Dec 16, 2020 | Volume 10 - Issue 4
Dodie Limberg, Therese Newton, Kimberly Nelson, Casey A. Barrio Minton, John T. Super, Jonathan Ohrt
We present a grounded theory based on interviews with 11 counselor education doctoral students (CEDS) regarding their research identity development. Findings reflect the process-oriented nature of research identity development and the influence of program design, research content knowledge, experiential learning, and self-efficacy on this process. Based on our findings, we emphasize the importance of mentorship and faculty conducting their own research as a way to model the research process. Additionally, our theory points to the need for increased funding for CEDS in order for them to be immersed in the experiential learning process and research courses being tailored to include topics specific to counselor education.
Keywords: grounded theory, research identity development, counselor education doctoral students, mentoring, experiential
Counselor educators’ professional identity consists of five primary roles: counseling, teaching, supervision, research, and leadership and advocacy (Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs [CACREP], 2015). Counselor education doctoral programs are tasked with fostering an understanding of these roles in future counselor educators (CACREP, 2015). Transitions into the counselor educator role have been described as life-altering and associated with increased levels of stress, self-doubt, and uncertainty (Carlson et al., 2006; Dollarhide et al., 2013; Hughes & Kleist, 2005; Protivnak & Foss, 2009); however, little is known about specific processes and activities that assist programs to intentionally cultivate transitions into these identities.
Although distribution of faculty roles varies depending on the type of position and institution, most academic positions require some level of research or scholarly engagement. Still, only 20% of counselor educators are responsible for producing the majority of publications within counseling journals, and 19% of counselor educators have not published in the last 6 years (Lambie et al., 2014). Borders and colleagues (2014) found that the majority of application-based research courses in counselor education doctoral programs (e.g., qualitative methodology, quantitative methodology, sampling procedures) were taught by non-counseling faculty members, while counseling faculty members were more likely to teach conceptual or theoretical research courses. Further, participants reported that non-counseling faculty led application-based courses because there were no counseling faculty members who were well qualified to instruct such courses (Borders et al., 2014).
To assist counselor education doctoral students’ (CEDS) transition into the role of emerging scholar, Carlson et al. (2006) recommended that CEDS become active in scholarship as a supplement to required research coursework. Additionally, departmental culture, mentorship, and advisement have been shown to reduce rates of attrition and increase feelings of competency and confidence in CEDS (Carlson et al., 2006; Dollarhide et al., 2013; Protivnak & Foss, 2009). However, Borders et al. (2014) found that faculty from 38 different CACREP-accredited programs reported that just over half of the CEDS from these programs became engaged in research during their first year, with nearly 8% not becoming involved in research activity until their third year. Although these experiences assist CEDS to develop as doctoral students, it is unclear which of these activities are instrumental in cultivating a sound research identity (RI) of CEDS. Understanding how RI is cultivated throughout doctoral programs may provide ways to enhance research within the counseling profession. Understanding this developmental process will inform methods for improving how counselor educators prepare CEDS for their professional roles.
Research Identity
Research identity is an ambiguous term within the counseling literature, with definitions that broadly conceptualize the construct in terms of beliefs, attitudes, and efficacy related to scholarly research, along with a conceptualization of one’s own overall professional identity (Jorgensen & Duncan, 2015; Lamar & Helm, 2017; Ponterotto & Grieger, 1999; Reisetter et al., 2011). Ponterotto and Grieger (1999) described RI as how one views oneself as a scholar or researcher, noting that research worldview (i.e., the lens through which they view, approach, and manage the process of research) impacts how individuals conceptualize, conduct, and interpret results. This perception and interpretation of research as important to RI is critical to consider, as it is common practice for CEDS to enter doctoral studies with limited research experience. Additionally, many CEDS enter into training with a strong clinical identity (Dollarhide et al., 2013), but coupled with the void of research experience or exposure, CEDS may perceive research as disconnected and separate from counseling practice (Murray, 2009). Furthermore, universities vary in the support (e.g., graduate assistant, start-up funds, course release, internal grants) they provide faculty to conduct research.
The process of cultivating a strong RI may be assisted through wedding science and practice (Gelso et al., 2013) and aligning research instruction with values and theories often used in counseling practice (Reisetter et al., 2011). More specifically, Reisetter and colleagues (2011) found that cultivation of a strong RI was aided when CEDS were able to use traditional counseling skills such as openness, reflexive thinking, and attention to cognitive and affective features while working alongside research “participants” rather than conducting studies on research “subjects.” Counseling research is sometimes considered a practice limited to doctoral training and faculty roles, perhaps perpetuating the perception that counseling research and practice are separate and distinct phenomena (Murray, 2009). Mobley and Wester (2007) found that only 30% of practicing clinicians reported reading and integrating research into their work; therefore, early introduction to research may also aid in diminishing the research–practice gap within the counseling profession. The cultivation of a strong RI may begin through exposure to research and scholarly activity at the master’s level (Gibson et al., 2010). More recently, early introduction to research activity and counseling literature at the master’s level is supported within the 2016 CACREP Standards (2015), specifically the infusion of current literature into counseling courses (Standard 2.E.) and training in research and program evaluation (Standard 2.F.8.). Therefore, we may see a shift in the research–practice gap based on these included standards in years to come.
Jorgensen and Duncan (2015) used grounded theory to better understand how RI develops within master’s-level counseling students (n = 12) and clinicians (n = 5). The manner in which participants viewed research, whether as separate from their counselor identity or as fluidly woven throughout, influenced the development of a strong RI. Further, participants’ views and beliefs about research were directly influenced by external factors such as training program expectations, messages received from faculty and supervisors, and academic course requirements. Beginning the process of RI development during master’s-level training may support more advanced RI development for those who pursue doctoral training.
Through photo elicitation and individual interviews, Lamar and Helm (2017) sought to gain a deeper understanding of CEDS’ RI experiences. Their findings highlighted several facets of the internal processes associated with RI development, including inconsistency in research self-efficacy, integration of RI into existing identities, and finding methods of contributing to the greater good through research. The role of external support during the doctoral program was also a contributing factor to RI development, with multiple participants noting the importance of family and friend support in addition to faculty support. Although this study highlighted many facets of RI development, much of the discussion focused on CEDS’ internal processes, rather than the role of specific experiences within their doctoral programs.
Research Training Environment
Literature is emerging related to specific elements of counselor education doctoral programs that most effectively influence RI. Further, there is limited research examining individual characteristics of CEDS that may support the cultivation of a strong RI. One of the more extensively reviewed theories related to RI cultivation is the belief that the research training environment, specifically the program faculty, holds the most influence and power over the strength of a doctoral student’s RI (Gelso et al., 2013). Gelso et al. (2013) also hypothesized that the research training environment directly affects students’ research attitudes, self-efficacy, and eventual productivity. Additionally, Gelso et al. outlined factors in the research training environment that influence a strong RI, including (a) appropriate and positive faculty modeling of research behaviors and attitudes, (b) positive reinforcement of student scholarly activities, (c) the emphasis of research as a social and interpersonal activity, and (d) emphasizing all studies as imperfect and flawed. Emphasis on research as a social and interpersonal activity consistently received the most powerful support in cultivating RI. This element of the research training environment may speak to the positive influence of working on research teams or in mentor and advising relationships (Gelso et al., 2013).
To date, there are limited studies that have addressed the specific doctoral program experiences and personal characteristics of CEDS that may lead to a strong and enduring RI. The purpose of this study was to: (a) gain a better understanding of CEDS’ RI development process during their doctoral program, and (b) identify specific experiences that influenced CEDS’ development as researchers. The research questions guiding the investigation were: 1) How do CEDS understand RI? and 2) How do CEDS develop as researchers during their doctoral program?
Method
We used grounded theory design for our study because of the limited empirical data about how CEDS develop an RI. Grounded theory provides researchers with a framework to generate a theory from the context of a phenomenon and offers a process to develop a model to be used as a theoretical foundation (Charmaz, 2014; Corbin & Strauss, 2008). Prior to starting our investigation, we received IRB approval for this study.
Research Team and Positionality
The core research team consisted of one Black female in the second year of her doctoral program, one White female in the first year of her doctoral program, and one White female in her third year as an assistant professor. A White male in his sixth year as an assistant professor participated as the internal auditor, and a White male in his third year as a clinical assistant professor participated as the external auditor. Both doctoral students had completed two courses that covered qualitative research design, and all three faculty members had experience utilizing grounded theory. Prior to beginning our work together, we discussed our beliefs and experiences related to RI development. All members of the research team were in training to be or were counselor educators and researchers, and we acknowledged this as part of our positionality. We all agreed that we value research as part of our roles as counselor educators, and we discussed our beliefs that the primary purpose of pursuing a doctoral degree is to gain skills as a researcher rather than an advanced counselor. We acknowledged the strengths that our varying levels of professional experiences provided to our work on this project, and we also recognized the power differential within the research team; thus, we added auditors to help ensure trustworthiness. All members of the core research team addressed their biases and judgments regarding participants’ experiences through bracketing and memoing to ensure that participants’ voices were heard with as much objectivity as possible (Hays & Wood, 2011). We recorded our biases and expectations in a meeting prior to data collection. Furthermore, we continued to discuss assumptions and biases in order to maintain awareness of the influence we may have on data analysis (Charmaz, 2014). Our assumptions included (a) the influence of length of time in a program, (b) the impact of mentoring, (c) how participants’ research interests would mirror their mentors’, (d) that beginning students may not be able to articulate or identify the difference between professional identity and RI, (e) that CEDS who want to pursue academia may identify more as researchers than in other roles (i.e., teaching, supervision), and (f) that coursework and previous experience would influence RI. Each step of the data analysis process provided us the opportunity to revisit our biases.
