E. Heather Thompson, Melodie H. Frick, Shannon Trice-Black
Counselors-in-training face the challenges of balancing academic, professional, and personal obligations. Many counselors-in-training, however, report a lack of instruction regarding personal wellness and prevention of personal counselor burnout. The present study used CQR methodology with 14 counseling graduate students to investigate counselor-in-training perceptions of self-care, burnout, and supervision practices related to promoting counselor resilience. The majority of participants in this study perceived that they experienced some degree of burnout in their experiences as counselors-in-training. Findings from this study highlight the importance of the role of supervision in promoting resilience as a protective factor against burnout among counselors-in-training and provide information for counselor supervisors about wellness and burnout prevention within supervision practice
Keywords: counselors-in-training, wellness, burnout, supervision, resilience
Professional counselors, due to often overwhelming needs of clients and heavy caseloads, are at high risk for burnout. Research indicates that burnout among mental health practitioners is a common phenomenon (Jenaro, Flores, & Arias, 2007). Burnout is often experienced as “a state of physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion caused by long-term involvement in emotionally demanding situations” (Gilliland & James, 2001, p. 610). Self-care and recognition of burnout symptoms are necessary for counselors to effectively care for their clients as well as themselves. Counselors struggling with burnout can experience diminished morale, job dissatisfaction (Koeske & Kelly, 1995), negative self-concept, and loss of concern for clients (Rosenberg & Pace, 2006). Clients working with counselors experiencing burnout are at serious risk, as they may not receive proper care and attention to often severe and complicated problems.
The potential hazards for counselor distress in practicum and internship are many. Counselors-in-training often begin their professional journeys with a certain degree of idealism and unrealistic expectations about their roles. Many assume that hard work and efforts will translate to meaningful work with clients who are eager to change and who are appreciative of the counselor’s efforts (Leiter, 1991). However, clients often have complex problems that are not always easily rectified and which contribute to diminished job-related self-efficacy for beginning counselors (Jenaro et al., 2007). In addition, counselor trainees often experience difficulties as they balance their own personal growth as counselors while working with clients with immense struggles and needs (Skovholt, 2001). Furthermore, elusive measures for success in counseling can undermine a new counselor’s sense of professional competence (Kestnbaum, 1984; Skovholt, Grier, & Hanson, 2001). Client progress is often difficult to concretely monitor and define. The “readiness gap,” or the lack of reciprocity of attentiveness, giving, and responsibility between the counselor-in-training and the client, are an additional job-related stressor that may increase the likelihood of burnout (Kestnbaum, 1984; Skovholt et al., 2001; Truchot, Keirsebilck, & Meyer, 2000).
Counselors-in-training are exposed to emotionally demanding stories (Canfield, 2005) and situations which may come as a surprise to them and challenge their ideas about humanity. The emotional demands of counseling entail “constant empathy and one-way caring” (Skovholt et al., 2001, p. 170) which may further drain a counselor’s reservoir of resilience. Yet, mental health practitioners have a tendency to present themselves as caregivers who are less vulnerable to emotional distress, thereby hindering their ability to focus on their own needs and concerns (Barnett, Baker, Elman, & Schoener, 2007; Sherman, 1996). Counselors who do not recognize and address their diminished capacity when stressed are likely to be operating with impaired professional competence, which violates ethical responsibilities to do no harm.
Counselor supervision is designed to facilitate the ethical, academic, personal, and professional development of counselors-in-training (CACREP, 2009). Bolstering counselor resilience in an effort to prevent burnout is one aspect of facilitating ethical, personal, and professional development. Supervisors who work closely with counselors-in-training during their practicum and internship can promote the hardiness and sustainability of counselors-in-training by helping them learn to self-assess in order to recognize personal needs and assert themselves accordingly. This may include learning to say “no” to the demands that exceed their capacity or learning to actively create and maintain rejuvenating relationships and interests outside of counseling (Skovholt et al., 2001). Supervisors also can teach and model self-care and positive coping strategies for stress, which may influence supervisees’ practice of self-care (Aten, Madson, Rice, & Chamberlain, 2008). In an effort to bolster counselor resilience, supervisors can facilitate counselor self-understanding about overextending oneself to prove professional competency to achieve a sense of self-worth (Rosenburg & Pace, 2006). Supervisors can help counselors-in-training come to terms with the need for immediate positive reinforcement related to work or employment, which is limited in the counseling profession as change rarely occurs quickly (Skovholt et al., 2001). Counselor resiliency also may be bolstered by helping counselors-in-training establish realistic measures of success and focus on the aspects of counseling that they can control such as their knowledge and ability to create strong therapeutic alliances rather than client outcomes. In sum, distressing issues in counseling, warning signs of burnout, and coping strategies for dealing with stress should be discussed and the seeds of self-care should be planted so they may grow and hopefully sustain counselors-in-training over the course of their careers.
