Jul 20, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 2
Dee C. Ray, David D. Huffman, David D. Christian, Brittany J. Wilson
The vast majority of graduate students in the social sciences, especially in mental health fields, are females (Crothers et al., 2010; Healey & Hays, 2012). In a recent report on counseling programs, an average of 76% of students admitted and graduated yearly from entry-level counseling programs were women (Schweiger, Henderson, McCaskill, Clawson, & Collins, 2012). Although counseling is one field that attracts mostly female graduate level students, a historical review indicates that males made up approximately 80% of counselor education faculties in the 1980s (Anderson & Rawlins, 1985). In recent years, as the number of females who seek doctoral degrees in counseling has increased, so has the number of female counselor educators, correlating to fewer males entering the field of counselor education. Currently, the average number of males admitted and graduated yearly from doctoral-level counseling programs has been reported at a meager 25% (Schweiger et al., 2012). As counselor educators strive to build best practices for working with diverse populations, it seems relevant to explore the experiences of male counselor educators as well as suggest practices that improve conditions for male counselor education faculty.
In the preparation of counselors, counselor educators are encouraged to build relationships with students that lead to greater self-awareness, personal development and interpersonal learning, which inform their work as counselors. Literature cites the importance of the relationships between counseling faculty and students as “paramount” (Dollarhide & Granello, 2012, p. 290), suggesting that it “stands out above all other factors” (McAuliffe, 2011, p. 32) in the education of adults. It seems reasonable to assume that if counselor educators espouse the importance of the relationship between client and counselor, they extend this value to their students, building relationships that facilitate learning. Thus, a belief that the relationship between teacher and student leads to mutual support and growth comprises the hallmark of humanistic education (Dollarhide & Granello, 2012).
Although the American Counseling Association (ACA) Code of Ethics (2014) asserted that counselor educators are restricted from sexual or romantic relationships with students, universities and counselor education programs typically do not clearly articulate boundaries when approaching the multiple roles adopted by faculty members (Owen & Zwahr-Castro, 2007). In the absence of guidelines and open discussion regarding faculty–student relationships, legal concerns can permeate the university environment. Sexual harassment suits have increased, and many universities have responded by going beyond sexual harassment policies and adding additional policies that restrict sexual or romantic consensual relationships between faculty and students (Bartlett, 2002; Kiley, 2011). Male faculty members seem especially affected by the legal environment and Nicks (1996) reported males had significantly higher concerns than females regarding unjust accusations of harassing a student. In the current environment of legality and ambiguous ethical guidelines, Kress and Dixon (2007) cautioned that counselor educators might choose to distance themselves from students to avoid the appearance of impropriety or placing themselves in complex ethical situations. However, there is a dearth of literature regarding issues of relationship dynamics based on sexuality and gender in academia over the last 20 years.
Further complicating the issue of faculty–student relationships is that female professors and students are more likely to perceive complex relationship issues as unethical when compared to their male counterparts. In a comparison between female and male counselor educators and counselor education students, Bowman, Hatley, and Bowman (1995) found that females were significantly more likely to rate activities outside the traditional student–teacher relationship as unethical. This finding has been supported in multiple studies regarding undergraduate students (Ei & Bowen, 2002; Oldenburg, 2005; Owen & Zwahr-Castro, 2007). Female undergraduate students were more likely to rate a relationship scenario as unethical when the professor was identified as a male as compared to scenarios with female professors (Oldenburg, 2005) and more likely to be negative than males about questionable scenarios such as sexual relationships, doing favors for a professor, and doing things alone with an instructor (Ei & Bowen, 2002). Owen and Zwahr-Castro (2007) found that female undergraduate students judged approximately one-third of faculty–student interaction scenarios as significantly more inappropriate than male students, identifying nonacademic-related interaction that occurred off campus as most inappropriate. Although not specifically explored, the tendency of females to find behaviors unethical when compared to the perceptions of males has been attributed in the literature to sensitivity of women to power differentials and potential for exploitation based on cultural experience (Ei & Bowen, 2002; Owen & Zwahr-Castro, 2007). In the context of current ratios in counselor education of a majority number of female faculty to a minority number of male graduate students, it is difficult to ascertain the perception of power dynamics based on gender.
The changing context of counselor education may present unique challenges for male faculty to navigate with little guidance. A review of the literature highlights a complex environment where male counselor educators engage in faculty–student relationships within a context of power differences and potential legal complications. The current study was conceived in a doctoral level clinical course in which male and female doctoral students processed their teaching experiences with master’s students. During the discussion, male doctoral students serving as instructors shared experiences regarding relationships with their students that appeared uniquely different from experiences shared by female colleagues. Concerns emerged regarding practices of male counselor educators when entering a female-prevalent field as a person in a position of power. As a result, we proposed that the following factors might influence the interactions of male counselor educators on a daily basis in their roles with students: majority of female graduate students, decreasing number of male faculty, increases in legal action, ambiguity of ethical guidelines, possible attraction between professors and students, and a contextual field that values human relationships. The purpose of this study was to discover attitudes and practices of male counselor educators regarding faculty-student relationships. Our research questions included: (a) what are the practices and attitudes of male counselor educators related to relationships with students and colleagues? and (b) what specific practices do male counselor educators employ to maintain boundaries with students?
Methodology
Participants and Data Collection
Using Schweiger et al.’s (2012) compilation of counseling program information, a member of the research team identified names typically attributed to males among listed faculty names, resulting in the identification of 330 males within the United States. The research team then matched the names with e-mails on university Web sites. An initial recruitment e-mail was sent to the identified sample asking for participation. Following the initial recruitment e-mail, 41 of the identified original sample responded as ineligible (22 contact e-mails were immediately returned as unavailable; 6 identified as female; and 13 identified as no longer working as a counselor educator or having never worked as a counselor educator). This resulted in a potential sample of 289. Two more e-mails were sent as reminders regarding participation. The final sample consisted of 163 male counselor educators who completed the survey, resulting in a response rate of 56%.
A summary of demographic characteristics of the 163 male counselor educators who completed the survey is presented in Table 1. In this sample, male counselor educators were mostly White, non-Hispanic (n=125). African American (n=14) and Hispanic (n=11) males also were represented, but only in small numbers, and Asian males (n=4) were few. Most of the sample identified as married/partnered (87%) and heterosexual (89%), with gay or bisexual males represented by approximately 10% of participants. The sample was more diverse in areas of age, rank, child status, and years as counselor educators.
Survey Development
We developed our survey in two phases. The research team brainstormed issues that emerged during discussion, such as the possible attitudes of male counselor educators, including feeling isolated or unsupported due to fewer numbers of male colleagues, or practices that might emerge in working with students of the opposite gender with the intent of ensuring a sense of safety. Based on discussion and an extensive literature review, the research team created a list of quantitative items surveying demographics, attitudes and practices of male counselor educators. We distributed the survey to a pilot group of six male counselor educators who represented diversity in age, experience, ethnicity and sexual orientation. The pilot participants reviewed each question and commented on its usefulness, acceptability and clarity. Based on pilot feedback, the research team modified the survey to include 22 demographic questions, 32 attitude and practice questions, and four open-ended questions. The survey was formatted for the Survey Research Suite (Qualtrics) and final quantitative data was transferred into SPSS for analysis.
Demographic questions included items regarding personal, family and program characteristics of the faculty members, and questions regarding the faculty members’ professional designations and teaching assignments. Attitude items (Cronbach’s α = .66) consisted of questions related to the impact of being male on both collegial and student relationships. Practice items (Cronbach’s α = .64) consisted of questions related to the participant’s actual practices in relating to students (e.g., private meetings, lunch/dinner, after class). For the full scale, Cronbach’s α was calculated at .70. Four open-ended questions addressed ethical challenges, thoughts related to being male, ways the counselor educator might act differently, and strategies used to avoid complications with students.
Table 1
Demographic Characteristics of Male Counselor Educator Participants
|
Variable
|
N
|
%
|
M
|
SD
|
Mdn
|
Range
|
| Age |
155
|
|
51.61
|
11.08
|
53
|
27–76
|
| Ethnicity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| African American |
14
|
8.6
|
|
|
|
|
| Asian |
4
|
2.5
|
|
|
|
|
| White, Non-Hispanic |
125
|
76.7
|
|
|
|
|
| White, Hispanic |
11
|
6.7
|
|
|
|
|
| Self-Identified as Other |
8
|
4.9
|
|
|
|
|
| Relationship Status |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Single |
14
|
8.6
|
|
|
|
|
| Married/Partnered |
142
|
87.1
|
|
|
|
|
| Divorced/Separated |
5
|
3.1
|
|
|
|
|
| Widowed |
1
|
.6
|
|
|
|
|
| Sexual Identity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gay |
13
|
8.0
|
|
|
|
|
| Heterosexual |
145
|
89.0
|
|
|
|
|
| Bisexual |
3
|
1.8
|
|
|
|
|
| Status Regarding Children |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No Children |
30
|
18.4
|
|
|
|
|
| Adult Children |
74
|
45.4
|
|
|
|
|
| Minor Children in Home |
55
|
33.7
|
|
|
|
|
| Minor Children Part Home |
1
|
.6
|
|
|
|
|
| Minor Children Not in Home |
2
|
1.2
|
|
|
|
|
| Years As Counselor Educator |
161
|
|
15.07
|
10.85
|
12
|
1–45
|
| Faculty Rank |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Assistant |
38
|
23.3
|
|
|
|
|
| Associate |
50
|
30.7
|
|
|
|
|
| Full |
58
|
35.6
|
|
|
|
|
| Lecturer/Interim |
4
|
2.5
|
|
|
|
|
| Other |
13
|
8.0
|
|
|
|
|
| Total Number of Male Faculty |
156
|
|
4.04
|
1.81
|
4
|
1–10
|
| Total Number of Female Faculty |
155
|
|
4.27
|
2.27
|
4
|
0–13
|
| Estimated % of Male Students |
163
|
|
18.21
|
11.24
|
16
|
0–78
|
| Estimated % of Female Students |
162
|
|
77.66
|
18.55
|
80
|
0–99
|
The first three open-ended questions were used for qualitative analysis and the final question was used to create a list of strategies employed by male counselor educators to aid in their student relationships.
Analysis and Results
The research team used a parallel mixed-methods design (Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2009) to explore the experiences of male counselor educators. We utilized qualitative thematic analysis for data generated from three open-ended questions and optional comments following each quantitative survey question and quantitative statistical analysis for multiple-choice survey questions. By conducting independent quantitative and qualitative analyses in a parallel simultaneous nature, we allowed the separate analyses to inform one another and provide a more integrated understanding of the data (Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2009). Due to overlap in analysis and results consequential from a mixed-methods approach, we chose to present analyses and results categorized by method (qualitative and quantitative) in the following section.
Qualitative Analyses
Responses to the three open-ended questions and optional comments were analyzed from a perspective of transcendental phenomenology to explore the lived experiences of participants (Creswell, 2007; Moustakas, 1994). Within this qualitative tradition, we worked to bracket or set aside our own preconceptions about the phenomenon as much as possible to remain focused on the views of participants (Moerer-Urdahl & Creswell, 2004; Moustakas, 1994). The research team, consisting of two male doctoral students and one female tenured faculty member, discussed our student–teacher relationship experiences regarding gender and power differences. Through reflection and discussion, we developed greater awareness of how our experiences have influenced our views of being and working with male counselor educators. Team discussion allowed us to understand and bracket our positions in the development of data collection and analysis methods.
Because the experiences of male counselor educators have received little attention in literature and research, a phenomenological approach allowed for understanding to emerge from participants’ written reports as data was broken down into smaller units of meaning and reconstructed into broader themes that were clearly defined (Creswell, 2007; Giorgi, 1985). Following data collection, we independently coded responses to three open-ended questions, a smaller portion of the data, to identify initial concepts. Next, we met to review and compare our concepts. Silverman and Marvasti (2008) identified the appropriate use of smaller portions of data to establish preliminary categories. We discussed each unit of meaning in the text that was relevant to the focus of study (Giorgi, 1985), compared each concept to previous statements and discovered an initial list of broader themes suggesting common experiences among participants (Creswell, 2007). The research team clarified category definitions by comparing data units within each category for similarities and differences. Responses to optional comments sections in the survey were reviewed for inclusion in the text. Comments that offered information beyond the scope of the survey question referenced were included in the text for qualitative analysis. Then individual team members independently examined the entire text and coded each unit of meaning under the appropriately perceived category. Finally, we met as a group to develop consensus on final categories and to assign textural excerpts to appropriate themes. As suggested by Potrata (2010), research team members focused on exploring potential differences in coding rather than focusing on consistency when coming to consensus in order to illuminate complexities of the male counselor educator experience. Frequencies were tabulated to represent the magnitude of each category within the sample, and verbatim illustrative quotes were selected to clarify the meaning of each category. Saldaña (2013) suggested that magnitude coding adds supplemental texture to provide richer results in qualitative analysis.
Qualitative Results
In order to address our first research question regarding practices and attitudes of male counselor educators, participants were asked to respond to three open-ended questions to address their experiences and practices as male counselor educators. Seventy-one responses were recorded for the first question, “What ethical challenges, if any, are related to being male in counselor education?” One hundred responses were recorded for the second question, “What are your thoughts related to being male in counselor education?” Ninety-six responses were recorded for the third question, “What are the ways you act differently in student relationships because you are male?” We also coded additional comments of significance that followed each survey item. In all, qualitative analysis included the coding of 359 answers of varying lengths. During qualitative analysis, the research team discovered that participants’ answers appeared to be addressing similar themes across all questions. Hence, all answers were collapsed into one analysis.