Participants and Procedure
Individuals who were currently enrolled in CACREP-accredited counselor education and supervision doctoral programs were eligible for participation in the study. We used purposive sampling (Glesne, 2011) to strategically contact eight doctoral program liaisons at CACREP-accredited doctoral programs via email to identify potential participants. The programs were selected to represent all regions and all levels of Carnegie classification. The liaisons all agreed to forward an email that included the purpose of the study and criteria for participation. A total of 11 CEDS responded to the email, met selection criteria, and participated in the study. We determined that 11 participants was an adequate sample size considering data saturation was reached during the data analysis process (Creswell, 2007). Participants represented eight different CACREP-accredited doctoral programs across six states. At the time of the interviews, three participants were in the first year of their program, five were in their second year, and three were in their third year. To prevent identification of participants, we report demographic data in aggregate form. The sample included eight women and three men who ranged in age from 26–36 years (M = 30.2). Six participants self-identified as White (non-Hispanic), three as multiracial, one as Latinx, and one as another identity not specified. All participants held a master’s degree in counseling; they entered their doctoral programs with 0–5 years of post-master’s clinical experience (M = 1.9). Eight participants indicated a desire to pursue a faculty position, two indicated a desire to pursue academia while also continuing clinical work, and one did not indicate a planned career path. Of those who indicated post-doctoral plans, seven participants expected to pursue a faculty role within a research-focused institution and three indicated a preference for a teaching-focused institution. All participants had attended and presented at a state or national conference within the past 3 years, with the number of presentations ranging from three to 44 (M = 11.7). Nine participants had submitted manuscripts to peer-reviewed journals and had at least one manuscript published or in press. Finally, four participants had received grant funding.
Data Collection
We collected data through a demographic questionnaire and semi-structured individual interviews. The demographic questionnaire consisted of nine questions focused on general demographic characteristics (i.e., gender, age, race, and education). Additionally, we asked questions focused on participants’ experiences as researchers (i.e., professional organization affiliations, service, conference presentations, publications, and grant experience). These questions were used to triangulate the data. The semi-structured interviews consisted of eight open-ended questions asked in sequential order to promote consistency across participants (Heppner et al., 2016) and we developed them from existing literature. Examples of questions included: 1) How would you describe your research identity? 2) Identify or talk about things that happened during your doctoral program that helped you think of yourself as a researcher, and 3) Can you talk about any experiences that have created doubts about adopting the identity of a researcher? The two doctoral students on the research team conducted the interviews via phone. Interviews lasted approximately 45–60 minutes and were audio recorded. After all interviews were conducted, a member of the research team transcribed the interviews.
Data Analysis and Trustworthiness
We followed grounded theory data analysis procedures outlined by Corbin and Strauss (2008). Prior to data analysis, we recorded biases, read through all of the data, and discussed the coding process to ensure consistency. We followed three steps of coding: 1) open coding, 2) axial coding, and 3) selective coding. Our first step of data analysis was open coding. We read through the data several times and then started to create tentative labels for chunks of data that summarized what we were reading. We recorded examples of participants’ words and established properties of each code. We then coded line-by-line together using the first participant transcript in order to have opportunities to check in and share and compare our open codes. Then we individually coded the remainder of the participants and came back together as a group to discuss and memo. We developed a master list of 184 open codes.
Next, we moved from inductive to deductive analysis using axial coding to identify relationships among the open codes. We identified relationships among the open codes and grouped them into categories. Initially we created a list of 55 axial codes, but after examining the codes further, we made a team decision to collapse them to 19 axial codes that were represented as action-oriented tasks within our theory (see Table 1).
Last, we used selective coding to identify core variables that include all of the data. We found that two factors and four subfactors most accurately represent the data (see Figure 1). The auditor was involved in each step of coding and provided feedback throughout. To enhance trustworthiness and manage bias when collecting and analyzing the data, we applied several strategies: (a) we recorded memos about our ideas about the codes and their relationships (i.e., reflexivity; Morrow, 2005); (b) we used investigator triangulation (i.e., involving multiple investigators to analyze the data independently, then meeting together to discuss; Archibald, 2015); (c) we included an internal and external auditor to evaluate the data (Glesne, 2011; Hays & Wood, 2011); (d) we conducted member checking by sending participants their complete transcript and summary of the findings, including the visual (Creswell & Miller, 2000); and (e) we used multiple sources of data (i.e., survey questions on the demographic form; Creswell, 2007) to triangulate the data.
Table 1
List of Factors and Subfactors
Factor 1: Research Identity Formation as a Process
unable to articulate what research identity is
linking research identity to their research interests or connecting it to their professional experiences
associating research identity with various methodologies
identifying as a researcher
understanding what a research faculty member does
Factor 2: Value and Interest in Research
desiring to conduct research
aspiring to maintain a degree of research in their future role
making a connection between research and practice and contributing to the counseling field
Subfactor 1: Intentional Program Design
implementing an intentional curriculum
developing a research culture (present and limited)
active faculty mentoring and modeling of research
Subfactor 2: Research Content Knowledge
understanding research design
building awareness of the logistics of a research study
learning statistics
Subfactor 3: Research Experiential Learning
engaging in scholarly activities
conducting independent research
having a graduate research assistantship
Subfactor 4: Research Self-Efficacy
receiving external validation
receiving growth-oriented feedback (both negative and positive)
Figure 1
Model of CEDS’ Research Identity Development
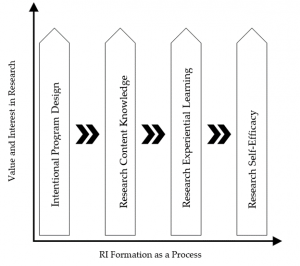
Results
Data analysis resulted in a grounded theory composed of two main factors that support the overall process of RI development among CEDS: (a) RI formation as a process and (b) value and interest in research. The first factor is the foundation of our theory because it describes RI development as an ongoing, formative process. The second main factor, value and interest in research, provides an interpersonal approach to RI development in which CEDS begin to embrace “researcher” as a part of who they are.
Our theory of CEDS’ RI development is represented visually in Figure 1. At each axis of the figure, the process of RI is represented longitudinally, and the value and interest in research increases during the process. The four subfactors (i.e., program design, content knowledge, experiential learning, and self-efficacy) contribute to each other but are also independent components that influence the process and the value and interest. Each subfactor is represented as an upward arrow, which supports the idea within our theory that each subfactor increases through the formation process. Each of these subfactors includes components that are specific action-oriented tasks (see Table 1). In order to make our findings relevant and clear, we have organized them by the two research questions that guided our study. To bring our findings to life, we describe the two major factors, four subfactors, and action-oriented tasks using direct quotes from the participants.
Research Question 1: How Do CEDS Describe RI?
Two factors supported this research question: RI formation as a process and value and interest in research.
Factor 1: Research Identity Formation as a Process
Within this factor we identified five action-oriented tasks: (a) being unable to articulate what research identity is, (b) linking research identity to their research interests or connecting it to their professional experiences, (c) associating research identity with various methodologies, (d) identifying as a researcher, and (e) understanding what a research faculty member does. Participants described RI as a formational process. Participant 10 explained, “I still see myself as a student. . . . I still feel like I have a lot to learn and I am in the process of learning, but I have a really good foundation from the practical experiences I have had [in my doctoral program].” When asked how they would describe RI, many were unable to articulate what RI is, asking for clarification or remarking on how they had not been asked to consider this before. Participants often linked RI to their research interests or professional experiences. For example, Participant 11 said, “in clinical practice, I centered around women and women issues. Feminism has come up as a product of other things being in my PhD program, so with my dissertation, my topic is focused on feminism.” Several participants associated RI with various methodologies, including Participant 7: “I would say you know in terms of research methodology and what not, I strongly align with quantitative research. I am a very quantitative-minded person.” Some described this formational process as the transition to identifying as a researcher:
I actually started a research program in my university, inviting or matching master’s students who were interested in certain research with different research projects that were available. So that was another way of me kind of taking on some of that mentorship role in terms of research. (Participant 9)
As their RI emerged, participants understood what research-oriented faculty members do:
Having faculty talk about their research and their process of research in my doc program has been extremely helpful. They talk about not only what they are working on but also the struggles of their process and so they don’t make it look glamorous all the time. (Participant 5)
Factor 2: Value and Interest in Research
All participants talked about the value and increased interest in research as they went through their doctoral program. We identified three action-oriented tasks within this factor: (a) desiring to conduct research, (b) aspiring to maintain a degree of research in their future role, and (c) making a connection between research and practice and contributing to the counseling field. Participant 6 described, “Since I have been in the doctoral program, I have a bigger appreciation for the infinite nature of it (research).” Participants spoke about an increased desire to conduct research; for example, “research is one of the most exciting parts of being a doc student, being able to think of a new project and carrying out the steps and being able to almost discover new knowledge” (Participant 1). All participants aspired to maintain a degree of research in future professional roles after completion of their doctoral programs regardless of whether they obtained a faculty role at a teaching-focused or research-focused university. For example, Participant 4 stated: “Even if I go into a teaching university, I have intentions in continuing very strongly my research and keeping that up. I think it is very important and it is something that I like doing.” Additionally, participants started to make the connection between research and practice and contributing to the counseling profession:
I think research is extremely important because that is what clinicians refer to whenever they have questions about how to treat their clients, and so I definitely rely upon research to understand views in the field and I value it myself so that I am more well-rounded as an educator. (Participant 6)
Research Question 2: How Do CEDS Develop Their RI During Their Doctoral Program?
The following four subfactors provided a description of how CEDS develop RI during their training: intentional program design, research content knowledge, research experiential learning, and research self-efficacy. Each subfactor contains action-oriented tasks.
Subfactor 1: Intentional Program Design
Participants discussed the impact the design of their doctoral program had on their development as researchers. They talked about three action-oriented tasks: (a) implementing an intentional curriculum, (b) developing a research culture (present and limited), and (c) active faculty mentoring and modeling of research. Participants appreciated the intentional design of the curriculum. For example, Participant 5 described how research was highlighted across courses: “In everything that I have had to do in class, there is some form of needing to produce either a proposal or being a good consumer of research . . . it [the value of research] is very apparent in every course.” Additionally, participants talked about the presence or lack of a research culture. For example, Participant 2 described how “at any given time, I was working on two or three projects,” whereas Participant 7 noted that “gaining research experience is not equally or adequately provided to our doctoral students.” Some participants discussed being assigned a mentor, and others talked about cultivating an organic mentoring relationship through graduate assistantships or collaboration with faculty on topics of interest. However, all participants emphasized the importance of faculty mentoring:
I think definitely doing research with the faculty member has helped quite a bit, especially doing the analysis that I am doing right now with the chair of our program has really helped me see research in a new light, in a new way, and I have been grateful for that. (Participant 1)
The importance of modeling of research was described in terms of faculty actually conducting their own research. For example, Participant 11 described how her professor “was conducting a research study and I was helping her input data and write and analyze the data . . . that really helped me grapple with what research looks like and is it something that I can do.” Participant 10 noted how peers conducting research provided a model:
Having that peer experience (a cohort) of getting involved in research and knowing again that we don’t have to have all of the answers and we will figure it out and this is where we all are, that was also really helpful for me and developing more confidence in my ability to do this [research].
