Jul 14, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 2
James Ikonomopoulos, Javier Cavazos Vela, Wayne D. Smith, Julia Dell’Aquila
Master’s level counseling programs accredited by the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Education Programs (CACREP, 2016) require students to complete practicum and internship courses that involve group and individual or triadic supervision. Although clinical supervision provides students with effective skill development (Bernard & Goodyear, 2004), counseling students may begin practicum with low self-efficacy regarding their counseling abilities and skills. Given the importance of clinical supervision and counselor self-efficacy, it is surprising that there are limited studies that have examined the impact of supervision and practicum experience from the perspectives of supervisees. Almost all studies within this domain are qualitative and involve personal interviews with supervisees or supervisors (e.g., Hein & Lawson, 2008). In order to fill a gap in the literature and document the impact of the practicum experience, this study examined the effectiveness of the practicum experience encompassing direct counseling services, group supervision and triadic supervision to increase counseling students’ self-efficacy. First, we provide a literature review regarding group supervision, triadic supervision and counselor self-efficacy. Next, we present findings from a study with 11 counseling practicum students. Finally, we provide a discussion regarding the importance of these findings as well as implications for counseling practice and research.
Supervision in Counselor Education Coursework
CACREP requires an average of one and a half hours of weekly group supervision in practicum courses that involves an instructor with up to six counseling graduate students (Degges-White, Colon, & Borzumato-Gainey, 2012). Borders et al. (2012) identified that group supervisors use leadership skills, facilitate and monitor peer feedback, and encourage supervisees to take ownership of group process in group supervision. Borders and colleagues (2012) identified several benefits in group supervision, including exposure to multiple counselor styles and ability to learn about various educational issues. There also were challenges such as limited helpful feedback, brevity of case presentations, timing of group meetings and lack of educational opportunities. In another study, Conn, Roberts, and Powell (2009) compared hybrid and face-to-face supervision among school counseling interns. There were similarities in perceptions of quality of supervision, suggesting that distance learning can provide effective group supervision. CACREP counseling programs also require students to receive one hour of weekly supervision from a faculty member or doctoral student supervisor. Triadic is one form of supervision that involves a process whereby one supervisor meets and provides feedback with two supervisees (Hein & Lawson, 2008). Hein and Lawson (2008) explored supervisors’ perspectives on triadic supervision and found increased demands on the role of the supervisor. For example, supervisors felt additional pressure to support both supervisees in supervision. Additionally, Lawson, Hein, and Stuart (2009) investigated supervisees’ perspectives of triadic supervision. Noteworthy findings included: some students perceived less time and attention to their needs; importance of compatibility between supervisees; and careful attention must be given when communicating feedback, particularly if negative feedback must be given.
Finally, Borders et al. (2012) explored supervisors’ and supervisees’ perceptions of individual, triadic and group supervision. Benefits included vicarious learning experiences, peer-learning opportunities, and better supervisor feedback, while challenges included peer mismatch and difficulty keeping both supervisees involved.
Counselor Self-Efficacy
One of the most important outcome variables in counseling is self-efficacy. Bandura (1986) defined self-efficacy as individuals’ confidence in their ability to perform courses of action or achieve a desired outcome. Self-efficacy in counselor education settings might influence students’ thoughts, behaviors and feelings toward working with clients (Bandura, 1997). In the current study, counseling self-efficacy is defined as “one’s beliefs or judgments about his or her capabilities to effectively counsel a client in the near future” (Larson & Daniels, 1998, p. 1). Counselor self-efficacy also can refer to students’ confidence regarding handling the therapist role, managing counseling sessions and delivering helping skills (Lent et al., 2009). In higher education settings, researchers identified relationships between practicum students’ counseling self-efficacy and various client outcomes in counseling (Halverson, Miars, & Livneh, 2006). Self-efficacy also is positively related to performance attainment (Bandura, 1986), perseverance in counseling tasks, less anxiety (Larson & Daniels, 1998), positive client outcomes (Bakar, Zakaria, & Mohamed, 2011), and counseling skills development (Lent et al., 2009). Halverson et al. (2006) evaluated the impact of a CACREP program on counseling students’ conceptual level and self-efficacy. Longitudinal findings showed that counseling students’ perceptions of self-efficacy increased over the course of the program, primarily as a result of clinical experiences.
In another investigation, Greason and Cashwell (2009) examined mindfulness, empathy and self-efficacy among masters-level counseling interns and doctoral counseling students. Mindfulness, empathy and attention to meaning accounted for 34% of the variance in counseling students’ self-efficacy. Finally, Barbee, Scherer, and Combs (2003) investigated the relationship among prepracticum service learning, counselor self-efficacy and anxiety. Substantial counseling coursework and counseling-related work experiences were important influences on counseling students’ self-efficacy.
