Integrating a Multi-Tiered System of Supports With Comprehensive School Counseling Programs
Jolie Ziomek-Daigle, Emily Goodman-Scott, Jason Cavin, Peg Donohue
A multi-tiered system of supports, including Response to Intervention and Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, is a widely utilized framework implemented in K–12 schools to address the academic and behavioral needs of all students. School counselors are leaders who facilitate comprehensive school counseling programs and demonstrate their relevance to school initiatives and centrality to the school’s mission. The purpose of this article is to discuss both a multi-tiered system of supports and comprehensive school counseling programs, demonstrating the overlap between the two frameworks. Specific similarities include: leadership team and collaboration, coordinated services, school counselor roles, data collection, evidence-based practices, equity, cultural responsiveness, advocacy, prevention, positive school climate, and systemic change. A case study is included to illustrate a school counseling department integrating a multi-tiered system of supports with their comprehensive school counseling program. In the case study, school counselors are described as interveners, facilitators and supporters regarding the implementation of a multi-tiered system of supports.
Keywords: multi-tiered system of supports, Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, Response to Intervention, comprehensive school counseling programs, coordinated services
A multi-tiered system of supports (MTSS), including Response to Intervention (RTI) and Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS), has been embedded in many public schools for the last decade. Specifically, these data-driven frameworks promote positive student academic and behavioral outcomes, as well as safe and favorable school climates (Ockerman, Mason, & Hollenbeck, 2012; Sugai & Horner, 2009). School counselors design and implement comprehensive school counseling programs that promote students’ academic, career, social, and emotional success as well as equitable student outcomes and systemic changes (American School Counselor Association [ASCA], 2012). As school leaders, school counselors should understand MTSS and play a leadership role in the development and implementation of such frameworks (ASCA, 2014; Goodman-Scott, 2014; Goodman-Scott, Betters-Bubon, & Donohue, 2016).
In a 2014 position statement on MTSS, ASCA described school counselors as important stakeholders in its implementation plan, stating “professional school counselors align their work with MTSS through the implementation of a comprehensive school counseling program designed to improve student achievement and behavior” (p. 38). Several scholars have discussed the alignment of RTI and comprehensive school counseling programs (Gruman & Hoelzen, 2011; Ockerman et al., 2012; Ryan, Kaffenberger, & Carroll, 2011; Ziomek-Daigle & Heckman, under review) as well as PBIS and comprehensive school counseling programs (Donohue, 2014; Goodman-Scott, 2014; Goodman-Scott et al., 2016; Shepard, Shahidullah, & Carlson, 2013), including school counselors’ roles in both. However, there remains a need to examine MTSS as an overarching construct and its overlap with comprehensive school counseling programs. In this article, we present information on MTSS, including RTI and PBIS, discuss comprehensive school counseling programs and the overlap of the two frameworks, and culminate with a case study illustrating the role of school counselors as interveners, facilitators, and supporters integrating MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs in a middle school.
Multi-Tiered System of Supports
The use of MTSS offers school counselors opportunities to have a lasting impact on student academic success and behavior development while integrating these frameworks with comprehensive school counseling programs. MTSS, often used as an overarching construct for PBIS and RTI, is a schoolwide, three-tiered approach for providing academic, behavioral and social supports to all students based on their needs and skills (Cook, Lyon, Kubergovic, Wright, & Zhang, 2015; Harlacher, Sakelaris, & Kattelman, 2014; Sugai & Horner, 2009; Sugai & Simonsen, 2012). Harlacher et al. (2014) described six key tenets of the MTSS framework: (a) all students are capable of grade-level learning with adequate support; (b) MTSS is rooted in proactivity and prevention; (c) the system utilizes evidence-based practices; (d) decisions and procedures are driven by school and student data; (e) the degree of support given to each student is based on their needs; and (f) implementation occurs schoolwide and requires stakeholder collaboration.
MTSS consists of a continuum of three tiers of prevention: primary, secondary, and tertiary (Harlacher et al., 2014; Sugai & Horner, 2009). In Tier 1, or primary prevention, all students receive academic and behavioral support (Harlacher et al., 2014). Approximately 80% of students in a school are successful while receiving only primary prevention, or the general education academic and behavioral curriculum for all students. Examples include teaching expected behaviors schoolwide and the use of evidence-based academic strategies and curriculums. Students with elevated needs receive more specialized secondary and tertiary prevention, typically 15% and 5% of students, respectively (Harlacher et al., 2014; Sugai & Horner, 2009). Educators provide increasing degrees of interventions and supports in order for each student to be successful academically and behaviorally.
In regards to prevention, students are usually screened using academic benchmark assessments and behavioral data to determine their level of need (Harlacher et al., 2014; Sugai & Horner, 2009; Sugai & Simonsen, 2012). Some schools have moved to the use of universal screening to identify students with emerging mental health needs such as anxiety and depression (Lane, Oakes, & Menzies, 2010). Those with elevated needs receive interventions and are monitored to determine their progress and the interventions’ effectiveness. Further, the prevention activities in all three tiers are evidence-based practices (e.g., scientifically-based interventions; Harlacher et al., 2014; Sugai & Horner, 2009) and data-driven. Specifically, data is used to determine students’ needs and to measure progress. In the next section, two examples of MTSS will be discussed: RTI and PBIS.
