting private practice, counselor education programs should consider placing a higher emphasis on facilitating the development of knowledge and skills associated with the successful creation and management of a clinical practice.
To address this lack of training, the authors developed and implemented a graduate-level elective course titled Entrepreneurship in Clinical Settings open to both masters and doctoral-level students enrolled in graduate-level helping profession programs (e.g., counselor education, clinical psychology, social work, nursing, kinesiology, etc.) at a university located in the southeast United States. Those actually enrolled in the course included masters and doctoral-level students from counselor education. The course was advertised as an opportunity to obtain the knowledge needed to develop and run a successful private practice. The purpose of developing the course was to advance students’ knowledge and related skills in formulating an individualized business plan for establishing a clinical practice and thereby preparing them to successfully manage a small business.
The purpose of this article is to provide counselor educators and other interested readers with the information needed to adapt or develop a similar course or workshop that fits the needs of their counselor preparation programs. Subsequently, the development, implementation, evaluation and implications of a clinical entrepreneurship course specifically designed to assist students in the acquisition of the knowledge and skills necessary to develop a counseling practice in their desired setting are described.
Entrepreneurial Pedagogy
The semester-long course was co-taught by a counselor educator (second author) and a leadership consultant working in private practice (third author). The course was developed from a pedagogical structure grounded in problem-based learning (PBL) (Albanese & Mitchell, 1993). PBL typically involves the presentation of a set of carefully constructed problems to a small group of students consisting of observable phenomena or events that need explanation. The task of students is to discuss these problems and produce explanations for the phenomena (Norman & Schmidt, 1992). PBL has been implemented in a variety of educational contexts including medical training (Albanese & Mitchell, 1993), teacher preparation (Brocato, 2009) and counselor education (Stewart, 1998). With PBL, the instructor places the ownership of learning directly into the hands of students by posing a problem they must solve prior to the learning of concepts that will assist them in solving the problem (Bouhuijs & Gijselaers, 1993). Subsequently, PBL relies not on didactic instruction but on the provision of resources to aid students in developing practical knowledge needed to solve the problem at hand (Savery, 2006). Within a PBL teaching framework, the instructor is viewed as an expert resource that facilitates critical thinking by asking guided questions and providing feedback as students attempt to solve the problem at hand rather than lecturing about predetermined material (Stewart, 1998). For this course, the instructor (second author) who was a counselor educator also had over 15 years of experience as a part-time private practitioner providing counseling to children, adolescents and adults as well as couple and family counseling. He had successfully established counseling practices in two states treating a wide array of clinical issues, was knowledgeable about billing, insurance panels, marketing, accounting and related issues, had completed training in PBL pedagogy, and had extensive training in business (e.g., a B.A. in business administration). The co-instructor (third author) had obtained a Ph.D. in counselor education and supervision and spent over 15 years as a leadership development consultant to persons in positions of leadership in private industry. He had owned his own successful consulting firm for 12 years, possessing extensive training in executive coaching, consulting and leadership enhancement.
For the Entrepreneurship in Clinical Settings course, students were charged with formulating the specific components of a business plan (see Table 1), which required them to creatively align their own interests with the plan elements while accounting for practical factors that would facilitate or hinder the success of their plan. To meet this goal, each student developed a series of proposals to address the assigned problem, and then worked in small groups to challenge one another through a cyclical feedback process enhanced through the progressive acquisition of relevant knowledge. The PBL cyclical feedback process is hallmarked by the development of multiple iterations of proposals in response to the problem presented by the course instructor (Brocato, 2009). The proposals are presented for peer, self and instructor feedback in a repeating cycle until an end or desired product is developed.
Table 1
Business Plan Outline
The PBL approach was utilized for this particular course because the goal of the course was for students to develop, maintain and enhance a sense of ownership over their visions for a counseling practice they hoped to pursue. Students were challenged to develop their business plan through multiple iterations of their proposal informed by course readings, in-class discussion, guest lectures, and peer and instructor feedback. The course and its structure are described below.
Learning Goals and Objectives
The primary learning goal of the course was to support students as they labored through the PBL approach to develop a detailed business plan relevant to their identified area of focus for a counseling practice (e.g., men in transition, couples and family, children, women’s issues). This goal was addressed by meeting the following objectives taken from the course syllabus, all of which provided students with practical knowledge about the development of a counseling practice:
1. Students will articulate the benefits and problems associated with starting a counseling practice and/or provide self-employed private services as an adjunct to other employment.
2. Students will think critically about entrepreneurship and the role of business in society.
3. Students will establish a coherent counseling practice value-proposition and a profitable value-delivery model.
4. Students will analyze the options for financing a counseling practice (e.g., grants, public monies, private funds).
5. Students will analyze the importance of marketing and its role in a successful business.
6. Students will understand the basics of business budgeting, bookkeeping and third-party payments.
Course Structure
The course utilized two textbooks that served as foundation for class discussion and weekly reading assignments. Grodzki’s (2000) Building Your Ideal Private Practice is a self-help book directed toward practitioners in the helping professions who wish to improve upon or develop their own counseling practices. Readings also were assigned from the textbook Entrepreneurial Small Business (Katz & Green II, 2011), which was written for students taking a course in entrepreneurship. These texts served as key resources to students in developing their business plans.
The instructors approached class time from the PBL framework, affording students the opportunity to critically think alone and within group settings about the feasibility of their individual counseling business-related ideas. Prior to each class students worked on one aspect of their business plan (e.g., vision statements, feasibility assessment, value proposition); these assignments served as the focus of class activities. Class time was structured to include substantial peer and instructor feedback, occasional guest speakers, mini-lectures by instructors on topics related to an aspect of the business plan, and student presentations. The instructors approached the class from a Socratic rather than a didactic style in order to provide students with the opportunity to take full ownership over their business ideas and plans. Because the course content could be covered efficiently and because the PBL design allowed for students to work independently, the class met two to three times each month for two hours each session; there were a total of ten sessions across the semester for the two–semester hour course.
Elements of class included brief, interactive PowerPoint presentations with handouts as a way for the instructors to bridge the gap between students’ lack of knowledge of business-related concepts and their developing business plans. In order to add an out-of-class component to student interaction, students used a classroom online forum (Blackboard Learning Technologies) where they posted 500- to 800-word reflections about assigned readings. In addition, students were required to provide feedback regarding the postings of two peers in order to provoke additional intellectual challenge to the reading-learning assignments. Beginning in the second class session, students provided one another in-class feedback about each assignment leading up to the final business plan; this feedback was transmitted in the form of peer reviews in pairs or in triads. Near the end of the course, students provided written feedback to a peer on a draft of their partner’s business plan, which was composed of all of the assignments up to that point. In the final class meeting each student presented his or her completed business plan and responded to comments and questions by fellow course participants from the perspective of “would you invest start-up money in this practice/ business concept?” The idea was that a well-developed and clearly articulated business plan could be used to seek startup investment if needed (Grodzki, 2000). Such an environment was facilitated to help students present clear and concise descriptions of their hypothetical counseling practices. Finally, guest speakers joined class discussions on two different occasions. One speaker was a counselor who had founded and ran a successful counseling practice that provided an array of clinical services including individual, group, and family counseling; in-home counseling; trauma-focused CBT; child-parent psychotherapy; grant-funded parent skills and development; mental health consultation to Head Start; safe touch programs; school-based counseling; as well as traditional insurance-based fee-for-service outpatient counseling. This practice employed multiple counselors, and the speaker provided students a rich sense of entrepreneurial possibilities that exist with a clinical practice. The other speaker ran a successful coaching and business development practice designed to assist mental health practitioners in developing or expanding their own clinical practice.
Class Assignments
Students developed their full business plans by completing a series of related subcomponent assignments outside of class that were discussed and critiqued in class. A brief overview of assignments regarding the development of the business plan is described in Table 1. The first two weeks of the course were dedicated to students thinking about and sharing their broad counseling practice ideas and narrowing these ideas into vision and mission statements that required the development of clarity as to the nature and scope of their proposed practice, including constituents served and market niche. Students were encouraged to contact and interview clinicians in private practice in their community of interest to provide greater clarity into their potential market niche and ask different questions related to the practitioners’ business structures. Students completed several iterations of their vision and mission statements and shared these in pairs and with the class. Students were then assigned a task from the Grodzki text to develop an “elevator pitch” for the practice, which was a brief, one- to two-sentence statement regarding the nature of the practice that an uninformed person could understand. The intention of developing such a statement was, according to Grodzki, to help students describe their practices in plain, nontechnical language that the potential consumer could easily grasp (i.e., “I work with couples and families who are tired of being tired and looking for a new way of doing their relationships”). Students shared, critiqued and modified these statements several times following the PBL model. Another assignment asked students to identify their perceived level of business-related competencies through completion of a business and technical skills self-assessment (e.g., sales, accounting, industry expertise, market knowledge) (Katz & Green, 2011, p. 61). This self-assessment served as an important foundation for a discussion that allowed students to share and normalize comforts and discomforts associated with their own self-efficacy in regard to business- and counseling-related competencies.
The feasibility assessment assignment challenged students to think critically about the viability of their proposed vision and mission statements by identifying their market niche, conducting an industry profile (i.e., identifying competitors), forecasting their one- and two-year expected revenues and examining market conditions in the location of their intended practice. Students found this assignment challenging because it forced them to achieve specific clarity about their mission and vision statements. The instructors responded to student needs in the development of the fundamental vision for their business by allowing students to progress on their assignments at a somewhat different pacing. Given the high-stakes nature of business feasibility, it was important not to arbitrarily rush this step to completion.
After students had developed clear mission statements and conducted feasibility assessments, the assignments flowed more cohesively. The subsequent assignment directed students to ascertain risk management strategies by identifying appropriate professional credentials, professional liability insurance, legal structure for their practice and a financial strategy for the business (e.g., self-pay, private insurance, grants, Medicaid). Students then were challenged to articulate a value proposition for their business by indicating how aspects of their practice would add value for their clients (i.e., what a client could expect to receive for the time and resources invested). Next, students developed marketing strategies, modeled how they would deliver value, and identified the time, logistical, regulatory, economic and expertise constraints that their practices would operate under. They also specified particular support that would be necessary to make their businesses thrive, including accounting, legal and any other relevant services to position their practice for success.
In week eight students developed a budget and financial plan to determine how much capital they would need to sustain the business to profitability over a two-year span. During the final two weeks of the course, students completed their business plans and provided one another detailed feedback about those plans. In the final iteration of their business plan, students identified critical success factors, including their strengths and areas for growth to help them succeed in implementing their plans.
Use of Class Time
Typically, the first 10–15 minutes of class were utilized to discuss students’ questions about business plan components that were the topic during that class. All students presented to the class a progress update on their business plans. This allowed students to provide one another with rich feedback and suggestions in tackling components of the plan. The instructors often placed students into dyads or triads for 20–30 minutes and asked students to provide thoughtful, yet honest feedback on their partners’ work. As this occurred, the instructors would listen in and provide strategic feedback in attempts to promote group interaction and group problem-solving. The class would reconvene and present overlying concerns that ran across business plans and consider how these concerns might be addressed in the next iteration of the plan. In the latter weeks of the course, the instructors invited several guest speakers to talk about their experiences in private practice. Class generally ended with a discussion of the upcoming aspect of the business plan, how students might approach this exercise, and brainstorming of resources that might assist students in answering questions.
Course Effectiveness: A Qualitative Exploration
Because the material in the course as well as the PBL pedagogy is likely unfamiliar to many counselor educators, below we provide readers what we consider to be key learnings for instructors as well as important feedback from students. Following the conclusion of the course, 12 qualitative interview questions were developed to collect feedback associated with the beneficial and/or challenging aspects of the course, fulfillment of course purposes, the utility of course activities, the evaluation of readings, the impact of the course on students ability to develop a business plan, and recommendations for improvements. A counselor educator with experience in developing qualitative interview questions provided feedback on the questions prior to data collection. The primary author completed semi-structured interviews with all students lasting from 15–30 minutes. Interviews were audio-recorded and later reviewed to capture general themes.