Subfactor 2: Research Content Knowledge
All participants discussed the importance of building their research content knowledge. Research content knowledge consisted of three action-oriented tasks: (a) understanding research design, (b) building awareness of the logistics of a research study, and (c) learning statistics. Participant 1 described their experience of understanding research design: “I think one of the most important pieces of my research identity is to be well-rounded and [know] all of the techniques in research designs.” Participants also described developing an awareness of the logistics of research study, ranging from getting IRB approval to the challenges of data collection. For example, Participant 9 stated:
Seeing what goes into it and seeing the building blocks of the process and also really getting that chance to really think about the study beforehand and making sure you’re getting all of the stuff to protect your clients, to protecting confidentiality, those kind of things. So I think it is kind of understanding more about the research process and also again what goes into it and what makes the research better.
Participants also explained how learning statistics was important; however, a fear of statistics was a barrier to their learning and development. Participant 2 said, “I thought before I had to be a stats wiz to figure anything out, and I realize now that I just have to understand how to use my resources . . . I don’t have to be some stat wiz to actually do [quantitative research].”
Subfactor 3: Research Experiential Learning
Research experiential learning describes actual hands-on experiences participants had related to research. Within our theory, three action-oriented tasks emerged from this subfactor: (a) engaging in scholarly activities, (b) conducting independent research, and (c) having a graduate research assistantship. Engaging in scholarly activities included conducting studies, writing for publication, presenting at conferences, and contributing to or writing a grant proposal. Participant 5 described the importance of being engaged in scholarly activities through their graduate assistantship:
I did have a research graduate assistantship where I worked under some faculty and that definitely exposed me to a higher level of research, and being exposed to that higher level of research allowed me to fine tune how I do research. So that was reassuring in some ways and educational.
Participants also described the importance of leading and conducting their own research via dissertation or other experiences during their doctoral program. For example, Participant 9 said:
Starting research projects that were not involving a faculty member I think has also impacted my work a lot, I learned a lot from that process, you know, having to submit [to] an IRB, having to structure the study and figure out what to do, and so again learning from mistakes, learning from experience, and building self-efficacy.
Subfactor 4: Research Self-Efficacy
The subfactor of research self-efficacy related to the process of participants being confident in identifying themselves and their skills as researchers. We found two action-oriented tasks related to research self-efficacy: (a) receiving external validation and (b) receiving growth-oriented feedback (both negative and positive). Participant 3 described their experience of receiving external validation through sources outside of their doctoral program as helpful in building confidence as a researcher:
I have submitted and have been approved to present at conferences. That has boosted my confidence level to know that they know I am interested in something and I can talk about it . . . that has encouraged me to further pursue research.
Participant 8 explained how receiving growth-oriented feedback on their research supported their own RI development: “People stopped by [my conference presentation] and were interested in what research I was doing. It was cool to talk about it and get some feedback and hear what people think about the research I am doing.”
Discussion
Previous researchers have found RI within counselor education to be an unclear term (Jorgensen & Duncan, 2015; Lamar & Helm, 2017). Although our participants struggled to define RI, our participants described RI as the process of identifying as a researcher, the experiences related to conducting research, and finding value and interest in research. Consistent with previous findings (e.g., Ponterotto & Grieger, 1999), we found that interest in and value of research is an important part of RI. Therefore, our qualitative approach provided us a way to operationally define CEDS’ RI as a formative process of identifying as a researcher that is influenced by the program design, level of research content knowledge, experiential learning of research, and research self-efficacy.
Our findings emphasize the importance of counselor education and supervision doctoral program design. Similar to previous researchers (e.g., Borders et al., 2019; Carlson et al., 2006; Dollarhide et al., 2013; Protivnak & Foss, 2009), we found that developing a culture of research that includes mentoring and modeling of research is vital to CEDS’ RI development. Lamar and Helm (2017) also noted the valuable role faculty mentorship and engagement in research activities, in addition to research content knowledge, has on CEDS’ RI development. Although Lamar and Helm noted that RI development may be enhanced through programmatic intentionality toward mentorship and curriculum design, they continually emphasized the importance of CEDS initiating mentoring relationships and taking accountability for their own RI development. We agree that individual initiative and accountability are valuable and important characteristics for CEDS to possess; however, we also acknowledge that student-driven initiation of such relationships may be challenging in program cultures that do not support RI or do not provide equitable access to mentoring and research opportunities.
Consistent with recommendations by Gelso et al. (2013) and Borders et al. (2014), building a strong foundation of research content knowledge (e.g., statistics, design) is an important component of CEDS’ RI development. Unlike Borders and colleagues, our participants did not discuss how who taught their statistics courses made a difference. Rather, participants discussed the value of experiential learning (i.e., participating on a research team), and conducting research on their own influenced how they built their content knowledge. This finding is similar to Carlson et al.’s (2006) and supports Borders et al.’s findings regarding the critical importance of early research involvement for CEDS.
Implications for Practice
Our grounded theory provides a clear, action-oriented model that consists of multiple tasks that can be applied in counselor education doctoral programs. Given our findings regarding the importance of experiential learning, we acknowledge the importance for increased funding to ensure CEDS are able to focus on their studies and immerse themselves in research experiences. Additionally, design of doctoral programs is crucial to how CEDS develop as researchers. Findings highlight the importance of faculty members at all levels being actively involved in their own scholarship and providing students with opportunities to be a part of it. In addition, we recommend intentional attention to mentorship as an explicit program strategy for promoting a culture of research. Findings also support the importance of coursework for providing students with relevant research content knowledge they can use in research and scholarly activities (e.g., study proposal, conceptual manuscript, conference presentation). Additionally, we recommend offering a core of research courses that build upon one another to increase research content knowledge and experiential application. More specifically, this may include a research design course taught by counselor education faculty at the beginning of the program to orient students to the importance of research for practice; such a foundation may help ensure students are primed to apply skills learned in more technical courses. Finally, we suggest that RI development is a process that is never complete; therefore, counselor educators are encouraged to continue to participate in professional development opportunities that are research-focused (e.g., AARC, ACES Inform, Evidence-Based School Counseling Conference, AERA). More importantly, it should be the charge of these organizations to continue to offer high quality trainings on a variety of research designs and advanced statistics.
Implications for Future Research
Replication or expansion of our study is warranted across settings and developmental levels. Specifically, it would be interesting to examine RI development of pre-tenured faculty and tenured faculty members to see if our model holds or what variations exist between these populations. Or it may be beneficial to assess the variance of RI based on the year a student is in the program (e.g., first year vs. third year). Additionally, further quantitative examination of relationships between each component of our theory would be valuable to understand the relationship between the constructs more thoroughly. Furthermore, pedagogical interventions, such as conducting a scholarship of teaching and learning focused on counselor education doctoral-level research courses, may be valuable in order to support their merit.
Limitations
Although we engaged in intentional practices to ensure trustworthiness throughout our study, there are limitations that should be considered. Specifically, all of the authors value and find research to be an important aspect of counselor education and participants self-selected to participate in the research study, which is common practice in most qualitative studies. However, self-selection may present bias in the findings because of the participants’ levels of interest in the topic of research. Additionally, participant selection was based on those who responded to the email and met the criteria; therefore, there was limited selection bias of the participants from the research team. Furthermore, participants were from a variety of programs and their year in their program (e.g., first year) varied; all the intricacies within each program cannot be accounted for and they may contribute to how the participants view research. Finally, the perceived hierarchy (i.e., faculty and students) on the research team may have contributed to the data analysis process by students adjusting their analysis based on faculty input.
Conclusion
In summary, our study examined CEDS’ experiences that helped build RI during their doctoral program. We interviewed 11 CEDS who were from eight CACREP-accredited doctoral programs from six different states and varied in the year of their program. Our grounded theory reflects the process-oriented nature of RI development and the influence of program design, research content knowledge, experiential learning, and self-efficacy on this process. Based on our findings, we emphasize the importance of mentorship and faculty conducting their own research as ways to model the research process. Additionally, our theory points to the need for increased funding for CEDS in order for them to be immersed in the experiential learning process and research courses being tailored to include topics specific to counselor education and supervision.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Archibald, M. (2015). Investigator triangulation: A collaborative strategy with potential for mixed methods research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 10(3), 228–250.
Association for Assessment and Research in Counseling. (2019). About us. http://aarc-counseling.org/abo
ut-us
Borders, L. D., Gonzalez, L. M., Umstead, L. K., & Wester, K. L. (2019). New counselor educators’ scholarly productivity: Supportive and discouraging environments. Counselor Education and Supervision, 58(4), 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12158
Borders, L. D., Wester, K. L., Fickling, M. J., & Adamson, N. A. (2014). Research training in CACREP-accredited doctoral programs. Counselor Education and Supervision, 53, 145–160.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2014.00054.x
Carlson, L. A., Portman, T. A. A., & Bartlett, J. R. (2006). Self-management of career development: Intentionality for counselor educators in training. The Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 45(2), 126–137.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-1939.2006.tb00012.x
Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing grounded theory (2nd ed.). SAGE.
Corbin, J., & Strauss, A. (2008). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2015). 2016 CACREP standards. http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/2016-Standards-with-citations.pdf
Creswell, J. W. (2007). Qualitative inquiry & research design: Choosing among five approaches (2nd ed.). SAGE.
Creswell, J. W., & Miller, D. L. (2000). Determining validity in qualitative inquiry. Theory Into Practice, 39(3), 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip3903_2
Dollarhide, C. T., Gibson, D. M., & Moss, J. M. (2013). Professional identity development of counselor education doctoral students. Counselor Education and Supervision, 52(2), 137–150.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2013.00034.x
Gelso, C. J., Baumann, E. C., Chui, H. T., & Savela, A. E. (2013). The making of a scientist-psychotherapist: The research training environment and the psychotherapist. Psychotherapy, 50(2), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028257
Gibson, D. M., Dollarhide, C. T., & Moss, J. M. (2010). Professional identity development: A grounded theory of transformational tasks of new counselors. Counselor Education and Supervision, 50(1), 21–38. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2010.tb00106.x
Glesne, C. (2011). Becoming qualitative researchers: An introduction (4th ed.). Pearson.