The research team identified 10 distinct themes expressed by participants regarding the experiences of being a male counselor educator. We identified “modify behavior” as the most predominant theme, magnified by frequency (32%). This theme included intentional changes in action or interpersonal expression related to being male in professional relationships. Another major theme, “no difference” (frequency 23%) included beliefs and experiences that no unique relationship challenges exist in counselor education related to being male. Expressions of feeling “isolated or lonely” (frequency 11%) described participant experiences of feeling a lack of support as well as awareness of being a minority in the profession. Responses regarding “sexual attraction” (frequency 11%) involved experiences of sexual attraction in professional relationships. A theme of “perception of impropriety” (frequency 10%) included attention to the perception of others regarding appropriate behavior. Expressions of “prejudice or discrimination” (frequency 9.5%) involved experiences of negative beliefs or actions of others related to one’s gender. Additionally, qualitative data revealed themes related to participants’ “awareness” of professional relationships, “awareness of power difference” in relationships, the importance of a “caring or safe environment,” and “ethnicity or orientation” as part of one’s identity as a male counselor educator. A comprehensive presentation of all themes is included in Table 2.
Our second research question regarding specific practices of male counselor educators was addressed through our fourth open-ended survey question, which indicated participants cited over 40 different strategies they used to structure their relationships with students. In general faculty–student interactions, respondents indicated that they did not meet alone with students; only met with students on campus; interacted in groups when others were present; avoided jokes, conversations or language that could be perceived as too friendly; referred to family/significant others in class and conversation; avoided sharing too much personal information; made no physical contact; and avoided being overtly interested in students’ relationship issues. When meeting with students, respondents reported that they kept their doors open, structured meetings with an agenda, met in classrooms, ensured others were around, and avoided engaging in counseling with students. Participants also indicated that they consulted with colleagues regarding student relationships, had colleagues present for potentially problematic student interactions, addressed student relationship issues as soon as they arose, notified department chairs of any concerns and documented interactions. On a personal level, participants reported that they focused on having a balanced personal life, increased self-awareness of interactions, reminded self of boundaries, and engaged in honest and transparent interactions.
Quantitative Analyses
We used results from qualitative analysis to inform decision making regarding variables of interest for quantitative analysis. Due to the extensive data resultant from the 32-question survey of practices and attitudes and need for manuscript brevity, we narrowed survey data results to the survey items that matched qualitative theme results. We chose to explore one survey item per qualitative theme that appeared to closely match the qualitative analysis. Following final coding discussion, the research team identified five attitude and practice questions from the survey that appeared to be related to content evolving from the qualitative analysis. The qualitative theme of modifying behavior appeared most closely linked to the survey item, “I interact differently with female students than male students.” The theme represented by some respondents, that there were no differences related to being male, most closely aligned with the item, “I have unique ethical challenges related to being male in counselor education.” The item linked to the qualitative theme of avoiding the appearance of impropriety, “I structure my individual interaction with students to avoid the appearance of impropriety,” was further explored. The qualitative themes of isolation and discrimination were matched to two items: “I feel isolated in my faculty because I am male,” and “I feel discriminated against by faculty members because I am male.” Although most respondents did not agree with these final two statements, we chose to explore them further due to the distinct voices of some respondents related to ethnicity and sexual orientation within the data.
Table 2
Themes Related to Male Counselor Educators’ Experiences
| Theme |
Definition
|
Freq.
|
Responses
|
Sample Statements
|
| Modify Behavior |
Intentional changes in action or interpersonal expression related to being male |
32%
|
115
|
“. . . crucial to make sure distinct boundaries are established”“. . . have to focus on being appropriately relational”“must balance being supportive with providing clear boundaries” |
| NoDifference |
No unique challenges in counselor education related to being male |
23%
|
82
|
“No specific challenges related to my gender”“Ethics are ethics, male or female”“How I act has little to do with being male” |
| Awareness |
Indicating awareness or self-awareness regarding professional relationships |
13%
|
47
|
“. . . we need to be very aware of situations and interactions with female students”“Know one’s self”“I am now more aware of how I interact” |
| IsolatedorLonely |
Experiencing lack of support and awareness of being a minority in profession |
11%
|
39
|
“I feel a bit like an endangered species”“There are simply some things I can only talk with other men about”“I recognize males are a minority in the field” |
| Sexual Attraction |
Experiences of sexual attraction in professional relationships |
11%
|
38
|
“Dealing with feelings of attraction with students and colleagues”“I am attracted to female students but do not act on it”“I have to refocus my thoughts if I feel an attraction to a student or colleague” |
| Perception of Impropriety |
Attention to the perception of others regarding appropriate behavior |
10%
|
37
|
“. . . don’t want to give the impression of being unethical”“Avoiding any appearance of misconduct”“. . . vigilant in protecting myself from false accusations” |
| Awareness of Power Difference |
Awareness of the impact of privilege and power in relationships |
10%
|
35
|
“Being aware of my male privilege and not abusing it”“I can be male without being dominating”“I do see the same gender politics and gender roles in my profession as I see in society…” |
| PrejudiceorDiscrimination |
Experiences of negative or devaluing beliefs or actions of others related to being male |
9.5%
|
34
|
“tendency to view males as the victimizer”“. . . uniquely male issues that could arise in counseling situations are downplayed”“I sometimes experience sexism against men in the comments of my female colleagues” |
| Caringor Safe Environment |
Intention to provide support and safety to students |
6%
|
21
|
“We want to provide a caring environment”“I want students to feel comfortable around me.”“. . . do not want any female to feel anxious” |
| Ethnicityor Orientation as Part of Identity |
Influences of ethnicity and sexual identity upon male professional experiences |
4%
|
15
|
“Being a male and an ethnic minority is challenging and often lonely”“. . . being Black and male is more of a challenge than being male alone”“I feel isolated not because I am male but because I am a gay male” |
Note: Frequency = Number of participants who shared theme-related statements
Quantitative Results
Descriptive results for the five survey items are presented in Table 3. In order to explore relationships between survey items of interest, we employed Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient analyses on the five variables. There were statistically significant positive correlations between perception of unique ethical challenges and the four other variables: feeling isolated
(r = .290, n = 149, p < .001); interacting differently with female students (r = .317, n = 147, p < .001); structuring interactions to avoid appearance of impropriety (r = .190, n = 148, p = .021); and feeling discriminated against (r = .217, n = 150, p = .008). The more a male counselor educator felt there were unique ethical challenges related to being male, the more likely he was to feel isolated and discriminated against, structure interactions with students to avoid the appearance of impropriety, and interact differently with females than males. Additionally, there was a statistically significant positive correlation between feeling isolated and feeling discriminated against (r = .371, n = 149, p < .001). The more isolated a male counselor educator felt, the more likely he was to feel discriminated.
Table 3
Survey Items Related to Relationships for Male Counselor Educators
|
|
|
|
Percent of Responses
|
|
Survey Item
|
N
|
|
Σ
|
SD
1
|
D
2
|
N
3
|
A
4
|
SA
5
|
| I feel isolated in my faculty because I am male. |
149
|
1.89
|
.94
|
36.8
|
36.8
|
11.7
|
5.5
|
1.2
|
| I interact differently with female students than male students. |
147
|
2.90
|
1.02
|
6.7
|
29.4
|
21.5
|
30.7
|
1.8
|
| I structure my individual interactions with students to avoid the appearance of impropriety. |
148
|
3.76
|
.92
|
1.8
|
9.2
|
13.5
|
50.9
|
15.3
|
| I have unique ethical challenges related to being male in counselor education. |
150
|
2.79
|
1.03
|
9.2
|
30.7
|
23.9
|
26.4
|
1.8
|
| I feel discriminated against by faculty members because I am male. |
150
|
2.05
|
1.06
|
31.9
|
39.9
|
6.1
|
12.3
|
1.8
|
Note: SD=Strongly Disagree, D=Disagree, N=Neutral, A=Agree, SA=Strongly Agree
We further explored ethnicity and sexual orientation in relationship to the dependent variables of isolation and discrimination based on qualitative findings that indicated these characteristics impact the views of male counselor educators. We conducted four separate one-way between-groups analyses of variance to explore the impact of ethnicity and gender on isolation and discrimination. There was a statistically significant difference in ethnicity for isolation, F(4, 144) = 5.78, p < .001, η2 = .14. Means for ethnicity included Asian x̅ = 2.0; African American x̅ = 1.71; White/Non-Hispanic x̅ = 1.84; White/Hispanic x̅ = 1.64; Self-Identified as Other x̅ = 3.43. There was a statistically significant difference in ethnicity for discrimination, F(4, 144) = 5.25, p = .001, η2 = .13. Means for ethnicity included Asian x̅ = 2.0; African American x̅ = 2.23; White/Non-Hispanic x̅ = 1.94; White/Hispanic x̅ = 1.91; Self-Identified as Other x̅ = 3.71. There was a statistically significant difference in sexual orientation for isolation, F(2, 145) = 3.81, p = .024, η2 = .05. Means for sexual orientation included Gay x̅ = 2.58; Heterosexual x̅ = 1.83; Bisexual x̅ = 1.67. There was no statistically significant difference in sexual orientation for discrimination, F(2, 145) = .70, p = .50, η2 = .01.
Discussion
The sample in this study reasonably represents the current population of male counselor educators in CACREP-accredited programs. Although the sample reported equivalent numbers between male and female faculty, they also reported a disproportionate number of female students (78%) to male students (18%), as indicated in previous literature (Schweiger et al., 2012). The sizeable response rate to this survey, as well as its representativeness, lends credibility to findings.
Themes and Characteristics Related to Being a Male in Counselor Education
Qualitative analyses indicated that participants expressed diversity of attitudes and practices regarding the impact of being male upon professional relationships. The most predominant theme, “modify behavior,” indicated that being male influenced choices made by male counselor educators in their interactions with students. Conversely, the second dominant theme, “no difference,” indicated that some counselor educators do not feel that there is any difference in interactions with students or colleagues related to being male. A lack of consensus existed among male counselor educators regarding the influence of being male upon their professional relationships.
When male counselor educators acknowledged there were differences related to being a male in the field, qualitative analysis revealed additional themes related to isolation, discrimination, fear of appearing inappropriate, interacting differently with females than males and need for awareness. We wanted to explore characteristics related to these feelings, which prompted the correlational analyses.
Quantitative and qualitative analyses indicated that the appearance of impropriety was of considerable concern for male counselor educators. A majority of participants agreed or strongly agreed that they structured their interactions to avoid appearance of impropriety. Results revealed a statistically significant positive relationship between expressing a perception of unique ethical challenges for males and structuring interactions to avoid appearance of impropriety. Participants who perceived unique challenges as males also tended to take steps to avoid appearing inappropriate in their professional relationships. This finding supports qualitative themes of male counselor educators’ concerns regarding the appearance of impropriety and fear of the cultural myth of the lecherous professor (Bellas & Gossett, 2001).
Sexual attraction emerged as a relevant issue through qualitative analyses. A vast majority of respondents reported that they had experienced being attracted to a student, with frequency of feelings ranging from rare to a regular occurrence. Also, a majority of the sample reported experiencing a student being attracted to them. These results suggest that sexual attraction was experienced as a common phenomenon in male teacher–student relationships. However, participants often described their feelings of attraction as natural reactions that posed no threat if not acted upon.
When addressing the influence of student gender upon their behavior with students, male counselor educators reported diverse perspectives. Participants were asked if they interacted differently with female students than male students. Responses were about evenly distributed from “disagree” to “agree.” The variance in responses may reflect the larger disagreement among participants regarding the influence of gender upon professional relationships. The qualitative themes of “modify behavior” and “no difference” may provide context for understanding diverse results regarding this question. Correlational analysis revealed that the more a participant perceived unique challenges as a male counselor educator, the more he reported interacting differently with female students compared to male students.
Some participants also reported experiencing isolation related to being a male counselor educator. Qualitative data revealed unique experiences of isolation related to ethnicity and sexual orientation. Although there were a small number of participants who identified as gay, bisexual, African American, Latino, Asian, or other ethnicity, we chose to conduct quantitative analysis to further explore their voices, which were clearly articulated as unique in qualitative analyses. Further quantitative analysis indicated that participants who self-identified as “other” for ethnicity were more likely to feel isolated in comparison with other ethnicities. Likewise, gay male counselor educators also were more likely to feel isolated in the profession. However, gay males did not report higher levels of feeling discriminated against as compared to heterosexual males. Previous research indicates gay males may experience isolation related to not being out to co-workers, often motivated by fear of discrimination (Wright, Colgan, Creegany, & McKearney, 2006). Another possible interpretation could be that gay male counselor educators feel isolated due to interacting with fewer colleagues who are similar to them, but who they experience as accepting or non-discriminatory.