Collectively, students articulated that they benefited from the conversational and practical tone of the class, profited from developing a business plan in their interest area regardless of whether the student was a second-year master’s student or a seasoned counselor and desired a more robust bridge to connect business-related information to their plans. If one is considering teaching such a course, the points below may provide clarity and guidance for making decisions as to the structure of the course and how to facilitate student learning in this rather nontraditional approach to education.
It’s simple, but it isn’t easy. The challenge in teaching this course was not assisting students in gaining mastery over the content; rather, the difficulty lies in helping students apply the content to their unique situation. Much like providing clinical supervision or leading groups, this graduate course was as much about the process as about skill mastery. Although students expressed anxiety about the business-related terminology and concepts, terms introduced in the course were kept basic and easy to understand. However, students did struggle with gaining personal clarity about the type of clinical practice they hoped to create and then matching that clarity to a method of providing services. Overall, students felt confident in their abilities to implement their business plans by the end of the course. One student stated, “I have developed a clearer understanding on what my practice will look like and confidence in what it will look like to get there.”
Students further commented on how learning and applying business concepts were less familiar to them compared to counseling concepts. Students found the Grodzki (2000) text to be written in accessible language and characterized as inspirational in the way business concepts were clearly translated. Students further described Grodzki’s writing as inspiring, provoking them to “dream big,” and a text that one “would have picked up in the bookstore.” Conversely, students (and instructors) described the Katz and Green II (2011) reading as more challenging as it was written as a textbook for business school majors. One student indicated her preference for an “entrepreneurship for dummies kind of book” that would allow her to access and understand business concepts more readily. Such feedback suggested to the instructors that in future offerings of the course reader-friendly texts that are related to counseling and fostering students’ confidence are important. Less technical information may be a better fit for counseling students who are often at an early stage of business knowledge. For example, a very accessible text targeted toward an owner-operated entrepreneurial startup such as The Big Book of Small Business (Gegax, 2007) appears ideal.
Group counseling skills are useful. The class began with many of the issues that are present in a newly formed counseling group, including heightened anxiety and uncertainty about performance and expectations. For counseling students, thinking about the business aspects of their career was like learning a foreign language and subsequently there was self-doubt about articulating their fledgling ideas to their peers and the instructors for scrutiny.
Nevertheless, students reported that verbalizing their thoughts and anxieties assisted them in clarifying their future business intentions. By sharing their ideas, they gained clarity and could evaluate the feasibility of their business plan. Students suggested that although they initially felt uncomfortable sharing their ideas to the group because they took the feedback personally, it was an important aspect of developing a well-crafted plan.
Over the course of the semester, students reported feeling more comfortable in sharing their work. Initially, one student recalled that she felt like she and her peers were “just being kind of nice to each other.” By the class’s final session, however, students reported feeling relaxed while delivering their business plan and receiving feedback. In fact, several students reported the final presentation as the highlight of the class experience. As one student stated, “people were comfortable enough to throw out honest feedback.” As a result of sharing their business plans throughout the semester in an informal atmosphere, students reported gaining more perspective and clearer visions in developing a high quality business proposal.
Expect anxiety. As is often reported in the PBL literature, students reported that they wanted more concrete answers and structure than could be provided with a PBL approach and this ambiguity caused anxiety. They often wanted to know whether something was “right” or “wrong.” Feelings of frustration and uncertainty escalated as they confronted roadblocks in their planning, but these would subside as clarity was achieved. It became clear to students that the task of the instructors was to provide appropriate support as anxiety was encountered, with the full awareness that fears could not be completely alleviated; that was the students’ work. Providing the opportunity to struggle with the implications of their business plans allowed students to overcome self-doubts as they owned their decisions; this appeared to increase self-efficacy and optimism in the development of the business plan. Students overcame challenges they previously thought were implausible. As one student recalled, “I didn’t think I would have a final business plan at the end of the class, and I did.”
You can’t teach someone to have a good idea. Students had to labor with their ideas to reach their own conviction about the feasibility of the clinical practice they hoped to create. Therefore, the instructors’ evaluation of student ideas as solid or weak proved less important than the students’ exertion through the steps of developing the business plan. Students had to reach clarity for themselves and this did not appear to come from the instructors. One student said:
When a person is developing a plan, it’s their baby and they get really invested in it and you better not criticize the baby…but you need that [criticism], you need a fresh set of eyes to look at it and say, “Did you think about that? You know, that won’t work.” And they might be wrong. It’s okay. If they’re bringing it to your attention, then that’s really good.
Students in a course such as this will be excited about and protective of their ideas, yet need assistance in challenging their ideas so that more mature thinking can emerge.
It is best to hear about “the real world” from an expert. It was important to bring in outsiders (e.g., counselors in private practice, a business coach) to discuss the process of developing a counseling practice. Even though the instructors had similar insights to share, the reality of starting and managing a clinical practice gained credibility when students heard it from “the horse’s mouth.” The instructors invited guests who ran successful clinical practices who spoke with students about their experiences in establishing and managing their business. Hearing from someone actively engaged in the day-to-day struggles of running a clinical practice was extremely valuable both in terms of offering encouragement and in modeling success.
As mentioned earlier, one speaker ran a coaching and business development practice designed to assist mental health practitioners in establishing and/or maximizing the effectiveness of their clinical practice. This speaker has worked with hundreds of counselors and therapists across the U.S. and was able to address many of the anxieties (e.g., Will I make enough money? How long will it take to get established? What sort of overhead might I expect?) Students found this practical yet highly motivating speaker to be particularly beneficial.
Course Improvements
The more experts the better. The instructors invited several guest speakers who were successful helping professionals and students consistently found these talks to be helpful. The opportunity to hear from a person who had expertise in running a clinical practice gave the students confidence that they too could learn the skills needed to run their own practice. Experts from areas outside of the helping professions were not included (e.g., business management, accounting, law) although several students commented that the opportunity to hear from experts in such specialties may have been helpful in shaping their business plans. Such experts may have made some assignments “less nebulous” as one student put it. Having guests that represent support services such as attorneys or insurance agents might have helped students better understand how to address such issues in business plans. For example, “Do I need to call law firms or call insurance companies or do I just need to be thinking what are my expenses going to be? More clarity would have been helpful,” stated one student. From the post-course perspective, the instructors concluded that the more multidisciplinary the experts the better in order to add specialist insights to the course.
Struggle is the way forward. Unlike a course in which students are asked to read, digest, and repeat material on papers or tests, this material was much more personally connected to their deeper hopes and dreams; while the building of an actual plan to manifest those dreams was the principal outcome. Subsequently, the material held significant salience for the students; thus, being patient with their struggle was crucial. Instructor gentleness was particularly salient as students were forced to struggle to match their vision with the practical reality of developing and running a small business. In the words of one student:
In other [counseling] courses we start out with a broad topic and then you narrow it down and we didn’t have that natural progression (in this class). Instead, we immediately began talking about our ideas, our vision for our careers and the uncertainty as to whether this was something we could make a reality. So from the very beginning this material was more challenging because it was personal.
Indeed, it was clear that the personal nature of the material added to the challenge of course assignments, yet it was equally apparent that the material facilitated student creativity, drive and determination to develop a plan that captured their truest vision for their clinical practice.
Sometimes the instructor needs to get out of the way of the students. The challenge for the instructors was to provide feedback that helped students move deeper into the practical reality of their ideas without discouraging vision and aspirations or taking the idea in a direction that lacked interest. For example, questions like, “Have you considered who else in the area is providing services similar to the ones you hope to offer?” is much more facilitative than, “I doubt there is a market for that.” All students commented on the importance of both instructor and student feedback. For example, one student stated, “I didn’t always feel comfortable with the feedback, but it was necessary to help with the planning process.” Another student commented on how she would have preferred more peer feedback as opposed to relying on the instructors for the expansion of her ideas. She stated:
Sometimes when we presented ideas the instructors would run with ideas of their own. This helped to create a lot of energy, which was nice, but a balance between staying true to the person’s vision versus expanding it would have been helpful.
This comment demonstrates the student’s ownership of their ideas. The instructors found it an imperative challenge to remain true to the core of students’ ideas and ask critical guiding questions while minimizing the instructor’s own contributions. The instructors had to constantly remind themselves; while they may have many years of experience, it does not always translate into expert knowledge in the areas of students’ passions.
The answer isn’t in the book. Students struggled to accept that ultimately their practice vision was not found in any of the materials they read; they had to find it in themselves. Needless to say, this was harder for some students than for others. Like many courses within counselor preparation programs, this course required students to engage in an internal process of self-examination and introspection. Students were given the additional challenge of educating themselves about business aspects of clinical practice through reading, interviews with private practitioners in their communities of interest, market research and seeking feedback. The level of self-examination required was more difficult for some as the business plans were a documentation of crystallized ideas about their hopes for entering the field. Confronting the reality of an actual plan for their future livelihood, as opposed to simply hoping to help others was not always easy. Well-considered plans to make a counseling practice successful are often difficult to come by.
Regardless of their prior counseling or business experience, all students indicated that they benefited from the course and envisioned themselves implementing their business plans. A concern the instructors initially had in developing the course was whether entry-level graduate students or those several years away from developing a counseling practice could fully benefit from such a course. Some students shared these same concerns in their interviews. One master’s student had her doubts initially, but ended up feeling accomplished at the end of the course. Another entry-level graduate student nearing the end of her program of study shared confidently that she had gained tremendously from taking the course and that it had helped her clarify the populations she would like to serve. She stated that, “Other [counseling] classes prepare you to be a generalist…this class really helped me to get the specificity and the passion that I needed behind what I wanted.” Students emphasized that the course helped them clarify their goals not just for establishing a clinical practice, but also in regards to who they wanted to be as practitioners. One student said, “Once you are clear, then you know what to ask for and when you can ask for it; then you are open to getting that.” In a similar way, another student noted, “Because of the course I was able to strip away all the extraneous things and focus on kind of the core of what I want my business to be.” This course impacted students’ level of confidence and clarity in not only the kinds of practices they wanted to develop, but also what they wanted their identities to be as professional counselors. Students at all levels of counseling and business-related experience reported gaining professionally from taking the course. Students indicated that they appreciated and were challenged by the seminar style that provided a process for facilitated student and instructor feedback. Even though at times they wanted more guidance on assignments, students gained clarity about the types of clients they intended to work with, the practices they hoped to develop and the professionals they aspired to be.
Discussion
Both student and instructor reflections identified the strengths as well as the challenges of implementing the course, Entrepreneurship in Clinical Settings. Students reported benefiting from their experience as the development of the business plan forced them to narrow their focus and develop a feasible strategy for implementing their small business ideas. Students went from having broad and poorly formed ideas to a tangible focus for their practice that allowed them to explore the feasibility of their business model. Although some students were several years away from developing a clinical practice, at the conclusion of the course all reported clarity about their proposed business ideas and a sense of confidence in both themselves and the plans they believed would help shape a more specific counselor identity.
The idea of teaching business concepts may be intimidating to some counselor educators, especially those lacking experience running a counseling practice. While counselor educators with experience running a clinical practice are likely more prepared to instruct this course, this may not always be a possibility. Subsequently, for counselor educators who lack experience with a private clinical practice, consider recruiting a co-instructor with practice experience to assist with discussions of business-related concepts and the structuring of a practice. Another option is to consult closely with local counselors who run clinical practices and who can serve as guest speakers to provide students with the foundation needed to integrate business concepts into their practice plans.