Hays, D. G., & Wood, C. (2011). Infusing qualitative traditions in counseling research designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89(3), 288–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00091.x
Heppner, P. P., Wampold, B. E., Owen, J., Thompson, M. N., & Wang, K. T. (2016). Research design in counseling (4th ed.). Cengage.
Hughes, F. R., & Kleist, D. M. (2005). First-semester experiences of counselor education doctoral students. Counselor Education and Supervision, 45(2), 97–108.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2005.tb00133.x
Jorgensen, M. F., & Duncan, K. (2015). A grounded theory of master’s-level counselor research identity. Counselor Education and Development, 54(1), 17–31.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2015.00067.x
Lamar, M. R., & Helm, H. M. (2017). Understanding the researcher identity development of counselor education and supervision doctoral students. Counselor Education and Supervision, 56(1), 2–18.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12056
Lambie, G. W., Ascher, D. L., Sivo, S. A., & Hayes, B. G. (2014). Counselor education doctoral program faculty members’ refereed article publications. Journal of Counseling & Development, 92(3), 338–346. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6676.2014.00161.x
Mobley, K., & Wester, K. L. (2007). Evidence-based practices: Building a bridge between researchers and practitioners. Association for Counselor Education and Supervision.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52(2), 250–260. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.52.2.250
Murray, C. E. (2009). Diffusion of innovation theory: A bridge for the research-practice gap in
counseling. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87(1), 108–116.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2009.tb00556.x
Ponterotto, J. G., & Grieger, I. (1999). Merging qualitative and quantitative perspectives in a research identity. In M. Kopala & L. A. Suzuki (Eds.), Using qualitative methods in psychology (pp. 49–62). SAGE.
Protivnak, J. J., & Foss, L. L. (2009). An exploration of themes that influence the counselor education doctoral student experience. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48(4), 239–256.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2009.tb00078.x
Reisetter, M., Korcuska, J. S., Yexley, M., Bonds, D., Nikels, H., & McHenry, W. (2011). Counselor educators and qualitative research: Affirming a research identity. Counselor Education and Supervision, 44(1), 2–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2004.tb01856.x
Dodie Limberg, PhD, is an associate professor at the University of South Carolina. Therese Newton, NCC, is an assistant professor at Augusta University. Kimberly Nelson is an assistant professor at Fort Valley State University. Casey A. Barrio Minton, NCC, is a professor at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville. John T. Super, NCC, LMFT, is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Central Florida. Jonathan Ohrt is an associate professor at the University of South Carolina. Correspondence may be addressed to Dodie Limberg, 265 Wardlaw College Main St., Columbia, SC 29201, dlimberg@sc.edu.
Dec 16, 2020 | Volume 10 - Issue 4
Vanessa Kent, Helen Runyan, David Savinsky, Jasmine Knight
When the pursuit of doctoral studies and motherhood intersect, the risk of attrition increases. Although other studies have explored the challenges of student mothers in academia, this study looked at how mentorship might mediate them. This phenomenological study examined the mentoring experiences of doctoral student mothers or recent graduates in counselor education and supervision programs (N = 12). Unanimously, participants articulated that their professional identity was enhanced by their identity as mothers, but balancing multiple roles required supportive mentors. Participants described the personal qualities of effective faculty and peer mentors, many also mothers who understood their needs. Mentoring served as a protective factor in helping navigate barriers, providing academic and emotional encouragement, reducing isolation, and creating realistic timelines. Suggestions for mentoring programs and advocacy are discussed.
Keywords: mentoring, doctoral student mothers, counselor education, phenomenology, advocacy
Over the past decade, surveys have indicated incoming doctoral students are less traditional than previous generations (National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics [NCSES], 2017; Offerman, 2011). These students (e.g., women, minorities, and international students) may experience cultural maladjustment while attending traditionally structured academic institutions (Holley & Caldwell, 2012; Ku et al., 2008; NCSES, 2017). This may lead to dissatisfaction, isolation, and subsequent attrition (Holley & Caldwell, 2012; Ku et al., 2008; NCSES, 2017; Offerman, 2011; Stimpson & Filer, 2011).
Focusing on women, the number earning doctoral degrees has steadily increased over the past 20 years (NCSES, 2017). Percentages reached a record high in 2008–2009 as women earned slightly over 50% of all doctoral degrees, except in male-dominated fields, including engineering, mathematics, and physical science (Miller & Wai, 2015; NCSES, 2015). Furthermore, with a ratio of six females to one male completing bachelor’s and master’s degree programs yearly, the majority of those entering the doctoral pipeline are expected to be female (Miller & Wai, 2015). These incoming female doctoral students are likely to be in their prime childbearing years, in dual-income households if married, and caring for dependents (Lester, 2013; Offerman, 2011; Stimpson & Filer, 2011). Finding ways to assist these doctoral student mothers in completing a doctorate requires further investigation.
Although earning a degree in higher education can bring personal satisfaction, higher professional status, and economic gains, the process can also result in unforeseen stress and challenges to work–life balance, leading to dissatisfaction and attrition (Brus, 2006; Lynch, 2008; Martinez et al., 2013; Offerman, 2011; Stimpson & Filer, 2011). Despite the rigorous selection process, attrition rates for doctoral students hover between 40%–60% (Council of Graduate Schools, 2010). Beyond academics, extenuating factors that contribute to the attrition of doctoral students include stress; financial hardship; commitment conflicts; unexpected life interruptions; mental and physical health issues; and changes in the family structure, including having children (Brus, 2006; Lynch, 2008; Martinez et al., 2013). When the doctoral student is a new mother or the primary caregiver, these factors become exacerbated (Brus, 2006; Holm et al., 2015; Lester, 2013; Lynch, 2008; Stimpson & Filer, 2011). Because of the structural design of higher education and cultural pressures of motherhood that seem at odds with each other, graduate student mothers are at higher risk of attrition than almost any other American academic group (Lester, 2013; Lynch, 2008).
Challenges Facing Doctoral Student Mothers
The challenges of student mothers navigating the competing roles of academic scholar and primary caretaker are well documented (Holm et al., 2015; Lester, 2013; Lynch, 2008; Pierce & Herlihy, 2013; Trepal et al., 2014). Mothers pursuing doctoral degrees may find balancing academics and employment a daily challenge, compounded by the second shift of childcare and housework (Lynch, 2008; Pierce & Herlihy, 2013; Stimpson & Filer, 2011). Despite movement toward an egalitarian view of child-rearing among contemporary couples, the burden of overseeing the household duties and childcare remain largely the mother’s responsibility (Lester, 2013; Medina & Magnuson, 2009; Misra et al., 2012). Student mothers juggling multiple roles report dissatisfaction in their work–life balance because of time and scheduling demands, as well as hindrances in the workplace and higher education (Brus, 2006; Holm et al., 2015; Lynch, 2008; Trepal et al., 2014). Research on support for this vulnerable population points to faculty and peer support as possible mitigating factors to attrition and dissatisfaction (Bruce, 1995; Holm et al., 2015; Trepal et al., 2014).
Mentoring Relationships That Mitigate Attrition
Research spanning almost two decades correlated strong advisor and mentor relationships with successful student outcomes (Bruce, 1995; Clark et al., 2000; Holley & Caldwell, 2012; Patton & Harper, 2003). Mentoring has been especially important for underrepresented populations such as international students; students of color; first-generation college graduates; women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines; and female students/faculty who were also mothers (Brown et al., 1999; Holm et al., 2015; Kendricks et al., 2013; Ku et al., 2008). A mentor is a person who provides professional and personal support to assist the less skilled mentee in becoming a full member of a particular profession (Brown et al., 1999; Clark et al., 2000). This study focuses on academic mentors, both formal and informal. Formal mentoring involves a faculty member, formally assigned to or requested by the student, whose roles may include but also extend well beyond that of an advisor, dissertation committee member, supervisor, or instructor (Hayes & Koro-Ljungberg, 2011; Patton & Harper, 2003). Informal mentoring can be categorized by who provides the mentoring: faculty or a peer. Informal faculty mentoring occurs as a faculty member organically connects with a student on common interests to provide support, often around motherhood, suggesting the importance of access to a faculty member who is also a mother (Hermann et al., 2014; Holm et al., 2015; Trepal et al., 2014). Peer mentoring provides that connection through an informal relationship between a more senior doctoral student and a junior doctoral student (Noonan et al., 2007). Peer mentoring may occur as part of a structured program, but it more often occurs organically as upperclassmen fill this need through joint interests, scholarly activities, or motherhood (Lynch, 2008; Noonan et al., 2007).
Shifting from a traditional hierarchical model, relational mentoring encompasses not only the advising relationship to promote career and professional development but also the genuine empathic relationship that emerges from a reciprocal, collaborative approach (Gammel & Rutstein-Riley, 2016; Kelch-Oliver et al., 2013). Results are greater accessibility to the mentor, opportunities to share knowledge in research and publishing, extended support to students, knowing students on a more personal level, fostering friendships, and building community (Brown et al., 1999; Bruce, 1995; Hadjioannou et al., 2007; Hayes & Koro-Ljungberg, 2011). Benefits of relational mentoring include mutual growth opportunities for both the mentor and mentee, greater academic achievement, personal satisfaction, and increased social and emotional support (Gammel & Rutstein-Riley, 2016; Kelch-Oliver et al., 2013).
Connections with other student mothers is an important support mechanism, reducing isolation with increased social support (Hermann et al., 2014; Lynch, 2008; Patton & Harper, 2003; Trepal et al., 2014). Chief factors influencing female doctoral students’ satisfaction in their programs were female faculty and peers serving in supportive/mentoring roles, sharing resources (such as childcare), addressing stress, and encouraging healthy choices around family life (Bruce, 1995; Brus, 2006; Holm et al., 2015; Trepal et al., 2014). Studies specific to African American women in psychology found that same race/gender mentorship was imperative in recruitment, retention, and training of this population (Kelch-Oliver et al., 2013; Patton, 2009).
Female mentorship may be an untapped resource in counselor education and supervision (CES), as there is little research exploring the mentoring of doctoral student mothers (Bruce, 1995; Holm et al., 2015; Trepal et al., 2014). Without clear guidelines on how mentoring might support doctoral student mothers, current mentoring programs and training practices may be inadequate. In this study, we sought to investigate the mentoring experiences of students who were navigating the dual roles of mother and student in CES programs. Although past studies have explored mentoring programs of doctoral students (Clark et al., 2000; Holley & Caldwell, 2012; Ku et al., 2008) and the experiences of student mothers in doctoral programs (Holm et al., 2015; Trepal et al. 2014), we sought to determine how mentoring benefits doctoral student mothers.