Response to Intervention
The No Child Left Behind Act (2002) clearly emphasized that educators have unique opportunities to provide early intervention, quality instruction and data-driven decisions for all students. RTI, an outcome of the accountability movement, is “a systematic and structured approach to increase the efficiency, accountability, and impact of effective practices” (Crockett & Gillespie, 2007, p. 2). This framework was designed in 2004 as an alternative to states’ use of the discrepancy model of special education assessment, which compared children’s current ability and achievement levels (Ryan et al., 2011). By using only the discrepancy model to identify students in need of special education services, inconsistencies prevailed among school districts and states. Concerns about the discrepancy model included: (a) students of color were being over-identified as being in need of special education services as compared to White peers; (b) difficulty determining if low achievement was due to a possible learning disability or inadequate teacher performance; (c) educators waiting for students to fail instead of proactively identifying discrete literacy and numeracy skills that merited remediation (Fuchs & Fuchs, 2006). As RTI has evolved over the years, educators expanded the model to include behavioral and social interventions that are universal (e.g., whole-school) as well as intensive services (e.g., individual or small group), more fully responding to students with varied development.
RTI is currently used in school systems as a way to decrease referrals for special education services (Gersten & Dimino, 2006). The framework and the use of tiered supports ensure that students receive the appropriate level of intervention needed (Fuchs & Fuchs, 2006). Previously, students who exhibited difficulties in a single academic area would be referred to special education services, potentially removing them from the general education classroom. With RTI implementation, students now receive supports that allow them to remain in the general education classroom and reduce the rate of unnecessary referrals for special education services (Gersten & Dimino, 2006). RTI can be further described as instructional and behavioral.
Instructional RTI
Most educators report having a thorough knowledge of RTI to establish early literacy and math fluency and to provide additional supports in academic areas where needed (Shepard et al., 2013). Instructional RTI often is used to describe the process in which teachers work with students to mitigate the labeling and negative effects often associated with learning disabilities (Johnston, 2010). The teacher tailors the instruction to address the perceived deficit the student is exhibiting. Most often this delivery is used in the context of reading instruction (Shinn, 2010). The focus on instructional practice can take place on the first tier with whole class instruction, on the second tier with a small reading group, or on the third tier with intensive one-on-one instruction (Fuchs & Fuchs, 2006).
Behavioral RTI
Students may not only struggle with academic challenges, but behavioral, social and emotional challenges as well. Many students experience a host of challenging situations occurring in their homes and communities, such as poverty, homelessness, immigration and residency barriers, and the lack of fulfillment of basic needs such as adequate nutrition, transportation, and medical care (Shepard et al., 2013). Supporting social behavior is central for students to achieve academic gains, although this area is not often represented in traditional RTI implementation that may focus primarily on learning and instruction. More recent RTI frameworks reveal pyramids split in half showing both the academic and behavioral domains, more fully recognizing the complex entanglement between academic, social and emotional learning (Stormont, Reinke, & Herman, 2010). Behavioral RTI emphasizes a continuum of services that can be provided to students by school counselors and integrated into comprehensive school counseling programs.
A hallmark of both the instructional and behavioral RTI models is the focus on differentiation among the three tiers of intervention. Each approach delimits critical factors and components at the primary levels; interventions become more intense and personalized as students are provided more individualized supports. As with any type of intervention, data tracking is necessary to the success of the outcome (Utley & Obiakor, 2015). Both instructional and behavioral RTI use a system of data tracking known as continuous regeneration, in which the data is analyzed on an ongoing basis and interventions are evaluated based on recorded outcomes (McIntosh, Filter, Bennett, Ryan, & Sugai, 2010). The use of continuous regeneration means students receive the most applicable form of intervention throughout the course of their academic career. The following section will discuss the use of the RTI within school counseling programs.
School Counseling and RTI
Researchers have discussed the school counselor’s role and involvement in the RTI process (Ockerman et al., 2012; Ryan et al., 2011). Studies reveal that school counseling interventions using tiered approaches, such as universal instruction via classroom guidance programming and subsequent small group follow-up, have increased student achievement and motivation (Luck & Webb, 2009; Ryan et al., 2011). Ziomek-Daigle and Cavin (2015) discussed that positive behavior support strategies, which can be designed for students with behavioral issues in classrooms or at home, can be taught to teachers and parents for children who need more individualized support and monitoring. Additionally, school counselors have been identified as integral members to RTI teams by using behavioral observations to determine the responsiveness and effectiveness of services (Gruman & Hoelzen, 2011).
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
PBIS, a multi-tiered system of supports, is grounded in the principles of applied behavior analysis (Johnston, Foxx, Jacobson, Green, & Mulick, 2006) and implemented in over 21,000 schools across the United States (Sugai, 2016). Further, PBIS is often described as a function of RTI, including the “application of RTI principles to the improvement of social behavior outcomes for all students” (Sugai & Simonsen, 2012, p. 4). Thus, PBIS uses the three-tiered preventative continuum of data-driven and evidence-based practices to improve students’ academics and social behaviors (Sugai & Horner, 2009; Sugai & Simonsen, 2012). PBIS is implemented schoolwide, including evidence-based primary prevention for all students, and secondary and tertiary prevention for students with elevated needs (Shepard et al., 2013). Examples of primary prevention include universal behavioral expectations, discipline procedures, and acknowledgements, also known as positive reinforcement. Secondary and tertiary prevention can include behavioral contracts, social skill instruction and wraparound services.