One approach that could prove fruitful to teach foundational business concepts is to analyze an existing clinical practice as a case study to examine how networking, marketing, budgeting, operations, risk management, accounting and training are implemented. Analyzing a counseling practice with objectivity early in the course might enhance student relationship building and allow time to transition into a more highly interactive approach in the course’s remaining activities. The instructors learned from conversations with students that including a practice case study in the first portion of the course could be beneficial. Future iterations of the course will include a case study assignment to help students’ transition into developing their own business plans in the latter part of the course.
The class assignments and activities described help students think through and solve the problem of developing their own business plan. However, delaying the start of the PBL approach until after the initial concept-building stage may be a wise consideration. With the increased comfort caused by greater familiarity and higher competence in speaking the language of business with the knowledge accrued in the first segment of the course, students could better engage in lively and productive discussions as “roundtable advisors” about others’ clinical practice ideas and businesses. Students will have a greater ownership of the outcome of the course, if they see a strong link between course-content and outcomes that benefit them directly.
Overall, students enjoyed the seminar structure of the course and PBL pedagogy. They found the classroom environment to be a comfortable, conversational process as opposed to a top-down lecture-based method. Through this structure and the PBL pedagogy, equal responsibility was placed on all classroom participants to facilitate the learning process rather than relying on the instructors to provide information. Despite this freedom and overall satisfaction, students wanted to know in greater detail what the instructors expected from each assignment. When PowerPoint mini-lectures were included, students reported feeling better able to predict the knowledge and skills the instructors expected them to obtain.
Following the completion of the course an unsolicited email was received that described the impact of the course for a particular student. Although the statement’s generalizability is limited, it captures the instructors’ intention of teaching the course:
I cannot express to you how valuable and impactful your course has already been on me in my professional journey as a counselor, but I want to try. Throughout the course of graduate school, I was on the very necessary track of opening my understanding and competence in new areas. Every time I took a class, I could envision myself doing that kind of work: children, families, assessments, adults, adolescents, career, substance abuse, you get the idea. What that gave me in the end was the feeling that I could do anything – I could accept any entry-level counseling job and be successful. What I was lacking, however, was direction. What was my passion in all of this – beyond my desire to be a helper, to be a counselor? Through the progression of Entrepreneurship in Clinical Settings, I was forced to think about not just what I could do, but what I wanted to do and that idea kept refining itself until I became very clear about the fact that I want to work with pregnant women and women parenting young children. Getting clear about this gave me energy and purpose in my job search. Instead of looking on job boards for what was being advertised, I was able to look for agencies that offered the services I wanted to provide. I was able to put out the message into the universe that this was the type of job I wanted. Three days after graduation I was offered a job as an in-home therapist. I am working with pregnant women and women who are parenting children under the age of five who are working with a caseworker on child development issues, but have also requested a therapist to work on their own mental health issues. Not only do I have a job, I can honestly say I have my dream job, and I credit your class. I still plan to start a counseling practice after licensure, but until then I am getting invaluable experience and training working with my ‘ideal clients.’
References
Albanese, M. A., & Mitchell, S. (1993). Problem-based learning: A review of literature on its outcomes and implementation issues. Academic Medicine, 68, 52–81. Retrieved from http://journals.lww.com/academicmedicine/pages/default.aspx.
Bouhuijs, P. A. J., & Gijselaers, W. H. (1993). Course construction in problem-based learning. In P. A. J. Bouhuijs, H. G. Schmidt & H. J. M. van Berkel (Eds.), Problem-based learning as an educational strategy (pp. 79–90). Maastricht: Network Publications.
Brocato, K. (2009). Studio based learning: Proposing, critiquing, iterating our way to person-centeredness for better classroom management. Theory Into Practice, 48, 138–146. doi:10.1080/00405840902776459
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2009). 2009 CACREP Standards. Retrieved from http://www. cacrep.org.
Cummings, N. A., Cummings, J. L., & O’Donohue, W. (2009). We are not a healthcare business: Our inadvertent vow of poverty. Journal of Contemporary Psychotherapy 39, 7–15.
Gegax, T. (2007). The big book of small business: You don’t have to run your business by the seat of your pants. New York, NY: Harper Collins.
Green, R. G., Baskind, F. R., Mustian, B. E., Reed, L. N., & Taylor, H. R. (2007). Professional education and private practice: Is there a disconnect? Social Work, 52, 151–159.
Grodzki, L. (2000). Building your ideal private practice. New York, NY: W. W. Norton.
Katz, J. A., & Green II, R. P. (2011). Entrepreneurial small business (3rd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Knaup, A., & Piazza, M. (2007). Business employment dynamics data: Survival and longevity, II. Monthly Labor Review, 130, 3–10. Retrieved from http://stats.bls.gov/opub/mlr/mlrhome.htm.
Norman, N. R., & Schmidt, H. G., (1992). The psychological basis of problem-based learning: A review of the evidence. Academic Medicine, 67, 557–565. Retrieved from http://journals.lww.com/academicmedicine/pages/default.aspx.
Reynolds, G. P. (2010). Private practice: Business considerations. Retrieved from http://counselingoutfitters.com/vistas/vistas10 Article_36.pdf.
Savery, J. R. (2006). Overview of problem-based learning: Definitions and distinctions. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning, 1, 9–20. Retrieved from http://www.mendeley.com/research/overview-problembased-learning-definitions-distinctions/.
Shallcross, L. (2011, March). Breaking away from the pack. Counseling Today. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/Publications/CounselingTodayArticles.aspx?AGuid=0dc6886d-24d8-48b7-bb69-74712df6ea71.
Shane, S. (2012). Failure rates by sector: The real numbers. Small Business Trends. Retrieved from http://smallbiztrends.com/2012/09/failure-rates-by-sector-the-real-numbers.html.
Stewart, J. B. (1998). Problem-based learning in counsellor education. Canadian Journal of Counselling, 32, 37–49.
Ryan F. Reese, NCC, is an Instructor at Oregon State University-Cascades. J. Scott Young, NCC, is Professor and Department Chair of Counseling and Educational Development at the University of North Carolina at Greensboro. Gerald A. Hutchinson is President of AnovaLogic Management and Leadership, LLC in Greensboro, NC. Correspondence can be addressed to Ryan F. Reese, 2600 NW College Way, Bend, OR 97701, rfr1202@gmail.com.
Oct 15, 2014 | Article, Volume 3 - Issue 1
Neal D. Gray, Paul Erickson
The present paper advocates for standardized regulations and laws for supervision of pre-licensed counselors in the United States, particularly for direct observation of clinical skills. A review of regulations by the American Counseling Association (ACA) Office of Professional Affairs (2012) reveals that only two states (Arizona and North Carolina) specify requiring supervision interventions that include the use of reviewing audio or videotapes, or live supervision modalities, to help evaluate pre-licensed counselors’ competence. Literature on the current state of regulations, extant research on supervision practices, and effects on satisfaction with supervision and self-efficacy are presented and framed in terms of standardized policy.
Keywords: pre-licensed counselors, regulations, laws, satisfaction with supervision, self-efficacy, direct observation
A review of regulations by the American Counseling Association (ACA) Office of Professional Affairs (2012) reveals that all 50 states require the practice of counseling under supervision for two or more years after the completion of the master’s degree prior to licensure. However, there are no unified national standards that govern post-master’s degree supervision (e.g., ACA, 2012; Borders & Cashwell, 1992). Supervised counseling experience range from 1000 to 4500 hours (ACA, 2012), with the amount of face-to-face clinical supervision occurring either in an individual or group setting varying greatly (ACA, 2007). Furthermore, only two states (Arizona and North Carolina) specify requiring supervision interventions that include the use of reviewing audio or videotapes, or live supervision modalities, to help evaluate pre-licensed counselor competence (ACA, 2012). Some studies have investigated supervision in this counselor pre-licensure stage, including factors related to counselor effectiveness such as self-efficacy and satisfaction (e.g., Bernard & Goodyear, 2004; Fall & Sutton, 2004; Magnuson, Norem, & Wilcoxon, 2002). The use of direct observation of skills in supervision is noted to lead to more positive effects in terms of counseling performance and outcomes. Standardization of required direct observation of clinical skills is especially necessary. The literature indicates that observation of skills is crucial to counselor professional development and practice (Herbert & Trusty, 2006). Moreover, standardization of required direct observation of clinical skills is a key factor in licensure policy. The following review calls for such standardization, with a summary of current regulations, extant research in counseling outcomes and supervision practice, and recommendations and advocacy for regulation.
Supervision Background and Standards
ACA, the Association for Counselor Education and Supervision (ACES), and the American Association of State Counseling Licensure Boards (AASCB) have all attempted to define best practices in counselor supervision. The ACA Code of Ethics standard F.1.a discusses a primary obligation of supervisors in the role of monitoring services of counselors-in-training. This consists of monitoring case notes, samples of clinical work or live observation of the trainee (Herlihy & Corey, 2006). In 1990, model legislation for licensed professional counselors was developed by the American Counseling Association to promote acceptable professional standards within the realm of counseling. This proposed licensure bill recommended state licensure boards consider “what is the nature of the supervision co-therapy, direct observation, audio and/or videotaping” (Bloom et al., p. 520). ACES also addressed this issue in two different documents. First, the Ethical Guidelines for Counseling Supervisors states that supervisors are responsible for “actual work samples via audio or videotape or live observation . . .” which “should be reviewed by the supervisor as a regular part of the ongoing supervisory process” (ACES, 1995, p. 272). Secondly, the document titled Standards for Counseling Supervisors outlines eleven core competencies necessary for successful supervision. This document recommends that effective supervisors are skilled in using appropriate methods and techniques to promote counselor development; included are the review of video and audio tapes and live supervision (ACA, 1990). Lastly, the AASCB’s Approved Supervision Model (2007) recommends “some type of actual counseling session reviewed on a regular basis (i.e., videotaped session at least once a month)” (p. 2).
Methods of Supervision
Utilizing direct observation of counseling skills in supervision is recommended by various counseling associations. Numerous studies have shown the most common method of supervision during graduate-level training and the pre-licensure stage is self-report (e.g., Amerikaner & Rose, 2012; Bernard & Goodyear, 2014; Borders, Cashwell, & Rotter, 1995; Borders & Cashwell, 1992; Borders & Usher, 1992; Coll, 1995; Culbreth, Woodford, Levitt, & May 2004; Fall & Sutton, 2004; Herbert & Trusty, 2006). The information about the content of counseling sessions is based exclusively on the pre-licensed counselor’s subjective beliefs (Noelle, 2003). A limitation of this method may involve a supervisor’s lack of observable information about the pre-licensed counselor’s session, preventing accurate evaluation of the counselor’s effectiveness (Bernard & Goodyear, 2004). Rogers and McDonald (1995) found that when social work instructors in the field practicum experience used student self-evaluation as the primary content focus of supervision, they more often rated students as prepared for professional practice. However, when instructors employed direct observation of skills as the primary focus of their teaching and discussion surrounding the supervision session, they were less likely to assess the students as being prepared for clinical work. Similarly, Amerikaner and Rose (2012) state that direct knowledge of pre-licensed individuals’ work allows more precise evaluation of clinical skill demonstration. Furthermore, Herbert and Trusty (2006) state that without direct observation “the supervisor can neither affirm nor refute counselor impressions concerning the client-counselor relationship” (p. 76).
Extant literature also suggests supervision beyond self-report may enhance the supervision experience. Anderson, Schlossberg, and Rigazio-DiGilio (2000), in a study of family therapy trainees’ experiences in supervision, found that live supervision and videotape review were related to an enhanced supervision experience. Ellis (2010) states that thorough feedback helps supervisees develop new skills and hone existing skills needed to be successful. Although highly recommended, possible reasons the direct observation of clinical skills in supervision is not more commonly utilized could be due to a lack of time clinical supervisors have to provide adequate supervision due to other job-related duties (e.g., administrative), limited contact between the supervisor and the pre-licensed counselor (Borders & Usher, 1992; Magnuson, Norem, & Wilcoxen, 2000; Rogers & McDonald, 1995), difficulty in obtaining informed consent permission to tape or view counseling sessions (Herbert & Trusty, 2006), or the unavailability of apparatus necessary to directly observe skills such as video-recording technology and one-way mirrors (Amerikaner & Rose, 2012).