Purpose of Study
This study evaluated practicum experiences by using a single-case research design (SCRD) to measure the impact on students’ self-efficacy. In a recent special issue of the Journal of Counseling & Development, Lenz (2015) described how researchers and practitioners can use SCRDs to make inferences about the impact of treatment or experiences. SCRDs are appropriate for counselors or counselor educators for the following reasons: minimal sample size, self as control, flexibility and responsiveness, ease of data analysis, and type of data yielded from analyses. In the current study, the rationale for using an SCRD to examine the effectiveness of the practicum experience and triadic supervision was to provide counselor educators with insight regarding potential strategies that increase students’ self-efficacy. With this goal in mind, we implemented an SCRD (Lenz, Perepiczka, & Balkin, 2013; Lenz, Speciale, & Aguilar, 2012) to identify and explore trends of students’ changes in self-efficacy while completing their practicum experience. We addressed the following research question: to what extent does the practicum experience encompassing direct counseling services, group supervision and triadic supervision influence counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy?
Methodology
Instructors of record for three practicum courses formulated a plan to investigate the impact of the practicum experience on counseling students’ self-efficacy. We focused on providing students with a positive practicum experience with support, constructive feedback, wellness checks and learning experiences. With this goal in mind, we implemented a single case research design (Hinkle, 1992; Lenz et al., 2013; Lenz et al., 2012) to identify and explore trends of students’ changes in self-efficacy while completing their practicum experience. We selected this design to evaluate data that provides inferences regarding treatment effectiveness (Lenz et al., 2013). All practicum courses followed the same course requirements, and instructors shared the same level of teaching experience.
Participant Characteristics
We conducted this study with a sample of Mexican American counseling graduate students (N = 11) enrolled in a CACREP-accredited counseling program in the southwestern United States. This Hispanic Serving Institution had an enrollment of approximately 7,000 undergraduate and graduate students (approximately 93% of students at this institution are Latina/o) at the time of data collection. As a result, we were not surprised that all of the participants in the current study identified as Mexican American. Fifteen participants were solicited; four declined to participate. Participants (four men and seven women) ranged in age from 24 to 57 (M = 31; STD = 9.34). All participants were enrolled in practicum; we assigned participants with pseudonyms to protect their identity. Participants had diverse backgrounds in elementary education, secondary education, case management and behavioral intervention services. Participants also had aspirations of obtaining doctoral degrees or working in private practice, school settings, and community mental health agencies.
Instrumentation
Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy Scale. The Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy Scale (CASES) is a self-report measure of counseling self-efficacy (Lent, Hill, & Hoffman, 2003). This scale consists of 31 items with a 10-point Likert-type scale in which respondents rate their level of confidence from 0 (i.e., having no confidence at all) to 9 (i.e., having complete confidence). Participants respond to items on exploration skills, session management and client distress (Lent et al., 2003), with higher scores reflective of higher levels of self-efficacy. The total score across these domains represents counseling self-efficacy. Reliability estimates range from .96 to .97 (Greason & Cashwell, 2009; Lent et al., 2003). We used the total score as the outcome variable in our study.
Treatment
Over the course of a 14-week semester, participants received 12 hours of triadic supervision and approximately 25 hours of group supervision. We followed Lawson, Hein, and Getz’s (2009) model through pre-session planning, in-session strategies, administrative considerations and evaluations of supervisees. During triadic supervision meetings with two practicum students, the instructor of record conducted wellness checks assessing students’ well-being and level of stress, listened to concerns about clients, observed recorded sessions, provided support and feedback, and encouraged supervisees to provide feedback. The instructor of record also facilitated group supervision discussions on clients’ presenting problems, treatment planning, note-writing, and wellness and self-care strategies. All practicum instructors collaborated and communicated bi-weekly to monitor students’ progress as well as students’ work with clients. All students obtained a minimum of 40 direct hours while working at their university counseling and training clinic, where services are provided to individuals with emotional, developmental, and interpersonal issues. Treatment for depression, anxiety and family issues are the most common issues. The population receiving services at this counseling and training clinic are mostly Mexican American and Spanish-speaking clients who are randomly assigned to a practicum student after an initial phone screening.
Procedure
We evaluated treatment effect using an AB SCRD (in our case, we referred to this more precisely as BT for baseline and treatment), using scores on the CASES as an outcome measure. During an orientation before the semester, practicum students were informed that their instructors were interested in evaluating changes in self-efficacy. Students who agreed to participate in the current study completed baseline measure one at this time. Following this, we selected a pseudonym to identify each participant when completing counselor self-efficacy activity (CSEA) scales throughout the study. The baseline phase consisted of data collection for 3 weeks before the practicum experience. The treatment phase began after the third baseline measure, when the first triadic supervision session was integrated into the practicum experience. Individual cases under investigation were practicum students who agreed to document their changes in self-efficacy while completing the practicum experience. Given that participants serve as their own control group in a single case design, the number of participants in the current study was considered sufficient to explore the research question (Lenz et al., 2013).
Data Collection and Analysis
We implemented an AB, SCRD (Lundervold & Belwood, 2000; Sharpley, 2007) by gathering weekly scores of the CASES. We did not use an ABA design with a withdrawal phase given that almost all students enrolled in internship immediately after the semester. As a result, we did not want to collect data that would have tapped into students’ internship experiences. After three weeks of data collection, the baseline phase of data collection was completed. The treatment phase began after the third baseline measure where the first triadic supervision session occurred. After the 13th week of data collection, the treatment phase of data collection was completed due to nearing completion of the semester, for a total of three baseline and ten treatment phase collections. We did not collect additional treatment data points given that students were scheduled to begin internship at the conclusion of the semester. We only wanted to measure the impact of the practicum experience.