Method
The purpose of this exploratory study was to investigate counselor-in-training perceptions of self-care, burnout, and supervision practices related to promoting counselor resilience. The primary research questions that guided this qualitative study included: (a) What are master’s-level counselors-in-training’s perceptions of counselor burnout? (b) What are the perceptions of self-care among master’s-level counselors-in-training? (c) What, if anything, have master’s-level counselors-in-training learned about counselor burnout in their supervision experiences? And (d) what, if anything, have master’s level counselors-in-training learned about self-care in their supervision experiences?
The consensual qualitative research method (CQR) was used to explore the supervision experiences of master’s-level counselors-in-training. CQR works from a constructivist-post-positivist paradigm that uses open-ended semi-structured interviews to collect data from individuals, and reaches consensus on domains, core ideas, and cross-analyses by using a research team and an external auditor (Hill, Knox, Thompson, Williams, Hess, & Ladany, 2005; Ponterotto, 2005). Using the CQR method, the research team examined commonalities and arrived at a consensus of themes within and across participants’ descriptions of the promotion of self-care and burnout prevention within their supervision experiences (Hill et al., 2005; Hill, Thompson, & Nutt Williams, 1997).
Participants
Interviewees. CQR methodologists recommend a sample size of 8–15 participants (Hill et al., 2005). The participants in this sample included 14 individuals; 13 females and 1 male, who were graduate students in master’s-level counseling programs and enrolled in practicum or internship courses. The participants attended one of three universities in the United States (one in the Midwest and two in the Southeast). The sample consisted of 10 participants in school counseling programs and 4 participants in clinical mental health counseling programs. Thirteen participants identified as Caucasian, and one participant identified as Hispanic. The ages of participants ranged from 24 to 52 years of age (mean = 28).
Researchers. An informed understanding of the researchers’ attempt to make meaning of participant narratives about supervision, counselor burnout, and self-care necessitates a discussion of potential biases. This research team consisted of three Caucasian female faculty members from three different graduate-level counseling programs. All three researchers are proficient in supervision practices and passionate about facilitating counselor growth and development through supervision. All members of the research team facilitate individual and group supervision for counselors-in-training in graduate programs. The three researchers adhere to varying degrees of humanistic, feminist, and constructivist theoretical leanings. All members of the research team believe that supervision is an appropriate venue for bolstering both personal and professional protective factors that may serve as buffers against counselor burnout. It also is worth noting that the three members of the research team believed they had experienced varying degrees of burnout over the course of their careers. The researchers acknowledge these shared biases and attempted to maintain objectivity with an awareness of their personal experiences with burnout, approaches to supervision, and beliefs regarding the importance of addressing protective factors, wellness and burnout prevention in supervision. This study also was influenced by an external auditor who is a former counselor educator with more than 20 years of experience in qualitative research methods and supervision practice. As colleagues in the field of counselor education and supervision, the research team and the auditor were able to openly and respectfully discuss their differing perspectives throughout the data analysis process, which permitted them to arrive at consensus without being stifled by power struggles.
Procedures for Data Collection
Criterion sampling was used to select participants in an intentional manner to understand specified counseling students’ experiences in supervision. Criteria for participation in this study included enrollment as a graduate student in a master’s-level counseling program and completion of a practicum experience or participation in a counseling internship in a school or mental health counseling agency. Researchers disseminated information about this study by email to master’s-level students in counseling programs at three different universities. Interested students were instructed to contact, by email or phone, a designated member of the research team, who was not a faculty member at their university. All participants were provided with an oral explanation of informed consent and all participants signed the informed consent documents. All procedures followed those established by the Institutional Review Board of the three universities associated with this study.
Within the research team, researchers were designated to conduct all communication, contact, and interviews with participants not affiliated with their respective universities, in order to foster a confidential and non-coercive environment for the participants. Interviews were conducted on one occasion, in person or via telephone, in a semi-structured format. Participants in both face-to-face and telephone interviews were invited to respond to questions from the standard interview protocol (see Appendix A) about their experiences and perceptions of supervision practices that addressed counselor self-care and burnout prevention. Participants were encouraged to elaborate on their perceptions and experiences in order to foster the emergence of a rich and thorough understanding. The transferability of this study was promoted by the rich, thick descriptions provided by an in-depth look at the experiences and perceptions of this sample of counselors-in-training. Interviews lasted approximately 50–70 minutes. The interview protocol was generated after a thorough review of the literature and lengthy discussions about researcher experiences as a supervisee and a supervisor. Follow-up surveys (see Appendix B) were administered electronically to participants six weeks after the interview to capture additional thoughts and experiences of the participants.