One appealing aspect of PBIS is the use of systematic data collection for monitoring student referrals as well as PBIS implementation and fidelity (Simonsen & Sugai, 2013). Thus, data is used to continually determine student and school needs and related progress, and to guide future decisions in an iterative cycle. Examples of student data utilized include suspensions and office discipline referrals, grades, attendance, and other student outcomes (Sugai & Horner, 2009). Student data is often analyzed for patterns in office discipline referrals, such as frequency, location and time of year. Patterns can be analyzed using tools such as the School Wide Information System, a web-based tool for organizing and analyzing office discipline referral trends (May et al., 2006). Standardized assessments can be used to determine schoolwide data trends, including the School Wide Evaluation Tool, a research-validated instrument that measures the degree of PBIS implementation (Todd et al., 2012).
A plethora of researchers have demonstrated the positive impact of PBIS implementation as related to a number of school, student and staff benefits. Schools implementing PBIS have demonstrated better student academic outcomes (Horner et al., 2009; Simonsen et al., 2012), a decrease in student discipline incidences (Bradshaw, Mitchell, & Leaf, 2010; Bradshaw, Waasdorp, & Leaf, 2012; Curtis, Van Horne, Robertson, & Karvonen, 2010; Sherrod, Getch, & Ziomek-Daigle, 2009; Simonsen et al., 2012), and a more positive and safer school climate and work environment (Bradshaw, Koth, Bevans, Ialongo, & Leaf, 2008; Horner et al., 2009; Waasdorp, Bradshaw, & Leaf, 2012).
School Counseling and PBIS
Several scholars have discussed school counselors’ roles in PBIS implementation. Goodman-Scott et al. (2016) described the alignment between comprehensive school counseling programs and PBIS, particularly the use of data-driven, evidence-based practices and a tiered continuum of supports: prevention for all students and intervention for students with elevated needs. Further, through case studies, several researchers have demonstrated school counselors’ roles in PBIS implementation in their schools. Specifically, Sherrod et al. (2009) found a decrease in schoolwide and small group office discipline referrals and described school counselors’ roles in creating and implementing schoolwide interventions addressing student behaviors. Further, school counselors utilized student outcome data generated by the PBIS team to determine students’ needs for and progress in school counselor interventions such as small group counseling (Goodman-Scott, Hays, & Cholewa, under review). While in PBIS leadership roles, school counselors have demonstrated collaboration and consultation with stakeholders, contributed to a safe school environment and schoolwide systems of reinforcement, utilized student outcome data, implemented universal screening, facilitated PBIS-specific bullying prevention and conducted small group interventions (Curtis et al., 2010; Donohue, 2014; Donohue, Goodman-Scott & Betters-Bubon, 2016; Goodman-Scott, 2014; Goodman-Scott, Doyle, & Brott, 2014; Martens & Andreen, 2013).
PBIS and Behavioral RTI
Behavioral RTI and PBIS, although similar in their focus on schoolwide behaviors within a three-tiered framework, are remarkably different. First, all students are exposed to behavioral RTI, but only students who attend schools implementing PBIS receive the behavioral supports of the latter. The implementation and mandate of RTI is a direct outcome of the No Child Left Behind Act (2002). On the other hand, PBIS, a manualized approach, requires ongoing training and a specific evaluation process. PBIS fidelity is necessary for successful implementation and requires ongoing data collection and analysis. The behavioral RTI approach allows schools to design and develop their own frameworks in a contextual manner to best support their students, and the method and training for implementation remains flexible. School counselors can be active in both RTI and PBIS implementation in their schools, as several of these roles overlap with comprehensive school counseling programs.
Comprehensive School Counseling Programs
Comprehensive school counseling programs were initially conceptualized in the 1960s and 1970s, have evolved over time, are tied to the school’s academic mission, and are based on student competencies in the academic, career, social and emotional domains (Gysbers & Henderson, 2012). One well-known and widely used comprehensive school counseling framework is the ASCA National Model (ASCA, 2012; Gysbers & Henderson, 2012). The model was based on (a) the ASCA National Standards for School Counseling Programs, which defined student standards and competencies regarding academic, career, personal and social development (Campbell & Dahir, 1997), and (b) the Education Trust’s Transforming School Counseling Initiative, which emphasized school counselors’ roles in closing the achievement gap for low-income and minority students, and performing leadership, advocacy, systemic change, and collaboration and teaming (Martin, 2015). The model was created in 2003, was updated in both 2005 and 2012, and has provided the school counseling professional with a unified vision, voice, and identity in regards to the school counselors’ roles (ASCA, 2012; Gysbers & Henderson, 2012).
Many scholars have reported positive outcomes related to comprehensive school counseling program implementation. For example, Wilkerson, Pérusse, and Hughes (2013) found that elementary schools designated as fully implemented ASCA Model Programs had higher standardized English and Language Arts and Math scores than those schools without the designation. Similarly, other scholars have associated comprehensive school counseling program implementation with higher student achievement scores (Sink, Akos, Turnbull, & Mvududu, 2008; Sink & Stroh, 2003). In a similar vein, Hatch, Poynton, and Pérusse (2015) reported that the increased national emphasis on comprehensive school counseling programs over the last decade has positively impacted school counselors’ related beliefs and priorities.