Percentage of data points exceeding the median (PEM) procedure was implemented to analyze the quantitative data from the AB single case design (Ma, 2006). A visual trend analysis was reported as data points from each phase were graphically represented to provide visual representations of change over time (Ikonomopoulos, Smith, & Schmidt, 2015; Sharpley, 2007). An interpretation of effect sizes was conducted to determine the effectiveness of triadic supervision integrated into the practicum experience when comparing each phase of data collection (Sharpley, 2007). Interpreting effect sizes for the PEM procedure yields a proportion of data overlap between a baseline and treatment condition expressed in a decimal format that ranges from zero and one. Higher scores represent greater treatment effects while lower scores represent less effective treatments. This procedure is conceptualized as the analysis of treatment phase data that is contingent on the overlap with the median data point within the baseline phase. Ma (2006) suggested that PEM is based on the assumption that if the intervention is effective, data will be predominately on the therapeutic side of the median. If an intervention is ineffective, data points in the treatment phase will vacillate above and below the baseline median (Lenz, 2013). To calculate the PEM statistic, data points in the treatment phase on the therapeutic side of the baseline are counted and then divided by the total number of points in the treatment phase. Scruggs and Mastropieri (1998) suggested the following criteria for evaluation: effect sizes of .90 and greater are indicative of very effective treatments; those ranging from .70 to .89 represent moderate effectiveness; those between .50 to .69 are debatably effective; and scores less than .50 are regarded as not effective
Results
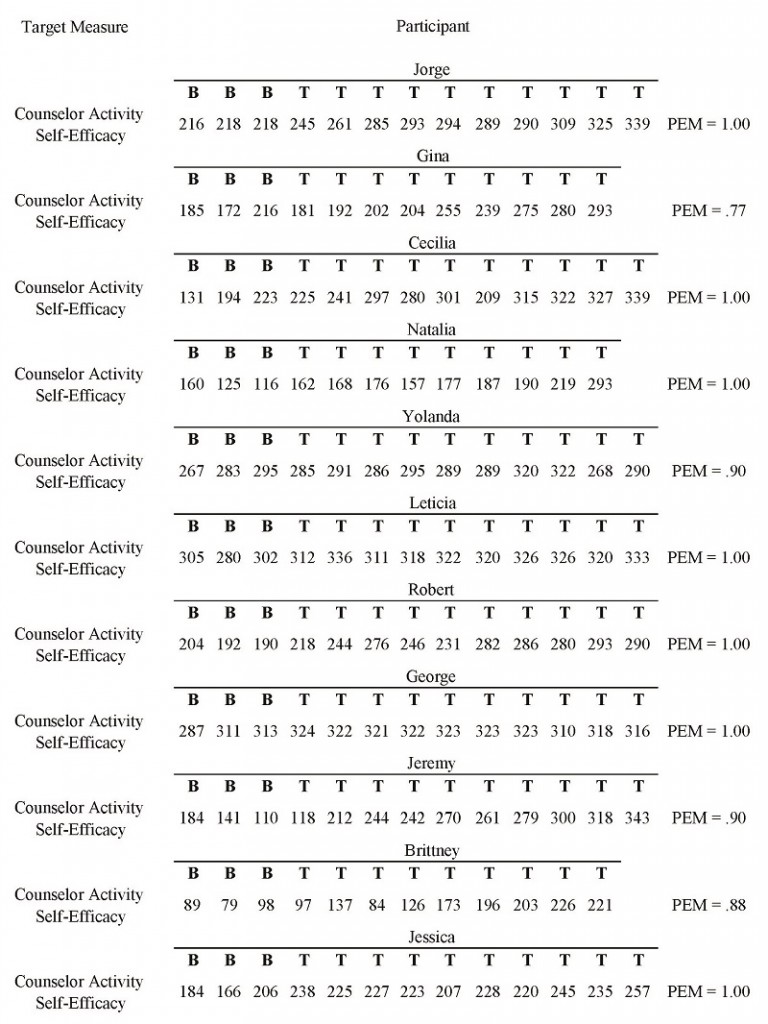
Figure 1 and Table 1 depict estimates of treatment effect using PEM across all participants. Detailed descriptions of participants’ experiences are provided below.
Participant 1
Jorge’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience involving triadic supervision and group supervision was very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Jorge’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123, which considers an individual to have low counseling self-efficacy for the CASES. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 217). Scores above the PEM line were within a 122-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 2
Gina’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience involving triadic supervision and group supervision was moderately effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Gina’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.77) indicated that seven scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 194). Scores above the PEM line were within a 99-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the second treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills, session management and client distress.
Participant 3
Cecilia’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Cecilia’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 177). Scores above the PEM line were within a 162-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills and session management.
Figure 1.