Data Analysis
All interviews were audio-taped and transcribed verbatim for data analysis. Transcripts were checked for accuracy by comparing them to the audio-recordings after the transcription process. Participant names were changed to pseudonyms to protect participant anonymity. Participants’ real names and contact information were only used for scheduling purposes. Information linking participants to their pseudonyms was not kept.
Coding of domains. Prior to beginning the data analysis process, researchers generated a general list of broad domain codes based on the interview protocol, a thorough understanding of the extant literature, and a review of the transcripts. Once consensus was achieved, each researcher independently coded blocks of data into each domain code for seven of the 14 cases. Next, as a team, the researchers worked together to generate consensus on the domain codes for the seven cases. The remaining cases were analyzed by pairs of the researchers. The third team member reviewed the work of the pair who generated the domain coding for the remaining seven cases. Throughout the coding process, domains were modified to best capture the data.
Abstracting the core ideas within each domain. Each researcher worked independently to capture the core idea for each domain by re-examining each transcript. Core ideas consisted of concise statements of the data that illuminated the essence of the participant’s expressed perspectives and experiences. As a group, the researchers discussed the wording of core ideas for each case until consensus was achieved.
Cross analysis. The researchers worked independently to identify commonalities of core ideas within domains across cases. Next, as a group, the research team worked to find consensus on the identified categories across cases. Aggregated core ideas were placed into categories and frequency labels were applied to indicate how general, typical, or variant the results were across cases. General frequencies refer to findings that are true for all but one of the cases (Hill et al., 2005). Typical frequencies refer to findings that are present in more than half of the cases. Variant frequencies refer to finding in at least two cases, but less than half.
Audit. An external auditor was invited to question the data analysis process and conclusions. She was not actively engaged in the conceptualization and implementation of this study, which gave the research team the benefit of having an objective perspective. The external auditor reviewed and offered suggestions about the generation of domains and core ideas, and the cross-case categories. Most feedback was given in writing. At times, feedback was discussed via telephone. The research team reviewed all auditor comments, looked for evidence supporting the suggested change, and made adjustments based on team member consensus.
Stability check. For the purpose of determining consistency, two of the 14 transcripts were randomly selected and set aside for cross-case analysis until after the remaining 12 transcripts were analyzed. This process indicated no significant changes in core domains and categories, which suggested consistency among the findings.
Results
A final consensus identified five domains: counselor burnout, counselor self-care, faculty supervision, site supervision, and improvements (see Table 1). Cross-case categories and subcategories were developed to capture the core ideas. Following CQR procedures (Hill et al., 1997, 2005), a general category represented all or all but one of the cases (n = 13–14); a typical category represented at least half of the cases (n = 7–12); and a variant category represented less than half but more than two of the cases (n = 3 – 6). Categories with fewer than three cases were excluded from further analysis. General categories were not identified from the data.
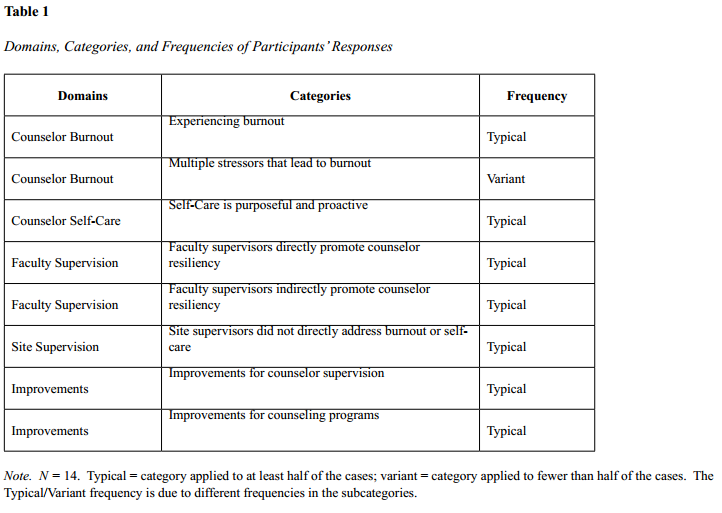
Counselor Burnout
Experiencing burnout. Most participants reported knowledge of or having experiences with burnout. Participants identified stressors leading to burnout as a loss of enthusiasm and compassion, the struggle to balance school, work, and personal responsibilities and relationships, and difficulty delineating and separating personal and professional boundaries.