Method
Qualitative research is a suitable choice for investigating questions pertinent to counselor education, as it lends itself to rich data collection through interactions between the researcher and participants (Hays & Singh, 2012). A subset of qualitative research, phenomenological research is aimed at increasing understanding of the complexity of people’s lives by examining the individual and collective experience of a particular phenomenon (Creswell, 2013). We chose a phenomenological approach to understand how student mothers experienced mentoring while in a CES program. This seemed to be the best lens through which to explore our research question: What is the lived experience of doctoral student mothers formally or informally mentored by faculty and/or peers? With a greater understanding of this phenomenon, counselor educators may apply this knowledge in recognizing and meeting the needs of student mothers to reduce attrition.
Research Team
Our research team consisted of a doctoral student mother (first author and now a faculty member) and three faculty members in a CACREP-accredited CES program at a small, private university. During their doctoral studies, two of the three women were mothers of young children and the male faculty member became a first-time father. Currently, the faculty researchers are advancing through their tenure track while parenting elementary-age children.
Before the study, we met as a team to discuss our experiences of mentorship as students and junior faculty as well as how we experienced the climate of our institution toward families. The first author shared that her research interest grew out of her own experience as well as the struggles of doctoral student mothers in her cohort, necessitating support from peers and faculty members. Eager to learn how doctoral student mothers experienced faculty and peer mentoring across institutions, we watched this study begin to take shape. Acknowledging our biases and bracketing our assumptions, we set them aside to allow a fresh perspective of the participants’ experiences to emerge. LeVasseur (2003) described this process of bracketing as suspending understanding of the topic to shift toward a position of curiosity.
Procedure and Participants
After receiving approval from the university’s Human Subject Review Committee, we recruited participants using a professional counseling electronic mailing (CESNET-L) and by emailing CES department heads at four universities in the Eastern United States. The email provided criteria for the study with a link to the demographic questionnaire and informed consent form. Criteria included: (a) completed at least one year of doctoral studies in a CACREP-accredited CES program or had graduated within 2 years; (b) formally or informally mentored by faculty, peers, or both; and (c) mother of at least one child below the age of 18 residing with them during their counselor education doctoral training. Not wanting to limit participants because of location, we chose to interview participants using a telehealth video platform. This resulted in a wide geographical sample as shown in Table 1. University types included three Research 1, one historically Black college and university (HBCU), one hybrid, and seven liberal arts institutions. Twelve participants were selected to be interviewed based on meeting criteria and in keeping with sample size guidelines for phenomenological studies (Creswell, 2013). Participants ranged in age from 29–37 (M = 34, SD = 2.4). Participants identified racially as European American (n = 9) and African American (n = 3). Ten became pregnant during their doctoral studies: six were first-time mothers, and two miscarried twice. Children’s ages ranged from 10 months to 12 years, with most under the age of 3. In addition to being students, all participants were employed during their studies as school counselors, in private practice, or in agency clinical work. Six of the seven interviewees were employed as an adjunct professor, school counselor, researcher/consultant, program director of a counseling department, private practice counselor, and university counseling center director; the seventh was a new doctoral graduate.
Table 1
Participant Demographic Information
| Geographic
Location |
Status in CES
Program |
Pregnant While in Program |
Ages of Participants’ Children |
Type of Mentor
by Gender |
| Midwest |
2 |
2nd year |
2 |
1st year |
2 |
3 years or under |
6 |
Faculty |
Female: 16
Male: 4 |
| Northeast |
2 |
3rd year |
3 |
2nd year |
3 |
4–6 years old |
6 |
Peer |
Female: 13 |
| Northwest |
2 |
Graduated
< 6 months |
5 |
3rd year |
4 |
7–12 years old |
4 |
Supervisor |
Female: 7 |
| Southeast |
4 |
| Southwest |
2 |
Graduated
2 years |
2 |
4th year |
2 |
13 years old + |
1 |
Other |
Female: 1 |
Data Sources
Each participant completed a demographic questionnaire and signed an informed consent form for voluntary participation. The questionnaire inquired about age; sex; race/ethnicity; relationship status; length of time in the CES program; year graduated; if they were pregnant or adopted children and the number of children/their ages while in the program; and if they were mentored by faculty, peer, or both.
The first author conducted the 12 interviews through V-SEE, a Stanford-created, telehealth videoconferencing application that supports online collaboration. It allowed the participants and research interviewer to interact synchronously via audio and video. Interview length ranged from 60–75 minutes as participants described their mentoring experiences. The interview settings were descriptively “in the field,” as they were interviewed in their offices, cars, and homes. Three had their babies/toddlers with them during the home interviews. Participants described their university type, cohort structure, and employment status. The first author asked each participant open-ended questions using a semi-structured interview format developed from our review of the literature on mentoring, motherhood, and issues concerning doctoral student mothers. The questions included: (a) “What factors, if any, influenced your decision to be mentored?” (b) “Can you describe your mentoring experience in detail?” (c) “Can you speak to your work–study–life balance while being mentored?” (d) “Can you speak of your academic progress and/or professional development while being mentored?” (e) “Describe the characteristics or traits of a mentor that are important for doctoral student mothers,” and (f) “What, if anything, could a counselor education department do to promote successful mentoring experiences for doctoral student mothers?” With qualitative inquiry, the goal is to include enough participants to adequately understand the phenomenon in question (Hays & Singh, 2012). Wanting to capture a fresh perspective from these doctoral students who were mentored, many while becoming mothers for the first time, all 12 interviews were retained, yielding in-depth descriptions of their experiences. Pseudonyms were assigned to participants prior to data analysis to protect their identities.
Data Analysis
Phenomenological data analysis is concerned with examining participants’ experiences to understand the depth and meaning of those lived experiences (Hays & Singh, 2012; Moustakas, 1994). Delving into large amounts of transcription data, the goal is to develop a composite description or essence of the experience that represents the group as a whole (Moustakas, 1994). The first author began the inductive method of analysis by engaging in horizontalization, the process of identifying non-repetitive, non-overlapping statements from the first three interview transcripts (Hays & Singh, 2012; Moustakas, 1994). Next, the first author clustered these statements in units of meaning or themes and then wrote textual descriptions of “what” the participants experienced, including verbatim examples from the transcripts (Creswell, 2013; Moustakas, 1994). The first and second investigators met weekly to discuss and rework these themes. From there, they wrote a structural description, “how” the experience happened in the context of the setting or circumstances and who was involved (Creswell, 2013; Moustakas, 1994). The first author used these themes to analyze the rest of the transcripts with care given to reanalyzing previous interviews as new themes or subthemes emerged. The team met to finalize the central themes and subthemes that emerged collectively from the participants’ reflections, contextualizing them into a holistic understanding of the essence of the mentoring experience (Hays & Singh, 2012).
Validation strategies included recognizing and controlling for research bias through bracketing, capturing participants’ viewpoints through substantial engagement, and triangulation through cross-checking codes and themes and by using thick participant descriptions (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011; Lincoln & Guba, 1985). Using basic member checking, participants reviewed their transcripts for accuracy, with two making clarifying comments (Creswell, 2013; Hays & Singh, 2012). The first and second authors met weekly to process reflection notes to bracket any biases and discuss themes to allow triangulation of data (Creswell, 2013; Hays & Singh, 2012). The two other members of the team reviewed the themes/subthemes matched with descriptive statements for cross-checking purposes (Hays & Singh, 2012; Lincoln & Guba, 1985). To address confirmability and transferability, they kept an audit trail beginning with interview notes, transcripts, reflective journals, and coding pages with descriptive statements. Finally, the authors provided thick descriptions, allowing the reader to enter into the study to a greater degree to reach their own conclusions and stir further discourse around these critical issues in counselor education (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011).
Results
Three overarching themes centered on identity: the qualities and shifting identities of doctoral student mothers, the qualities and roles of faculty/professional and peer mentors, and the barriers and hardships that led to losses and unmet goals despite mentorship experiences. Participants shared how mentoring evolved around their identities as mothers, students, and professionals; what they experienced as support or discrimination by faculty and peers; how their mentors served as a protective factor despite hardships and barriers; and what was needed in terms of advocacy to successfully develop counselor educator identities.
Theme I: Identities and Qualities of Doctoral Student Mothers
Perseverance and resilience characterized the lived experiences of these doctoral student mothers facing unexpected challenges that threatened to slow progress or impede career goals. Sara, who found out she was pregnant shortly after being accepted into her doctoral program, shared, “I ended up having a really horrible labor and a C-section. My baby spent the first week in ICU. We were only home a short time after having major surgery, but I still went back to school 3 weeks later.” Natalie also shared her version of perseverance: “I took my comps when I was 38 weeks pregnant [laughter]. I had to keep standing up and going to the bathroom. ‘Then I said, I can have this baby now!’”
Making the shift from student to mother or mother to professional requires integrating multiple identities and corresponding roles. “I always had it drilled into my head by my mother that I would be called ‘doctor’ before I was called ‘mom.’ So many of us are both education-oriented and family-oriented, being in counseling,” remarked Allison. Similarly, Lisa voiced how she embraced her changing identity: “You grow in confidence as a person and through motherhood. Learning what worked and what didn’t work. Just having a better sense of myself, my strengths, knowing my worth, knowing my value, and just feeling secure in it.”
With the multiple identities came the challenge of meeting academic rigor and motherhood responsibilities, often with conflicting timelines. Although all the participants described themselves as serious students, they made it clear that their children were their number one priority. They willingly sacrificed time and personal needs in hopes of careers that offered greater flexibility and financial stability. “Yes, you’re exhausted because you are running a marathon every single day. At the end of the day, you don’t have that little space for yourself,” said Lisa. Mothers often felt the pull between having to choose work or studies and time with their families. Bethany, a school counselor, explained, “I struggle with mommy guilt even with my job, as my child is one of the first ones in the building and last ones to leave every day.” Bethany also recounted, “One of the biggest mom guilts is a picture of my child around the age of 5. I am sitting in a chair surrounded by books and papers as he fell asleep on the couch waiting for me to do something with him. That was really tough.” Amy described her typical schedule:
I get up at 6:00, play with the kids, get them off, and get to work . . . until 10:00 pm, kids come in my bed and snuggle. Then I finish grades and go to bed at 3:00 am. 100% of the weekends are dedicated to the children. Want them to say . . . ‘Mom was present.’ That’s hard when the career path and academics are so consuming.