The ASCA National Model and a Multi-Tiered System of Supports
School counselors are crucial in students’ learning and social development and are invested in early interventions that are at the root of comprehensive school counseling programs (Ryan et al., 2011). MTSS aligns with the ASCA National Model’s chief inputs of advocacy, collaboration, systemic change, prevention, intervention and the use of data. Thus, both the ASCA National Model (2012) and MTSS are inherently connected given their overlapping foci (see Figure 1).
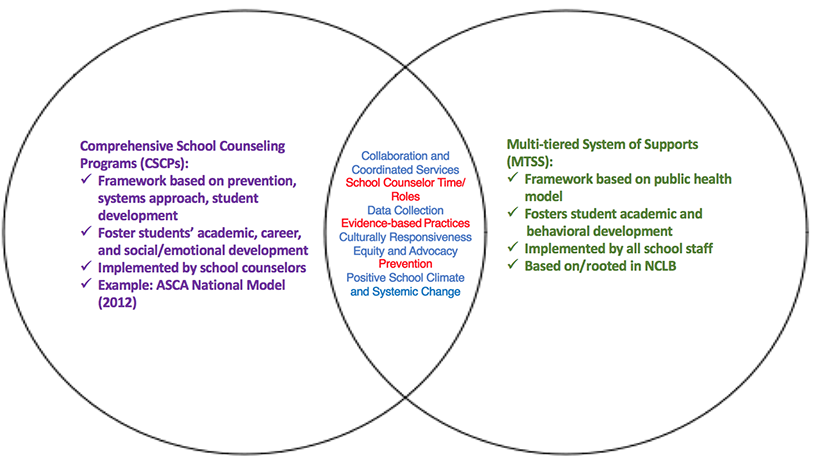
Figure 1. Overlap and similarities between a multi-tiered system of supports and comprehensive school counseling programs
Overlap exists between these two frameworks, especially prominent when school counselors take on roles as supporters, interveners and facilitators in offering indirect as well as direct services (Ockerman et al., 2012; Ziomek-Daigle & Heckman, under review). In the role as supporters, school counselors share data related to interventions, discuss needs assessment data and increase awareness regarding equity gaps that may be present at the school (Ockerman et al., 2012). School counselors are interveners and facilitators as active members of RTI teams who provide behavioral interventions and services and, through progress monitoring, collect and review data and make recommendations (Ockerman et al., 2012; Ziomek-Daigle & Heckman, under review).
The ASCA National Model (2012) provides the necessary components for comprehensive school counseling programs grounded in student data and based on student academic, career, social and emotional development. The model includes four components: foundation, delivery, management, and accountability. Next, we discuss the integration of a multi-tiered system of supports into the four components of the model.
Foundation. Establishing the program’s foundation is the initial step in building a comprehensive school counseling program (ASCA, 2012). As programs are developed, school counselors should examine their own personal beliefs about their role with students. Program mission and vision statements should also be created, using measurable language. Additionally, student competencies in the academic, career, social and emotional domains are reflected in comprehensive programs along with school counselors’ ethical decision making and professional practice. School counselors’ program visions and goals should reflect priorities also highlighted in the school’s multi-tiered framework (Goodman-Scott et al., 2016). For example, Goodman-Scott et al. (2016) suggested school counselors’ vision and mission statements should represent school and district current trends and goals, such as PBIS delivery and implementation.
Delivery. The delivery component of the framework identifies the types of services that school counselors directly offer students such as classroom guidance programming and core curriculum (Ziomek-Daigle, 2015), individual student planning, small group and individual counseling, consultation, and referral (ASCA, 2012). Many approaches used within a multi-tiered system of supports also can be utilized within the delivery system of school counseling programs, such as prevention activities (e.g., teaching schoolwide expectations in classroom guidance programming) and interventions (e.g., check in/check out; Goodman-Scott et al., 2016; Goodman-Scott et al., under review; Ziomek-Daigle & Heckman, under review). Further, school counselors can integrate more intensive interventions for students with multiple, complex needs, including wraparound services (Shepard et al., 2013).
Accountability and Management. Accountability and management are at the root of any comprehensive school counseling program, as data is collected, analyzed and reported, identifying how students are different as a result of the program (ASCA, 2012). Further, school counselors utilize a variety of tools and assessments to gather evidence of program and school counselor effectiveness (ASCA, 2012). Data generated from a multi-tiered system of supports, such as student achievement and behavior, are continuously collected and reviewed to determine student needs and intervention effectiveness. School counselors can use this data from a multi-tiered system of supports to determine student and school needs and create curriculum, small group and closing-the-gap action plans accordingly (Goodman-Scott et al., 2016). After implementing interventions, school counselors can measure the impact of their interventions on the desired student outcomes including attendance, office referrals and grades, thus determining their effectiveness and impact through the use of result reports. MTSS overlaps with comprehensive school counseling programs; thus, the two can be integrated to strengthen both. The following section discusses the commonalities between MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs.