Participants described counselor burnout as no longer having compassion or enthusiasm for counseling clients. One participant defined counselor burnout as, “it seems routine or [counselors] feel like they’ve dealt with so many situations over time that they’re just kind of losing some compassion for the field or the profession.” Another participant described counselor burnout as no longer seeing the unique qualities of individuals seen in counseling:
I wouldn’t see [clients] as individuals anymore…and that’s where I get so much of it coming at me, or so many clients coming at me, that they’re no longer an individual they’re just someone that’s sitting in front of me, and when they leave they write me a check….they are not people anymore, they’re clients.
Participants often discussed a continual struggle to balance personal and professional responsibilities. One participant described burnout as foregoing pleasurable activities to focus on work-related tasks:
I can tell when I am starting to get burned out when I am focusing so much on those things that I forgo all of those things that are fun for me. So I am not working out anymore, I am not reading for fun, and I am putting off hanging out with my friends because of my school work. There’s school work that maybe doesn’t have to get done at that moment, but if I don’t work on it I’m going to be thinking about it and not having fun.
Another participant described burnout as having a hard time balancing professional and personal responsibilities stating, “I think I don’t look forward to…working with…people. I’m just kind of glad when they don’t show up. And this kind of sense that I’m losing the battle to keep things in balance.”
Boundary issues were commonly cited by participants. Several participants reported that they struggled to be assertive, set limits, maintain realistic expectations, and not assume personal responsibility for client outcomes. One participant described taking ownership of a client’s outcome and wanting to meet all the needs of her clients:
I believe part of it is internalizing the problem on myself, feeling responsible. Maybe loosing sight of my counseling skills and feeling responsible for the situation. Or feeling helpless. Also, in school counseling there tends to be a larger load of students. And this is frustrating to not meet all the needs that are out there.
Participants reported experiences with burnout and multiple stressors that lead to burnout. Participants defined counselor burnout as a loss of compassion for clients, diminished enthusiasm, difficulty maintaining a life-work balance, and struggles to maintain boundaries.
Counselor Self-Care
Self-care is purposeful and proactive. Participants were asked to describe self-care for counselors and reported that self-care requires purposeful efforts to set time aside to engage in activities outside of work that replenish energy and confidence. Most participants identified having and relying on supportive people, such as family, friends, and significant others to help them cope with stressors. Participants also identified healthy eating and individualized activities such as exercise, reading, meditation, and watching movies as important aspects of their self-care. One participant described self-care as:
Anything that can help you reenergize and refill that bucket that’s being dipped into every day. If that’s going for a walk in the park…so be it. If that’s going to Starbucks…go do it….Or something that makes you feel good about yourself, something that makes you feel confident, or making someone else feel confident….Whatever it is, something that makes you feel good about yourself and knowing that you’re doing what you need to be doing.
Participants reported that self-care requires proactive efforts to consult with supervisors and colleagues; one of the first steps is recognizing when one needs consultation. One participant explained:
I think in our program, [the faculty] were very good about letting us know that if you can’t handle something, refer out, consult. Consult was the theme. And then if you feel you really can’t handle it before you get in over your head, make sure you refer out to someone you feel is qualified.
Participants described self-care as individualized and intentional, and included activities and supportive people outside of school or work settings that replenished their energy levels. Participants also discussed the importance of identifying when counselor self-care is necessary and seeking consultation for difficult client situations.
Faculty Supervision
Faculty supervisors directly promote counselor resiliency. More than half of the participants reported that faculty supervisors directly initiated conversations about self-care. A participant explained, “Every week when we meet for practicum, [the faculty supervisor] is very adamant, ‘is everyone taking care of themselves, is anyone having trouble?’ She is very open to listening to any kind of self-care situation we might have.” Similarly, another participant stated, “Our professors have told us about the importance of self-care and they have tried to help us understand which situations are likely to cause us the most stress and fatigue.” One participant identified preventive measures discussed in supervision:
In supervision, counselor burnout is addressed from the perspective of prevention. We develop personal wellness plans, and discuss how well we live by them during supervision….Self-care is addressed in the same conversation as counselor burnout. In supervision, the mantra is good self-care is vital to avoiding burnout.
Faculty supervisors indirectly promote counselor resiliency. Participants also reported that faculty supervisors indirectly addressed counselor self-care by being flexible and supportive of participants’ efforts with clients. Participants repeatedly expressed appreciation for supervisors who processed cases and provided positive feedback and practical suggestions. One participant explained, “I know that [my supervisor] is advocating for me, on my side, and allowing me to vent, and listening and offering advice if I need it….giving me positive feedback in a very uncomfortable time.”