Counselor effectiveness also has been linked to self-efficacy and satisfaction, which are important components of therapeutic skill. Some work has investigated these variables in the context of the pre-licensed counselors’ supervisory experience, particularly related to the method of supervision (Gray, Erickson, & Kahsheena, 2009).
Satisfaction with Supervision
Ramos-Sanchez et al. (2002) found that the supervisory relationship was a critical factor in supervisee development. Patton and Kivlighan (1997) found that the bond between supervisee and supervisor affected the quality of the rapport in the supervisees’ relationship with clients. Larson (1998) stated that supervisor support and encouragement (in addition to structured learning situations such as direct observation of skills) would affect supervisee self-efficacy. Learning occurs through both skill practice and within a supportive, satisfactory relationship (Frymier & Houser, 2000). Thus, if the supervisee and supervisor have a satisfactory supervisory relationship, the supervisee is more likely to gain competency in clinical skills, and further, the production of self-efficacy through direct observation of skills within that relationship is likely to lead to a greater satisfaction with supervision.
Self-Efficacy
Assisting the pre-licensed counselor in producing efficacious actions with clients is a primary goal of the supervisor (Larson & Daniels, 1998). Cormier and Bernard (1982) state that the most important goal of supervision is the protection of clients’ welfare and that directly observing the pre-licensed counselor’s skills is useful in meeting this goal. Abbott and Lyter (1999) posit that supervisor observation of the supervisee during field supervision, whether by direct observation or via audio or videotaped recordings, is an essential for professional growth. Lent et al. (2006) state that one function of effective supervisors is that of building efficacy, through support, encouragement and observation of skills. Direct observation of skills is related to confidence in skills, or self-efficacy.
Self-efficacy is a component of social cognitive theory, which partially is a theory of learning through observation. In terms of counseling, the theory posits that to successfully conduct therapy, counselors must believe they are capable of providing successful treatment and be able to master techniques and interventions (Bandura, 1986; Larson, 1998). Mastery is one of four factors that contribute to the development of self-efficacy (Carruth & Woodside, 2010). If pre-licensed counselors have experienced previous success with an intervention, they are more likely to engage in that behavior again. It appears as if direct observation of skills better determines the effectiveness of interventions than case conceptualization does (Bandura, 1986; Bandura, 1997; Larson, 1998).
Direct observation of skills helps more with gaining self-efficacy than more widely-used methods of training in medical settings, such as through paper and pencil testing (du Pre, 2010). For instance, in a study of supervisory observation of medical trainees’ clinical skills by Kogan, Holmboe, and Hauer (2009), the authors found that direct observation of skills is related to quicker attainment of clinical skills and more effective client care. Most importantly, confidence and the ability to apply clinical skills in practice directly influences quality of services provided (Bradley & Fiorini, 1999). Gray et al. (2009) found that pre-licensed counselors’ self-efficacy is affected by more frequent direct observation of clinical skills. Self-efficacy is thus an important component of clinical skill-building in counseling. Given the evidence for this and other elements of supervisory practice and positive outcomes in supervisees, standards for effectiveness in practice are warranted.
Discussion
Currently there are no unified national standards that govern the post-master’s degree supervision experience (e.g., ACA Office of Professional Affairs, 2012; Borders & Cashwell, 1992). Additionally, only a small minority of states require direct observation of pre-licensed counselors’ skills during the supervisory process (ACA Office of Professional Affairs, 2012). Direct observation and practice of skills are linked to self-efficacy (Bandura, 1986). Gray, et al. (2009) found higher levels of counselor self-efficacy in those receiving greater amounts of direct supervision. Thus, it is likely that increased levels of direct observation during supervision are related to both counselors’ self-efficacy and satisfaction with the supervisory experience.
Counselor performance also has been found to be related to self-efficacy and the supervisory environment (Larson & Daniels 1998); counselors who feel confident in their skills and have had adequate supervision have been shown to perform better clinically. Further, Kanno, and Koeske (2010) found social work interns who rated the supervisory experience as positive (i.e., helpful, receiving positive feedback) felt more empowered and reported higher levels of self-efficacy, linking positive supervisory experiences to self-efficacy and confidence. This work should directly translate to changes in supervision standards. Standards requiring practices that lead to such outcomes across states are necessary to provide a vehicle for optimal performance in counselor practice (Herbert & Trusty, 2006). Supervisees and educators should consider direct obervation of counseling practices to optimize the experience of supervision and counselor performance.
Implications for Supervisors
Observation of skills is clearly relevant to many aspects of supervisor-supervisee interaction. While numerous studies indicate that the most common form of conducting supervision is by self-report (e.g., Amerikaner & Rose, 2012; Bernard & Goodyear, 2014; Borders et al., 1995; Borders & Cashwell, 1992; Borders & Usher, 1992; Coll, 1995; Culbreth et al., 2004; Fall & Sutton, 2004; Herbert & Trusty; 2006), research indicates that observing counselors through the use of audio or video tapes or live supervision is beneficial to supervisee growth. Research further suggests that even minimal amounts of observation of skills has a significantly greater effect on the pre-licensed counselor’s skill development than no observation at all, and that observing the pre-licensed counselor’s skills at least half of the time in supervision is related to greater supervisee self-efficacy than less amounts of clinical skill observation (Gray et al., 2009). Self-efficacy is associated with counselor effectiveness and thus, if direct observation of skills contributes to greater self-efficacy, such observation may be linked to more effective counselor performance. Supervisee observation of supervisors performing counseling, or co-counseling between supervisor and supervisee, is another possible pathway to skill building and self-efficacy (Baird, 2011). It is recommended that supervisees take the initiative in requesting to directly observe supervisors counsel, as it has been found there can be resistance of supervisors to tape sessions for teaching purposes (Levenson & Evans, 2000).
It is paramount during discussions of expectations, roles and responsibilities in the supervisory relationship that supervisors emphasize to counselors that their skills will be observed during the pre-licensure stage (Remley & Herlihy, 2010). If not mandated by supervisors, it is doubtful that pre-licensed counselor’s will solicit direct observation of their skills. Borders and Usher (1992), in a study conducted to determine preferred supervision modalities of pre-licensed counselors, found that they preferred self-report over observation of skills. The authors state “respondents may have considered other methods (e.g., live observation, videotaping) to be too inconvenient, intrusive or threatening” (Borders & Usher, 1992, p. 598). Furthermore, at the conclusion of the pre-licensure experience, supervisors will be required to formally report to state licensure boards a judgment of the supervisees’ competence to practice independently as a counselor (Cobia & Boes, 2000). Observing skills on a regular basis throughout the relationship can aid in this decision. Lastly, it is recommended that if supervisors are not trained in using these methods of direct observation, they should consider completing continuing education training, workshops or graduate courses (Borders et al., 1995; Culbreth et al., 2004).
Implications for Counselor Educators
The Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) requires supervisors in master’s and doctoral practicum experiences to include during the experience “the development of program-appropriate audio/video recordings for use in supervision or live supervision of the student’s interactions with clients” (CACREP, 2009, p. 17). It also is common that evaluation for course success utilizes audio/videotapes or live observation of clinical sessions in practicum and internship. However, at the post-master’s degree level this is usually not a requirement, but a recommendation. As previously noted, research studies point out that the observation of clinical work is a rarity and that self-report of clinical sessions is the norm (Amerikaner & Rose, 2012; Bernard & Goodyear, 2014; Borders et al., 1995; Borders & Cashwell, 1992; Borders & Usher, 1992; Coll, 1995; Culbreth et al., 2004; Fall & Sutton, 2004; Herbert & Trusty, 2006). Extant work has found that during the pre-licensure phase of supervision, counseling skills are usually never or rarely observed, but that viewing supervisees’ skills significantly affects their beliefs positively concerning their levels of self-efficacy (Gray et al. 2009).
It is recommended that counselor educators in master’s and doctoral degree programs discuss the post-master’s degree process with students during their graduate school experience, specifically recommending that when selecting a supervisor, pre-licensed counselors broach the issue of how their counseling skills will be evaluated. It also is necessary that counselor educators encourage future counselors to choose supervisors committed to using direct observation as a method to enhance counselee growth, following CACREP requirements that mandate direct observation of skills in graduate practicum and internship experiences. Research such as that cited here can demonstrate to future pre-licensure counselors that despite the possible feelings of anxiety associated with having their clinical skills examined, requesting this observation will benefit their growth as counselors greatly (Borders & Usher, 1992; Overholser, 2004).
Since counselor educators have experience and skill in using these methods of direct observation, it also is recommended that they provide supervision trainings or continuing education opportunities for supervisors in their communities to enhance their competence in supervision (Coll, 1995). Furthermore, as more states call for supervisors to become board certified, counselor educators should advocate for state licensure boards to require supervisory training in methods of clinical skill observation. In addition, it is also recommended that counselor educators support licensure boards mandating a certain percentage of time that counselors’ skills are directly observed. Herbert and Trusty (2006) state that “given the clearly expressed preference for counselors to provide verbal reports of counseling sessions, it is unlikely that other, more direct methods, such as those available through audiotape, videotape, one-way mirror, will evolve without policy changes” (p. 76).
Conclusion
The post-master’s degree supervision experience is critically important in the development of competent counselors, and some research has been conducted to determine which factors in supervision produce more satisfied or capable counselors. However, individual state licensure boards in the United States lack specific requirements concerning methods of supervision (e.g., verbal exchange, direct observation). While the case consultation method is the most directly utilized method of supervision, it should not be the only approach utilized in the supervisory environment. Direct observation of skills by supervisors is a necessary component in the pre-licensed counselors’ professional development. Furthermore, direct observation of skill development will enhance counselor performance, possibly leading to more successful clinical outcomes (Herbert & Trusty, 2006). Given extant work in supervision outcomes, observational learning, and instructive relationships, standard policy regarding supervision of direct skills must be mandated across state licensure boards.
References
Abbott, A. A., & Lyter, S. C. (1999). The use of constructive criticism in field supervision. The Clinical Supervisor, 17(2), 43–57 doi:10.1300/J001v17n02 02
American Association of State Counseling Boards (2007). Approved supervisor model. Alexandria VA: Author.
American Counseling Association Office of Public Policy Legislation (2007). Mental health professional supervised experience requirements for state licensure. Alexandria, VA: Author.
American Counseling Association Office of Professional Affairs. (2012). Licensure requirements for professional counselors: A state-by-state report. Alexandria, VA: Author.
American Counseling Association (1990). Standards for counseling supervisors. Journal of Counseling and Development, 69, 30–32.
Amerikaner, M., & Rose, T. (2012). Direct observation of psychology supervisees’ clinical work: A snapshot of current practice. The Clinical Supervisor, 31(1), 61–80.
Anderson, S. A., Schlossberg, M., & Rigazio-DiGilio, S. (2000). Family therapy trainees’ evaluations of their best and worst supervision experiences. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 26, 79–91.
Association for Counselor Education and Supervision. (1995). Ethical guidelines for counseling supervisors. Counselor Education and Supervision, 34, 270–276
Baird, B. N. (2011). The internship, practicum, and field placement handbook (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York, NY: W.H. Freeman.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2004). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (3rd ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2014). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (5th ed.). Columbus, OH: Pearson.
Bloom, J., Gerstein, L., Tarvydas, V., Conaster, J., Davis, E., Kater, D., Sherrard, P., & Esposito, R. (1990). Model legislation for licensed professional counselors. Journal of Counseling and Development, 68, 511–523.