Commonalities Between a Multi-Tiered System of Supports and Comprehensive School Counseling Programs
Several similarities exist between MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs (see Figure 1). Similarities include utilizing collaboration and coordinated services; efficiently using the school counselors’ time through tiered supports; collecting and reviewing student and school data; using evidence-based practices; developing culturally responsive interventions that close achievement gaps; promoting prevention and intervention for students through a tiered continuum; and facilitating schoolwide systemic change and a positive school climate. First, both frameworks have established leadership teams that guide program design and implementation, represent the stakeholders within the building and offer support in program development and accessing resources. Next, tiered approaches provide school counselors time to address whole-school needs while also providing services to and advocating on behalf of students in crisis or with significant needs. Thus, using tiered approaches may assist school counselors directly and indirectly serve students. Ongoing progress monitoring through continuous data collection keeps MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs focused and stakeholders informed, which may lead to greater stakeholder awareness and support for school counseling initiatives. Similarly, the use of evidence-based practices, recommended by MTSS and comprehensive school counseling, offers students quality, empirically-backed academic and behavioral services across all three tiers. A successful MTSS also allows school counselors to address achievement gaps and increase equitable practices by strengthening social supports for students in the classroom, school building and community who present with challenging behavior. A case study illustrating the role of school counselors as interveners, facilitators and supporters of integrating both MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs follows.
Case Study
Example Middle School (EMS) is located in a suburban setting with approximately 700 students across sixth, seventh and eighth grades; 25% of students come from households considered economically disadvantaged. The majority of students identify as Caucasian (45%) or African American (30%). RTI has been implemented in EMS for approximately seven years, while PBIS has been implemented for four years. The school administration consists of one principal and three assistant principals (APs), and the school counseling department includes three school counselors with a school counselor to student ratio of 1:233. Each grade level is assigned one AP and one school counselor.
The grade levels each meet bi-weekly to discuss academic planning and share information regarding students (both concerns and accomplishments). The EMS student support team is an interdisciplinary team that meets to create and discuss academic and behavioral interventions and related progress for students demonstrating consistent academic and behavioral challenges that were not successfully addressed by the grade-level Tier 1 meetings. The student support team is facilitated by a teacher and attended by the grade-level AP and school counselor as well as the school psychologists. Parents of the reviewed student also are invited. In addition, EMS has a PBIS team comprised of representatives from all grade levels and specialties, including one school counselor; parents and students are represented on the PBIS team. The school counselor and AP together oversee the PBIS data collection and analysis. Lastly, the school counseling team meets weekly and over the last seven years has developed a comprehensive school counseling program based on the ASCA National Model. All school counselors at EMS have essential roles in the program implementation.
Tier One
The school counselors act as supporters, interveners and facilitators in Tier 1. As supporters, EMS school counselors attend all regular grade-level meetings and provide background information on students as appropriate. As interveners, school counselors collaborate and consult with teachers on their instruction and curriculum as well as teachers’ monitoring and screening of all students to identify those with elevated academic and behavioral needs. For example, at the most recent seventh-grade-level meeting, the school counselor reviewed grade-level office discipline referrals, attendance records and teachers’ anecdotal feedback. The grade-level team expressed concern about a student, Elena, who had several absences and office discipline referrals in the last month. The seventh-grade school counselor provided non-confidential background information on Elena to the grade-level team members.
The school counselor on the PBIS team holds a number of additional roles as supporter. First, the counselor provides information on school climate generated by the comprehensive school counseling program, including both anecdotal observations and data-driven findings. The school counselor also assists the PBIS team in developing a common school language and protocols (i.e., school expectations: Be Responsible, Be Respectful, Be Safe), schoolwide and individual acknowledgements for students and staff, and discipline procedures (i.e., the office discipline referral process). In the role as facilitator, the school counselors assist the PBIS team as they plan schoolwide pep rallies to further teach the school expectations, acknowledge students, classes and staff with certain achievements (e.g., the homeroom with the lowest office discipline referrals per quarter; staff who distributed the highest number of school tickets). As an intervener, all school counselors teach the PBIS-generated school expectations during their regular monthly classroom lessons and engage in student acknowledgements (e.g., distributing EMS tickets for positive behaviors). Intervener roles also include school counselors engaging in student advising and schoolwide programming, such as teaching students and staff the bullying prevention strategies from Expect Respect, an evidence-based bully prevention program (Stiller, Nese, Tomlanovich, Horner, & Ross, 2013). Additionally, in roles as interveners, school counselors deliver a social skills curriculum to students during weekly homeroom advisory periods or through regular guidance lessons (Ziomek-Daigle, 2015). Further, school counselors collaborate with school psychologists to engage in universal mental health screening for student depression and anxiety and provide evidence-based classroom lessons to all students to promote positive mental health, as interveners (Donohue et al., 2016).
The school counseling program holds advisory team meetings quarterly. Members include all school counselors, a student and parent representative, a general education teacher from all grade levels, the PBIS coach, the AP who reviews PBIS data and one special education teacher. At the end of each year, the advisory team reviews a number of data points, including the comprehensive school counseling program goals from the previous year and related outcomes and results reports, schoolwide PBIS behavioral data, RTI instructional and behavioral data, and the school data profile. Next, the advisory team makes goals for the subsequent year based on data-determined needs. Then, based on the advisory team’s recommendations, the school counselors create closing-the-gap action plans and goals for the next year (i.e., SMART goals,). School counselors present the results of their advisory team meetings, action plans, SMART goals, and results reports to the administrative team (principal and APs), as well as the PBIS team, RTI team and whole school faculty.