Graphical Representation of Ratings for Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy by Participants
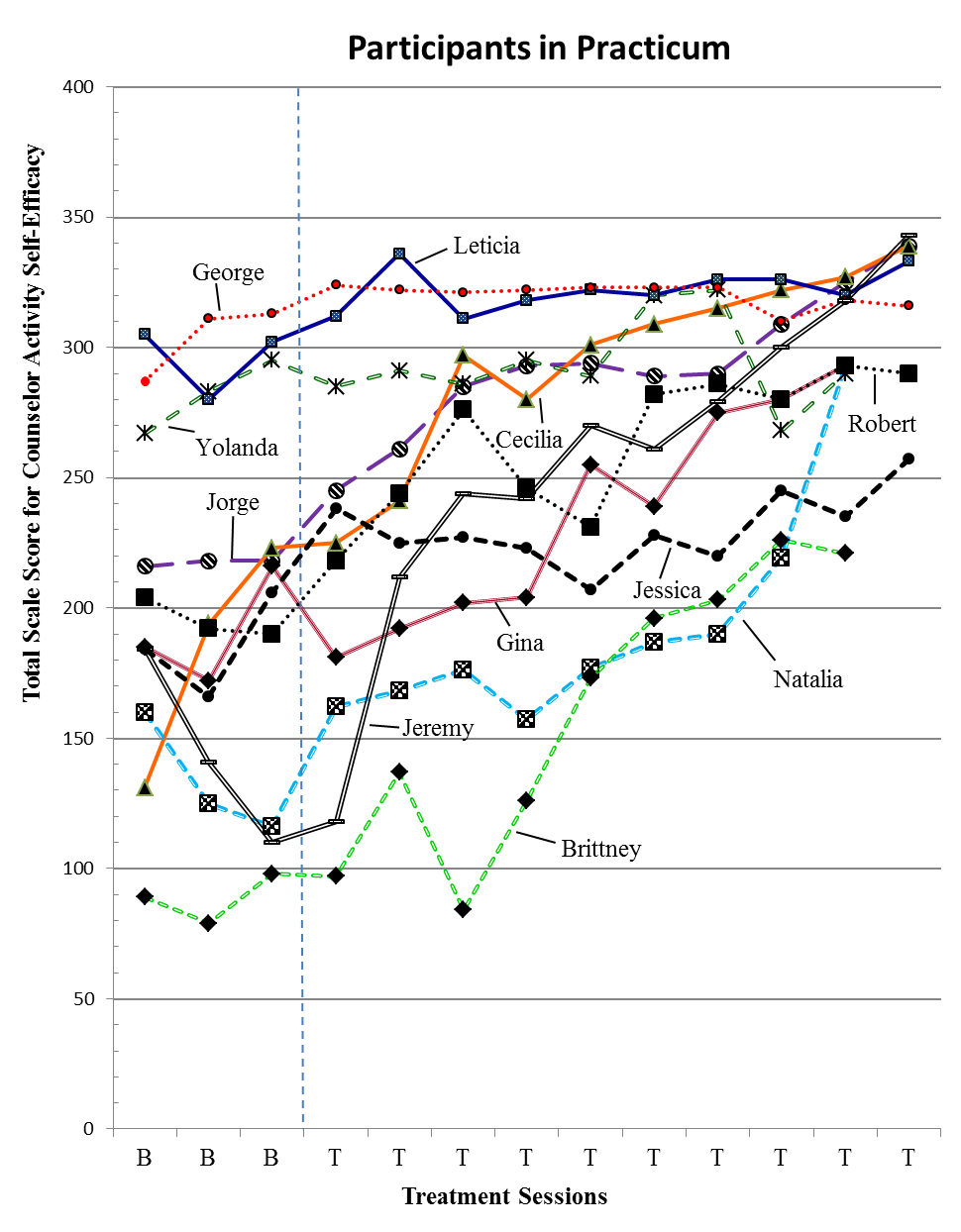
Table 1
Participants’ Sessions and Their CASES Total Scale Score for Counselor Activity Self-Efficacy
Participant 4
Natalia’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, two of Natalia’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that nine scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 138). Scores above the PEM line were within a 155-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 5
Yolanda’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Yolanda’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.90) indicated that nine scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 295). Scores above the PEM line were within a 27-point range. Trend analysis depicted a minimal level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 6
Leticia’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Leticia’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 293). Scores above the PEM line were within a 43-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring client distress.
Participant 7
Robert’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Robert’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 197). Scores above the PEM line were within a 96-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring client distress.
Participant 8
George’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving his counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of George’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the counselor activity self-efficacy measure (1.00) indicated that ten scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 300). Scores above the PEM line were within a 24-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Participant 9
Jeremy’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving his counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, two of Jeremy’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.90) indicated that nine scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 142). Scores above the PEM line were within a 201-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the second treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring session management and client distress.
Participant 10
Brittney’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were moderately effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Brittney’s baseline measurements were below the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (0.88) indicated that eight scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 94). Scores above the PEM line were within a 132-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the fourth treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring session management.
Participant 11
Jessica’s ratings on the CASES illustrate that the practicum experience and triadic supervision were very effective for improving her counselor self-efficacy. Before the treatment phase began, three of Jessica’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the CASES with a total scale score of 123. Evaluation of the PEM statistic for the CASES (1.00) indicated that 10 scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (total scale score of 186). Scores above the PEM line were within a 71-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. The majority of improvement in confidence was found on items measuring exploration skills.