Lisa felt inadequate in both roles at times: “I’m working so hard. . . . and I am not a good enough mom and I’m not a good enough student. . . . not doing a great job at anything.”
Several participants reported that their mentors helped them establish healthy boundaries and taught them how to prioritize commitments. Tonya shared, “Today is going to be about work . . . or today is going to be about school. I appreciated having faculty members who had young families, knowing that someone understood that.” When the demands of work became unhealthy, Bethany revealed it was her mentor who said, “You’ve got to reshuffle. You are drowning, and you are miserable. You have to let some of this school stuff go.” On prioritizing, Natalie shared, “When I went into this program, I said that I am not going to miss anything in my personal life, even if it takes 4 or 5 years.”
Doctoral student mothers commonly identified as non-traditional students. Not only was this gender-influenced, it was also the result of added caregiving responsibilities that prevented them from engaging in opportunities afforded to traditional students. They often felt isolated from their peers or labeled as less committed, which resulted in differential treatment and exclusions. Lisa explained:
I always felt like some kind of outlier . . . like all the other cohorts are like these tight little units. I’m always slipping in and then dropping back out. Would see them on Facebook all hanging out and going out for drinks . . . or they would be publishing or going to conferences. I was working and taking care of children.
On being non-traditional, Morgan, a mother of two, working 25–27 hours per week, shared, “No one in my cohort had children and none had outside jobs.” Several participants noted how their male counterparts were able to go full-time without having to deal with family-related interruptions, be questioned for having babies, experience guilt when traveling, or juggle as many commitments. Kayla, reflecting on experiencing negative remarks about her clingy child when she had to travel for work, noted, “They had wives that stayed at home, so their experience has been completely different.” On comparing her needs to those of traditional students, Lisa shared, “Mentoring for students who don’t have kids, it’s . . . talking about publishing together or presenting together. For me, it really is how are you helping me navigate this program.”
Theme II: Identities and Qualities of Effective Mentors
For all participants, mentoring was more than academic advising. Often, it was the mentor’s combined qualities of temperament, leadership, scholarship, and friendship that helped these doctoral student mothers navigate their programs effectively. Participants described the criteria for selecting their mentors: specific personality traits, women who were also mothers, who shared research interests, and those who modeled career–life balance. The three African American women also considered race an essential factor in mentor selection. Tonya, the sole woman of color in her cohort, connected with other African American faculty outside her department and graduates who were mothers, while Dana experienced mentoring by most of the faculty at her HBCU. Allison based her mentorship selection on personality: “I needed someone who doesn’t have my exact personality but who can keep my ideas focused and keep me on track—tough, but supportive.”
Some chose female mentors because they believed they would provide greater support and speak to the female experience in academia. Lisa’s mentor selection was through gender matching: “I chose the only woman in my program that has children . . . so I feel like she gets me, and she gets the experience of motherhood and has a great perspective on things.” Amy shared that her mentor “could speak to my strengths and could commiserate the experience of being a woman in academia.”
Participants described effective mentors as encouraging, supportive, and flexible, displaying qualities of warmth, empathy, and trustworthiness. Most depicted their mentors as master cheerleaders and challengers. Morgan explained that two mentors filled different roles: “I have the mentor’s office that I go cry into . . . and the office that I go in and come out sharper for. I think you need both of them.” Sharon chose four mentors: “One was especially about writing and research . . . one that was just about my self-care and well-being, and one primarily about the academics. . . . [and] one that kind of combined it all, but who I could talk to about the mommy guilt.”
Mentors provided a balance between the demand for excellence and practicality and compassion. Creative flexibility and realistic expectations without judgment rounded out the mentors’ qualities. Mentors were available beyond the usual office hours and willing to meet at convenient locations such as a coffee shop or home. Morgan commented on the open-door policy of her mentor: “Availability is important. You can walk in and talk . . . whether it is just casual conversation or coming in with a need.” Participants described how their mentors went above and beyond to provide creative accommodations. Lisa shared the flexibility of her mentor: “We co-taught and she would work around whatever my schedule was. We would have meetings after the kids went to bed. She really understood my situation and was just so affirming.”
Mentoring had a personal side that provided not only a safe interchange of ideas but allowed for vulnerability and transparency. As doctoral student mothers verbalized their hardships, their trusted mentors were not only an emotional outlet but a therapeutic balm providing empathy and care. Their mentors often shared similar lived experiences that created a deeper connection, emotional bonding, and lasting friendship. Sharon found comfort when she faced a personal challenge: “My youngest child was diagnosed with autism very early. When I went to my mentor, she shared that her child was diagnosed with autism as well. We were able to connect and really process our lives as working moms.” During hardships and personal challenges, mentors provided comfort and encouragement. Tonya shared how her mentor was there for her after her miscarriage: “I told [my mentor] that I had this little person inside of me and now I don’t. She started crying and asked me, ‘What do you need right now?’” Tonya’s mentor encouraged her to put off writing her comps for a semester to process the loss.
Effective mentors provided professional modeling and career guidance, being personally supportive while navigating the logistics of becoming a counselor educator. Mentors endorsed them for leadership positions, taught them how to negotiate salaries, and helped create a pathway for career satisfaction. On developing their professional identity, graduates were indebted to the mentors. Bethany explained how mentorship groomed her for research: “When I was accepted to the program, [my mentor] took me under her wing and said, ‘Let’s find a research project to do together.’ So we wrote a grant for it and she mentored me through that whole process.” Natalie explained how her mentor helped develop her professional identity: “She pushed me to see myself better. . . . something that women have a hard time doing is advocating for themselves in the workplace. She not only modeled that, but she taught me how to do it.”
Participants valued the family orientation of their mentors and voiced the need for their mentors to be family advocates. Without these advocates, many felt unequipped to compete with negative voices and dismissive attitudes. Allison shared her experience of feeling supported in her decision to get pregnant:
My advisor/mentor and I were having one of those heart-to-heart conversations. I actually started crying and said, “All my husband and I talk about is babies . . . every weekend. I’m ready; but education-wise, it just doesn’t seem like a possibility.” My advisor looked me straight in the eye and said, “If you want a baby, have a baby.” I shouldn’t have needed permission, but I wanted to know that I was going to be supported.
Mentors helped doctoral student mothers create timelines that respected their family needs as well as their academic and professional goals. Morgan’s mentor said, “We’ll navigate your schedule in an appropriate way that works for the program and for your family.” She then built her plan based upon her schedule and personal journey.
Effective mentoring paralleled hallmarks of counselor education in promoting wellness, advocacy, and empowerment. Seven of the 12 described how their mentors practiced good self-care and modeled positive well-being. Allison discussed how her mentor helped to put work–life balance in perspective: “She was a role model of balance. She would say, ‘You’re working too hard. You need to spend some time with your family.’ I have been able to come out of the program . . . [with] great work–life balance.” Mentors’ practice of self-care made it easier to emulate wellness practices and achieve greater work–life balance. Allison summed it up: “My mentor has this beautiful, wonderfully doting family. . . . Successful children, a supportive husband, and a career—that’s the type of woman I want to be.”
Participants described how mentoring served as a protective factor in reducing attrition. Their rich mentoring experiences helped them succeed in the program and manage the challenges of conflicting roles. Their mentors’ encouragement and support became their lifeline through transitions such as marriage, pregnancy, divorce, and illness. Mentors were especially protective of participants facing cultural or institutional barriers, advocating during their pregnancies and beyond. Allison described how she felt protected from other faculty by her mentor throughout her pregnancy: “I was tired a lot during my pregnancy. If other faculty members got upset that I wasn’t able to fulfill a requirement, she went to bat for me . . . supporting me by saying, ‘Well, in all fairness, she is pregnant.’”
Qualities of Peer Mentors
Three-fourths of the participants were peer mentored, having sought out peers who were also mothers. Although only two of the participants were involved in a peer mentoring program, all 12 conveyed the value of having a more senior member of their program available for questions, advice, encouragement, and engagement in academic activities. Many shared how mentors offered supportive advice, as they were familiar with the journey ahead. Nicole said, “Peer mentoring is beneficial because you get to see someone who has recently been there, and having others from older cohorts can provide help and insight.” Participants gravitated toward other mothers who understood their plight and built mentorships based on the common ground of motherhood intersecting with student life. Peer mentors shared their journeys, insider information on coursework, and realistic timelines; they became fellow presenters and publishers, and provided encouragement along the way. Bethany shared that she often wrote with a peer mentor who understood when she said, “Let’s have a realistic mom timeline.” Natalie shared the reciprocal nature of peer mentoring: “She and I relied a lot on each other just for support and mentorship. She had her baby 6 months before I did and I am learning a lot about the work–life balance and stuff from her.”
Peer mentorship was relational as well as academic. Several participants shared how peer mentoring helped reduce feelings of isolation, as their availability for meet-ups and socializing differed greatly from their peers who did not have children. Tonya explained how she was able to receive encouragement over mommy guilt from a peer mentor who was also a mother. She “talked to her a lot about what worked for her, how she really tried to put her son first . . . which was helpful for me to hear, because I just felt terrible about it all the time.” Navigating the program without a faculty mentor, Kayla found much of her support through her peer mentor: “We became close and she would let me know about the things to be looking for, to be preparing for upcoming classes. She really had my best interest in mind.” On the close friendships forged through mentorship, Dana stated, “She has become my sister. . . . We talk about frustrations, helping me lay boundaries and be okay leaving my child.”
Participants provided specific ideas as to how to implement peer mentorship programs. Ideas included identifying other student mothers for networking opportunities and information, such as childcare services, understanding school policies, and general support. They also recommended working through organizations such as Chi Sigma Iota to create networks, organizing graduate student meet-ups that are family-friendly, and having older cohorts reach out to newer cohorts throughout the year.