Tiers Two and Three
When providing Tier 2 and 3 supports and services, the EMS school counselors engage in supporter, interventionist and facilitator roles. To follow up from the grade-level meetings, the EMS school counselors act as interveners by consulting and collaborating with teachers individually regarding evidence-based academic and behavioral interventions for struggling students as well as teachers’ classroom management. As part of the PBIS team, the school counselor acts as a supporter by discussing schoolwide behavioral trends, students with elevated office discipline referrals, and students who are otherwise considered at risk (e.g., absences, class failures, poor standardized and benchmark tests) and recommending interventions. One intervention may be referral to the student support team.
In a role as supporter, school counselors attend the student support team meetings and, along with this team, recommend increasingly individualized evidence-based student academic and behavioral interventions and monitor students’ progress at subsequent meetings. Tier 3 interventions are greater in duration and intensity than Tier 2 and have greater individualization. The student support team works together to identify students in need of Tier 2 or Tier 3 interventions, facilitates service implementation and decides to decrease and end interventions due to students maintaining positive progress. The student support team recommends interventions which may include individual or small group counseling and function-based behavioral mentoring interventions such as Check In, Check Out and Check & Connect (Baker & Ryan, 2014). As interveners, school counselors often provide counseling and mentoring or coordinate other staff and community members’ involvement in mentoring programs. In addition, the school counselor may be trained to use the Check & Connect program and continuously review attendance, behavioral and academic data (i.e., check) and provide interventions (i.e., connect) to a small caseload of students who are being served through Tier 2 and 3 services. As facilitators, school counselors also may develop and access a list of health care providers so that students and families participate in a seamless referral process. In this role, counselors also may coordinate quarterly interdisciplinary meetings for a few students whose needs are complex and who receive community-based agency assistance. Some examples of interdisciplinary collaborative team members include: school counselors, mental health counselors, psychologists, nurses, probation officers and case workers. Lastly, the EMS school counselors, acting as interveners and facilitators, analyze the results of the universal mental health screener for depression and anxiety.
In regards to student Elena, the seventh-grade school counselor and grade-level team agreed that the school counselor would meet with Elena individually to gather additional background information on her absences and office discipline referrals. When Elena did not improve over the subsequent two-week period, more intensive and continued interventions were discussed with the grade-level team, including a referral to the student support team. After review by the student support team, Elena began Check & Connect with the school counselor, and the school counselor maintained communication with Elena’s mother and stepfather, teachers and members of the student support team.
Conclusion
ASCA (2014) recommends that school counselors can implement MTSS in alignment with facilitating a comprehensive school counseling program. Further, several scholars have contended that school counselors can be leaders in MTSS, incorporating these duties into aspects of a comprehensive school counseling program (Cressey, Whitcomb, McGilvray-Rivet, Morrison, & Shander-Reynolds, 2014; Goodman-Scott et al., 2016). As described in this article, MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs share many overlapping characteristics, and school counselors may act as leaders in both, vacillating between the roles of supporter, intervener and facilitator (Ockerman et al., 2012; Ziomek-Daigle & Heckman, under review). In implementing both frameworks, school counselors are able to focus on student achievement and behavior, as well as collaboration, data collection, evidence-based practices and social justice advocacy, to close achievement and equity gaps. Additionally, school counselors can utilize the existing MTSS in the schools to enhance, expand and challenge their own comprehensive programs and present new, relevant and critical research and practical implications to the field. Goodman-Scott et al. (2016) suggested that aligning both frameworks may be a strategy to advocate at local and national levels for the school counseling field and comprehensive school counseling program implementation. Presenting school counseling programs in this manner also can increase stakeholder involvement, access additional resources and increase job stability. Focusing on the overlap between MTSS and comprehensive school counseling programs leads to a data-driven, evidence-based focus on improving school climate, as well as student equity, access, and academic and behavioral success, meeting the needs of students across all three tiers.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
American School Counselor Association. (2012). The ASCA national model: A framework for school counseling programs (3rd ed.). Alexandria, VA: Author.
American School Counselor Association. (2014). The professional school counselor and multitiered system of supports. American School Counselor Association Position Statement. Retrieved from https://www.schoolcounselor.org/asca/media/asca/PositionStatements/PS_MultitieredSupportSystem.pdf
Baker, B., & Ryan, C. (2014). The PBIS team handbook: Setting expectations and building positive behavior. Minneapolis, MN: Free Spirit Publishing.
Bradshaw, C. P., Koth, C. W., Bevans, K. B., Ialongo, N., & Leaf, P. J. (2008). The impact of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports (PBIS) on the organizational health of elementary schools. School Psychology Quarterly, 23, 462–473. doi:10.1037/a0012883
Bradshaw, C. P., Mitchell, M. M., & Leaf, P. J. (2010). Examining the effects of schoolwide positive behavioral interventions and supports on study outcomes: Results from a randomized controlled effectiveness trial in elementary schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 12, 133–148. doi:10.1177/1098300709334798
Bradshaw, C. P., Waasdorp, T. E., & Leaf, P. J. (2012). Effects of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports on child behavior problems. Pediatrics, 130, 1136–1145. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-0243
Campbell, C. A., & Dahir, C. A. (1997). Sharing the vision: The national standards for school counseling programs.
Alexandria, VA: American School Counselor Association.