Linked to isolation, we also asked male counselor educators if they had faculty colleagues with whom they could discuss challenges. This point seemed especially salient due to qualitative results indicating male counselor educators rely on consultation as one intervention for dealing with student relationship issues. A majority of respondents agreed or strongly agreed to having a colleague on their faculty with whom they could discuss male-related issues. Qualitative and quantitative analyses identified ethnicity as an important contributor to the experiences of male counselor educators. Qualitative data included a small but consistent voice of African American male counselor educators who expressed increased isolation due to a combination of ethnicity and gender. Quantitative analysis also indicated that participants who identified as African American reported more frequent experiences of discrimination in their professional environment. These findings coincide with research indicating that African American males experience prejudice and discrimination in higher education due to stereotype images of African American males as underachieving, disengaged and threatening (Harper, 2009). Brooks and Steen (2010) discussed concerns related to the lack of African American male counselor educators and the obstacles they face in the academic setting. Participants who self-identified as “other” on ethnicity also showed increased experiences of discrimination as well as isolation. Correlational analysis confirmed the co-occurrence of these two themes, revealing a positive relationship between feeling isolated and feeling discriminated against. Asian males were more likely to feel isolated and structure their interactions to avoid appearances of impropriety, which reflects previous accounts of Asian professors in the literature (Culotta, 1993) in which they experienced isolation from their colleagues and increased student mentoring demands because of their minority status.
In returning to the issue of concern related to practices of male counselor educators in building humanistic and growth-inspiring relationships with students, the results of the current study provide some insight. Many male counselor educators appear to be aware and concerned that being male may influence how they are perceived by students and how they approach their relationships with students. However, results indicate that participants sought methods and strategies that allowed them to pursue relationships while also being sensitive to students’ perceptions of safety. Figure 1 provides specific strategies highlighted by participants that allow male counselor educators to engage in student–teacher relationships that recognize the power differential between student and teacher, inherent challenges with sexual attraction, and yet still allow the student and teacher to benefit from an accepting, inspiring relationship that mirrors the therapeutic relationship.
Limitations
The survey method used for this study was selected for exploratory purposes and did not involve the use of a rigorous assessment designed to interpret results through reliability and validity procedures; hence, results must be interpreted with caution. Additionally, the survey sample may not represent the views of the entire population of male counselor educators.
Figure 1.
Strategies Used by Male Counselor Educators to Build Student Relationships.
Note: General Interactions = strategies used in everyday interactions; Student Meetings = strategies used when having to meet with students individually; Interventions = strategies used when complications arise.
Due to the extensiveness of collected data, we were unable to report all findings related to the uniqueness of the sample. Respondents reported rich qualitative narratives and variations in their attitudes and practices. The variations are not fully represented in this report. The use of a one-time open-ended questionnaire precluded use of qualitative interviews that would reveal further depth of themes. Additionally, minority groups, such as specific ethnicities and those who identified as gay and bisexual, appeared to have a distinct voice in this survey. However, due to low representation, data analysis was limited in representing their experiences. We attempted to rectify this limitation by voicing those narratives in the qualitative analysis.
Implications
The purpose of this research was to reveal attitudes and practices of male counselor educators, allowing the reader an understanding of how the experience of being male influences the daily choices of male counselor educators. Implications of this research study include better understanding of the experiences of counselor educators that lead to enhanced job satisfaction for males, best practices to improve faculty–student relationships and possible areas for further investigation. Additionally, in Figure 1, we provide a list of behaviors used by male counselor educators to ensure appropriate student–teacher boundaries. This list offers male counselor educators possible strategies to address perceptions of impropriety or misconduct.
If male counselor educators experience greater job satisfaction, then more males may choose the counseling field, as they observe possible role models with whom they identify. Substantial variables identified by this study that might influence job satisfaction are feelings of isolation, discrimination, fear of appearing inappropriate and hypervigilance to behavioral interactions with students. Qualitative data revealed a desire by male counselor educators to offer a safe, caring environment, qualified by some respondents as an authentic relationship. Findings indicate that if male counselor educators feel limited by personal loneliness or concern for appearances, this will most likely interfere with their student and faculty relationships. Consultation with and support of colleagues appeared to be a process regularly utilized by many of the male counselor educators in this study. Counselor education departments would benefit from engaging in practices that promote collegiality and support among faculty members as well as formalizing mentoring processes.
Male counselor educators revealed that they take measures to modify their behaviors with students, especially female students. Our results indicate that fear of impropriety, awareness of cultural power differentials, desire to create safe relationships with students and realistic awareness of potential sexual attraction prompt male counselor educators to engage in behaviors that will provide safety for students and for themselves. These strategies reveal concrete behavioral actions taken to ensure the maintenance of boundaries with students. Kolbert, Morgan, and Brendel (2002) concluded that faculty must consider student perceptions of a relationship as the primary criterion in making decisions regarding their interactions with students. This conclusion requires considerable awareness from male counselor educators related to how they present themselves and how students perceive them. One common strategy used by male counselor educators and commonly supported in the literature (Ei & Bowen, 2002) is engaging in group activities, as opposed to one-on-one activities, in order to establish authentic relationships in a safe environment.
The most cited strategy among this sample was not being alone or out of sight from others when engaging in personal interactions with students. In a field where confidentiality is the base of intervention, this particular strategy seems incongruous, especially for professionals who value relationship in teacher–student interactions. Additionally, students may question a faculty member’s authenticity if intimacy is avoided in the relationship. However, contextual, legal and cultural considerations appear to encourage these types of restraints. Counselor education departments may benefit from discussion of these issues of behavior, relationship, philosophy and safety in an open forum among faculty and with students.
The relational experiences of male counselor educators have gone virtually unexamined in literature and research, leaving many opportunities for further inquiry. Some participants indicated that ethnicity influenced their experiences and relationships, yet sample size prevented meaningful exploration. Further research may investigate the unique experiences of African American, Latino and Asian male counselor educators. Likewise, sexual orientation emerged as a major influence for some participants. An exploration of experiences of gay male counselor educators is needed to enhance understanding of their relational experiences and the influence of gender.
Participants expressed concerns about perceptions of impropriety with students, feelings of isolation within the profession, and experiences of prejudice and discrimination in their work environments. These elements require further exploration to better understand the nature of these experiences and investigate causal factors to heighten sensitivity and identify appropriate measures for creating a safe environment for faculty and students. Participants also indicated that they alter behavior in student relationships to avoid the appearance of impropriety and maintain professional boundaries. Further research could explore the implications of those decisions for the quality of relationships with students. A study of student perspectives would greatly enhance understanding of these relational dynamics. Additionally, a study of ways in which female counselor educators approach their relationships with students, in regard to feeling restricted or limited in intimacy, is warranted.
This study provides an enhanced understanding of male counselor educators’ perceptions and experiences of their relationships with students and colleagues. Male counselor educators shared a unique voice of experience. Further research may expand understanding of male counselor educator experiences, provide insights to improve the quality of faculty–student relationships and assist in developing male role models for the future of our profession.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
American Counseling Association. (2014). 2014 American Counseling Association Code of Ethics. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/docs/ethics/2014-aca-code-of-ethics.pdf?sfvrsn=4
Anderson, J. A., & Rawlins, M. (1985). Availability and representation of women in counselor education with strategies for recruitment, selection, and advancement. Counselor Education and Supervision, 25, 56–65. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.1985.tb00512.x
Bartlett, T. (2002, April 5). The question of sex between professors and students. The Chronicle of Higher Education. Retrieved from http://chronicle.com/article/The-Question-of-Sex-Between/33174
Bellas, M. L., & Gossett, J. L. (2001). Love or the “lecherous professor”: Consensual sexual relationships between professors and students. The Sociological Quarterly, 42, 529–558. doi:10.1111/j.1533-8525.2001.tb01779.x
Bowman, V. E., Hatley, L. D., & Bowman, R. L. (1995). Faculty-student relationships: The dual
role controversy. Counselor Education and Supervision, 34, 232–242. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.1995.tb00245.x
Brooks, M., & Steen, S. (2010). “Brother where art thou?” African American male instructors’ perceptions of the counselor education profession. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 38, 142–153. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1912.2010.tb00122.x
Creswell, J. W. (2007). Qualitative inquiry & research design: Choosing among five approaches. Thousand
Oaks, CA: Sage.
Crothers, L. M., Hughes, T. L., Schmitt, A. J., Theodore, L. A., Lipinski, J., Bloomquist, A. J., & Altman, C. L. (2010). Has equity been achieved? Salary and promotion negotiation practices of a national sample of school psychology university faculty. The Psychologist-Manager Journal, 13, 40–59. doi:10.1080/10887150903553790
Culotta, E. (1993). Finding—and keeping—minority professors. Science, 262, 1091–1096.
doi:10.1126/science.262.5136.1091
Dollarhide, C. T., & Granello, D. H. (2012). Humanistic perspectives on counselor education and
supervision. In M. B. Scholl, A. S. McGowan, & J. T. Hansen (Eds.), Humanistic perspectives on contemporary counseling issues (pp. 277–303). New York, NY: Routledge.
Ei, S., & Bowen, A. (2002). College students’ perceptions of student-instructor relationships. Ethics & Behavior, 12, 177–190. doi:10.1207/S15327019EB1202_5
Giorgi, A. (1985). Sketch of a psychological phenomenological method. In A. Giorgi (Ed.),
Phenomenology and psychological research. Pittsburgh, PA: Duquesne University Press.
Harper, S. R. (2009). Niggers no more: A critical race counternarrative on black male student
achievement at predominately white colleges and universities. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, 22, 697–712. doi:10.1080/09518390903333889
Healey, A. C., & Hays, D. G. (2012). A discriminant analysis of gender and counselor
professional identity development. Journal of Counseling & Development, 90, 55–62. doi:10.1111/j.1556-6676.2012.00008.x
Kiley, K. (2011, August 30). Relationship problems. Inside Higher Education. Retrieved from
https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2011/08/30/idaho_student_s_death_and_ties_to_former_
professor_highlights_difficulty_of_preventing_faculty_student_relationships
Kolbert, J. B., Morgan, B., & Brendel, J. M. (2002). Faculty and student perceptions of dual relationships within counselor education: A qualitative analysis. Counselor Education and Supervision, 41, 193–206. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2002.tb01283.x
Kress, V. E., & Dixon, A. (2007). Consensual faculty–student sexual relationships in counselor
education: Recommendations for counselor educators’ decision making. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 110–122. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2007.tb00042.x
McAuliffe, G. J. (2011). Guidelines for constructivist-developmental counselor education. In G. J. McAuliffe & K. P. Eriksen (Eds.), Handbook of counselor preparation: Constructivist, developmental,
and experiential approaches (pp. 31–48). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Moerer-Urdahl, T., & Creswell, J. W. (2004). Using transcendental phenomenology to explore the “ripple effect” in a leadership mentoring program. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 3, 1–28.
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Nicks, S. D. (1996). Fear in academia: Concern over unmerited accusations of sexual harassment. The Journal of Psychology, 130, 79–82. doi:10.1080/00223980.1996.9914990
Oldenburg, C. M. (2005). Students’ perceptions of ethical dilemmas involving professors: Examining the impact of the professor’s gender. College Student Journal, 39, 129–140.
Owen, P. R., & Zwahr-Castro, J. (2007). Boundary issues in academia: Student perceptions of faculty–student boundary crossings. Ethics & Behavior, 17, 117–129. doi:10.1080/10508420701378065
Potrata, B. (2010). Rethinking the ethical boundaries of a grounded theory approach. Research Ethics, 6, 154–158. doi:10.1177/174701611000600408
Saldaña, J. (2013). The coding manual for qualitative researchers (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA:
Sage.
Schweiger, W. K., Henderson, D. A., McCaskill, K., Clawson, T. W., & Collins, D. R. (2012).
Counselor preparation: Programs, faculty, trends (13th ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Silverman, D., & Marvasti, A. (2008). Doing qualitative research: A comprehensive guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Teddlie, C. B., & Tashakkori, A. M. (2009). Foundations of mixed methods research: Integrating
quantitative and qualitative approaches in the social and behavioral sciences. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Wright, W., Colgan, F., Creegany, C., & McKearney, A. (2006). Lesbian, gay and bisexual workers: Equality, diversity and inclusion in the workplace. Equal Opportunities International, 25, 465–470. doi:10.1108/02610150610713782
Dee C. Ray, NCC, is a Professor at the University of North Texas. David D. Huffman is an Adjunct Professor at the University of North Texas. David. D. Christian is an Assistant Professor at the University of Arkansas. Brittany J. Wilson, NCC, is Assistant Director, Child and Family Resource Clinic, University of North Texas. Correspondence can be addressed to Dee C. Ray, University of North Texas, 1155 Union Circle, Box 310829, Denton, TX 76203, dee.ray@unt.edu.
Jul 20, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 2
Kathleen Brown-Rice, Susan Furr
It has been found that 10% of counselors-in-training are ill-suited for the profession (Gaubatz & Vera, 2002). In that, they have problems of professional competence (PPC) that impede their ability to function as professional counselors (Elman & Forrest, 2007). These PPC include skill competencies, ethical behaviors and appropriate personal functioning (Kaslow et al., 2007). To evaluate students in terms of professional competence and prevent those with inadequate skills and dispositions from entering the profession, gatekeeping is utilized. Counselor educators are required to be transparent in their gatekeeping procedures with students. Students are to be informed of “the levels of competency expected, appraisal methods, and timing of evaluations for both didactic and clinical competencies” and be provided “ongoing feedback” (American Counseling Association [ACA], 2014, p. 15). There has been significant research to provide counselor educators with information to establish gatekeeping and remediation procedures (Gaubatz & Vera, 2002; Homrich, DeLorenzi, Bloom, & Godbee, 2014; Hutchens, Block, & Young, 2013; Kerl, Garcia, McCullough, & Maxwell, 2002; McAdams, Foster, & Ward, 2007; Pease-Carter & Barrio Minton, 2012; Vacha-Haase, Davenport, & Kerewsky, 2004; Zoimek-Daigle & Christensen, 2010). However, little research has been done to examine the impact on counselor educators when interacting with students who have PPC and the roadblocks that impede educators’ ability to gatekeep.