Borders, L. D., & Cashwell, C., S. (1992). Supervision regulations in counselor licensure legislation.Counselor Education and Supervision, 31, 209–218.
Borders, L. D., Cashwell, C., S., & Rotter, J. C. (1995). Supervision of counselor licensure applicants: A comparative study. Counselor Education and Supervision, 35, 54–69.
Borders, L. D., & Usher, C. H. (1992). Post degree supervision: Existing and preferred practices. Journal of Counseling and Development, 70, 594–599.
Bradley, C., & Fiorini, J. (1999). Evaluation of counseling practicum: National study of programs accredited by CACREP. Counselor Education and Supervision, 39, 110–119.
Carruth, E. K., & Woodside, M. (2010). The development of counseling self-efficacy: A case study. North Carolina Perspectives, 3, 4–17.
Cobia, D. C., & Boes, S. R. (2000). Professional disclosure statements and formal plans for supervision: Two strategies for minimizing the risk of ethical conflicts in post-master’s supervision. Journal of Counseling and Development, 78, 293–296.
Coll, K. M. (1995). Clinical supervision of community college counselors: Current and preferred practices. Counselor Education and Supervision, 35, 111–117.
Cormier, L. S., & Bernard, J. M. (1982). Ethical and legal responsibilities of clinical supervisors. The Personnel and Guidance Journal, 60, 486–491.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2009). 2009 CACREP accreditation manual Alexandria, VA: Author.
Culbreth, J. R., Woodford, M. S., Levitt, D. H., & May, K. M. (2004). Current and preferred clinical supervision experiences of home based treatment providers. The Clinical Supervisor, 23(1), 83–99. doi:10.1300/J001v23n0106
du Pré, A. (2010). Communicating about health: Current issues and perspectives (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Oxford.
Ellis, M. V. (2010). Bridging the science and practice of clinical supervision: Some discoveries, some misconceptions. The Clinical Supervisor, 29(1), 95–116.
Fall, M., & Sutton, J. M. (2004). Supervision of entry level licensed counselors. The Clinical Supervisor, 22(2), 139–151. doi: 10.1300/J001v22n02_09
Frymier, A. B., & Houser, M. L. (2000). The teacher-student relationship as an interpersonal relationship. Communication Education, 49, 207–219. doi: 10.1080/03634520009379209
Gray, N. D., Erickson, P., & Kahsheena, Z. (2009, March). The optimal supervision experience: A post-masters’ supervisee perspective. Presentation conducted at the Annual Convention and Exposition of the American Counseling Association, Charlotte, NC.
Herbert, J.T., & Trusty, J. (2006). Clinical supervision practices and satisfaction within the public vocational rehabilitation program. Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin, 49(2), 66–80.
Herlihy, B., & Corey, G. (2006). ACA ethical standards casebook (6th ed.). Alexandria, VA: Author.
Kanno, H., & Koeske, G. F. (2010). MSW students’ satisfaction with their field placements: The role of preparedness and supervision quality. Journal of Social Work Education, 46, 23–38.
Kogan, J. R., Holmboe, E. S., & Hauer, K. E. (2009). Tools for direct observation and assessment of clinical skills of medical trainees: A systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Association, 302(12), 1316–1326. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1365
Larson, L. M. (1998). The social cognitive model of counselor training. The Counseling Psychologist, 26, 219–273.
Larson, L. M., & Daniels, J. A. (1998). Review of the counseling self-efficacy literature. The Counseling Psychologist 26(2), 179–218.
Lent, R. W., Hoffman, M. A., Hill, C. E., Treistman, D., Mount, M., & Singley, D. (2006). Client-specific counselor self-efficacy in novice counselors: Relation to perceptions of session quality. Journal of Counseling Psychology 53, 453–463.
Levenson, H., & Evans, S. (2000). The current state of brief therapy training in American Psychological
Association-accredited graduate and internship programs. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 31, 446–452.
Magnuson, S., Norem, K., & Wilcoxon, S. A. (2000). Clinical supervision of prelicensed counselors: Recommendations for consideration and practice. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 22, 176–190.
Magnuson, S., Norem, K., & Wilcoxon, S. A. (2002). Clinical supervision for licensure: A consumer’s guide. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 41, 52–60.
Noelle, M. (2003). Self-report in supervision. The Clinical Supervisor, 21(1), 125–134. doi: 10.1300/J001v21n01_10
Overholser, J. C. (2004). The four pillars of psychotherapy supervision. The Clinical Supervisor, 23(1), 1–13. doi: 10.1300/J001v23n01 01
Patton, M. J., & Kivlighan, D. M. (1997). Relevance of the supervisory alliance to the counseling alliance and to treatment adherence in counselor training. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 44, 108–115.
Ramos-Sanchez, L., Esnil, E., Goodwin, A., Riggs, S., Touster, L. O., Wright, L. K., Ratanasiripong, P., & Rodolfa, E. (2002). Negative supervisory events: Effects on supervision satisfaction and supervisory alliance. Professional Psychology, Research and Practice, 33, 197–203.
Remley, T. P., & Herlihy, B. (2010). Ethical, legal, and professional issues in counseling (3rd ed).Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill.
Rogers, G., & McDonald, P. L. (1995). Expedience over education: Teaching methods used by field instructors. The Clinical Supervisor, 13(2), 41–61. doi: 10.1300/J001v13n02_04
Neal D. Gray is the Chairperson of the Counselor Education program at Lenoir-Rhyne University. Paul Erickson is an Associate Professor and Director of Educational Research Assessment and Technology at Eastern Kentucky University. Correspondence can be addressed to Neal D. Gray, 625 7th Avenue NE, Hickory, NC 28601, neal.gray@lr.edu.
Oct 15, 2014 | Article, Volume 3 - Issue 1
Dodie Limberg, Hope Bell, John T. Super, Lamerial Jacobson, Jesse Fox, M. Kristina DePue, Chris Christmas, Mark E. Young, Glenn W. Lambie
The professional identity of a counselor educator develops primarily during the individual’s doctoral preparation program. This study employed consensual qualitative research methodology to examine the phenomenon of professional identity development in counselor education doctoral students (CEDS) in a cohort model. Cross-sectional focus groups were conducted with three cohorts of doctoral students in counselor education (N = 18) to identify the experiences that contributed to their professional identity development. The findings identified that (a) programmatic goals to develop professional identity align with the experiences most influential to CEDS, (b) experiential learning opportunities enhanced CEDS professional identity development, (c) the relationships with mentors and faculty contribute to their identity as counselor educators, and (d) being perceived as a counselor educator by faculty influences professional identity development. Implications for counselor education and the counseling profession are discussed.
Keywords: consensual qualitative research, counseling, counselor education and supervision, doctoral student development, professional identity development
Professional identity development is central to counseling professionals’ ethical practice (Corey, Corey, & Callanan, 2010; Granello & Young, 2012). The process of professional identity development is defined as the “successful integration of personal attributes and professional training in the context of a professional community” (Gibson, Dollarhide, & Moss, 2010, pp. 23–24). Counselor education doctoral students (CEDS) develop their identity as counselor educators primarily during their doctoral preparation program (Calley & Hawley, 2008; Carlson, Portman, & Bartlett, 2006; Zimpfer, Cox, West, Bubenzer, & Brooks, 1997). Specifically, intentional experiences designed by faculty and/or initiated by CEDS during their doctoral preparation program promote their professional identity development as counselor educators, supporting an effective transition into academia (Carlson et al., 2006). Counselor education doctoral programs employ diverse pedagogical strategies to promote their students’ identity development (e.g., Zimpfer et al., 1997). However, the impact that the experiences and strategies developed within programs has on students and their professional identity has not been examined in previous research. Therefore, an increased understanding of CEDS’ professional identity development might offer insight into pedagogical experiences that enhance doctoral students’ transition from counseling practitioners to faculty members in higher education (Calley & Hawley, 2008; Magnuson et al., 2003).
Professional identity development within counselor education can be described as both an intrapersonal and interpersonal process (Gibson et al., 2010). The intrapersonal process is an internalization of knowledge shared by faculty members and supervisors (e.g., recognizing personal strengths; areas of growth in academic roles). The interpersonal process develops during immersion into the norms of the professional community (e.g., submitting manuscripts for publication, presenting papers at conferences, teaching courses). These two developmental processes co-occur while counselor education trainees are conceptualizing their specific roles and tasks within academia.
Within counselor educators’ professional identity development, three primary roles emerge: (a) teaching and supervision, (b) research and scholarship, and (c) service (Calley & Hawley, 2008). An exploration of the tasks and/or experiences that facilitate doctoral students’ understanding of their future roles as counselor educators is needed (Calley & Hawley, 2008; Gibson et al., 2010). Carlson and colleagues (2006) developed a conceptual model of professional identity development in counselor education consisting of eight roles or tasks: (a) program expectations, (b) teaching and supervision, (c) research, (d) publications, (e) grants and funding, (f) service and conferences, (g) networking, and (h) professional development. Doctoral preparation programs are tasked with guiding future counselor educators’ understanding of these eight roles. Within doctoral preparation programs, three programmatic structure models are employed: (a) independent, (b) part-time, or (c) cohort (Walker, Golde, Jones, Bueschel, & Hutchings, 2008). For the purposes of this manuscript, we focus on the doctoral preparation cohort model. A doctoral preparation cohort model is defined as a group of students entering their preparation program together (same semester), taking the majority of coursework together, and moving through the program concurrently (Paisley, Bailey, Hayes, McMahon, & Grimmett, 2010).
In doctoral counselor education and supervision preparation programs, professional identity development is crucial as students move from their roles as counseling practitioners to counselor educators: making the paradigm shift from thinking like a counselor to thinking like an educator, supervisor, researcher, and leader (e.g., Carlson et al., 2006; Hall & Burns, 2009). In addition, the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Education Programs (CACREP, 2009) Standards state that doctoral preparation program facilitate experiences for doctoral students to collaborate “with program faculty in teaching, supervision, research, professional writing, and service to the profession and the public” (p. 54). Furthermore, the American Counseling Association (ACA) and the Association for Counselor Education and Supervision (ACES) provide professional development opportunities (e.g., conferences, publications) for CEDS to develop their professional identity as future counselor educators. Nevertheless, limited research has investigated professional identity development of CEDS during their cohort model doctoral preparation program.
The shift of identity for CEDS may be from a counselor identity, a student identity, or other professional identity, depending on vocation before entering a counselor education doctoral program. Development of identity as a counselor educator requires a sometimes-difficult shift from previous occupational foci to that of counselor education. Regardless of previous identity, the counselor educator identity is unique in its focus on scholarship, service, and teaching. Without investing oneself in these qualities of counselor education, CEDS risk making a full transition from their previous identity to that of the counselor educator, thus shorting themselves and future students and employers the benefits of an invested counselor educator, such as being student-centered, contributing to the field through research, and giving back to the counseling community. Given the importance of professional identity development in CEDS, the purpose of the present study was to (a) gain a better understanding of the professional identity development process of CEDS during their cohort model doctoral preparation program and (b) identify the specific experiences of CEDS that influenced their professional identity development. The research question guiding the investigation was: How do CEDS develop their professional identities as counselor educators during their cohort model doctoral preparation program?