Further, participants stated they appreciated supervisors who actively created a safe space for personal exploration. One participant explained:
[Supervision] was really a place for us to explore all of ourselves, holistically. The forum existed for us for that purpose. [The supervisors] hold the space for us to explore whatever needs to be explored. That was the great part about internship with the professor I had. He sort of created the space, and we took it. It took him allowing it, and us stepping into the space.
Modeling self-care also is an indirect means of addressing counselor burnout and self-care. Half of the participants reported that their faculty supervisors modeled self-care. For example, faculty supervisors demonstrated boundaries with personal and professional obligations, practiced meditation, performed musically, and exercised. Conversely, participants reported that a few supervisors demonstrated a lack of personal self-care by working overtime, sacrificing time with their families for job obligations, and/or having poor diet and exercise habits.
Participants reported that faculty supervisors directly and indirectly addressed counselor burnout and self-care in supervision. Supervisors who intentionally checked in with the supervisees and used specific techniques such as wellness plans were seen as directly affecting the participants’ perspective on counselor self-care. Supervisors who were present and available, created safe environments for supervision, provided positive feedback and suggestions, and modeled self-care were seen as indirectly addressing counselor self-care. Both direct and indirect means of addressing counselor burnout and self-care were seen as influential by participants.
Site Supervision
Site supervisors did not directly address burnout or self-care. Participants reported that site supervisors rarely initiated conversations about counselor burnout or self-care. One participant reported that counselor burnout was not addressed and as a result she felt a lack of support from the supervisor:
[Site Supervisors] don’t ask about burnout though. Every time I’m bringing it up, the answers I’m getting are ‘well, when you’re in grad school you don’t get a life.’ You know, yeah, I get that, but that’s not really true, so I get a lot of those responses, ‘well, you know, welcome to the club.’
One participant stated that her site supervisor did not specifically address counselor burnout or self-care, stating “I think that is less addressed in a school setting than it is in the mental health field….I think that because we see such a small picture of our students, I think it is not as predominantly addressed.” Some participants, however, reported that their site supervisors indirectly addressed self-care by modeling positive behaviors. One participant stated:
[My site supervisor] has either structured her day or her life in such a way that no one cuts into that time unless she allows it. In that sense, she’s great at modeling what’s important…She just made a choice….She was protective. She made her priorities. Her family was a priority. Her walk was a priority, getting a little activity. Other things, house chores, may have fallen by the wayside. She had a good sense of priorities, I thought. That was good to watch.
In summary, participants reported that counselor burnout and self-care were not directly addressed in site supervision. Indeed, some participants felt a lack of support when feeling overwhelmed by counseling duties, and that school sites may address burnout and self-care less than at mental health sites. At best, self-care was indirectly modeled by site supervisors with positive coping mechanisms.
Improvements for Counselor Supervision and Training
Improvements for counselor supervision. More than half of the participants reported wanting more understanding and empathy from their supervisors. One participant complained:
A lot of my class mates have a lot on their plates, like I do, and our supervisors don’t have as much on their plate as we do. And it seems like they don’t quite get where we are coming from. They are not balancing all the things that we are balancing….a lot of the responses you get demonstrate their lack of understanding.
Another participant suggested:
I think just hearing what the person is saying. If the person is saying, I need a break, just the flexibility. Not to expect miracles, and just remember how it felt when you were in training. Just be relatable to the supervisees and try to understand what they are going through, and their point of view. You don’t have to lower your expectations to understand where we’re at…and to be honest about your expectations…flexible, honest, and understanding. If [supervisors] are those three things, it’ll be great.
Participants also suggested having counselor burnout and self-care more thoroughly addressed in supervision, including more discussions on balancing personal and professional responsibilities, roles, and stressors. One participant explained:
What would be really helpful when the semester first begins is one-on-one time that is direct about ‘how are you approaching this internship in balance with the rest of your life?’ ‘What are any issues that it would be worthwhile for me to know about?’ How sweet for the supervisor to see you as a whole person. And then to put out the invitation: the door’s always open.
Improvements for counselor training programs. More than half of the participants wanted a comprehensive and developmentally appropriate approach to self-care interwoven throughout their counselor training, with actual practice of self-care skills rather than “face talk.” One participant commented:
Acknowledge the reality that a graduate-level program is going to be a challenge, talking about that on the front end….[faculty] can’t just say you need to have self-care and expect [students] to be able to take that to the next level if we don’t learn it in a graduate program….how much better would it be for us to have learned how to manage that while we were in our program and gotten practice and feedback about that, and then that is so important of a skill to transfer and teach to our clients.