Cook, C. R., Lyon, A. R., Kubergovic, D., Wright, D. B., & Zhang, Y. (2015). A supportive beliefs intervention to facilitate the implementation of evidence-based practices within a multi-tiered system of supports. School Mental Health, 7, 49–60. doi:10.1007/s12310-014-9139-3
Cressey, J. M., Whitcomb, S. A., McGilvray-Rivet, S. J., Morrison, R. J., & Shander-Reynolds, K. J. (2014). Handling PBIS with care: Scaling up to school-wide implementation. Professional School Counseling, 18, 90–99. doi:10.5330/prsc.18.1.g1307kql2457q668
Crockett, J. B., & Gillespie, D. N. (2007, Fall). Getting ready for RTI: A principal’s guide to response to intervention. ERS Spectrum, 25(4), 1–9.
Curtis, R., Van Horne, J. W., Robertson, P., & Karvonen, M. (2010). Outcomes of a school-wide positive behavioral support program. Professional School Counseling, 13, 159–164. doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2010-13.159
Donohue, M. D. (2014). Implementing school wide positive behavioral supports (SWPBIS): School counselors’ perceptions of student outcomes, school climate, and professional effectiveness. Retrieved from http://digitalcommons.uconn.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6616&context=dissertations
Donohue, P., Goodman-Scott, E., & Betters-Bubon, J. (2016). Using universal screening for early identification of students at risk: A case example from the field. Professional School Counseling, 19, 133–143. doi:10.5330/1096-2409-19.1.133
Fuchs, D., & Fuchs, L. S. (2006). Introduction to response to intervention: What, why, and how valid is it? Reading Research Quarterly, 41, 93–99.
Gersten, R., & Dimino, J. A. (2006). RTI (Response to Intervention): Rethinking special education for students with reading difficulties (yet again). Reading Research Quarterly, 41, 99–108. doi:10.1598/RRQ.41.1.5
Goodman-Scott, E. (2014). Maximizing school counselors’ efforts by implementing school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports: A case study from the field. Professional School Counseling, 17, 111–119. doi:10.5330/prsc.17.1.518021r2x6821660
Goodman-Scott, E., Betters-Bubon, J., & Donohue, P. (2016). Aligning comprehensive school counseling programs and positive behavioral interventions and supports to maximize school counselors’ efforts. Professional School Counseling, 19, 57–67. doi:10.5330/1096-2409-19.1.57
Goodman-Scott, E., Doyle, B., & Brott, P. (2014). An action research project to determine the utility of bully prevention in positive behavior support for elementary school bullying prevention. Professional School Counseling, 17, 120–129. doi:10.5330/prsc.17.1.53346473u5052044
Goodman-Scott, E., Hays, D. G., & Cholewa, B. (under review). “It takes a village:” A case study of positive behavioral interventions and supports implementation in an exemplary middle school.
Gruman, D. H., & Hoelzen, B. (2011). Determining responsiveness to school counseling interventions using behavioral observations. Professional School Counseling, 14(3), 183–190. doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2011-14.183
Gysbers, N. C., & Henderson, P. (2012). Developing and managing your school guidance and counseling program (5th ed.). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Harlacher, J. E., Sakelaris, T. L., & Kattelman, N. M. (2014). Practitioner’s guide to curriculum-based evaluation in reading. New York, NY: Springer.
Hatch, T., Poynton, T., & Pérusse, R. (2015). Comparison findings of school counselor beliefs about ASCA National Model school counseling program components using the SCPCS. SAGE Open, 1–10. doi:10.1177/2158244015579071
Horner, R. H., Sugai, G. M., Smolkowski, K., Eber, L., Nakasato, J., Todd, A. W., & Esperanza, J. (2009). A
randomized, wait-list controlled effectiveness trial assessing school-wide positive behavior support in elementary schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 11(3), 133–144. doi:10.1177/1098300709332067
Johnston, P. (2010). An instructional frame for RTI. The Reading Teacher, 63, 602–604. doi:10.1598/RT.63.7.8
Johnston, J. M., Foxx, R. M., Jacobson, J. W., Green, G., & Mulick, J. A. (2006). Positive behavior support and applied behavior analysis. The Behavior Analyst, 29, 51–74.
Lane, K. L., Oakes, W., & Menzies, H. (2010). Systematic screenings to prevent the development of learning and behavior problems: Considerations for practitioners, researchers, and policy makers. Journal of Disability Policy Studies, 21(3), 160–172. doi:10.1177/1044207310379123
Luck, L., & Webb, L. (2009). School counselor action research: A case example. Professional School Counseling, 12, 408–412.
Martens, K., & Andreen, K. (2013). School counselors’ involvement with a school-wide positive behavior support intervention: Addressing student behavior issues in a proactive and positive manner. Professional School Counseling, 16, 313–322.
Martin, P. J. (2015). Transformational thinking in today’s schools. In B. T. Erford (Ed.), Transforming the school counseling profession (4th ed., pp. 45–65). Boston, MA: Pearson.
May, S., Ard, W., Todd, A. W., Horner, R. H., Glasgow, A., Sugai, G., & Sprague, J. R. (2006). School wide information system. Eugene: Educational and Community Supports, University of Oregon.