Discussion
The results of this study found that in all 11 investigated cases, the practicum experience ranged from moderately effective (PEM = .77) to very effective (PEM = 1.00) for improving or maintaining counselor self-efficacy during practicum coursework. For most participants, counseling self-efficacy continued to improve throughout the practicum experience as evidenced by high scores on items such as “Helping your client understand his or her thoughts, feelings and actions,” “Work effectively with a client who shows signs of severely disturbed thinking,” and “Help your client set realistic counseling goals.” Participants shared that the most helpful experiences during practicum to improve their counselor self-efficacy came from direct experiences with clients. This finding is consistent with Bandura’s (1977) conceptualization of direct mastery experiences where participants gain confidence with successful experiences of a particular activity. Participants also shared how obtaining feedback from clients on their outcomes and seeing their clients’ progress was important for their development as counselors. Other helpful experiences included processing counseling sessions with a peer during triadic supervision, and case conceptualization and treatment planning during group supervision. Obtaining feedback during triadic supervision from peers and instructors after observing recorded counseling sessions also was beneficial.
Qualitative benefits of supervision included vicarious learning experiences, peer-learning opportunities and better supervisor feedback (Borders et al., 2012). Findings from this study extend qualitative findings regarding benefits of the practicum experience and triadic supervision. The results of this study yielded promising findings related to the integration of triadic supervision into counseling graduate students’ practicum experiences. First, the practicum experience appeared to be effective for increasing and maintaining participant scores on the CSEA scale. Inspection of participant scores within treatment targets revealed that the practicum experience was very effective for nine participants and within the moderately effective range for two participants.
Lastly, informal conversations with participants indicate that triadic supervision provided participants with an opportunity to receive peer feedback. Participants also commented that weekly wellness checks were important due to stress from the practicum experience. Trends were observed for the group as a majority of participants improved self-efficacy consistently after their fourth treatment measure. In summary, direct services with clients, triadic supervision with a peer and group supervision as part of the practicum experience may assist counseling graduate students to improve self-efficacy.
Implications for Counseling Practice
There are several implications for practice. First, triadic supervision has been helpful when there is compatibility between supervisor and supervisees (Hein & Lawson, 2008). Compatibility between supervisees is helpful, as participants shared how having similar knowledge and experience contributed to their development. While all participants in the current study selected their partner for supervision, Hein and Lawson (2008) commented that the responsibility to implement and maintain clear and achievable support to supervisees lies heavily on supervisors. As a result, additional trainings should be offered to supervisors regarding clear, concise and supportive feedback. Such trainings and discussions can focus on clarity of roles and expectations for both supervisor and supervisee before triadic supervision begins. More training in providing feedback to peers in group supervision also can be beneficial as students learn to provide feedback to promote awareness of different learning experiences. We suggest that additional trainings will help practicum instructors and students identify ways to provide clear, constructive and effective feedback.
Practicum instructors can administer weekly or bi-weekly wellness checks and discuss responses on individual items on the Mental Well-Being Scale to monitor progress (Tennant et al., 2007). Additionally, counselor education programs would benefit from bringing self-efficacy to the forefront in the practicum experience as well as prepracticum coursework. Findings from the current study could be presented to students in group counseling and practicum coursework to facilitate discussion regarding how the practicum experience can increase students’ self-efficacy. Part of this discussion should focus on assessing baseline self-efficacy in order to help students increase perceptions of self-efficacy. As such, counselor educators can administer and interpret the CSEA scale with practicum students. There are numerous scale items (e.g., silence, immediacy) that can be used to foster discussions on perceived confidence in dealing with counseling-related issues. Finally, CACREP-accredited programs require 1 hour of weekly supervision and allow triadic supervision to fulfill this requirement. We recommend that CACREP and non-CACREP-accredited programs consider incorporating triadic supervision into the practicum experience and suggest that triadic supervision as part of the practicum experience might help students’ increase self-efficacy.
Implications for Counseling Research
The practicum experience seemed helpful for improving counseling students’ self-efficacy. However, information regarding reasons for this effectiveness of the practicum experience and triadic supervision was not explored. Qualitative research regarding the impact of the practicum experience on counselors’ self-efficacy can provide incredible insight into specific aspects of group or triadic supervision that increase self-efficacy. Second, more outcome-based research with ethnic minority counseling students is necessary. There might be aspects of group or triadic supervision that are conducive when working with Mexican American students (Cavazos, Alvarado, Rodriguez, & Iruegas, 2009). Third, exploring different models of group or triadic supervision to increase counseling self-efficacy is important. As one example, researchers could explore the impact of the Wellness Model of Supervision (Lenz & Smith, 2010) on counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy. Finally, all participants in our study attended a CACREP counseling program with mandatory individual or triadic supervision. Comparing changes in self-efficacy between students in CACREP and non-CACREP programs where weekly individual or triadic supervision outside of class is not mandatory would be important.
Limitations
There are several limitations that must be taken into consideration. First, we did not use an ABA design with withdrawal measures that would have provided stronger internal validity to evaluate changes to counselor self-efficacy (Lenz et al., 2012). Most practicum students in our study began internship immediately after the conclusion of the semester. As a result, collecting withdrawal measures in an ABA design would have tapped into students’ internship experiences. Second, although three baseline measurements are considered sufficient in single-case research (Lenz et al., 2012), employing five baseline measures might have allowed self-efficacy scores to stabilize prior to their practicum experience (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2015).