Most of the participants suggested the inclusion of concrete approaches to counselor self-care. Participants provided examples such as preparing students for their work as counselors-in-training by giving them an overview of program expectations at the beginning of their programs, and providing students with self-care strategies to deal with the added stressors of graduate school such as handling administrative duties during internship, searching for employment prior to graduation, and preparing for comprehensive exams.
Discussion
Findings from this study highlight the importance of the role of supervision in promoting resilience as a protective factor against burnout among counselors-in-training. The majority of participants in this study perceived that they experienced some degree of burnout in their experiences as counselors-in-training. Participants’ perceptions of experiencing burnout are a particularly meaningful finding because it indicates that these counselors-in-training see themselves as over-taxed during their education and training. If, during their master’s programs, counselors-in-training are creating professional identities based on cognitive schemas for being a counselor, then perhaps these counselors-in-training have developed schemas for counseling that include a loss of compassion for clients, diminished enthusiasm for counseling, a lopsided balance of personal and professional responsibilities, and struggles to maintain boundaries. Counselors-in-training should be aware of these potential pitfalls as these counselors-in-training reported experiencing symptoms of burnout which were rarely addressed in supervision.
In contrast to recent literature, which suggests that counselor burnout is related to overcommitment to client outcomes (Kestnbaum, 1984; Leiter, 1991; Shovholt et al., 2001), many counselor trainees in this study did not perceive that their supervisors directly addressed their degree of personal commitment to their clients’ success in counseling. Similarly, emotional exhaustion is commonly identified as a potential hazard for burnout (Barnett et al., 2007); yet, few participants believed that their supervisors directly inquired about the degree of emotional investment in their clients. Finally, elusive measures of success in counseling are often indicated as a potential factor for burnout (Kestnbaum, 1984; Skovholt, et al., 2001). The vast majority of participants interviewed for this study did not perceive that these elusive measures of success were addressed in their supervision experiences. Supervisors who are interested in thwarting counselor burnout early in the training experiences of counselors may want to consider incorporating conversations about overcommitment to client outcomes, emotional exhaustion, degree of emotional investment, and elusive measures of success into their supervision with counselors-in-training. In an effort to promote more resilient schemas and expectations for counseling work, supervisors can take an active role in helping counselors-in-training understand the importance of awareness and protective factors to protect against a lack of compassion, enthusiasm, life-work balance, and professional boundaries, similar to the way a pilot is aware that a plane crash is possible and therefore employs purposeful and effective methods of prevention and protection.
Participants in this study conceptualized self-care as purposeful behavioral efforts. Proactive behavioral choices such as reaching out to support others are ways that many counselors engage in self-care. However, self-care cannot be solely limited to engagement in specific behaviors. Self-care also should include discussions about cognitive, emotional, and spiritual coping skills. Supervisors can help counselors-in-training create a personal framework for finding meaning in their work in order to promote hardiness, resilience, and the potential for transformation (Carswell, 2011). Because of the nature of counseling, it is necessary for counselors to be open and have the courage to be transformed. Growth and transformation are often perceived as scary and something to be avoided. Yet, growth and transformation can be embraced and understood as part of each counselor’s unique professional and personal process. Supervisors can normalize and validate these experiences and help counselors-in-training narrate their inspirations and incorporate their personal, spiritual, and philosophical frameworks in their counseling. In addition, supervisors can directly address misperceptions about counseling, which often include: “I can fix the problem,” “I am responsible for client outcomes,” “Caring more will make it better,” and “My clients will always appreciate me” (Carswell, 2011). While these approaches to supervision are personal in nature, counselors-in-training in this study reported an appreciation for time spent discussing how the personal informs the professional. This finding is consistent with Bernard & Goodyear’s (1998) model of supervision which emphasizes personal development as an essential part of supervision. Models for personal development in counselor education programs have been proposed by many professionals in the field of counseling (Myers, 1991; Myers & Williard, 2003; Witmer & Granello, 2005).
Counselors-in-training in this study reported an appreciation for supervision experiences in which their supervisors provided direct feedback and positive reinforcement. Counselors-in-training often experience performance anxiety and self-doubt (Aten et al., 2008). In an effort to diminish counselor-in-training anxiety, supervisors may provide additional structure and feedback in the early stages of supervision. Once the counselor-in-training becomes more secure, the supervisor may facilitate a supervisory relationship that promotes supervisee autonomy and higher-level thinking.