Gatekeeping Procedures
Gatekeeping is a mechanism for counselor educators to determine the fitness of students to enter the counseling profession (Vacha-Haase et al., 2004). Gatekeeping begins as part of the admission process of a counseling program (Kerl & Eichler, 2007). During the admission process, counselor educators do not allow entry to prospective students who show traits, qualities or behaviors that would result in them not being able to meet professional competencies or who lack the prescribed academic requirements (Lumadue & Duffey, 1999; Swank & Smith-Adcock, 2013). However, gatekeeping is not just part of the admission process. Ziomek-Daigle and Christensen (2010) found that gatekeeping is a progressive activity that includes four phases, including preadmission screening, postadmission screening, remediation plan and remediation outcome.
Informing Students of Program Expectations
The American Counseling Association Code of Ethics (2014) provides that counseling students be aware of what type and degree of skill and knowledge will be required of them to be successful in the program, specific training goals and objectives, what students’ evaluations are based on, and the policies and procedures for students’ evaluations. One of the most important methods of ensuring understanding of expectations is informing students of the program’s expectations at the beginning of the program. Once clearly defined behaviors are established, sharing these expectations with students can result in fewer problematic situations (Kerl et al., 2002; McAdams et al., 2007). Furthermore, not providing students with clear expectations for conduct may be viewed as unfair to those wanting to become counselors (Homrich et al., 2014).
It is recommended that professional standards be made clear to students and applied consistently (Hutchens et al., 2013). Using multiple methods of distributing information is desired by students who have stated they want information shared both orally and in written form, and want the information presented throughout the program (Pease-Carter & Barrio Minton, 2012). Pease-Carter and Barrio Minton (2012) found that students desired information not only about academic expectations but also wanted to know about self-disclosure, reflection, personal growth and student rights.
Assessing Students’ PPC Behaviors
Individual programs have developed standards for evaluating students on professional competencies and use these evaluations to provide formative feedback (Kerl et al., 2002). Historically, the most commonly cited problematic behaviors have been inadequate clinical skills, defensiveness in supervision and deficient interpersonal skills (Vacha-Haase et al., 2004). Efforts to identify criteria for evaluating students in terms of professional behaviors, interpersonal behaviors and intrapersonal behaviors have recently been undertaken (Homrich et al., 2014), and these criteria provide a platform for developing clear expectations for counseling trainees.
Roadblocks to Gatekeeping
There are a variety of reasons that counselor educators do not engage in the gatekeeping process. Gateslipping rates have been reported as higher in programs where faculty members reported that their colleagues were concerned about being sued or receiving less than favorable teaching evaluations (Gaubatz & Vera, 2002; Jacobs et al., 2011). In some settings, colleagues and administration provide support for engaging in gatekeeping; however, lack of clear evidence and bias toward leniency lead to gateslippage (Brear & Dorrian, 2010). Absence of well-defined program policies may make it difficult to initiate gatekeeping conversations with a student as well (Jacobs et al., 2011).
Gatekeeping demands a great amount of time and energy, and situations involving PPC often seem unending (Gizara & Forrest, 2004). Not only do PPC have to be identified and communicated to the student, remediation plans need to be developed. Such plans may include helping the counselor-in-training obtain remedial assistance, providing intensified supervision, documenting the activities of the plan and ensuring the student understands due process options (Ziomek-Daigle & Christensen, 2010). When remediation plans are not successful, decisions about dismissal must be made, and the actions taken must be transparent (Kaslow et al., 2007).
There may be occasions where the gatekeeping responsibility is diffused among different entities. In a review of ethical issues around professional competence problems (Johnson et al., 2008), Johnson labeled this issue as the “hot potato game” (p. 589), where the last entity engaged with the problematic student is stuck with the issue. If a student is allowed to gateslip through the graduate program, then the training facility and licensing board now become involved. Rather than address the issue when it is first recognized, the student may be allowed to move to the next stage of training with the hope that the problem disappears or that that it is addressed at the next level. Addressing issues early in the training may help avoid more serious issues, like the empathy veil, later when students go to clinical sites.
The Empathy Veil
This term was coined by Brown-Rice and Furr (2014) and refers to the counselor educator’s need to empathize with the counselor-in-training, which can result in reluctance to engage in gatekeeping activities. Role tension may be one factor in developing an empathy veil. This term evolved from work by Sue and Sue (2012) where a person’s worldview is seen as having an invisible veil that is created by cultural conditioning and is believed to operate outside of consciousness. Forrest et al. (2013) found that empathy may contribute to avoiding confronting student issues for fear of damaging the relationship. Because of the role that faculty play in fostering growth and development, which often involves compassion and support, it may become difficult to provide accurate summative evaluations of trainees’ behaviors (Johnson et al., 2008). Given that many faculty members also are professional counselors, they may view their role as assisting the student in behavior change and thus work with the student to address interpersonal issues that interfere with developing counseling skills (Kerl et al., 2002). This empathy can be both a support and a challenge when difficult conversations about problematic professional, interpersonal and intrapersonal behaviors need to take place (Jacobs et al., 2011). Although empathy can create a safe environment in which to discuss difficulties, an educator’s empathy also can lead to overprotective behaviors that may actually interfere with the student’s development (Gizara & Forrest, 2004).
Role of Diversity
Another important area of consideration is how cultural differences intersect with PPC. When there is a cross-cultural student PPC situation, a complex power differential arises that not only is associated with the faculty–student relationship, but also related to cultural differences (Goodrich & Shin, 2013). Kaslow et al. (2007) proposed that consideration should be given to the impact of beliefs, values and attitudes when assessing competence problems. Fear of appearing biased may complicate identifying trainees with PPC and how decisions are made regarding students (Shen-Miller, Forrest, & Elman, 2009). The counselor educator’s own cultural background may influence how counselors-in-training are evaluated, and it is recommended that cultural dynamics be assessed when addressing PPC (Rust, Raskin, & Hill, 2013). Shen-Miller, Forrest, and Burt (2012) identified two approaches that often are used by faculty in assessing students—culture-attentive (i.e., approaches that include attention to aspects of diversity) or colorblind (i.e., inattention or minimization of differences associated with diversity). These views represent two ends of a “continuum of conceptualizing intersections between diversity and professional standards” (Shen-Miller et al., 2012, p. 1207). In trying to find a place on this continuum to address PPC, do counselor educators underidentify PPC because of fear of being biased? Or, are counselor educators more prone to overidentify PPC because of not examining contextual factors that influence competence? In this study, an attempt is made to examine counselor educators’ views of what interferes with their ability to address issues of counselor education student PPC.
Other Barriers
Previous research has found that educators believe that they have not been provided with sufficient training related to gatekeeping and remediation procedures, and they do not feel supported by their agency and colleagues (Gizara & Forrest, 2004; Vacha-Haase et al., 2004). Additionally, counselor educators may be reluctant to dismiss a student for dread of potential litigation and personal recrimination (Crawford & Gilroy, 2012; Hutchens et al., 2013) and receiving poor teaching evaluations (Gaubatz & Vera, 2002). Recent court cases have increased awareness about the legal consequences of gatekeeping. The Ward and Keeton cases have highlighted the need for counseling programs to establish clear statements about student expectations (Herlihy, Hermann, & Greden, 2014). Other cases have taught faculty members the importance of providing regular process evaluations and thorough documentation (McAdams & Foster, 2007). Reflection on the results of facing a court challenge includes the significance of having a measure of performance that helps faculty retain objectivity and the importance of adhering to established procedures (McAdams et al., 2007).
The purpose of this study was to answer the following research questions: (a) What types of master’s students’ PPC do Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) counselor educators perceive have the greatest impact on them as educators? (b) What do CACREP counselor educators perceive are roadblocks that interfere with their ability to engage in the gatekeeping of master’s students with PPC? and (c) What is CACREP counselor educators’ knowledge of their programs’ protocol for addressing a student with PPC? In this study, student refers to a master’s student enrolled in the participant’s counseling program, colleague is another counselor educator teaching in the participant’s counseling program, and impact means to have a strong effect. PPC refers to attitudes and behaviors that could interfere with the professional competence of a counselor-in-training, including: (a) a lack of ability or opposition to acquire and integrate professional standards into one’s professional counseling behavior; (b) a lack of ability to attain professional skills and reach an acceptable level of competency; (c) a lack of ability to manage one’s stress, psychological dysfunction or emotional responses that may impact professional performance; or (d) engagement in unethical behavior (Falender, Collins, & Shafranske, 2009).
Methods
Participants and Procedures
Prior to initiating the study, institutional review board approval was obtained. Recruitment of participants was conducted by an e-mail to all faculty employed at CACREP-accredited programs in the United States. The researchers of this study obtained a list of accredited programs from the official CACREP Web site and then visited each program’s Web site to obtain the e-mail addresses of the program’s counselor educators. Seven programs did not list faculty e-mails on their university Web sites. The exact number of educators teaching in CACREP-accredited programs is not known, as the programs’ Web sites might have imprecise or out-of-date information. Based upon the e-mail addresses gathered from the university Web sites, a list of 1,584 faculty members was created. Thereafter, one e-mail solicitation was sent to all identified faculty that directed participants to an online survey entitled, Problems of Professional Competency Survey – Counselor Educator Version (PPCS-CE), which was located on Psychdata.com. Of the 1,584 e-mails that were sent, 71 were undeliverable due to lacking a valid address or security issues, 15 were returned with automatic responses that the faculty member was absent (e.g., on sabbatical, no longer at university, ill, professor emeritus), and five responses indicated that the receiver of the e-mail was not a counselor educator. This left a total sample size of 1,493 CACREP counselor educators. For a population of 1,500, a sample size of 306 is adequate to generalize with a confidence interval of 95% (Gay, Mills, & Airasian, 2009). A total of 382 participants completed the survey; however, respondents with missing or invalid data (n = 12, less than 4%) were eliminated via listwise deletion, leaving a total number of 370 participants included in this study. This resulted in an adequate sample size of 370 participants and a final response rate of 25%. Frequencies and percentages of the demographic variables in this study are reported in Table 1.
| Table 1 Numbers and Percentages of Demographic Variables |
| Variable |
Number |
Percentage |
| Gender: |
|
|
| Female |
213
|
58
|
| Male |
157
|
42
|
| Background: |
|
|
| Caucasian |
310
|
84
|
| African American |
24
|
6
|
| Hispanic/Latino |
12
|
3
|
| Multi-Racial |
15
|
4
|
| Asian/Pacific Islander |
8
|
2
|
| Native American |
1
|
1
|
| Age: |
|
|
| 20 years to 29 years |
7
|
2
|
| 30 years to 39 years |
77
|
21
|
| 40 years to 49 years |
97
|
26
|
| 50 years to 59 years |
76
|
21
|
| 60 years or older |
113
|
31
|
| Sexual Orientation: |
|
|
| Heterosexual |
331
|
90
|
| Bisexual |
9
|
2
|
| Gay or Lesbian |
30
|
8
|
|
|
|
| Description of Program: |
|
|
| Predominantly on Campus |
318
|
86
|
| Predominantly Online |
7
|
2
|
| Hybrid of Online/on Campus |
45
|
12
|
|
|
|
| Location of Program: |
|
|
| South |
146
|
40
|
| Northeast |
93
|
25
|
| Midwest |
74
|
20
|
| West |
57
|
15
|
| Highest Degree: |
|
|
| PhD – CACREP Program |
201
|
54
|
| PhD – Non-CACREP Program |
38
|
10
|
| EdS in Counseling |
10
|
3
|
| PhD – Counseling Psychology |
31
|
8
|
| PhD – Clinical Psychology |
4
|
1
|
| Other (doctoral in another discipline ormaster’s in counseling or related field) |
86
|
23
|
| Academic Rank: |
|
|
| Assistant Professor |
145
|
39
|
| Associate Professor |
102
|
28
|
| Professor |
92
|
25
|
| Clinical Instructor |
8
|
2
|
| Adjunct Instructor |
6
|
.2
|
| Other |
17
|
5
|
|
|
|
| Years Teaching in a CACREP-Accredited Program: |
|
|
| Less than 2 years |
59
|
16
|
| 2 to 5 years |
84
|
23
|
| 6 to 10 years |
90
|
24
|
| 11 to 15 years |
66
|
18
|
| 16 to 20 years |
28
|
8
|
| Over 20 years |
43
|
12
|
| Licenses and Certifications Held: |
|
|
| Licensed Professional Counselor |
201
|
55
|
| Licensed Alcohol and Drug Counselor |
21
|
6
|
| Provisionally Licensed Professional Counselor |
14
|
4
|
| Licensed Marriage & Family Counselor |
33
|
9
|
| Licensed Psychologist |
37
|
10
|
| Licensed Social Worker |
7
|
2
|
| Certified School Counselor |
95
|
26
|
| National Certified Counselor |
199
|
54
|
Instrument
The survey for this present study was designed based upon the Problems of Professional Competency Survey – Master Student Version (PPCS-MS) developed by Brown-Rice and Furr (2013), related to determining master’s students’ enrolled in CACREP-accredited programs knowledge of classmates with PPC. The PPCS-MS was constructed based upon the literature regarding PPC in psychology, counseling and social work. To establish content validity and reliability, the PPCS-MS underwent an expert review process and two pilot studies to provide clarity and conciseness of the survey questions. Additionally, a principal components analysis created components representative of what the review of the literature provided on these issues (Brown-Rice & Furr, 2013). The questions and format of the PPCS-MS were used and adjusted to create a self-report survey entitled the Problems of Professional Competency Survey – Counselor Educator Version (PPCS-CE). This instrument was divided into three parts: Part I – Demographic Information, Part II – Counselor Educators and Students with PPC, and Part III – Counselor Educators’ Knowledge of Colleagues’ PPC (removed from this analysis). Part II included three sections. Section I, Counselor Educators’ Knowledge of Students’ Problems of Professional Competency, included one question to determine whether participants have observed students with PPC and two questions to determine participants’ knowledge of the type of students’ PPC and the impact of the problematic behavior. Each PPC was rank ordered from 1 being the most common and 9 being the least common observed behavior, and the impact of having a student with PPC was ranked ordered with 1 having the most impact and 9 having the least impact. Chi square analyses of each of the rank ordered items led to a rejection of the null hypotheses of the categories of the item occurring with equal probabilities.