Conclusion
Based on results from this study, the practicum experience shows promise as an effective strategy to increase counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy. Implementing triadic supervision as part of the practicum experience for counseling students is a strategy that counselor education programs might consider. Provided are guidelines for counselor educators to consider when integrating triadic supervision into the practicum experience. Researchers also can use different methodologies to address how different aspects of the practicum experience influence counseling students’ self-efficacy. In summary, we regard the practicum experience with triadic supervision as a promising approach for improving counseling graduate students’ self-efficacy.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Bakar, A. R., Zakaria, N. S., & Mohamed, S. (2011). Malaysian counselors’ self-efficacy: Implication for career counseling. The International Journal of Business and Management, 6, 141–147. doi:10.5539/ijbm.v6n9p141
Bandura, A. (1977). Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84, 191–215.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York, NY: Freeman.
Barbee, P. W., Scherer, D., & Combs, D. C. (2003). Prepracticum service-learning: Examining the relationship with counselor self-efficacy and anxiety. Counselor Education and Supervision, 43, 108–120.
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2004). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (3rd ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Borders, L. D. (2014). Best practices in clinical supervision: Another step in delineating effective supervision practice. American Journal of Psychotherapy, 68, 151–162.
Borders, L. D., Welfare, L. E., Greason P. B., Paladino, D. A., Mobley, A. K., Villalba, J. A., & Wester, K. L. (2012). Individual and triadic and group: Supervisee and supervisor perceptions of each modality. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 281–295.
Cavazos, J., Alvarado, V., Rodriguez, I., & Iruegas, J. R. (2009). Examining Hispanic counseling students’ worries: A qualitative approach. Journal of School Counseling, 7, 1–22.
Conn, S. R., Roberts, R. L., & Powell, B. M. (2009). Attitudes and satisfaction with a hybrid model of counseling supervision. Educational Technology and Society, 12, 298–306.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2016). 2016 CACREP standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/2016-Standards-with-Glossary-rev-2.2016.pdf
Degges-White, S., Colon, B. R., & Borzumato-Gainey, C. (2013). Counseling supervision within a feminist framework: Guidelines for intervention. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 52, 92–105.
doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2013.00035.x
Greason, P. B., & Cashwell, C. S. (2009). Mindfulness and counseling self-efficacy: The mediating role of attention and empathy. Counselor Education and Supervision, 49, 2–19.
Halverson, S. E., Miars, R. D., & Livneh, H. (2006). An exploratory study of counselor education students’ moral reasoning, conceptual level, and counselor self-efficacy. Counseling and Clinical Psychology Journal, 3, 17–30.
Hein, S., & Lawson, G. (2008). Triadic supervision and its impact on the role of the supervisor: A qualitative examination of supervisors’ perspectives. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48, 16–31.
Hinkle, J. S. (1992). Computer-assisted career guidance and single-subject research: A scientist-practitioner approach to accountability. Journal of Counseling & Development, 70, 391–395.
Ikonomopoulos, J., Smith, R. L., & Schmidt, C. (2015). Integrating narrative therapy within rehabilitative programming for incarcerated adolescents. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93, 460–470. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2014.00000.x
Larson, L. M., & Daniels, J. A. (1998). Review of the counseling self-efficacy literature. The Counseling Psychologist, 26, 179–218.
Lawson, G., Hein, S. F., & Getz, H. (2009). A model for using triadic supervision in counselor education preparation programs. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48, 257–270.
Lawson, G., Hein, S. F., & Stuart, C. L. (2009). A qualitative investigation of supervisees’ experiences of triadic supervision. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87, 449–457.
Lent, R. W., Cinamon, R. G., Bryan, N. A., Jezzi, M. M., Martin, H. M., & Lim, R. (2009). Perceived sources of changes in trainees’ self-efficacy beliefs. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training, 46, 317–327. doi:10.1037/a0017029
Lent, R. W., Hill, E., & Hoffman, M. A. (2003). Development and validation of the counselor activity self-efficacy scales. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 50, 97–108.
Lenz, A. S. (2013). Calculating effect size in single-case research: A comparison of nonoverlap methods. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 46, 64–73.
Lenz, A. S. (2015). Special issue editor’s introduction: Using single-case research designs to demonstrate evidence for counseling practices. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93, 387–393.
doi:10.1002/jcad.12036
Lenz, A. S., Perepiczka, M., & Balkin, R. S. (2013). Evidence of the mitigating effects of a support group for attitude toward statistics. Counseling Outcome Research & Evaluation, 4, 26–40. doi:10.1177/2150137812474000
Lenz, A. S., & Smith, R. L. (2010). Integrating wellness concepts within a clinical supervision model. The Clinical Supervisor, 29, 228–245. doi:10.1080/07325223.2020.518511
Lenz, A. S., Speciale, M., & Aguilar, J. V. (2012). Relational-cultural therapy intervention with incarcerated adolescents: A single-case effectiveness design. Counseling Outcome Research & Evaluation, 3, 17–29. doi:10.1177/2150137811435233
Lundervold, D. A., & Belwood, M. F. (2000). The best kept secret in counseling: Single-case (N = 1) experimental designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 78, 92–102.
Ma, H. H. (2006). An alternative method for quantitative synthesis of single-subject researches: Percentage of data points exceeding the median. Behavior Modification, 30, 598–617.