Theme III: Identifying Barriers Facing Doctoral Student Mothers
Stigma and discrimination, lack of accommodations, and need for advocacy emerged from the participant interviews. These barriers produced the hardships these mothers encountered, generating losses and unmet career aspirations. Ten out of 12 expressed awareness of faculty and students’ bias toward non-traditional students, especially women who had families. A majority of the participants felt that as doctoral student mothers, they did not have a strong voice in the institutions that they represented. Often, attitudes of faculty toward doctoral student mothers were dismissive and discriminating when they did not fit into the traditional mold of academia. Others determined that faculty and department heads were simply unaware of the hardships and needs of student mothers and therefore perceived them as less motivated or incapable of meeting the rigorous demands of academia. Perhaps some experienced it most deeply through the lack of research and training opportunities, such as graduate assistantships (GA). Amy discussed her frustration and discouragement at being overlooked for a GA position: “I got the strong inclination that it was because I [got] married and that I couldn’t dedicate myself as a typical GA. . . . I would have liked to have been given a chance to prove myself.”
Others also felt that their limited visibility resulted in biased and discriminatory attitudes from faculty and peers. Lisa explained feeling written off as “not the person looked [at] to do a presentation with someone or to do a publication.” While her peers were writing with faculty, she regretted that she couldn’t “be physically present . . . especially when [she] was working and trying to juggle all of these roles.”
Over half of the participants experienced negative attitudes toward their decisions to marry or start their families while in their doctoral programs. Lisa shared that “a faculty member told me point blank that I shouldn’t have a second child in the program.” Amy shared the messages she received on becoming pregnant in her last year of coursework: “Comments from students and faculty were like ‘Why can’t you just wait until after you are done as you are so close?’ or ‘What are your plans when you have a kid?’” Bethany explained how the faculty’s lack of understanding of her minimum progress on her dissertation during her season as a mom, new wife, and full-time school counselor was demoralizing: “For my [program evaluation] this year, I received a grade of no progress in all areas . . . so I have two articles published and won a regional school counselor of the year award. I walked away feeling like I don’t measure up.”
Many participants spoke of the feeling of invisibility as doctoral student mothers by the lack of accommodations such as lactation facilities, childcare options, and clear or even existent leave of absence policies. Of the participants interviewed, only two spoke of having access to childcare on campus. Most had to rely on partners, parents, babysitters, or other students to meet these needs, especially those needing evening hours or experiencing long commutes. During emergencies, when childcare failed or a child was sick, these mothers were at the mercy of professors, department chairs, and supervisors to decide if they could get coverage for their duties or bring their babies to meetings, classes, or groups. Few felt childcare issues or illnesses were justification for missing classes or meetings. Similarly, lactation facilities were haphazard, as the majority of buildings had no dedicated nursing rooms. These new mothers had to use student lounges, borrow windowless offices, pump in their cars, or get up early to pump to avoid the hassle on campus. Sharon revealed that “the only place to pump was the bathroom or car. I don’t feed my child in the bathroom so I’m not pumping in the bathroom.”
Finally, participants described frustration over the lack of clear policies when attempting to stop the doctorate clock for maternity leave and in taking time off from assistantship positions that carried weighty financial penalties. Some maneuvered through with placeholder internships, others accumulated hours so that they could take off after their babies were born, and still others shifted down to part-time. In most cases, their mentors helped them find the path of least hardship and greatest flexibility. Lisa reflected on a lack of clear policies: “There need to be better structures to support women and support children. It shouldn’t all have to fall on me, because I’m always going to come up short.” Despite these barriers, five participants were satisfied with the support provided and viewed their department as accommodating non-traditional students effectively even with ambiguous policies.
Regardless of the hardships encountered, what participants regretted the most was their unmet career aspirations. These doctoral student mothers worked diligently to complete their programs but often had significant delays. The range of doctoral completion/expected completion was 3–7 years. Some regrets included not being able to complete hours for licensure, having fewer research opportunities, presenting less often at conferences, and missing out on other duties that would have enhanced their curriculum vitae. Allison lamented her losses: “I wasn’t able to commit the time to seeing clients, as I didn’t want to be at the clinic until 9:00 pm when my son goes to bed.” Lisa added humor to her dilemma of unfulfilled aspirations: “I want to be a full-time faculty member, tenure track at the end of this. That is going to be really challenging because my CV is very short. I am going to attach pictures of my children.”
Call for Advocacy and Awareness
Although discrimination and other barriers in higher education institutions were fairly commonplace, participants articulated several solutions: (a) expand mentorship opportunities, (b) teach and model work–life balance, (c) improve accommodations for students with families, (d) provide professional opportunities around flexible scheduling, (e) increase awareness and support from faculty, and (f) promote advocacy at departmental and university levels. Five participants had already positioned themselves in the role of mentors and advocates for those coming behind them. Three were involved with research that highlighted these issues. “Mentorship should be a requirement and not an option because we know we work well if we have mentors,” remarked Sharon. Dana suggested that graduate programs should survey students to determine the climate of the program and if students are receiving mentorship, and identify mentors who could best address their needs. Bethany believed that universities must expand mentorship, even if it means extending beyond department lines: “Counselor ed departments need to say, ‘Hey, we can’t meet all of your needs as a mother, or a single mother, but I know someone who can, and I want to be intentional and connect you with this person.’” Bethany also suggested that “peer support groups would be really cool. I was the ‘lone wolf’ for a little bit. Could create campus-wide support groups for graduate students . . . and provide childcare and free pizza for the kids.” The important piece was not having to navigate this alone, as Sara remarked: “Facilitating connection between doctoral student mothers, rather than us having to find our own connections, would be helpful. Making sure there’s a space for moms.”
The main component named was to increase the visibility of the needs of student mothers and provide an understanding of their experiences by shifting the mindset of lowered expectations by faculty and peers to knowing that they can and will be successful with support. Advocacy requires understanding the experiences of women, especially mothers, and identifying the barriers they still face in academia and the workplace. Sara shared the need for greater equity for doctoral student mothers, saying that it “isn’t fair that women who have decided to be moms have to put their own dreams secondary. Women need to know that they are welcome and there is a place for them if they do decide to get pregnant.”
Participants suggested that counselor education programs should teach how to create a framework of work–life balance. Flexible timelines were part of the template for success. Allison suggested that timelines could be a helpful option for those considering doing both doctoral work and motherhood, because her mentor said, “Don’t do it until after second year . . . [it’s a] lot easier to stop and start the dissertation process.”
Providing for physical needs, such as having a lactation room, was also critical to sending a welcoming message. Participants described the need for maternity and sick leave policies that were family-friendly. Participants agreed that they needed faculty and departments to acknowledge their capability to complete their doctorates, accept their value to the profession, and support their life choices. Allison voiced a clear directive for faculty and peer mentors:
The biggest characteristic needed for a mentor is supporting and that it just takes one person . . . one relationship at the school who was going to be accepting of me regardless and who was going to help me with my goals . . . not just my goals to be a PhD but [my] goal to be a mother and a good wife.
Discussion
Participants’ voices highlighted how, with the support of their mentors, they were able to navigate the often murky waters of a PhD program. Perhaps because 10 of the 12 mothers were pregnant while in their program, they neither cared nor were able to hide their motherhood identity. This is only the second study at the time of this review that specifically included women who were pregnant while in CES programs. Similar to the findings of Holm and colleagues (2015), these participants viewed motherhood as a positive attribute that blended well with CES principles in enhancing their work and vice versa.
Participants experienced mentoring as relational and protective. Building on the findings of several studies that suggested mentoring might add a protective factor for success and satisfaction (Holm et al., 2015; Lynch, 2008; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015; Trepal et al., 2014), this study found that mentors focused on providing logistical support to bolster academic progress while fostering work–life balance to promote the overall well-being of the student. These mentors provided emotional support for the participants’ decision to become pregnant and provided regular check-ins throughout the pregnancy, new motherhood, and in many cases, beyond graduation into a professorship.
Also important to this study was the reciprocal relationship. Beyond responding with care and compassion, mentors shared their own motherhood experiences that mirrored their mentees. Supervisors who expressed vulnerability increased the feeling of friendship and deepening of the relationship. This supported other research that described mentoring relationships that include an emotional connection that was both empathic and empowering (Gammel & Rutstein-Riley, 2016; Holm et al., 2015; Trepal et al., 2014). In a similar finding to that emerging from Kelch-Oliver and colleagues’ (2013) study of mentorship, the three African American participants experienced “mothering” by female African American faculty mentors and the “sisterhood” of peer mentoring that went beyond academic walls. For these women, mentoring helped navigate cultural barriers. Not only was it important that they have female faculty, but also choosing women who lived under “double minority” as Patton (2009, p. 71) described gave them both perspective and support around the complexity of race, gender, and motherhood in academic settings and society as a whole.
Doctoral student mothers connecting with other student mothers reported experiencing greater encouragement and satisfaction in those academic peer relationships compared with their relationships with peers without children. Similar to previous findings (Lynch, 2008; Trepal et al., 2014), peer mentoring by other student mothers reduced feelings of isolation, as often these women were the sole mothers in their cohort. They relied on other mothers in earlier cohorts or recent graduates to guide them on how to balance academics and family life.
Participants who had wellness and work–life balance modeled felt better equipped to pursue an academic career path, while those who had poor work–life balance modeled felt less prepared to be successful in academic institutions. Participants who experienced greater discrimination from their institution lacking in family-friendly policies shared their intentions to put their family’s needs first by accepting non-academic jobs, moving closer to relatives, or waiting until their children were older to enter a tenure-track position. This coincides with decades of research (Alexander-Albritton & Hill, 2015; Wolfinger et al., 2008) on graduate women with academic careers that are perceived as non-supportive of family–work balance.
Results also gave voice to the need for change that promotes advocacy concerning parenthood and family-friendly accommodations to aid in decreasing discrimination, both structurally and psychologically. These women had already become advocates and peer mentors. Congruent to earlier research findings, participants identified the need for institutional support in the form of establishing peer mentorship networks that connect other mothers across cohorts and departments, clarifying maternity leave policies, adopting non-penalizing pause-the-clock policies for dissertation work, offering accommodations such as lactation rooms and childcare, and providing flexibility around timelines (Holley & Caldwell, 2012; Holm et al., 2015; Lester, 2013; Lynch, 2008; Stimpson & Filer, 2011). Finally, participants challenged counselor educators to lead the way in addressing inequalities and dismissive attitudes of motherhood in academia by creating a level of openness to family life and choosing to support their students’ goals as counselor educators and mothers.
Limitations and Future Directions
This study has limitations because of transferability issues, the possibility of research bias, and delimiting criteria. Although major geographic regions and university types were represented, participants were racially, culturally, and economically similar, as all were married and in dual-income families. As this study recruited only mothers in CES programs, implications from this study for doctoral student fathers who are primary caregivers or doctoral student mothers in other disciplines may not be transferable. Additionally, several mothers in this study had children with medical or mental health issues, but this study did not specifically set out to focus on families with special needs.