McIntosh, K., Filter, K. J., Bennet, J. L., Ryan, C., & Sugai, G. (2010). Principles of sustainable prevention: Designing scale-up of schoolwide positive behavior support to promote durable systems. Psychology in the Schools, 47, 5–21. doi:10.1002/pits.20448
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001, P.L. No. 107–110. 115, Stat. 1425 (2002).
Ockerman, M. S., Mason, E. C. M., & Hollenbeck, A. F. (2012). Integrating RTI with school counseling programs: Being a proactive professional school counselor. Journal of School Counseling, 10(15), 1–37.
Ryan, T., Kaffenberger, C. J., & Carroll, A. G. (2011). Response to intervention: An opportunity for school counselor leadership. Professional School Counseling, 14, 211–221. doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2011-14.211
Shepard, J. M., Shahidullah, J. D., & Carlson, J. S. (2013). Counseling students in levels 2 and 3: A PBIS/RTI Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Sherrod, M. D., Getch, Y. Q., & Ziomek-Daigle, J. (2009). The impact of positive behavior support to decrease discipline referrals with elementary students. Professional School Counseling, 12, 421–427.
doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2010-12.421
Shinn, M. R. (2010). Building a scientifically based data system for progress monitoring and universal screening across three tiers including RTI using Curriculum-Based Measurement. In M. R. Shinn & H. M. Walker (Eds.), Interventions for achievement and behavior problems in a three-tier model, including RTI (pp. 259–292).Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Simonsen, B., Eber, L., Black, A. C., Sugai, G., Lewandowski, H., Sims, B., & Myers, D. (2012). Illinois statewide positive behavioral interventions and supports: Evolution and impact on student outcomes across years. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 14, 5–16. doi:10.1177.1098300711412601
Simonsen, B., & Sugai, G. (2013). PBIS in alternative educational settings: Positive support for youth with high-risk behavior. Education and Treatment of Children, 36, 3–14.
Sink, C. A., Akos, P., Turnbull, R. J., & Mvududu, N. (2008). An investigation of comprehensive school counseling programs and academic achievement in Washington state middle schools. Professional School Counseling, 12, 43–53. doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2010-12.43
Sink, C. A., & Stroh, H. R. (2003). Raising achievement test scores of early elementary school students through comprehensive school counseling programs. Professional School Counseling, 6, 350–364.
Stiller, B. C., Nese, R. N. T., Tomlanovich, A. K., Horner, R. H., & Ross, S. W. (2013). Bullying and harassment prevention in positive behavior support: Expect respect. Eugene: Educational and Community Supports, University of Oregon.
Stormont, M., Reinke, W. M., & Herman, K. C. (2010). Introduction to the special issue: Using prevention science to address mental health issues in schools. Psychology in the Schools, 47, 1–4.
Sugai, G. (2016). Positive behavioral interventions and supports [Powerpoint slides]. Retrieved from http://www.pbis.org/
Common/Cms/files/pbisresources/3%20Feb%202016%20SAfrica%20PBIS%20HAND%20gsugai.pdf
Sugai, G., & Horner, R. H. (2009). Responsiveness-to-intervention and school-wide positive behavior supports: Integration of multi-tiered system approaches. Exceptionality, 17, 223–237. doi:10.1080/09362830903235375
Sugai, G., & Simonsen, B. (2012). Positive behavioral interventions and supports: History, defining features, and misconceptions. Retrieved from http://www.pbis.org/common/cms/files/pbisresources/PBIS_revisited_
June19r_2012.pdf
Todd, A. W., Lewis-Palmer, T., Horner, R. H., Sugai, G., Sampson, N. K., & Phillips, D. (2012). School wide evaluation (SET) implementation manual. Retrieved from http://www.pbis.org/common/cms/files/pbisresources/SET_Manual_02282012.pdf
Utley, C. A., & Obiakor, F. E. (2015). Special issue: Research perspectives on multi-tiered system of support. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 12, 1–2.
Waasdorp, T. E., Bradshaw, C. P., & Leaf, P. J. (2012). The impact of schoolwide positive behavioral interven-tions and supports on bullying and peer rejection. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 166, 149–156. doi:10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.755
Wilkerson, K., Pérusse, R., & Hughes, A. (2013). Comprehensive school counseling programs and student achievement outcomes: A comparative analysis of RAMP Versus Non-RAMP Schools. Professional School Counseling, 16, 172–184. doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2013-16.172.
Ziomek-Daigle, J. (Ed.). (2015). School counseling classroom guidance: Prevention, accountability, and outcomes. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Ziomek-Daigle, J., & Cavin, J. (2015). Shaping youth and families through positive behavior support: A call for counselors. The Family Journal, 23, 386–373. doi:10.1177/1066480715601106
Ziomek-Daigle, J., & Heckman, B. (under review). Unpacking the behavioral Response to Intervention model for school counseling: Evidence-based practices across the tiers.
Jolie Ziomek-Daigle is an Associate Professor at the University of Georgia. Emily Goodman-Scott, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at Old Dominion University. Jason Cavin is the Director of Behavior Support and Consultation at the School of Public Health at Georgia State University and a doctoral candidate at the University of Georgia. Peg Donohue is an Assistant Professor at Central Connecticut State University. Correspondence can be addressed to Jolie Ziomek-Daigle, 402 Aderhold Hall, Athens, GA 30602, jdaigle@uga.edu.