Section II of Part II of the survey investigated counselor educators’ reactions to students’ PPC and consisted of seven questions. The answers to all these questions were based on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree). Section III, Counselor Educators’ Knowledge of Counseling Program’s Protocol for Addressing Problems of Professional Competency, included questions relating to responsibility for being aware of students PPC and programs’ protocols for addressing PPC. The first nine questions were evaluated on a 5-point Likert scale. The tenth item was unstructured to provide a place for participants to provide additional information.
Results
Types and Impact of Students’ Problematic Behavior
Of the 370 participants, the majority (91%, n = 338) reported that they had observed students with PPC in their programs. Additionally, 2% (n = 8) of the respondents indicated they did not know if there were students with PPC in their programs, leaving 7% (n = 24) who had not observed any students with PPC. To answer the first research question regarding the types and impact of master’s students’ PPC observed by CACREP counselor educators, the responses for the 338 participants who reported observing a student with PPC were examined according to the rank order question regarding the types of PPC that participants most observed with counselors-in-training in their programs. The most frequently identified problematic behaviors included inadequate clinical skills (M = 2.90, SD = 1.88), inadequate interpersonal skills (M = 3.15, SD = 1.69), inadequate academic skills (M = 3.38, SD = 2.29), inability to regulate emotions (M = 4.16, SD = 1.88), and unprofessional behavior (M = 4.29, SD = 2.13). Those behaviors ranked as less impactful were unprofessional behavior (M = 4.29, SD = 2.13), unethical behavior (M = 5.63, SD = 2.03), psychological concern (M = 6.20, SD = 1.84), personality disorder (M = 7.60, SD = 1.61), and substance use disorder (M = 7.69, SD = 1.68).
The responses for the rank order question regarding the type of impact of having counselors-in-training in their program with PPC focused on the behaviors having the most impact on the faculty member. Included in this list were disrupted the classroom learning environment (M = 2.99, SD = 1.86), negatively affected other students (M = 3.26, SD = 1.52), increased participant’s workload (M = 3.29, SD = 2.05), and increased participant’s stress (M = 3.39, SD = 1.64). Additional items that were ranked as less impactful included negatively affected client care (M = 5.06, SD = 2.44), negatively affected relationship with students (M = 5.47, SD = .87), negatively affected relationship with colleagues (M = 6.59, SD = 1.42), negatively affected reputation of the program (M = 6.81, SD = 1.90), and a grievance or litigation occurred (M = 8.25, SD = 1.94).
Roadblocks to Gatekeeping
All participants (n = 370) completed Section II, Part II of the PPCS-CE, and these participants’ responses for strongly agree and agree were combined to report the subsequent findings. Each of the participants reported degree of agreement or disagreement regarding beliefs around the roadblocks that interfere with their ability to engage in the gatekeeping of master’s students with PPC. Fifty-three percent (n = 197) reporting struggling emotionally to balance being empathetic with a student demonstrating PPC and their gatekeeping duties. When looking at addressing PPC with a student who is culturally different from the participant, 38% (n = 141) stated they were reluctant to do so due to the fear they would appear culturally insensitive, and 36% (n = 137) were reluctant to do so due to the fear of allegations of discrimination. Regarding being supported by others, 13% (n = 47) provided they did not feel supported by their chair to address a student who demonstrated PPC, and 13% (n = 47) stated they did not feel supported by their colleagues to address a student who demonstrated PPC. Further, 92% (n = 339) were concerned about the counseling profession when a student with PPC was allowed to pass through the program. Additionally, 30% (n = 110) provided they were reluctant to address a student demonstrating PPC for fear of recrimination (e.g., negative teaching evaluations, legal action).
Protocol for Addressing Students with PPC
When the participants’ responses for strongly agree and agree were combined, 99% (n = 368) believed it was their responsibility to be aware of students with PPC, 91% (n = 335) believed that it was their chair’s responsibility, and 96% (n = 354) believed it was both their chair and respondents’ responsibility to be aware of students with PPC. Additionally, 94% (n = 347) were aware of their programs’ procedures regarding how to address problematic behavior, 71% (n = 263) reported their chair had discussed their programs’ procedures regarding addressing PPC with them, and 38% (n = 140) stated they had received training from their program regarding how to intervene with a student who they believe is demonstrating PPC. Further, 87% (n = 321) were aware of the appropriate intervention to take with students with PPC, 51% (n = 189) would like more information regarding how to identify students with PPC, and 61% (n = 226) of the participants would like more information on how to respond to a student with PPC.
Discussion and Implications
The PPC identified in this study as being observed most frequently are consistent with those problematic behaviors identified in other studies. Vacha-Haase et al. (2004) also identified that inadequate clinical skills and deficient interpersonal skills were most commonly cited as problematic behaviors. In a study examining a proposed set of standards for clinical training, Homrich et al. (2014) identified three categories of behaviors needed by graduate students in clinical training, which included professional behaviors, interpersonal behaviors and intrapersonal behaviors. The types of PPC counselor educators observed in this study parallel the findings of Homrich et al. (2014) in that inadequate clinical skills and unprofessional behavior are similar to their theme of professional behaviors, and the category of inadequate interpersonal skills is comparable to their theme of interpersonal behaviors. Inability to regulate emotions is analogous to their theme of intrapersonal behaviors. Because they were examining clinical training standards, there was no mention of academic skills, yet this type of PPC was cited as a concern by many of the respondents in this study.
Examination of these data leads to questions about how counseling programs admit students. Both academic skills and interpersonal skills are areas that can be addressed through the admissions process. Smaby, Maddox, Richmond, Lepkowski, and Packman (2005) found that undergraduate GPA and GRE Verbal scores could be predictive of scores on the Counselor Preparation Comprehensive Examination (CPCE), which focus on knowledge, but were not highly predictive of personal development. Given the level of concern over academic skills, using these cognitive measures is important, but expanding the way of assessing academic ability also needs to be sensitive to issues around diversity and bias in standardized measures.
In a survey on admission screening measures, training directors indicated that the personal interview was the most effective screening measure (Leverett-Main, 2004). Using creative group strategies during the admission process has been advocated to help assess academic potential as well as dispositions (Swank & Smith-Adcock, 2013). Smith, Robinson, and Young (2007) found that an assessment of wellness might uncover issues around psychological distress that could affect performance in a counseling graduate education program.
Previous research has indicated that faculty members have concerns about addressing PPC because of their desire to be supportive of students (Johnson et al., 2008; Kerl et al., 2002), which would support the concept of the empathy veil (Brown-Rice & Furr, 2014). In this study, 53% of respondents reported struggling emotionally to balance empathy with their gatekeeping duties to intercede with a counselor-in-training with PPC. When the open-ended responses were reviewed, participants’ responses supported this empathetic struggle. For example, one respondent stated, “I have heard many times how a grade should be considered through compassion for student circumstances rather than demonstrated competency.” Another participant provided, “Our empathy wants to give them another chance, but our ethics don’t necessarily allow for it. It’s a struggle for me. It is not a part of the job that I anticipated. Although I remember learning the concept in my doctoral program, I wasn’t prepared to address it.” Therefore, it would appear that these counselor educators are struggling with empathy veils.
When looking at other roadblocks (e.g., lack of peer and institutional support, diversity in gatekeeping, threat of litigation or recrimination from a counselor-in-training), there were some interesting findings. Previous research has found a lack of support for counselor educators from administration and colleagues in dealing with problematic students (Gizara & Forrest, 2004; Vacha-Haase et al., 2004). This concern has been found to be especially true for field supervisors (Bogo, Regehr, Power, & Regehr, 2007; Homonoff, 2008). However, the results of the current study found that only 13% stated they did not feel supported by their chair or colleagues to address a student who demonstrated PPC. The open-ended responses supported these findings. For example, participants stated, “We have a culture and climate of supporting our gatekeeping role in the counseling profession”; “My colleagues and I work as a team in addressing student concerns”; and “I feel supported by my chair and department when dealing with such issues. We deal with these issues as a department. No one is alone in addressing such issues.” Therefore, for this study, lack of institutional and peer support do not seem to be roadblocks. This could be due to the fact that all the participants in this study worked at programs that were accredited by CACREP. CACREP (2016) requires a procedure for addressing student professional and personal development. Counselor educators at programs that are not CACREP-accredited may report different findings. A limitation of this study is that only faculty from CACREP-accredited programs were contacted. Future research focusing on non-CACREP programs and site supervisors regarding this issue may be beneficial. Those working in the field may not have a deep understanding of the role of gatekeeping and may need to develop clear guidelines for their role as supervisors for both counselors-in-training and for counselors seeking licensure.
When the counselor-in-training was from a different cultural background than the counselor educator, 38% of the respondents expressed concern about appearing culturally insensitive, and 36% were concerned about allegations of discrimination. Because this survey was a self-report measure, there is risk that some participants provided answers they considered to be socially desirable (which is a limitation of the study). The field of counseling is committed to multicultural competence in skills, knowledge and awareness, which could make it difficult for counselor educators to acknowledge problematic behaviors in students who are different from themselves. Research has indicated that White counselors tend to favor the colorblind approach in disposition cases (Neville, Lilly, Duran, Lee, & Browne, 2000). Yet fear of responding in a way that appears insensitive may have contributed to responding in socially desirable ways on this instrument. More exploration is needed in this area. While recent literature has addressed how to be culturally responsive when intervening with counseling students’ problematic behavior (Goodrich & Shin, 2013), there is a lack of research regarding culturally responsive performance standards. Until the counseling profession establishes clear performance expectations that are culturally sensitive, the tension between colorblind and culture-attentive expectations will continue to complicate responding to PPC. For example, class performance often has an evaluation component concerning class participation. If a student is from a culture where students do not contribute unless called upon by the professor, then this student may perform poorly because of not understanding expectations. The professor needs to be sensitive to this type of difference and work with the student to develop ways of being successful.
Few participants reported involvement in a legal action related to gatekeeping and remediation with a student demonstrating PPC; however, 30% stated they were reluctant to address a student for fear of retaliation from the student. Given that counselor educators who have been involved in such cases have disclosed the emotional toll these processes take on a program and its faculty members (Dugger & Francis, 2014; McAdams et al., 2007), it seems understandable that there is concern. Therefore, support from ACA, resources in the form of consultation with other campuses and endorsement of gatekeeping processes from one’s own campus are essential in navigating this demanding process. Although legal actions are not common, developing appropriate gatekeeping procedures will help prevent negative outcomes (Dugger & Francis, 2014).
In addition, Brown-Rice and Furr (2014) provided that counselor educators and supervisors should “maintain appropriate ethical boundaries and avoid dual relationships with counselors-in-training, inform and educate themselves regarding the proper gatekeeping protocols and limit their own hypocrisy regarding acting in a competent and ethical manner” (p. 5). There has been substantial research and discussion regarding ethical boundaries, dual relationships and establishing proper gatekeeping procedures (Brown, 2013; Kolbert, Morgan, & Brendel, 2002; Morrissette & Gadbois, 2006; Ziomek-Daigle & Christensen, 2010). However, there seems to be a lack of attention to the competence of counselor educators and how counselors-in-training perceive educators’ professional and personal competence. Do students see faculty members engaging in the same attitudes, skills, behaviors and self-awareness that they are required to adhere to? Are counselor educators modeling the behaviors they want to see in their students or do they hold students to different standards?