The majority of participants interviewed reported a desire for supervisors to place a greater emphasis on life-work balance and learning to cope with stress. These findings suggest the importance of counselor supervisors examining their level of expressed empathy and emphasis on preventive, as well as remedial, measures to ameliorate symptoms and stressors that lead to counselor burnout. Participants expressed a need to be more informed about additional stressors in graduate school such as administrative tasks in internship, preparing for comprehensive exams, and how to search for employment. These findings suggest the need for counselor educators and supervisors to examine how they indoctrinate counselors-in-training into training programs in order to help provide realistic expectations of work and personal sacrifice during graduate school and in the counseling field. Moreover, counselor educators and supervisors should strive to provide ongoing discussions on self-care throughout the program, specifically when students in internship are experiencing expanding roles between school, site placement, and searching for future employment. As mental health professionals, counselor educators and supervisors may also struggle with their own issues of burnout; thus, attentiveness to self-care also is recommended for those who teach and supervise counselors in training.
Limitations
Findings from this study will benefit counselor educators, supervisors, and counselors-in-training; however, some limitations exist. One limitation is the lack of diversity in the sample of participants. The majority of the participants identified as Caucasian females, which is representative of the high number of enrolled females in the counseling programs approached for this study. The purpose for this study, however, was not to generalize to all counselor trainees’ experiences, but rather to shed light on how counselor perceptions of burnout and self-care are being addressed, or not, in counselor supervision.
Participant bias and recall is a second limitation of this study. Recall is affected by a participant’s ability to describe events and may be influenced by emotions or misinterpretations. This limitation was addressed by triangulating sources, including a follow-up questionnaire, reinforcing internal stability with researcher consensus on domains, core ideas, and categories, and by using an auditor to evaluate analysis and prevent researcher biases.
Conclusion
Counselors should be holders of hope for their clients, but one cannot give away what one does not possess (Corey, 2000). Counselors who lack enthusiasm for their work and compassion for their clients are not only missing a critical element of their therapeutic work, but also may cause harm to their clients. Counseling is challenging and can tax even the most “well” counselors. A lack of life-work balance and boundaries can add to the already stressful nature of being a counselor. Discussions in supervision about the potential for emotional exhaustion, the counselor-in-training’s degree of emotional investment in client outcomes, elusive measures of success in counseling, coping skills for managing stress, meaning-making and sources of inspiration, and personalized self-care activities are several ways supervisors can promote counselor resilience and sustainability. Supervisors should discuss the definitions of burnout, how burnout is different from stress, how to identify early signs of burnout, and how to address burnout symptoms in order to promote wellness and prevent burnout in counselors-in-training. Counselor educators and supervisors have the privilege and responsibility of teaching counselors-in-training how to take care of themselves in addition to their clients.
References
Aten, J. D., Madson, M. B., Rice, A., & Chamberlain, A. K. (2008). Postdisaster supervision strategies for promoting supervisee self-care: Lessons learned from hurricane Katrina. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 2(2), 75–82. doi:10.1037/1931-3918.2.2.75
Barnett, J. E., Baker, E. K., Elman, N. S., & Schoener, G. R. (2007). In pursuit of wellness: The self-care imperative. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 38(6), 603–612. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.6.603
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (1998). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (2nd ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) (2009). 2009 Standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/ doc/2009%20standards %20with20cover.pdf
Canfield, J. (2005). Secondary traumatization, burnout, and vicarious traumatization: A review of the literature as it relates to therapists who treat trauma. Smith College Studies in Social Work, 75(2), 81–102. doi:10.1300 J497v75n02_06
Carswell, K. (2011, March). Lecture on combating compassion fatigue: Strategies for the long haul. Counseling Department, Western Carolina University, Cullowhee, NC.
Corey, G. (2000). Theory and practice of group counseling (5th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/Thompson Learning.
Hill, C. E., Knox, S., Thompson, S. J., Williams, E. N, Hess, S. A., & Ladany, N. (2005). Consensual qualitative research: An update. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 23(2), 196–205. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.52.2.196
Hill, C. E., Thompson, B. J., & Nutt Williams, E. (1997). A guide to conducting consensual qualitative research. The Counseling Psychologist, 25, 517–572. doi:10.1177/ 0011000097254001
Gilliland, B. E., & James, R. K. (2001). Crisis intervention strategies. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning.