Method
We utilized consensual qualitative research (CQR; Hill, Thompson, & Williams, 1997; Hill, Knox, Thompson, Williams, & Hess, 2005) for this study. By definition, CQR combines elements of phenomenological, comprehensive analysis, and grounded theory approach to focus on the subjective experiences of humans in their sociological context (Heppner, Wampold, & Kivlighan, 2008). CQR was selected for this study due to (a) the intention of analyzing the comprehensive, subjective experiences of professional identity development among CEDS; (b) its collaborative nature; and (c) data consistency through consensus (Hays & Wood, 2011). Hill and colleagues (2005) identified four main aspects of CQR: (a) the use of open-ended questions, (b) consensual judgment of meaning in the data, (c) the use of an auditor throughout data analysis, and (d) identifying domains and core ideas through cross-analysis. All four of these research aspects were utilized in our investigation. In addition, our study was initiated as an assignment for a first semester doctoral counselor education class and evolved into a genuine interest in understanding professional identity development processes. As a result, we adhered to all protocol for a research study (e.g., approval of university’s institutional review board).
Research Team
We (the research team and authors) consisted of: seven first-year CEDS within a counselor education and supervision doctorate of philosophy (Ph.D.) program at a large southeastern university, a professor within the counselor education and supervision program who assumed the role of the internal auditor and facilitated the focus group for the first-year cohort (i.e., the research team), and an associate professor, in counselor education and supervision, who fulfilled the role of the external auditor and was not involved in data collection and analysis. We ranged in age from mid 20s to late 50s and consisted of four female students, three male students and two male faculty members, and we are all Caucasian. Five members of the research team conducted focus groups, while all members contributed to analyzing the data with the exception of the external auditor. A master’s-level student, not associated with the data collection or analysis, transcribed the focus group data from an audio format.
Positionality and Trustworthiness
We attempted to separate or bracket our biases and judgments regarding the phenomenon under investigation to understand CEDS professional identity development processes with as much objectivity as possible (Creswell, 2007; Hays & Wood, 2011). Therefore, we recorded our biases and expectations in a meeting prior to data collection (Hill et al., 1997). Additionally, we discussed researcher biases and expectations throughout the duration of the study in order to promote awareness of the influence we, as researchers, may have on data analysis (Creswell, 2007). Our biases included the belief that professional identity development is an important aspect of our doctoral program design and that results from this investigation would exemplify specific experiences, in our program, that highlight the areas of teaching, supervision, research, and service in counselor education. The personal knowledge of the participants may have created bias and higher value in particular participant voices in the data analysis; however, this knowledge also added richness to the data collected through prolonged engagement (Creswell, 2007). Additionally, the power dynamic between a professor leading a focus group or a first-year cohort member leading a focus group may create bias in participant responses. Our expectations were that data would vary by cohort years based on the participants’ time in the program and their level of experience, and experiences in (a) teaching and supervision, (b) participating and publishing research, and (c) presenting at conferences would be more powerful than other experiences due to their emphasis in our doctoral program.
To reduce the effects of bias when coding data and to support trustworthiness for our investigation, we used investigator triangulation and an internal and external auditor to evaluate each step of data analysis (Glesne, 2011; Hays & Wood, 2011; Hill et al., 1997). Both auditors were part of the counselor education program in which the study was conducted; therefore, this internal knowledge of the program may have influenced their review of the data analysis. In addition, we used member checking to support trustworthiness, asking participants to review transcripts, preliminary findings and near-finished writings. Furthermore, we sought to be transparent in revealing unforeseen barriers that presented in the research process, supporting the credibility of the research findings. These barriers included various levels of participation in cohorts, the challenge of coding and analyzing data that the research team itself produced through the first-year cohort focus group, and the ability to identify certain participants through personal knowledge of doctoral students in the program. We sent the raw data and the analysis to external and internal auditors to review the consistency and integrity of the data. The external auditor, whose perspective was not influenced by the research team, may have been influenced from being in the same program. This auditor supported the identified themes and findings. The internal auditor confirmed that the raw data were accurately represented under the domains, core ideas and categories.
Participants
The participants were first-, second- and third-year CEDS enrolled in a counselor education and supervision Ph.D. program at a large research university in the southeastern United States. They were recruited and selected to participate based on purposive criteria (i.e., enrolled as a doctoral student in the counselor education program) through campus email. The doctoral program in counselor education and supervision from which the participants were recruited is a fulltime, three-year program that employs a cohort model and awards Ph.D. degrees (Paisley et al., 2010). Criterion-based selection was utilized to ensure participants had similar experiences and commonalities within their doctoral program and to capture the variety of research interests, skill levels and clinical experience among the three years (Creswell, 2007). Although CQR is a qualitative analysis focused on producing results that illustrate the participants’ life experience related to the phenomenon investigated, CQR methodology does suggest a sample size of at least three cases in order to perform the cross-analysis during the data analysis process. A total of 18 CEDS agreed to participate with fellow cohort members in a focus group designated by year, which was an appropriate sample size for CQR (Hays & Wood, 2011). The first-year cohort included seven focus group participants (100% of the first-year CEDS population at this university) consisting of four Caucasian females and three Caucasian males. The second-year cohort included eight focus group participants (78% of the second-year population) with two Caucasian females, one African-American female, one Asian male, and four Caucasian males. Finally, the third-year CEDS cohort included four focus group participants (67% of the third-year population) comprised of two African-American females, one Asian female, and one Caucasian male.
In this study, we acted as both participants and researchers (i.e., the first-year cohort). In qualitative research, the observers can range from complete observers to complete participants (Creswell, 2013), and while traditional research design encourages impartiality, qualitative research varies. Researchers participating in a study offers greater depth of what the participants are experiencing, helps establish greater rapport with the participants and provides an understanding of the context better than would be understood by nonparticipant observers (Creswell, 2013; Heppner et al., 2008). There were several drawbacks that emerged from engaging in the dual roles of researcher and participant. The primary challenge occurred in analyzing the data for the first-year cohort (our cohort). In the dual roles, a level of familiarity was added, as we knew the underlying meanings of statements that might have appeared unclear to outside researchers. While this dual role also was a strength in that the true meaning of the data was able to be analyzed, the same level and depth of understanding could not be given to coding the second-year and third-year cohort data, as they were not part of the research team.
Data Collection
Data collection consisted of facilitators(s), who were members of the research team, conducting focus groups for each CEDS cohort. The focus groups were semi-structured with five open-ended questions asked in sequential order to promote consistency across groups and allow for rich data collection and in-depth responses (Bell et al., 2012; Heppner et al., 2008). Focus groups were conducted, as opposed to individual interviews, to maximize group dynamics that contribute to richer data collection, with the responses of each cohort being observed and recorded. The questions used to facilitate the focus group were created by the research team based on the literature of doctoral student identity.
The open-ended questions were: (a) Describe your experience of transitioning from counselor to counselor-educator-in-training? (b) I am going to name several different experiences you have had so far during your doctoral program (i.e., clinical work with clients, conducting research, teaching, supervising students, service to the profession, attending or presenting at conferences, interviews with faculty members in your initial doctoral class, cohort membership). Please identify or talk about things that happened in any of these arenas that helped you think of yourself as a counselor educator. (c) What other experiences have you had that resonated with you that affected your development as a counselor educator? (d) What pivotal moments (or critical incidents such as important conversations or successes) have you experienced that have helped to form your identity as a counselor educator? and, (e) Can you talk about any experiences that have created doubts about adopting the identity of a counselor educator?
Focus groups lasted one to two hours, varying by the discussion duration. All participants were assured that answers would be kept confidential to protect relationships within the program and promote honest answers. Although confidentiality was explained as part of the consent process, participants were also reminded that researchers could not guarantee confidentiality of other participants within the focus group. While the focus group design offered an environment rich for discussion, it is possible that participants may have held back on full disclosure due to the close nature of the program and personal knowledge of other participants. A faculty member of the research team facilitated the first-year CEDS focus group in order to preserve group facilitator impartiality and allow the first-year cohort, serving dual roles of research members and participants, to fully participate in the focus group process. The second-year and third-year CEDS focus groups were facilitated by first-year CEDS from the research team. Following each focus group, facilitators were asked to debrief by reflecting on three structured open-ended questions: (1) What experiences did participants mention most frequently and with the most emotional intensity? (2) Were there questions that seemed to elicit more or less response? and (3) Anything else that was relevant or noticeable (to you) during this focus group? The purpose of the debriefing was to acknowledge bias from the focus group leaders and to ensure that each leader could express the experience and understanding of the focus group. All the focus groups and debriefing sessions were audiotaped and subsequently transcribed.
Data Analysis
When using CQR, data analysis is a three-step process of (a) clustering data and identifying domains, (b) summarizing core ideas from the domains with shorter descriptions, and (c) developing categories that classify the common themes in the core ideas that exist across cases (Hill et al., 2005). Figure 1 visually explains the data analysis process. We analyzed the data by focus group, and each focus group participant’s contribution was analyzed independently. The data were analyzed to identify domains that were common themes from members of the cohorts. From the domains we recognized core ideas developing within the domain and from the core ideas we recognized categories that developed that crossed the focus groups. Of the eight final domains identified, five domains have more than one category. The process for coding used several methods, using names from the social sciences and in vivo coding where exact words or phrases were used to identify the code.
Figure 1. Data analysis flow chart of the process of analyzing each domain.
Domains. Before collecting and analyzing the data, we collectively created a 12-item start list of domains to guide our data investigation, which is a suggested step of CQR (Hill et al., 2005; Miles & Huberman, 1994). Table 1 presents the start list of domains (bolded), in addition to domains that emerged during data analysis. The start list domains were based on our expectations, as well as the three areas of (a) teaching and supervision, (b) research, and (c) service within counselor education (CACREP, 2009; Calley & Hawley, 2008). A domain start list created by the research team through consensus and in accordance with previous literature related to the phenomenon studied serves several purposes. The start list familiarized the research team with previous findings and allowed for comparison of new emergent themes, and themes found in previous research that was not identified in the current study. Additionally, the start list acquainted the research team with the process of reaching consensus in data analysis. While domain start lists may serve to skew data analysis if not properly and carefully analyzed, all domains required support from the data to be kept or added. Thus, in viewing Table 1, one can see that the original start list did have domains that were dropped due to lack of support from within the data. In accordance with CQR, we analyzed the first-year CEDS data independently, then met as a consortium and evaluated the same data together until consensus was met and domains adjusted. The second-year and third-year CEDS focus groups’ data were then analyzed through us breaking into dyads and triads. Domains were added to the master list as they appeared in the data and were agreed upon by the entire research team. In addition, we collapsed or deleted any domains that were found to be redundant, insignificant, or not present.
Table 1
Domain List Used to Analyze Data
When analyzing the second-year and third-year focus group data, if a difference of opinion arose concerning the meaning of a response, we added subjective insight from the perspective of the group facilitator and how they interpreted the participants’ response in the greater context of the focus group. Additionally, if consensus was not met, we reviewed the original transcript to clarify and meet consensus of the meaning of the data (Hill et al., 2005).
Core ideas and categories. After categorizing the data by cohort year under domains, we continued to work in dyads and triads to formulate core ideas from the raw data (grouped by domain and not by cohort year). We then determined categories that each core idea fell under. Each core idea was assigned a category, and similar core ideas were collapsed under a category to best represent the data. The categories served an overall purpose to classify and determine frequency in the responses from participants within each domain. Categories were clarified through a cross-analysis (Hill et al., 2005) of the participants’ year in the program, and if more than one member of the cohorts identified a domain as an important task or experience. Figure 1 shows the process of categorizing the data from domains to core ideas and then to categories. In CQR, the number of cases in each category determines the frequency label (Hill et al., 2005). General frequency constitutes all, or almost all, cases; typical constitutes more than half of the cases; and variant for less than half of the cases. For this investigation, each focus group represented one case, so frequency labels were defined as general if the category was present in all three cohort groups, typical if the category was present in two groups and variant if the category only emerged in one cohort’s focus group. We reevaluated the domains based on the frequency of the categories within the domain and the relevance to the research question, resulting in the final domain list (see Table 1) that was agreed on through consensus with the entire research team. Finally, we asked the participants to review the preliminary findings (member check), supporting trustworthiness. Participants supported the findings and did not dispute them.