Almost all the participants (94%) provided they were aware of their programs’ procedures regarding how to address problematic behavior, and 87% were aware of the appropriate intervention to take with students with PPC. However, only 38% stated they had received training from their program regarding how to intervene with a problematic student. In the open-ended responses, participants stated that their programs had established procedures and all faculty members were aware of them; however, they also reported that PPC were minimized or not addressed. For example, one participant provided, “while there is often a policy in place . . . I find that colleagues fail to follow that policy in practice.” Another respondent stated, “It is also up to the adviser to address the issue with the student and create a plan of improvement. Not all faculty do this and this leads to students receiving different treatment.” Additionally, a participant shared that colleagues were resistant to “address inappropriate student attitudes, dispositions, personality characteristics, and behaviors unless they reach such a critical threshold that they pose a significant threat to clients or, in some cases, faculty egos.” It also appears that how a student is addressed may be related to faculty dynamics. For example, “Political alliances among faculty play a major role in determining which students are targeted for intervention.”
Participants overwhelmingly reported they were aware of their programs’ procedures and the appropriate interventions to take when they encounter counselors-in-training with PPC. However, they also reported that they struggle with their gatekeeping duties due to empathy, diversity issues and fear of recrimination; half of the participants (51%) stated they would like more information regarding how to identify students with PPC, and 61% would like more information on how to respond to these students. Apparently, counseling programs are doing a good job developing procedures and communicating these procedures to faculty members, as recommended by Gaubatz and Vera (2002). But there remains a disconnect between knowledge about procedures and the ability to implement a response to PPC that may be related to the roadblocks identified in this study.
Counselor educators and supervisors know what they are supposed to do if a PPC has been clearly delineated; however, they struggle with identifying problematic behavior that reaches a threshold of needing to be formally addressed and taking action related to problematic student behaviors. The gap between the recognition that a student is not meeting expectations and the point where formal action is initiated may be filled with the counselor educators’ own beliefs about how they can fix the problem as well as their own anxieties related to the barriers discovered in this study. The recognition of and intervention with students with PPC can be further complicated by counselor educators having to negotiate faculty politics. It would seem that more attention is needed on assisting counselor educators in negotiating these barriers to ensure students do not gateslip.
Conclusion
The results of this current study provide insight that educators are aware of counseling students with problematic behaviors, and these behaviors are impacting the learning environment, other students in the program and personal stress. It also appears that the largest roadblock present and impacting counselor educators’ ability to engage in gatekeeping procedures relates to their empathy veils. The authors of this article perceive that there is a struggle for counselor educators between balancing compassion for students’ life circumstances and developmental level with holding them to an acceptable level of professional competence. Counselor educators know it is their responsibility to engage in ethical gatekeeping procedures; however, they do not want to be excessively critical of students. Having an understanding of the empathy veil will assist educators in finding the balance between challenging and supporting students. Counselor educators must not accept students with PPC into their programs or allow them to move on without confronting and remediating their problematic behaviors. Educators need to do their due diligence and be willing to lift their empathy veils and engage in their gatekeeping responsibilities.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
American Counseling Association. (2014). 2014 American Counseling Association Code of Ethics. Alexandria, VA:
Author.
Bogo, M., Regehr, C., Power, R., & Regehr, G. (2007). When values collide: Field instructors’ experiences of providing feedback and evaluating competence. Clinical Supervisor, 26, 99–117. doi: 10.1300/J001v26n01_08
Brear, P., & Dorrian, J. (2010). Gatekeeping or gate slippage? A national survey of counseling educators in Australian undergraduate and postgraduate academic training programs. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 4, 264–273. doi:10.1037/a0020714
Brown, M. (2013). A content analysis of problematic behavior in counselor education programs. Counselor Education and Supervision, 52, 179–192. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2013.00036.x
Brown-Rice, K. A., & Furr, S. (2013). Preservice counselors’ knowledge of classmates’ problems of professional competency. Journal of Counseling & Development, 91, 224–233. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2013.00089.x
Brown-Rice, K. A., & Furr, S. (2014). Lifting the empathy veil: Engaging in competent supervision. In Ideas and research you can use: VISTAS 2014. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/knowledge-center/vistas
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2016). 2016 CACREP
Standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/2016-CACREP-Standards.pdf
Crawford, M., & Gilroy, P. (2012). Professional impairment and gatekeeping: A survey of master’s-level training programs. Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 5, 28–37.
Dugger, S. M., & Francis, P. C. (2014). Surviving a lawsuit against a counseling program: Lessons learned from Ward v. Wilbanks. Journal of Counseling & Development, 92, 135–141. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2014.00139.x
Elman, N. S., & Forrest, L. (2007). From trainee impairment to professional competence problems: Seeking new terminology that facilitates effective action. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 38, 501–509. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.5.501
Falender, C. A., Collins, C. J., & Shafranske, E. P. (2009). “Impairment” and performance issues in clinical supervision: After the 2008 ADA Amendments Act. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 3, 240–249. doi:10.1037/a0017153
Forrest, L., Elman, N. S., Huprich, S. K., Veilleux, J. C., Jacobs, S. C., & Kaslow, N. J. (2013). Training directors’ perceptions of faculty behaviors when dealing with trainee competence problems: A mixed method pilot study. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 7, 23–32. doi:10.1037/a0032068
Gaubatz, M. D., & Vera, E. M. (2002). Do formalized gatekeeping procedures increase programs’ follow-up with deficient trainees? Counselor Education and Supervision, 41, 294–305.
Gay, L. R., Mills, G. E., & Airasian, P. (2009). Educational research: Competencies for analysis and applications (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Gizara, S. S., & Forrest, L. M. (2004). Supervisors’ experiences of trainee impairment and incompetence at APA-accredited internship sites. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 35, 131–140.
doi:10.1037/0735-7028.35.2.131
Goodrich, K. M., & Shin, R. Q. (2013). A culturally responsive intervention for addressing problematic behaviors in counseling students. Counselor Education and Supervision, 52, 43–55.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2013.00027.x
Herlihy, B. J., Hermann, M. A., & Greden, L. R. (2014). Legal and ethical implications of using religious beliefs as the basis for refusing to counsel certain clients. Journal of Counseling & Development, 92, 148–153. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2014.00142.x
Homonoff, E. (2008). The heart of social work: Best practitioners rise to challenges in field instruction. Clinical Supervisor, 27, 135–169, doi:10.1080/07325 220802490828
Homrich, A. M., DeLorenzi, L. D., Bloom, Z. D., & Godbee, B. (2014). Making the case for standards of conduct in clinical training. Counselor Education and Supervision, 53, 126–144. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2014.00053.x
Hutchens, N., Block, J., & Young, M. (2013). Counselor educators’ gatekeeping responsibilities and students’ First Amendment rights. Counselor Education and Supervision, 52, 82–95. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2013.00030.x
Jacobs, S. C., Huprich, S. K., Grus, C. L., Cage, E. A., Elman, N. S., Forrest, L., . . . Kaslow, N. J. (2011). Trainees with professional competency problems: Preparing trainers for difficult but necessary conversations. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 5, 175–184. doi:10.1037/a0024656
Johnson, W., Elman, N. S., Forrest, L., Robiner, W. N., Rodolfa, E., & Schaffer, J. B. (2008). Addressing professional competence problems in trainees: Some ethical considerations. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 39, 589–599. doi:10.1037/a0014264
Kaslow, N. J., Rubin, N. J., Forrest, L., Elman, N. S., Van Horne, B. A., Jacobs, S. C., . . . Thorn, B. E. (2007). Recognizing, assessing, and intervening with problems of professional competence. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 38, 479–492, doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.5.479.
Kerl, S., & Eichler, M. (2007). The loss of innocence: Emotional costs to serving as gatekeepers to the counseling profession. Journal of Creativity in Mental Health, 1, 71–88.
Kerl, S. B., Garcia, J. L., McCullough, C. S., & Maxwell, M. E. (2002). Systematic evaluation of professional performance: Legally supported procedure and process. Counselor Education and Supervision, 41, 321–332.
Kolbert, J. B., Morgan, B., & Brendel, J. M. (2002). Faculty and student perceptions of dual relationships within counselor education: A qualitative analysis. Counselor Education and Supervision, 41, 193–206. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2002.tb01283.x
Leverett-Main, S. (2004). Program directors’ perceptions of admission screening measures and indicators of student success. Counselor Education and Supervision, 43, 207–219.
Lumadue, C. A., & Duffey, T. H. (1999). The role of graduate programs as gatekeepers: A model for evaluating student counselor competence. Counselor Education and Supervision, 39, 101–109.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.1999.tb01221.x
McAdams, C. R., III, & Foster, V. A. (2007). A guide to just and fair remediation of counseling students with professional performance deficiencies. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 2–13.
McAdams, C. R., III, Foster, V. A., & Ward, T. J. (2007). Remediation and dismissal policies in counselor education: Lessons learned from a challenge in federal court. Counselor Education and Supervision, 46, 212–229.
Morrissette, P. J., & Gadbois, S. (2006). Ethical consideration of counselor education teaching strategies. Counseling and Values, 50, 131–141. doi:10.1002/j.2161-007X.2006.tb00049.x
Neville, H. A., Lilly, R. L., Duran, G., Lee, R. M., & Browne, L. (2000). Construction and initial validation of the Color-Blind Racial Attitudes Scale (CoBRAS). Journal of Counseling Psychology, 47, 59–70.
Pease-Carter, C., & Barrio Minton, C. A. (2012). Counseling programs’ informed consent practices: A survey of student preferences. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 308–319. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00023.x
Rust, J. P., Raskin, J. D., & Hill, M. S. (2013). Problems of professional competence among counselor trainees: Programmatic issues and guidelines. Counselor Education and Supervision, 52, 30–42.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2013.00026.x
Shen-Miller, D. S., Forrest, L., & Burt, M. (2012). Contextual influences on faculty diversity conceptualizations when working with trainee competence problems. The Counseling Psychologist, 40, 1181–1219. doi:10.1177/0011000011431832
Shen-Miller, D. S., Forrest, L., & Elman, N. S. (2009). Training directors’ conceptualizations of the intersections of diversity and trainee competence problems: A preliminary analysis. The Counseling Psychologist, 37, 482–518. doi:10.1177/0011000008316656
Smaby, M. H., Maddux, C. D., Richmond, A. S., Lepkowski, W. J., & Packman, J. (2005). Academic admission requirements as predictors of counseling knowledge, personal development, and counseling skills. Counselor Education and Supervision, 45, 43–57.
Smith, H. L., Robinson, E. H. M., III, & Young, M. E. (2007). The relationship among wellness, psychological distress, and social desirability of entering master’s-level counselor trainees. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 96–109.
Sue, D. W., & Sue, D. (2012). Counseling the culturally diverse: Theory and practice (6th ed.). New York, NY: Wiley & Sons.
Swank, J. M., & Smith-Adcock, S. (2013). Creative group strategies for interviewing applicants for counselor education programs. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 5, 38–48.
Vacha-Haase, T., Davenport, D. S., & Kerewsky, S. D. (2004). Problematic students: Gatekeeping practices of academic professional psychology programs. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 35, 115– 122. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.35.2.115
Ziomek-Daigle, J., & Christensen, T. M. (2010). An emergent theory of gatekeeping practices in counselor education. Journal of Counseling & Development, 88, 407–415.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2010.tb00040.x
Kathleen Brown-Rice, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of South Dakota. Susan Furr is a Professor at the University of North Carolina Charlotte. Correspondence can be addressed to Kathleen Brown-Rice, 114E Clark Street, Vermillion, SD 57069, kathleen.rice@usd.edu.
Jul 14, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 2
James Ikonomopoulos, Javier Cavazos Vela, Wayne D. Smith, Julia Dell’Aquila
Master’s level counseling programs accredited by the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Education Programs (CACREP, 2016) require students to complete practicum and internship courses that involve group and individual or triadic supervision. Although clinical supervision provides students with effective skill development (Bernard & Goodyear, 2004), counseling students may begin practicum with low self-efficacy regarding their counseling abilities and skills. Given the importance of clinical supervision and counselor self-efficacy, it is surprising that there are limited studies that have examined the impact of supervision and practicum experience from the perspectives of supervisees. Almost all studies within this domain are qualitative and involve personal interviews with supervisees or supervisors (e.g., Hein & Lawson, 2008). In order to fill a gap in the literature and document the impact of the practicum experience, this study examined the effectiveness of the practicum experience encompassing direct counseling services, group supervision and triadic supervision to increase counseling students’ self-efficacy. First, we provide a literature review regarding group supervision, triadic supervision and counselor self-efficacy. Next, we present findings from a study with 11 counseling practicum students. Finally, we provide a discussion regarding the importance of these findings as well as implications for counseling practice and research.
Supervision in Counselor Education Coursework
CACREP requires an average of one and a half hours of weekly group supervision in practicum courses that involves an instructor with up to six counseling graduate students (Degges-White, Colon, & Borzumato-Gainey, 2012). Borders et al. (2012) identified that group supervisors use leadership skills, facilitate and monitor peer feedback, and encourage supervisees to take ownership of group process in group supervision. Borders and colleagues (2012) identified several benefits in group supervision, including exposure to multiple counselor styles and ability to learn about various educational issues. There also were challenges such as limited helpful feedback, brevity of case presentations, timing of group meetings and lack of educational opportunities. In another study, Conn, Roberts, and Powell (2009) compared hybrid and face-to-face supervision among school counseling interns. There were similarities in perceptions of quality of supervision, suggesting that distance learning can provide effective group supervision. CACREP counseling programs also require students to receive one hour of weekly supervision from a faculty member or doctoral student supervisor. Triadic is one form of supervision that involves a process whereby one supervisor meets and provides feedback with two supervisees (Hein & Lawson, 2008). Hein and Lawson (2008) explored supervisors’ perspectives on triadic supervision and found increased demands on the role of the supervisor. For example, supervisors felt additional pressure to support both supervisees in supervision. Additionally, Lawson, Hein, and Stuart (2009) investigated supervisees’ perspectives of triadic supervision. Noteworthy findings included: some students perceived less time and attention to their needs; importance of compatibility between supervisees; and careful attention must be given when communicating feedback, particularly if negative feedback must be given.