Scruggs, T. E., & Mastropieri, M. A. (1998). Summarizing single-subject research: Issues and applications. Behavior Modification, 22, 221–242.
Sharpley, C. F. (2007). So why aren’t counselors reporting n = 1 research designs? Journal of Counseling & Development, 85, 349–356.
Tennant, R., Hiller, L., Fishwick, R., Platt, S., Joseph, S., Weich, S., . . . Stewart-Brown, S. (2007). The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): Development and UK validation. Health & Quality of Life
Outcomes, 5, 63. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-5-63
James Ikonomopoulos, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Javier Cavazos Vela is an LPC-Intern at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Wayne D. Smith is an Assistant Professor at the University of Houston–Victoria. Julia Dell’Aquila is a graduate student at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Correspondence concerning this article can be addressed to James Ikonomopoulos, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Department of Counseling, Main 2.200F, One West Univ. Blvd., Brownsville, TX 78520, james.ikonomopoulos@utrgv.edu.
May 20, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 2
Melissa J. Fickling
Advocacy with and on behalf of clients is a major way in which counselors fulfill their core professional value of promoting social justice. Career counselors have a unique vantage point regarding social justice due to the economic and social nature of work and can offer useful insights. Q methodology is a mixed methodology that was used to capture the perspectives of 19 career counselors regarding the relative importance of advocacy interventions. A two-factor solution was reached that accounted for 60% of the variance in perspectives on advocacy behaviors. One factor, labeled focus on clients, emphasized the importance of empowering individual clients and teaching self-advocacy. Another factor, labeled focus on multiple roles, highlighted the variety of skills and interventions career counselors use in their work. Interview data revealed that participants desired additional conversations and counselor training concerning advocacy.
Keywords: social justice, advocacy, career counselors, Q methodology, counselor training
The terms advocacy and social justice often are used without clear distinction. Advocacy is the active component of a social justice paradigm. It is a direct intervention or action and is the primary expression of social justice work (Fickling & Gonzalez, 2016; Ratts, Lewis, & Toporek, 2010; Toporek, Lewis, & Crethar, 2009). Despite the fact that counselors have more tools than ever to help them develop advocacy and social justice competence, such as the ACA Advocacy Competencies (Lewis, Arnold, House, & Toporek, 2002) and the Multicultural and Social Justice Counseling Competencies (Ratts, Singh, Nassar-McMillan, Butler, & McCullough, 2015), little is known about practitioners’ perspectives on the use of advocacy interventions.
One life domain in which social inequity can be vividly observed is that of work. The economic recession that began in 2007 has had a lasting impact on the labor market in the United States. Long-term unemployment is still worse than before the recession (Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, 2016a). Further, in the United States, racial bias appears to impact workers and job seekers, as evidenced in part by the fact that the unemployment rate for Black workers is consistently about double that of White workers (e.g., 4.1% White unemployment and 8.2% Black unemployment as of May 2016; Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, 2016b). Recent meta-analyses indicate that unemployment has a direct and causal negative impact on mental health, leading to greater rates of depression and suicide (Milner, Page, & LaMontagne, 2013; Paul & Moser, 2009). Clearly, the worker role is one that carries significant meaning and consequences for people who work or want to work (Blustein, 2006).
The rate at which the work world continues to change has led some to argue that worker adaptability is a key 21st century skill (Niles, Amundson, & Neault, 2010; Savickas, 1997), but encouraging clients to adapt to unjust conditions without also acknowledging the role of unequal social structures is inconsistent with a social justice paradigm (Stead & Perry, 2012). Career counselors, particularly those who work with the long-term unemployed and underemployed, witness the economic and psychological impact of unfair social arrangements on individuals, families and communities. In turn, they have a unique vantage point when it comes to social justice and a significant platform from which to advocate (Chope, 2010; Herr & Niles, 1998; Pope, Briddick, & Wilson, 2013; Pope & Pangelinan, 2010; Prilleltensky & Stead, 2012).
It appears that although career counselors value social justice and are aware of the effects of injustice on clients’ lives, they are acting primarily at the individual rather than the systemic level (Cook, Heppner, & O’Brien, 2005; McMahon, Arthur, & Collins, 2008b; Prilleltensky & Stead, 2012; Sampson, Dozier, & Colvin, 2011). Some research has emerged that focuses on practitioners’ use of advocacy in counseling practice (Arthur, Collins, Marshall, & McMahon, 2013; Arthur, Collins, McMahon, & Marshall, 2009; McMahon et al., 2008b; Singh, Urbano, Haston, & McMahan, 2010). Overall, this research indicates that advocacy is challenging and multifaceted and is viewed as a central component of good counseling work; however, more research is needed if we are to fully understand how valuing social justice translates to use of advocacy interventions in career counseling practice. This study aims to fill this theory–practice gap by illuminating the perceptions of advocacy behaviors from career counselors as they reflect upon their own counseling work.
Methodology
Through the use of Q methodology, insight into the decisions, motivations and thought processes of participants can be obtained by capturing their subjective points of view. When considering whether to undertake a Q study, Watts and Stenner (2012) encouraged researchers to consider whether revealing what a population thinks about an issue really matters and can make a real difference. Given the ongoing inequality in the labor market, increased attention and energy around matters of social justice in the counseling profession, the lack of knowledge regarding practitioners’ points of view on advocacy, and career counselors’ proximity to social and economic concerns of clients, the answer for the present study is most certainly yes.