Jenaro, C., Flores, N., & Arias, B. (2007). Burnout and coping in human service practitioners. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 38, 80–87. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.1.80
Koeske, G. F., & Kelly, T. (1995). The impact of overinvolvement on burnout and job satisfaction. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 65, 282–292. doi:10.1037/h0079622
Kestnbaum, J. D. (1984). Expectations for therapeutic growth: One factor in burnout. Social Casework: The Journal of Contemporary Social Work, 65, 374–377.
Leiter, M. (1991). The dream denied: Professional burnout and the constraints of human service organizations. Canadian Psychology, 32(4), 547–558. doi:10.1037/h0079040
Myers, J. E. (1991). Wellness as the paradigm for counseling and development. The possible future. Counselor Education and Supervision, 30, 183–193.
Myers, J. E., & Williard, K. (2003). Integrating spirituality into counselor preparation: A developmental, wellness approach. Counseling and Values, 47, 142–155.
Ponterotto, J. G. (2005). Qualitative research in counseling psychology: A primer on research paradigms and philosophy of science. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52(2), 126–136. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.52.2.196
Rosenberg, T., & Pace, M. (2006). Burnout among mental health professionals: Special considerations for the marriage and family therapist. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 32(1), 87–99. doi:10.1111/j.1752- 0606.2006.tb01590
Sherman, M. D. (1996). Distress and professional impairment due to mental health problems among psychotherapists. Clinical Psychology Review, 16, 299–315. doi:10.1016/0272- 7358(96)00016-5
Skovholt, T. M. (2001). The resilient practitioner: Burnout prevention and self-care strategies for counselors, therapists, teachers, and health professionals. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Skovolt, T. M., Grier, T. L., & Hanson, M. R. (2001). Career counseling for longevity: Self-care and burnout prevention strategies for counselor resilience. Journal of Career Development, 27(3), 167–176. doi:10.1177/089484530102700303
Truchot, D., Keirsebilck, L., & Meyer, S. (2000). Communal orientation may not buffer burnout. Psychological Reports, 86, 872–878. doi:10.2466/PR0.86.3.872-878
Witmer, J. M., & Granello, P. F. (2005). Wellness in counselor education and supervision. In J. E. Myers & T. J. Sweeney (Eds.), Counseling for wellness: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 342–361). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
E. Heather Thompson is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Counseling Western Carolina University. Melodie H. Frick is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Counseling at West Texas A & M University. Shannon Trice-Black is an Assistant Professor at the College of William and Mary. Correspondence can be addressed to Shannon Trice-Black, College of William and Mary, School of Education, PO Box 8795, Williamsburg, VA, 23187-8795, stblack@wm.edu.
Appendix A
Interview Protocol
1. What do you know about counselor burnout or how would you define counselor burnout?
2. What do you think are possible causes of counselor burnout?
3. As counselors we often are overloaded with administrative duties which may include treatment planning, session notes, and working on treatment teams. What has this experience been like for you?
4. Counseling requires a tremendous amount of empathy which can be emotionally exhausting. What are your experiences with empathy and emotional exhaustion? Can you give a specific example?
5. How do you distinguish between feeling tired and the early signs of burnout?
6. As counselors, we sometimes become overcommitted to clients who are not as ready, motivated, or willing to engage in the counseling process. Not all of our clients will succeed in the way that we want them to. How do you feel when your clients don’t grow in the way you want them to? How has this issue been addressed in supervision?
7. What is your perception of how your supervisors have dealt with stress?
8. How has counselor burnout been addressed in supervision?
prompt: asked about, evaluated, provided reading materials, and how often
9. How have specific issues related to burnout been addressed in supervision such as: (a) over-commitment to clients who seem less motivated to change, (b) emotional exhaustion, and (c) elusive measures of success?
10. How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor burnout?
prompt: asked about, evaluated, provided reading materials, modeled by supervisor
11. What do you know about self-care or how would you define self-care for counselors?
12. What are examples of self-care, specifically ones that you use as counselors-in-training?
13. How has counselor self-care been addressed in supervision?
14. Sometimes we have to say “no.” How would you characterize your ability to say “no?” What have you learned in supervision about setting personal and professional boundaries?
15. What, if any, discussions have you had in supervision about your social, emotional, spiritual, and/or physical wellbeing? What is a specific example?
16. How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor self-care?
prompt: asked about, provided reading materials, modeled by supervisor
17. How could your overall counselor training be improved in addressing counselor burnout and counselor self-care?
Appendix B
Follow-Up Questionnaire
How would you describe counselor burnout?
How has counselor burnout been addressed in supervision?
How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor burnout?
How would you describe self-care for counselors?
How has counselor self-care been addressed in supervision?
How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor self-care?
How could your overall counselor training be improved in addressing counselor burnout and counselor self-care?