Finally, Borders et al. (2012) explored supervisors’ and supervisees’ perceptions of individual, triadic and group supervision. Benefits included vicarious learning experiences, peer-learning opportunities, and better supervisor feedback, while challenges included peer mismatch and difficulty keeping both supervisees involved.
Counselor Self-Efficacy
One of the most important outcome variables in counseling is self-efficacy. Bandura (1986) defined self-efficacy as individuals’ confidence in their ability to perform courses of action or achieve a desired outcome. Self-efficacy in counselor education settings might influence students’ thoughts, behaviors and feelings toward working with clients (Bandura, 1997). In the current study, counseling self-efficacy is defined as “one’s beliefs or judgments about his or her capabilities to effectively counsel a client in the near future” (Larson & Daniels, 1998, p. 1). Counselor self-efficacy also can refer to students’ confidence regarding handling the therapist role, managing counseling sessions and delivering helping skills (Lent et al., 2009). In higher education settings, researchers identified relationships between practicum students’ counseling self-efficacy and various client outcomes in counseling (Halverson, Miars, & Livneh, 2006). Self-efficacy also is positively related to performance attainment (Bandura, 1986), perseverance in counseling tasks, less anxiety (Larson & Daniels, 1998), positive client outcomes (Bakar, Zakaria, & Mohamed, 2011), and counseling skills development (Lent et al., 2009). Halverson et al. (2006) evaluated the impact of a CACREP program on counseling students’ conceptual level and self-efficacy. Longitudinal findings showed that counseling students’ perceptions of self-efficacy increased over the course of the program, primarily as a result of clinical experiences.
In another investigation, Greason and Cashwell (2009) examined mindfulness, empathy and self-efficacy among masters-level counseling interns and doctoral counseling students. Mindfulness, empathy and attention to meaning accounted for 34% of the variance in counseling students’ self-efficacy. Finally, Barbee, Scherer, and Combs (2003) investigated the relationship among prepracticum service learning, counselor self-efficacy and anxiety. Substantial counseling coursework and counseling-related work experiences were important influences on counseling students’ self-efficacy.
Purpose of Study
This study evaluated practicum experiences by using a single-case research design (SCRD) to measure the impact on students’ self-efficacy. In a recent special issue of the Journal of Counseling & Development, Lenz (2015) described how researchers and practitioners can use SCRDs to make inferences about the impact of treatment or experiences. SCRDs are appropriate for counselors or counselor educators for the following reasons: minimal sample size, self as control, flexibility and responsiveness, ease of data analysis, and type of data yielded from analyses. In the current study, the rationale for using an SCRD to examine the effectiveness of the practicum experience and triadic supervision was to provide counselor educators with insight regarding potential strategies that increase students’ self-efficacy. With this goal in mind, we implemented an SCRD (Lenz, Perepiczka, & Balkin, 2013; Lenz, Speciale, & Aguilar, 2012) to identify and explore trends of students’ changes in self-efficacy while completing their practicum experience. We addressed the following research question: to what extent does the practicum experience encompassing direct counseling services, group supervision and triadic supervision influence counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy?
Methodology
Instructors of record for three practicum courses formulated a plan to investigate the impact of the practicum experience on counseling students’ self-efficacy. We focused on providing students with a positive practicum experience with support, constructive feedback, wellness checks and learning experiences. With this goal in mind, we implemented a single case research design (Hinkle, 1992; Lenz et al., 2013; Lenz et al., 2012) to identify and explore trends of students’ changes in self-efficacy while completing their practicum experience. We selected this design to evaluate data that provides inferences regarding treatment effectiveness (Lenz et al., 2013). All practicum courses followed the same course requirements, and instructors shared the same level of teaching experience.
Participant Characteristics
We conducted this study with a sample of Mexican American counseling graduate students (N = 11) enrolled in a CACREP-accredited counseling program in the southwestern United States. This Hispanic Serving Institution had an enrollment of approximately 7,000 undergraduate and graduate students (approximately 93% of students at this institution are Latina/o) at the time of data collection. As a result, we were not surprised that all of the participants in the current study identified as Mexican American. Fifteen participants were solicited; four declined to participate. Participants (four men and seven women) ranged in age from 24 to 57 (M = 31; STD = 9.34). All participants were enrolled in practicum; we assigned participants with pseudonyms to protect their identity. Participants had diverse backgrounds in elementary education, secondary education, case management and behavioral intervention services. Participants also had aspirations of obtaining doctoral degrees or working in private practice, school settings, and community mental health agencies.
Instrumentation
Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy Scale. The Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy Scale (CASES) is a self-report measure of counseling self-efficacy (Lent, Hill, & Hoffman, 2003). This scale consists of 31 items with a 10-point Likert-type scale in which respondents rate their level of confidence from 0 (i.e., having no confidence at all) to 9 (i.e., having complete confidence). Participants respond to items on exploration skills, session management and client distress (Lent et al., 2003), with higher scores reflective of higher levels of self-efficacy. The total score across these domains represents counseling self-efficacy. Reliability estimates range from .96 to .97 (Greason & Cashwell, 2009; Lent et al., 2003). We used the total score as the outcome variable in our study.
Treatment
Over the course of a 14-week semester, participants received 12 hours of triadic supervision and approximately 25 hours of group supervision. We followed Lawson, Hein, and Getz’s (2009) model through pre-session planning, in-session strategies, administrative considerations and evaluations of supervisees. During triadic supervision meetings with two practicum students, the instructor of record conducted wellness checks assessing students’ well-being and level of stress, listened to concerns about clients, observed recorded sessions, provided support and feedback, and encouraged supervisees to provide feedback. The instructor of record also facilitated group supervision discussions on clients’ presenting problems, treatment planning, note-writing, and wellness and self-care strategies. All practicum instructors collaborated and communicated bi-weekly to monitor students’ progress as well as students’ work with clients. All students obtained a minimum of 40 direct hours while working at their university counseling and training clinic, where services are provided to individuals with emotional, developmental, and interpersonal issues. Treatment for depression, anxiety and family issues are the most common issues. The population receiving services at this counseling and training clinic are mostly Mexican American and Spanish-speaking clients who are randomly assigned to a practicum student after an initial phone screening.
Procedure
We evaluated treatment effect using an AB SCRD (in our case, we referred to this more precisely as BT for baseline and treatment), using scores on the CASES as an outcome measure. During an orientation before the semester, practicum students were informed that their instructors were interested in evaluating changes in self-efficacy. Students who agreed to participate in the current study completed baseline measure one at this time. Following this, we selected a pseudonym to identify each participant when completing counselor self-efficacy activity (CSEA) scales throughout the study. The baseline phase consisted of data collection for 3 weeks before the practicum experience. The treatment phase began after the third baseline measure, when the first triadic supervision session was integrated into the practicum experience. Individual cases under investigation were practicum students who agreed to document their changes in self-efficacy while completing the practicum experience. Given that participants serve as their own control group in a single case design, the number of participants in the current study was considered sufficient to explore the research question (Lenz et al., 2013).
Data Collection and Analysis
We implemented an AB, SCRD (Lundervold & Belwood, 2000; Sharpley, 2007) by gathering weekly scores of the CASES. We did not use an ABA design with a withdrawal phase given that almost all students enrolled in internship immediately after the semester. As a result, we did not want to collect data that would have tapped into students’ internship experiences. After three weeks of data collection, the baseline phase of data collection was completed. The treatment phase began after the third baseline measure where the first triadic supervision session occurred. After the 13th week of data collection, the treatment phase of data collection was completed due to nearing completion of the semester, for a total of three baseline and ten treatment phase collections. We did not collect additional treatment data points given that students were scheduled to begin internship at the conclusion of the semester. We only wanted to measure the impact of the practicum experience.
Percentage of data points exceeding the median (PEM) procedure was implemented to analyze the quantitative data from the AB single case design (Ma, 2006). A visual trend analysis was reported as data points from each phase were graphically represented to provide visual representations of change over time (Ikonomopoulos, Smith, & Schmidt, 2015; Sharpley, 2007). An interpretation of effect sizes was conducted to determine the effectiveness of triadic supervision integrated into the practicum experience when comparing each phase of data collection (Sharpley, 2007). Interpreting effect sizes for the PEM procedure yields a proportion of data overlap between a baseline and treatment condition expressed in a decimal format that ranges from zero and one. Higher scores represent greater treatment effects while lower scores represent less effective treatments. This procedure is conceptualized as the analysis of treatment phase data that is contingent on the overlap with the median data point within the baseline phase. Ma (2006) suggested that PEM is based on the assumption that if the intervention is effective, data will be predominately on the therapeutic side of the median. If an intervention is ineffective, data points in the treatment phase will vacillate above and below the baseline median (Lenz, 2013). To calculate the PEM statistic, data points in the treatment phase on the therapeutic side of the baseline are counted and then divided by the total number of points in the treatment phase. Scruggs and Mastropieri (1998) suggested the following criteria for evaluation: effect sizes of .90 and greater are indicative of very effective treatments; those ranging from .70 to .89 represent moderate effectiveness; those between .50 to .69 are debatably effective; and scores less than .50 are regarded as not effective
Results
Figure 1 and Table 1 depict estimates of treatment effect using PEM across all participants. Detailed descriptions of participants’ experiences are provided below.
Participant 1
Jorge’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience involving triadic supervision and group supervision was very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Jorge’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123, which considers an individual to have low counseling self-efficacy for the CASES. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 217). Scores above the PEM line were within a 122-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 2
Gina’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience involving triadic supervision and group supervision was moderately effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Gina’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.77) indicated that seven scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 194). Scores above the PEM line were within a 99-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the second treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills, session management and client distress.
Participant 3
Cecilia’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Cecilia’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 177). Scores above the PEM line were within a 162-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills and session management.
Figure 1.
Graphical Representation of Ratings for Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy by Participants
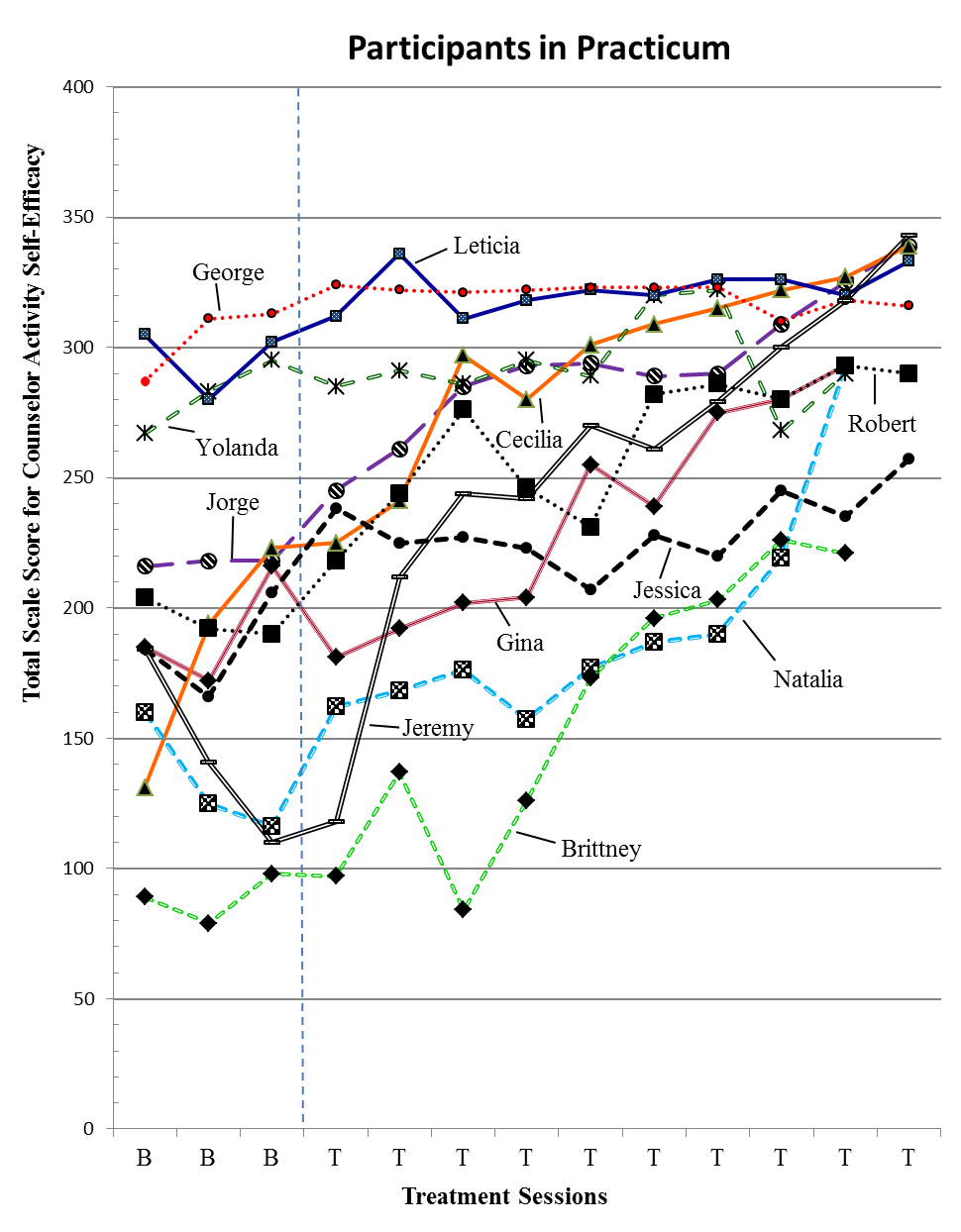
Table 1
Participants’ Sessions and Their CASES Total Scale Score for Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy
Participant 4
Natalia’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, two of Natalia’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that nine scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 138). Scores above the PEM line were within a 155-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 5
Yolanda’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Yolanda’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.90) indicated that nine scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 295). Scores above the PEM line were within a 27-point range. Trend analysis depicted a minimal level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 6
Leticia’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Leticia’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 293). Scores above the PEM line were within a 43-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring client distress.