Concerning the research design, as research instruments, we may have inadvertently interjected personal biases into the interview process and coding. The goal was to minimize this through bracketing, journaling, member checking, and reviewing themes with research members. Although semi-structured interview questions guided the research and allowed for organic responses, perhaps another approach might have yielded additional themes. All the participants held jobs in addition to their studies and motherhood duties. Several discussed the effects of work on life balance and needing to reduce hours to part-time, but no distinct theme emerged. Perhaps a specific question on how mentoring may mediate the strains of employment might reveal additional content. Finally, the experiences recorded represent women who remained in their programs. With attrition close to 50% (Council of Graduate Schools, 2010), this research did not address those who dropped out of the program, so other needs or barriers may be missed.
Suggestions for future research include either expanding the concept of caregiving or narrowing the focus to specific sub-groups. Specific to CES, research might investigate mentoring from a faculty point of view to determine why and how faculty choose to mentor, as well as any training for the role. A focus group or interviewing both the mentor and other faculty who interacted with these student mothers might also add to the thickness of the context. Revealed reciprocal benefits that mentors and mentees incur in their relationship could be applied to future training programs for counselor educators. A study specific to peer mentorship might yield unique findings and inform strategies for launching or enhancing successful programs. Quantitative studies might evaluate the effectiveness of existing mentoring programs and expand them for non-traditional students.
Conclusion
Findings from this phenomenological study are cautiously optimistic, as they appear to strengthen the body of knowledge around the importance of relational mentoring and suggest it may be an important protective factor for doctoral student mothers. Research suggests that mentoring is an effective means of support for women (Bruce, 1995; Holm et al., 2015; Kelch-Oliver et al., 2013), but in this study, it appeared to be the most salient component for successful completion of their doctoral programs. Combining the effects of dual roles, medical and mental health hardships, isolation, lack of family-friendly accommodations and policies, and struggles with work–life balance made the mentoring experience essential.
Adding to the body of knowledge around mentoring, this research denotes specific qualities of effective mentors and provides rich descriptions of the relationships and roles valued by these student mothers. This may be helpful in CES training, in selecting future mentors, and in setting up mentorship programs. Equipped with clear directives, CES departments can develop mentorship programs, pairing senior professor mentors with junior professors to teach mentoring skills, rewarding faculty for outstanding mentorship, establishing peer mentoring programs, and developing alumni mentorship opportunities. Within programs and across campus, faculty and staff can assist in connecting student and faculty mothers, promote family support groups, and organize family-inclusive activites. Meanwhile, counselor educators can provide flexibility around scheduling comprehensive exams, dissertation timelines, and research opportunities. Counselor educators can lead in bringing this issue to the discussion table around program development and advocacy initiatives. Medina and Magnuson’s (2009) statement that “Mothers are the people through whom others’ lives are changed” (p. 90) fits well with the ideals of counselor educators; therefore, retaining these mothers in higher education is an important endeavor.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Alexander-Albritton, C., & Hill, N. R. (2015). Familial and institutional factors: Job satisfaction for female counselor educators. Counselor Education and Supervision, 54(2), 109–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12008
Brown, M. C., II, Davis, G. L., & McClendon, S. A. (1999). Mentoring graduate students of color: Myths, models, and modes. Peabody Journal of Education, 74(2), 105–118. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327930pje7402_9
Bruce, M. A. (1995). Mentoring women doctoral students: What counselor educators and supervisors can do. Counselor Education and Supervision, 35(2), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.1995.tb00218.x
Brus, C. P. (2006). Seeking balance in graduate school: A realistic expectation or a dangerous dilemma? New Directions for Student Services, 2006(115), 31–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/ss.214
Clark, R. A., Harden, S. L., & Johnson, W. B. (2000). Mentor relationships in clinical psychology doctoral training: Results of a national survey. Teaching of Psychology, 27(4), 262–268. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15328023TOP2704_04
Council of Graduate Schools. (2010). Ph.D. completion and attrition: Analysis of baseline program data from the Ph.D. completion promotion project. https://cgsnet.org/phd-completion-project
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (4th ed.). SAGE.
Gammel, J. A., & Rutstein-Riley, A. (2016). A relational approach to mentoring women doctoral students. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 2016(147), 27–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.20196
Hadjioannou, X., Shelton, N. R., Fu, D., & Dhanarattigannon, J. (2007). The road to a doctoral degree: Co-travelers through a perilous passage. College Student Journal, 41(1), 160–177.
Hayes, S., & Koro-Ljungberg, M. (2011). Dialogic exchanges and the negotiation of differences: Female graduate students’ experiences of obstacles related to academic mentoring. Qualitative Report, 16(3), 682–710.
Hays, D. G., & Singh, A. A. (2012). Qualitative inquiry in clinical and educational settings. Guilford.
Hermann, M. A., Ziomek-Daigle, J., & Dockery, D. J. (2014). Motherhood and counselor education: Experiences with work-life balance. Adultspan Journal, 13(2), 109–119. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-0029.2014.00030.x
Holley, K. A., & Caldwell, M. L. (2012). The challenges of designing and implementing a doctoral student mentoring program. Innovative Higher Education, 37, 243–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10755-011-9203-y
Holm, J. M., Prosek, E. A., & Godwin Weisberger, A. C. (2015). A phenomenological investigation of counseling doctoral students becoming mothers. Counselor Education and Supervision, 54(1), 2–16.
https://doi.org/10.1002/J.1556-6978.2015.00066.x
Kelch-Oliver, K., Smith, C. O., Johnson, K., Welkom, J. S., Gardner, N. D., & Collins, M. H. (2013). Exploring the mentoring relationship among African American women in psychology. Advancing Women in Leadership, 33, 29–37. https://doi.org/10.18738/AWL.V33I0.98
Kendricks, K. D., Nedunuri, K. V., & Arment, A. R. (2013). Minority student perceptions of the impact of mentoring to enhance academic performance in STEM disciplines. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations and Research, 14(2), 38–46.
Ku, H.-Y., Lahman, M. K. E., Yeh, H.-T., & Cheng, Y.-C. (2008). Into the academy: Preparing and mentoring
international doctoral students. Education Technology Research and Development, 56, 365–377.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-007-9083-0
Lester, J. (2013). Family-friendly policies for doctoral students. New Directions for Higher Education, 2013(163), 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/he.20065
LeVasseur, J. J. (2003). The problem of bracketing in phenomenology. Qualitative Health Research, 13(3), 408–420. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732302250337
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. SAGE.
Lynch, K. D. (2008). Gender roles and the American academe: A case study of graduate student mothers. Gender and Education, 20(6), 585–605. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540250802213099
Martinez, E., Ordu, C., Della Sala, M. R., & McFarlane, A. (2013). Striving to obtain a school-work-life balance: The full-time doctoral student. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 8, 39–59. https://doi.org/10.28945/1765
Medina, S., & Magnuson, S. (2009). Motherhood in the 21st century: Implications for counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87(1), 90–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2009.tb00553.x
Miller, D. I., & Wai, J. (2015). The bachelor’s to Ph.D. STEM pipeline no longer leaks more women than men: A 30-year analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 6(37), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00037
Misra, J., Lundquist, J. H., & Templer, A. (2012). Gender, work time, and care responsibilities among faculty. Sociological Forum, 27(2), 300–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1573-7861.2012.01319.x
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. SAGE.
National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics. (2015). Doctorate recipients from U.S. universities: 2014. Special report NSF 16-300. National Science Foundation. https://www.nsf.gov/statistics/2016/nsf16300/digest/nsf16300.pdf
National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics. (2017). Doctorate recipients from U.S. universities: 2016. Special report NSF 18-304. National Science Foundation. https://www.nsf.gov/statistics/2018/nsf18304/static/report/nsf18304-report.pdf
Neale-McFall, C., & Ward, C. A. (2015). Factors contributing to counselor education doctoral students’ satisfaction with their dissertation chairperson. The Professional Counselor, 5(1), 185–194.
https://doi.org/10.15241/cnm.5.1.185
Noonan, M. J., Ballinger, R., & Black, R. (2007). Peer and faculty mentoring in doctoral education: Definitions, experiences, and expectations. International Journal of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, 19(3), 251–262.
Offerman, M. (2011). Profile of the nontraditional doctoral degree student. New Directions for Adult and Continuing Education, 2011(129), 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/ace.397
Patton, L. D. (2009). My sister’s keeper: A qualitative examination of mentoring experiences among African American women in graduate and professional schools. The Journal of Higher Education, 80(5), 510–537. https://doi.org/10.1353/jhe.0.0062
Patton, L. D., & Harper, S. R. (2003). Mentoring relationships among African American women in graduate and professional schools. New Directions for Student Services, 2003(104), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/ss.108
Pierce, L. A., & Herlihy, B. (2013). The experience of wellness for counselor education doctoral students who are mothers in the southeastern region of the United States. Journal of International Women’s Studies, 14(3), 108–120. https://vc.bridgew.edu/jiws/vol14/iss3/8
Stimpson, R. L., & Filer, K. L. (2011). Female graduate students’ work–life balance and the student affairs professional. In P. A. Pasque & S. E. Nicholson (Eds.), Empowering women in higher education and student affairs: Theory, research, narratives, and practice from feminist perspectives (pp. 69–84). Stylus.
Trepal, H. C., Stinchfield, T. A., & Haiyasoso, M. (2014). Great expectations: Doctoral student mothers in counselor education. Adultspan Journal, 13(1), 30–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-0029.2014.00024.x
Wolfinger, N. H., Mason, M. A., & Goulden, M. (2008). Problems in the pipeline: Gender, marriage, and fertility in the ivory tower. The Journal of Higher Education, 79(4), 388–405.
https://doi.org/10.1353/jhe.0.0015
Vanessa Kent, PhD, NCC, LCMHC-S, LMFT, is an assistant professor at Regent University. Helen Runyan, PhD, NCC, LPC, is an associate professor at Regent University. David Savinsky, PhD, ACS, LPC, LMFT, CSAC, is an associate professor at Regent University. Jasmine Knight, PhD, NCC, is an assistant professor at Regent University. Correspondence may be addressed to Vanessa Kent, 1000 University Drive, Virginia Beach, VA 23464, vaneken@regent.edu.