Results
The findings of the investigation are described using domains (i.e., topics used to group data; Hill et al., 2005) and categories used to conduct a cross-analysis to support the findings and connect the findings to the research question. Originally, we developed a start list (Miles & Huberman, 1994) of 12 domains based on previous literature and personal experiences (bolded in Table 1). The start list was expanded to 19 domains through the data analysis (not bolded in column 2 of Table 1). Through further examination, a cross-analysis of the core ideas and categories within each domain was conducted (as presented in Figure 1). After the cross-analysis, the auditors reviewed the data and provided feedback. We revisited the 19 domains, identifying eight domains as strong due to their relevance to the research question and the domain being supported through the clarification of categories (as described in the methods section). The eight domains identified as strong were: (a) teaching, (b) supervision of students, (c) conducting research, (d) attending or presenting at a conference, (e) cohort membership, (f) program design, (g) mentoring, and (h) perceived as a counselor educator by faculty (Column 3 of Table 1; Bell et al., 2012). The eight domains and cross-analysis results are presented in Table 2, which exemplifies the frequency of categories created to increase the level of abstraction in the data analysis (Hill et al., 2005). Not all domains had categories (e.g., cohort membership, program design, and being perceived as a counselor educator by others) because the data within these domains was not diverse enough to create separate categories.
Domain I: Teaching
The teaching domain generated a significant amount of data from the CEDS groups in creating and strengthening their identities as counselor educators. Additionally, the teaching domain produced three contributing categories. Teaching is a core component of a doctoral counselor education program (CACREP, 2009). For this particular university’s program, teaching begins in the first year and peaks in the second year. Teaching was defined as didactic instruction of master’s-level students by doctoral students and occurred in the form of teaching classes, facilitating psycho-educational groups and clinical instruction. The teaching domain was present throughout the first-year, second-year and third-year focus groups with varying emphasis in the categories of (a) teaching experience, (b) contributing factors, and (c) critical interactions with students (see Table 2 for the breakdown and frequencies of the categories within the teaching domain). Therefore, teaching experience during the doctoral program assisted the CEDS in developing their professional identity, specifically their role as counselor educators.
Table 2
Cross-Analysis Findings: Final Domain and Category List
Category 1: Teaching experience. Data generated on the teaching experience category originated from the second-year and third-year CEDS cohorts, designating it as a typical category. Some participants discussed previous teaching experience as vital, while others identified the learning of teaching theories as important. The data revealed the second year as the period in which teaching becomes relevant in this particular counselor education doctoral program. Additionally, first-hand teaching experiences were identified by the third-year cohort as important in counselor educator identity formation. The teaching experience provided doctoral students a way to practice and apply their teaching and learning theory, and an opportunity to build their confidence as teachers. One third-year CEDS stated, “I recognized myself as a counselor educator when I had to assign grades, especially those below a B.”
Category 2: Contributing factors. The category of contributing factors was a general category, present in all three CEDS cohorts. The first-year CEDS felt mandatory programmatic activities such as facilitating psycho-educational groups contributed to their counselor educator identity development in teaching. The second-year students noted the interrelation of teaching and supervision, in that using these skills in a classroom improved their efficacy and contributed to adopting a counselor educator persona. The interrelation is indicated in one student stating, “The second year allows you the opportunity to do everything, including teaching, that you will be doing as a counselor educator.” In addition, evaluating students’ knowledge and skills acquisition helped in developing teaching as a core component of the counselor educator identity. A second-year CEDS supported the importance of student evaluation by stating that teaching and grading were not skills used as a counselor, but differentiated the CEDS as a counselor educator.
Category 3: Critical interactions with students. Though a variant category, third-year cohort members found interactions with students to be influential in adopting the identity of a counselor educator. The third-year group discussed important moments with students that created an impact on them such as: (a) receiving teacher evaluations, (b) grading students, (c) managing student concerns, and (d) feeling pride at student accomplishments. One student stated:
In terms specifically of my teaching I remember grading and being, okay this is where I have to be a big boy, this is where I have to be the counselor educator. It falls to me to decide to pass evaluation and not just a verbal feedback, but a grade… it was a moment, a specific moment where I was like okay now I’m a counselor educator.
Domain II: Supervision of Students
Supervision was the second largest domain present in the CEDS focus groups that was relevant in the participants’ development of a counselor educator identity, which was not surprising due to the emphasis on supervision within counselor education. Data within the supervision domain yielded two categories: (a) supervision teaches future counselor educators about the development of counselors and (b) supervision profoundly affects CEDS’ professional identity transition from counselor to counselor educator (see Table 2 for frequency breakdown). One participant stated, “Supervision brings teaching and counseling skills together to see what students are grasping.”
Category 1: Development of counselors. Supervision as a critical part of counselor development was a general category within the supervision domain and included theoretical aspects of supervision (e.g., applying theories of supervision and adjusting those theories to the development of students), as well as the practical aspects within supervision (e.g., focusing on what students need to know in order to proceed in the field of counseling and in their own growth and development). One CEDS summarized the importance of observing and enhancing development of counselors-in-training as follows:
I would say…supervising students for me has been counselor education in its purest form. Because when you’re in front of a class you’re teaching counselor concepts to people you are wondering are they grasping it, how are they understanding it and when you’re sitting down one-on-one and really supervising a student while they’re counseling someone else over a year or a semester, it gives us an opportunity to be intimately aware of what they’re learning and for me it’s been one of the most energizing and rewarding elements of a counselor educator.
Category 2: Professional identity transition. The doctoral students represented in these focus groups begin their education and practice of supervision during the second year of their doctoral program. Aligning with program sequencing, the majority of responses in the professional identity transition category came from the second-year cohort with support from the third-year CEDS, designating it as a typical category. Second-year students noted that the introduction of supervising students during the second year of the program facilitated their role transition from counselor to counselor educator. A second-year CEDS stated, “I think really what solidified it for me was the supervision class… having two of those before teaching even. That’s when I remember making that shift into thinking as an educator and supervisor rather than a counselor.” Another second-year CEDS stated, “Supervising students has been helpful to be me, sitting on the other side of the table instead of me counseling the client; I’m supervising the counselor (who is) counseling the client.” The third-year CEDS also identified supervision as one of the most significant experiences in solidifying their counselor educator identity.
Domain III: Conducting Research
The domain of conducting research as an important identity-forming experience was present across all the CEDS cohorts. Although the importance of conducting research was present in first through third years, it appears to peak in the second year of the program where research is emphasized through coursework. CEDS in the second-year cohort reported an increased interest in research and awareness of the relevance of research in counselor education and identifying as a counselor educator. A second-year CEDS stated:
One thing that really clicked for me this year was speaking in terms of research and that was a new way of thinking for me. It was a struggle between wearing my counselor hat versus my counselor educator hat and was sort of manifested in my research ideas. I was doing a lot of counselor practitioner kind of thinking in terms of research and I switched that into thinking of counselor educator research and that helped my identity transition.
Two categories were identified within the conducting research domain: (a) research is a responsibility and (b) development of the researcher role (see Table 2 for category and frequency breakdown).
Category 1: Research is a responsibility. The theme that research inquiry is not just a duty of a counselor educator, but also a responsibility to the profession presented as a typical category. The third-year cohort focused on the feeling of responsibility toward conducting research. The second-year CEDS contributed the majority of data in the research is a responsibility category and focused on the responsibility of research, writing and contributing to the professional knowledge base. During the second-year CEDS focus group, a conversation thread emerged focused on intentionality of contributing to the field of literature with quality research. All second-year cohort members agreed that the responsibility of conducting research was an area that substantially helped in their transition from thinking like a counseling practitioner to thinking like a counselor educator.
Category 2: Development of the researcher role. Data assigned to the research category was fairly distributed between all three cohorts, designating it as a general category. The first-year CEDS focused on their initial experiences, including the process of writing the first manuscript and the first Institutional Review Board (IRB) submission and approval. A major theme of second-year CEDS was identifying and developing research interests. Third-year CEDS focused more on the products of conducting research, such as presenting research results at conferences and conducting follow-up research. These research themes appeared to be developmentally appropriate as they matched the educational structure of this particular doctoral counselor education program.
Domain IV: Conferences
Although the domain of conferences produced broad responses from participants, it was clear that conference attendance contributed to identity development. Data centered around two categories contributing to CEDS’ identity development as counselor educators: (a) attending and presenting papers at conferences and (b) networking with other professionals in counselor education.
Category 1: Presenting papers at conferences. Conference presentation was a general category, present across all three years of CEDS. First-year students discussed the importance of presenting papers in developing professional identity. One reason identified for the importance of presenting papers was that other professionals at conferences expressed interest in their work and this professional attention was affirming. Second-year CEDS felt conference presentations solidified their role as a counselor educator, making it “more real.” Third-year CEDS stated that presenting papers at conferences gave a feeling of “professional weightiness,” in that they felt respected when other professionals valued their contributions and recruited them for potential faculty positions.
Category 2: Networking with professionals at conferences. The category of networking with professionals at conferences was a typical category, present in the first and second-year cohort responses. First-year students felt conversations with counselor educators outside of their program that occurred during conferences were helpful in the formation of their counselor educator identity. A second-year CEDS emphasized:
Attending the conferences is really good… I’m able to see other professionals that have been successful going through what I’m in now. And to get advice from them, to hear some tips that they have about research or teaching…umm and just getting inspired and motivated and saying that “you know I can see myself in their positioning in another year and a half or so.”
Domain V: Cohort Membership
The university at which our research was conducted employs a cohort model for the doctoral program in counselor education. As noted, a cohort model is defined by a group of students entering the program together, taking the majority of coursework together and moving through the program concurrently (Paisley et al., 2010). In participants’ responses, we found cohort membership was valuable in both first-year and second-year students. First-year CEDS expressed that being a part of the cohort helped create a vision of the future as a counselor educator. The students also recognized cohort members as future colleagues. Second-year CEDS focused on learning from cohort members, such as relying on cohort members’ expertise in understanding new situations and how sharing experiences with cohort members helps support them through the doctoral preparation process. It was not surprising that cohort membership did not emerge in the third-year students, as course work ends in the second year so third-year students can focus on dissertations. The lack of coursework contributes to less time the CEDS are together, and thus less of an emphasis on cohort membership and dynamics.
Domain VI: Program Design
The program design domain appeared often, but only in the second-year cohort data. The data reflected the second-year CEDS’ beliefs that the program was intentionally designed to develop skills and knowledge incrementally bringing all the roles of a counselor educator together in the second year of the doctoral program. For example, evaluation by faculty and classroom assignments helped students understand their roles as counselor educators. A second-year student stated, “In the second year, the program is set up to do everything we will be doing in the profession.” While program design domain does not contain categories, it was one of three domains added to the final list that was not associated with the original start list of domains (see Table 1). As the focus groups were conducted in the beginning of the academic year, first-year students may not have recognized the program design as an asset in their identity development as counselor educators due to their newness to the program. We were somewhat surprised that the program design domain did not come up in the third-year focus group; however, as previously mentioned, the third year is centered on dissertation. Therefore, program design may seem less clear during the third year in the program, as the CEDS are working independently.
Domain VII: Mentoring
The data in the mentoring domain crossed all three CEDS cohorts emphasizing the importance of mentoring across the doctoral program. From the mentoring domain, two categories emerged: (a) the importance of mentoring on the student’s professional identity development and (b) the value of conversations with faculty members on their development. A mentoring relationship was beneficial in the CEDS’ professional identify development, which was identified in the data, but was not part of the original start list of domains (see Table 1).
Category 1: Importance of mentoring. The importance of mentoring was present in both first-year and second-year cohort CEDS focus groups, designating it a typical category. First-year CEDS recognized the mentor relationship as an integral part of doctoral education. Second-year CEDS focused on the modeling of teaching by faculty members and faculty assisting in the development of research interests and writing. One student stated, “just being taken under some faculty member’s wing and having them take an invested interest in me and having me connect what my interests are in the community…has been mentally helpful for me.”