Participant 7
Robert’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Robert’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 197). Scores above the PEM line were within a 96-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring client distress.
Participant 8
George’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving his counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of George’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the counselor activity self-efficacy measure (1.00) indicated that ten scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 300). Scores above the PEM line were within a 24-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 9
Jeremy’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving his counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, two of Jeremy’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.90) indicated that nine scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 142). Scores above the PEM line were within a 201-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the second treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring session management and client distress.
Participant 10
Brittney’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were moderately effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Brittney’s baseline measurements were below the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.88) indicated that eight scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 94). Scores above the PEM line were within a 132-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the fourth treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring session management.
Participant 11
Jessica’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Jessica’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 186). Scores above the PEM line were within a 71-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Discussion
The results of this study found that in all 11 investigated cases, the practicum experience ranged from moderately effective (PEM = .77) to very effective (PEM = 1.00) for improving or maintaining counselor self-efficacy during practicum coursework. For most participants, counseling self-efficacy continued to improve throughout the practicum experience as evidenced by high scores on items such as “Helping your client understand his or her thoughts, feelings and actions,” “Work effectively with a client who shows signs of severely disturbed thinking,” and “Help your client set realistic counseling goals.” Participants shared that the most helpful experiences during practicum to improve their counselor self-efficacy came from direct experiences with clients. This finding is consistent with Bandura’s (1977) conceptualization of direct mastery experiences where participants gain confidence with successful experiences of a particular activity. Participants also shared how obtaining feedback from clients on their outcomes and seeing their clients’ progress was important for their development as counselors. Other helpful experiences included processing counseling sessions with a peer during triadic supervision, and case conceptualization and treatment planning during group supervision. Obtaining feedback during triadic supervision from peers and instructors after observing recorded counseling sessions also was beneficial.
Qualitative benefits of supervision included vicarious learning experiences, peer-learning opportunities and better supervisor feedback (Borders et al., 2012). Findings from this study extend qualitative findings regarding benefits of the practicum experience and triadic supervision. The results of this study yielded promising findings related to the integration of triadic supervision into counseling graduate students’ practicum experiences. First, the practicum experience appeared to be effective for increasing and maintaining participant scores on the CSEA scale. Inspection of participant scores within treatment targets revealed that the practicum experience was very effective for nine participants and within the moderately effective range for two participants.
Lastly, informal conversations with participants indicate that triadic supervision provided participants with an opportunity to receive peer feedback. Participants also commented that weekly wellness checks were important due to stress from the practicum experience. Trends were observed for the group as a majority of participants improved self-efficacy consistently after their fourth treatment measure. In summary, direct services with clients, triadic supervision with a peer and group supervision as part of the practicum experience may assist counseling graduate students to improve self-efficacy.
Implications for Counseling Practice
There are several implications for practice. First, triadic supervision has been helpful when there is compatibility between supervisor and supervisees (Hein & Lawson, 2008). Compatibility between supervisees is helpful, as participants shared how having similar knowledge and experience contributed to their development. While all participants in the current study selected their partner for supervision, Hein and Lawson (2008) commented that the responsibility to implement and maintain clear and achievable support to supervisees lies heavily on supervisors. As a result, additional trainings should be offered to supervisors regarding clear, concise and supportive feedback. Such trainings and discussions can focus on clarity of roles and expectations for both supervisor and supervisee before triadic supervision begins. More training in providing feedback to peers in group supervision also can be beneficial as students learn to provide feedback to promote awareness of different learning experiences. We suggest that additional trainings will help practicum instructors and students identify ways to provide clear, constructive and effective feedback.
Practicum instructors can administer weekly or bi-weekly wellness checks and discuss responses on individual items on the Mental Well-Being Scale to monitor progress (Tennant et al., 2007). Additionally, counselor education programs would benefit from bringing self-efficacy to the forefront in the practicum experience as well as prepracticum coursework. Findings from the current study could be presented to students in group counseling and practicum coursework to facilitate discussion regarding how the practicum experience can increase students’ self-efficacy. Part of this discussion should focus on assessing baseline self-efficacy in order to help students increase perceptions of self-efficacy. As such, counselor educators can administer and interpret the CSEA scale with practicum students. There are numerous scale items (e.g., silence, immediacy) that can be used to foster discussions on perceived confidence in dealing with counseling-related issues. Finally, CACREP-accredited programs require 1 hour of weekly supervision and allow triadic supervision to fulfill this requirement. We recommend that CACREP and non-CACREP-accredited programs consider incorporating triadic supervision into the practicum experience and suggest that triadic supervision as part of the practicum experience might help students’ increase self-efficacy.
Implications for Counseling Research
The practicum experience seemed helpful for improving counseling students’ self-efficacy. However, information regarding reasons for this effectiveness of the practicum experience and triadic supervision was not explored. Qualitative research regarding the impact of the practicum experience on counselors’ self-efficacy can provide incredible insight into specific aspects of group or triadic supervision that increase self-efficacy. Second, more outcome-based research with ethnic minority counseling students is necessary. There might be aspects of group or triadic supervision that are conducive when working with Mexican American students (Cavazos, Alvarado, Rodriguez, & Iruegas, 2009). Third, exploring different models of group or triadic supervision to increase counseling self-efficacy is important. As one example, researchers could explore the impact of the Wellness Model of Supervision (Lenz & Smith, 2010) on counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy. Finally, all participants in our study attended a CACREP counseling program with mandatory individual or triadic supervision. Comparing changes in self-efficacy between students in CACREP and non-CACREP programs where weekly individual or triadic supervision outside of class is not mandatory would be important.
Limitations
There are several limitations that must be taken into consideration. First, we did not use an ABA design with withdrawal measures that would have provided stronger internal validity to evaluate changes to counselor self-efficacy (Lenz et al., 2012). Most practicum students in our study began internship immediately after the conclusion of the semester. As a result, collecting withdrawal measures in an ABA design would have tapped into students’ internship experiences. Second, although three baseline measurements are considered sufficient in single-case research (Lenz et al., 2012), employing five baseline measures might have allowed self-efficacy scores to stabilize prior to their practicum experience (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2015).
Conclusion
Based on results from this study, the practicum experience shows promise as an effective strategy to increase counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy. Implementing triadic supervision as part of the practicum experience for counseling students is a strategy that counselor education programs might consider. Provided are guidelines for counselor educators to consider when integrating triadic supervision into the practicum experience. Researchers also can use different methodologies to address how different aspects of the practicum experience influence counseling students’ self-efficacy. In summary, we regard the practicum experience with triadic supervision as a promising approach for improving counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Bakar, A. R., Zakaria, N. S., & Mohamed, S. (2011). Malaysian counselors’ self-efficacy: Implication for career counseling. The International Journal of Business and Management, 6, 141–147. doi:10.5539/ijbm.v6n9p141
Bandura, A. (1977). Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84, 191–215.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York, NY: Freeman.
Barbee, P. W., Scherer, D., & Combs, D. C. (2003). Prepracticum service-learning: Examining the relationship with counselor self-efficacy and anxiety. Counselor Education and Supervision, 43, 108–120.
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2004). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (3rd ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Borders, L. D. (2014). Best practices in clinical supervision: Another step in delineating effective supervision practice. American Journal of Psychotherapy, 68, 151–162.
Borders, L. D., Welfare, L. E., Greason P. B., Paladino, D. A., Mobley, A. K., Villalba, J. A., & Wester, K. L. (2012). Individual and triadic and group: Supervisee and supervisor perceptions of each modality. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 281–295.
Cavazos, J., Alvarado, V., Rodriguez, I., & Iruegas, J. R. (2009). Examining Hispanic counseling students’ worries: A qualitative approach. Journal of School Counseling, 7, 1–22.
Conn, S. R., Roberts, R. L., & Powell, B. M. (2009). Attitudes and satisfaction with a hybrid model of counseling supervision. Educational Technology and Society, 12, 298–306.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2016). 2016 CACREP standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/2016-Standards-with-Glossary-rev-2.2016.pdf
Degges-White, S., Colon, B. R., & Borzumato-Gainey, C. (2013). Counseling supervision within a feminist framework: Guidelines for intervention. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 52, 92–105.
doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2013.00035.x
Greason, P. B., & Cashwell, C. S. (2009). Mindfulness and counseling self-efficacy: The mediating role of attention and empathy. Counselor Education and Supervision, 49, 2–19.
Halverson, S. E., Miars, R. D., & Livneh, H. (2006). An exploratory study of counselor education students’ moral reasoning, conceptual level, and counselor self-efficacy. Counseling and Clinical Psychology Journal, 3, 17–30.
Hein, S., & Lawson, G. (2008). Triadic supervision and its impact on the role of the supervisor: A qualitative examination of supervisors’ perspectives. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48, 16–31.
Hinkle, J. S. (1992). Computer-assisted career guidance and single-subject research: A scientist-practitioner approach to accountability. Journal of Counseling & Development, 70, 391–395.
Ikonomopoulos, J., Smith, R. L., & Schmidt, C. (2015). Integrating narrative therapy within rehabilitative programming for incarcerated adolescents. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93, 460–470. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2014.00000.x
Larson, L. M., & Daniels, J. A. (1998). Review of the counseling self-efficacy literature. The Counseling Psychologist, 26, 179–218.
Lawson, G., Hein, S. F., & Getz, H. (2009). A model for using triadic supervision in counselor education preparation programs. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48, 257–270.
Lawson, G., Hein, S. F., & Stuart, C. L. (2009). A qualitative investigation of supervisees’ experiences of triadic supervision. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87, 449–457.
Lent, R. W., Cinamon, R. G., Bryan, N. A., Jezzi, M. M., Martin, H. M., & Lim, R. (2009). Perceived sources of changes in trainees’ self-efficacy beliefs. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training, 46, 317–327. doi:10.1037/a0017029
Lent, R. W., Hill, E., & Hoffman, M. A. (2003). Development and validation of the counselor activity self-efficacy scales. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 50, 97–108.
Lenz, A. S. (2013). Calculating effect size in single-case research: A comparison of nonoverlap methods. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 46, 64–73.
Lenz, A. S. (2015). Special issue editor’s introduction: Using single-case research designs to demonstrate evidence for counseling practices. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93, 387–393.
doi:10.1002/jcad.12036
Lenz, A. S., Perepiczka, M., & Balkin, R. S. (2013). Evidence of the mitigating effects of a support group for attitude toward statistics. Counseling Outcome Research & Evaluation, 4, 26–40. doi:10.1177/2150137812474000
Lenz, A. S., & Smith, R. L. (2010). Integrating wellness concepts within a clinical supervision model. The Clinical Supervisor, 29, 228–245. doi:10.1080/07325223.2020.518511
Lenz, A. S., Speciale, M., & Aguilar, J. V. (2012). Relational-cultural therapy intervention with incarcerated adolescents: A single-case effectiveness design. Counseling Outcome Research & Evaluation, 3, 17–29. doi:10.1177/2150137811435233
Lundervold, D. A., & Belwood, M. F. (2000). The best kept secret in counseling: Single-case (N = 1) experimental designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 78, 92–102.
Ma, H. H. (2006). An alternative method for quantitative synthesis of single-subject researches: Percentage of data points exceeding the median. Behavior Modification, 30, 598–617.
Scruggs, T. E., & Mastropieri, M. A. (1998). Summarizing single-subject research: Issues and applications. Behavior Modification, 22, 221–242.
Sharpley, C. F. (2007). So why aren’t counselors reporting n = 1 research designs? Journal of Counseling & Development, 85, 349–356.
Tennant, R., Hiller, L., Fishwick, R., Platt, S., Joseph, S., Weich, S., . . . Stewart-Brown, S. (2007). The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): Development and UK validation. Health & Quality of Life
Outcomes, 5, 63. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-5-63
James Ikonomopoulos, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Javier Cavazos Vela is an LPC-Intern at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Wayne D. Smith is an Assistant Professor at the University of Houston–Victoria. Julia Dell’Aquila is a graduate student at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Correspondence concerning this article can be addressed to James Ikonomopoulos, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Department of Counseling, Main 2.200F, One West Univ. Blvd., Brownsville, TX 78520, james.ikonomopoulos@utrgv.edu.