Category 2: Value of conversations with faculty. The value of conversations with faculty was a general category. First-year CEDS discussed conversations such as professors checking in on their progress and expressing pride in their work. One student stated, “Talking with a professor who has been successful and is similar to me has validated me in many ways.” Second-year and third-year CEDS focused on encouragement from faculty in terms of honing research interests and consulting with faculty about students, as exhibited in this statement:
A professor told me that my paper could be a manuscript and I didn’t view it like that. I didn’t understand what that meant (to write a manuscript) until the professor said that and I’m like, really? And I didn’t really have the self-efficacy to believe that until he started working with me and I realized the accuracy of his statement. Because I didn’t believe that of all the people out there making contributions (to the scholarly body of research) that I could actually be one of those people making contributions. It is due to the mentorship and support and somebody highlighting the opportunity.
Domain VIII: Perceived as Counselor Educator by Faculty
The domain of being perceived as counselor educator by faculty crossed all three CEDS cohorts and reflected the professors’ belief and vision of students as future counselor educators. The perceived belief of the faculty members was then reflected in the self-confidence of the CEDS. Students across cohorts gave examples of professors believing in their research, asking for recommendations, and being addressed by professors as counselor educators. One student said, “The professors seeing me as an educator helps me see myself that way.” In addition, one CEDS identified a defining moment while networking at a conference when a professor from an outside university asked for an opinion regarding which textbook to use. The professor’s request validated the student’s identity as a counselor educator and gave the perception of being accepted in the field. Being perceived as a counselor educator by faculty emerged as a domin through data analysis and was not part of the original domain start list (see Table 1).
Discussion
Previous research supports three primary counselor educator roles (teaching and supervision, research, and service; Calley & Hawley, 2008; Carlson et al., 2006). The teaching domain (subcategories: teaching experience, contributing factors, and critical interactions with students) and the supervision domain (subcategories: development of counselors and how it impacted counselor identity) generated the most data from our CEDS participants. Thus, teaching and supervision may serve as distinguishing factors of the transition from counseling practitioner to counselor educator. The perspective that the counselor educators’ researcher role develops during the beginning of this preparation program, and conducting and developing research interests are established through participation on research teams and presenting research results was consistent with previous findings (e.g., Calley & Hawley, 2008; Carlson et al., 2006). However, the responsibility and application of conducting research is important to emphasize throughout a doctoral program to enhance professional identity development. The role of service in counselor education (e.g., Calley & Hawley, 2008) was not supported in our data. The CEDS in our investigation may not have been aware of the opportunities to provide service to the counseling profession, or they may not view service as a priority. Therefore, the counselor educator role of service may be an area of growth for some doctoral programs to expand opportunities for CEDS to provide service in the field.
In addition, our findings support the premise that the development of CEDS professional identity as counselor educators is intimately linked to the students’ doctoral preparation program which was consistent with previous findings (e.g., Carlson, et al.,1997). Built within the participants’ program were opportunities for CEDS to take on the roles of counselor educator, including teaching, research, supervision, and participation in the greater community of counselor educators through conference participation. What is noticeably absent from our results is the lack of influence that the curriculum (e.g., attending class meetings, reading, writing papers, listening to lectures) played in the professional identity development of the CEDS. Although each participant was enrolled as a fulltime CEDS through the duration of their education, the influence of “learning by doing” seemed to develop the identity of each participant more than traditional didactic learning methods. Thus, it is important for counselor education doctoral programs to consider practical experiences for their students (e.g., opportunities’ for teaching, research and supervision).
The influence of faculty and networking (e.g., mentoring, being perceived by faculty as counselor educators, and attending and presenting at conferences) is crucial to CEDS’ professional identity development, and was a unique finding. However, it was noted that counselor education faculty members influenced their students primarily outside of the classroom setting. Faculty (including those outside of one’s program) helped their students grow into the identity of counselor educator through (a) consultation, (b) developing research interests, (c) believing in and treating the students as counselor educators, (d) encouraging students to present at conferences, and (e) mentorship. Our findings affirm the importance of counselor education faculty members’ influence on the development of future counselor educators and professional counselors.
Lessons Learned
As this investigation was our first time conducting qualitative research, specifically CQR, we reflected on lessons learned through this process. Three overarching lessons emerged: (a) coding qualitative data using CQR methodology is a lengthy process that requires significant and honest discussion, (b) the consensual aspect of CQR seemed to balance personal bias, and (c) applying a new research methodology while concurrently learning the process of the methodology presents many challenges. While the focus groups were an expedient method of collecting the data, we found coding the data required a significant amount of time to ensure the data were represented in the codes. Correct categorization of the data was somewhat remedied by dividing up the second-year and third-year CEDS data; however, each smaller team continued spending significant time with their respective data. Additionally, balancing the thoughts and opinions of seven of us was challenging; however, the guidelines for CQR methodology delineated that consensus must be reached in coding the data (Hill et al., 2005). Although a lengthy process, it appeared to balance bias allowing the data to speak for itself in producing new domains. Finally, we served as both researchers and participants, which we recognize as a limitation. However, the active learning process of conceptualizing and applying CQR simultaneously while serving as participants provided us an opportunity to develop our own professional identity as counselor educators, specifically in the area of research.
Limitations and Implications for Future Research
As in all research, limitations were apparent in our investigation. At the time the focus groups were facilitated, we were in the first year of the program, and all of us were from the same university. Our study involved only students in a single doctoral program, which is a cohort design; therefore, the results emphasize the specific goals and curriculum design of one cohort model in counselor education. In addition, we served as participants in representing the first-year doctoral student perspective. Though facilitated by a faculty member, we did have previous knowledge of the research questions and analyzed the data resulting from the focus group.
Although CQR is an emerging methodology that has not been used extensively in counselor education, we followed Hill et al.’s (1997; 2005) CQR guidelines and other scholarly writing guidelines (e.g., Hays & Wood, 2011; Lambie, Sias, Davis, Lawson, & Akos, 2008). After reviewing several CQR methodologies in various studies, Hill et al. (2005) found many advantages and disadvantages to the consensual process of qualitative data collection; one of the advantages may be the rigorous cross-analysis embedded within the CQR method. Our qualitative investigation used a meticulous cross-sectional approach to identify key components of professional identity development among CEDS. A limitation to CQR is researcher bias, which should be safeguarded by considering and reporting all biases (Hill et al., 2005). We spent a significant amount of time considering and discussing potential biases. Finally, we listed all potential biases and through consensus identified actual biases as reported earlier.
A recommendation for future research, based on our investigation, is to expand the sample to include other doctoral counselor education programs, specifically different models (e.g., part-time, independent), allowing domain consistency to be explored, as well as identifying similarities and differences across counselor education doctoral programs. In addition, future research may benefit from the exploration of pre-tenured faculty members’ experiences of professional identify development in comparison to CEDS. Furthermore, a quantitative design may be employed to examine significant relationships of specific domains and productivity of doctoral counselor education students.
In summary, our study examined CEDS’ experiences that helped build their professional identity as counselor educators. The data were collected from three cohorts representing different stages in their doctoral preparation program and analyzed using CQR methodology. The findings suggested that: (a) programmatic goals align with the experiences critical to CEDS professional identity development, (b) experiential learning opportunities (e.g., teaching courses under supervision, participating on a research team, and supervising students) appeared more influential than traditional content learning, and (c) the relationships with mentors and faculty members contribute to both the CEDS efficacy and development of their identity as counselor educators. Therefore, counselor education doctoral programs may want to evaluate current curricula to ensure their students have experiential learning opportunities, if they wish to promote the professional identity of counselor educators.
References
Bell, H., Limberg, D., Young, M. E., Robinson, E.H., Robinson, S., Hayes, G., . . . Christmas, C. (2012). Professional identity development of counselor education doctoral students. Paper presented at the British Association for Counselling & Psychotherapy, Scotland.
Calley, N. G., & Hawley, L. D. (2008). The professional identity of counselor educators. The Clinical Supervisor, 27, 3–16.
Carlson, L. A., Portman, T. A., & Bartlett, J. R. (2006). Self-management of career development: Intentionally for counselor educators in training. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 45, 126–137.
Corey, G., Corey, M. S., & Callanan, P. (2010). Issues and ethics in the helping professions (8th ed.). Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2009). CACREP accreditation manual. Alexandria, VA: Author.
Creswell, J. W. (2007). Qualitative inquiry & research design: Choosing among five approaches (2nd ed.).Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Qualitative inquiry & research design: Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Gibson, D. M., Dollarhide, C. T., & Moss, J. M. (2010). Professional identity development: A grounded theory of transformational tasks of new counselors. Counselor Education and Supervision, 50, 21–38.
Glesne, C. (2011). Becoming qualitative researchers: An introduction (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson.
Granello, D. H., & Young, M. E (2012). Counseling today: Foundations of professional identity. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Hall, L. A., & Burns, L. D. (2009). Identity development and mentoring in doctoral education. Harvard Educational Review, 79, 49–70.
Hays, D. G., & Wood, C. (2011). Infusing qualitative traditions in counseling research designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 288–295.
Heppner, P. P., Wampold, B. E., & Kivlighan, D. M. (2008). Research design in counseling. (3rd ed.). Belmont, CA: Thomson.
Hill, C. E., Knox, S., Thompson, B. J., Williams, E., Hess, S. A., & Ladany, N. (2005).Consensual qualitative research: An update. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52, 196–205.
Hill, C. E., Thompson, B. J., & Nutt Williams, E. (1997). A guide to conducting consensual qualitative research. The Counseling Psychologist, 25, 517–572.
Knox, S., Burkard, A. W., Janecek, J., Pruitt, N. T., Fuller, S. L., & Hill, C. E. (2012). Positive and problematic dissertation experiences: The faculty perspective. Counseling Psychology Quarterly, 24, 55–69.
Lambie, G. W., Sias, S. M., Davis, K. M., Lawson, G., & Akos, P. (2008). A scholarly writing resource for counselor educators and their students. Journal of Counseling & Development, 86, 18–25.
Magnuson, S., Davis, K. M., Christensen, T. M., Duys, D. Y., Glass, J. S., Portman, T., . . . Veach, L.J. (2003). How entry-level assistant professors master the art and science of successful scholarship. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 42, 209–222.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Paisley, P. O., Bailey, D. F., Hayes, R. L., McMahon, H., & Grimmett, M. A. (2010). Using a cohort model for school counselor preparation to enhance commitment to social justice. Journal for Specialists in Group Work, 35, 262–270.
Walker, G. E., Golde, C. M., Jones, L., Bueschel, A. C., & Hutchings, P. (2008). The formation of scholars: Rethinking doctoral education for the twenty-first century. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Zimpfer, D. G., Cox, J. A., West, J. D., Bubenzer, D. L., & Brooks, D. K. (1997). An examination of counselor preparation doctoral program goals. Counselor Education and Supervision, 36, 318–331.
Dodie Limberg is an Assistant Professor at Texas A&M-Commerce. Hope Bell is a doctoral candidate at the University of Central Florida. John T. Super, NCC, and Lamerial Jacobson are doctoral graduates of the University of Central Florida. Jesse Fox, NCC, is a doctoral candidate at the University of Central Florida. M. Kristina DePue, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of Florida. Chris Christmas is a doctoral candidate at the University of Central Florida. Mark E. Young is a Professor and Glenn W. Lambie, NCC, is an Associate Professor at the University of Central Florida. Correspondence regarding this article can be addressed to Dodie Limberg, University of Central Florida, College of Education, Department of Education and Human Services, P. O. Box 161250, Orlando, FL 32816-1250, dlimberg@knights.ucf.edu.