Q methodology is fundamentally different from other quantitative research methodologies in the social sciences. It uses both quantitative and qualitative data to construct narratives of distinct perspectives. The term Q was coined to distinguish this methodology from R; Q measures correlations between persons, whereas R measures trait correlations (Brown, 1980). Rather than subjecting a sample of research participants to a collection of measures as in R methodology, Q methodology subjects a sample of items (i.e., the Q sample) to measurement by a collection of individuals through a ranking procedure known as the Q sort (see Figure 1; Watts & Stenner, 2012). Individuals are the variables in Q methodology, and factor analysis is used to reduce the number of points of view into a smaller number of shared perspectives. Then interviews are conducted to allow participants to provide additional data regarding their rankings of the Q sample items. In this study, career counselors were asked to sort a set of advocacy behaviors according to how important they were to their everyday practice of career counseling. Importance to practice was used as the measure of psychological significance since career counselors’ perspectives on advocacy interventions were of interest, rather than self-reported frequency or competence, for example.
Q Sample
The Q sample can be considered the instrumentation in Q methodology. The Q sample is a subset of statements drawn from the concourse of communication, which is defined as the entire population of statements about any given topic (McKeown & Thomas, 2013). The goal when creating the Q sample is to provide a comprehensive but manageable representation of the concourse from which it is taken. For this study, the concourse was that of counselor advocacy behaviors.
The Q sampling approach used for this study was indirect, naturalistic and structured-inductive. Researchers should draw their Q sample from a population of 100 to 300 statements (Webler, Danielson, & Tuler, 2009). For this study, I compiled a list of 180 counselor social justice and advocacy behaviors from a variety of sources including the ACA Advocacy Competencies (Lewis et al., 2002), the Social Justice Advocacy Scale (SJAS; Dean, 2009), the National Career Development Association (NCDA) Minimum Competencies (2009), the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) Standards (2009), and key articles in counseling scholarly and trade publications.
Consistent with a structured-inductive sampling strategy, these 180 statements were analyzed to identify categories representing different kinds of advocacy behaviors. By removing duplicates and those items that were more aligned with awareness, knowledge or skill rather than behavior, I was able to narrow the list from 180 to 43 statements. These statements were sorted into five domains that were aligned with the four scales of the SJAS (Dean, 2009) and a fifth added domain. The final domains were: Client Empowerment, Collaborative Action, Community Advocacy, Social/Political Advocacy, and Advocacy with Other Professionals. Aligning the Q sample with existing domains was appropriate since advocacy had been previously operationalized in the counseling literature.
Expert reviewers were used to check for researcher bias in the construction of the Q sample, including the addition of the fifth advocacy domain. Three expert reviewers who were faculty members and published on the topic of social justice in career counseling were asked to review the potential Q sample for breadth, coverage, omissions, clarity of phrasing and the appropriateness of the five domains of advocacy. Two agreed to participate and offered their feedback via a Qualtrics survey, leading to a refined Q sample of 25 counselor advocacy behaviors (see Table 1). Five statements were retained in each of the five domains. Finally, the Q sample and Q sorting procedure were piloted with two career counselors, leading to changes in instructions but not in the Q sample itself. Pilot data were not used in the final analysis.
Participants
In Q methodology, participant sampling should be theoretical and include the intentional selection of participants who are likely to have an opinion about the topic of interest (McKeown & Thomas, 2013; Watts & Stenner, 2012). It also is important to invite participants who represent a range of viewpoints and who are demographically diverse. For the current study, the following criteria were required for participant inclusion: (a) holds a master’s degree or higher in counseling and (b) has worked as a career counselor for at least one year full-time in the past two years. For this study, career counselor was defined as having career- or work-related issues as the primary focus of counseling in at least half of the counselor’s case load. Regarding the number of participants in a Q study, emphasis is placed on having enough participants to establish the existence of particular viewpoints, not simply having a large sample since generalizability is not a goal of Q methodology (Brown, 1980). In Q methodology, it also is important to have fewer participants than Q sample items (Watts & Stenner, 2012; Webler et al., 2009).
Participants were recruited by theoretical sampling of my professional network of practitioners, and one participant was recruited through snowball sampling. Nineteen career counselors participated in the present study from six states in the Southeast, West and Midwest regions of the United States. The participant sample was 68% female (n = 13) and 32% male (n = 6); the sample was 84% White and included two Black participants and one multi-racial participant. One participant was an immigrant to the United States and was a non-native English speaker. The participant sample was 95% heterosexual with one participant identifying as gay. Sixty-three percent of participants worked in four-year institutions of higher education and one worked in a community college. Thirty-two percent (n = 6) provided career counseling in non-profit agencies. The average age was 43 (SD = 12) and the average number of years of post-master’s counseling experience was eight (SD = 7); ages ranged from 28 to 66, and years of post-master’s experience ranged from one and a half to 31 years.
Q Sorting Procedure
The Q sort is a method of data collection in which participants rank the Q sample statements according to a condition of instruction along a forced quasi-normal distribution (see Figure 1). There is no time limit to the sorting task and participants are able to move the statements around the distribution until they are satisfied with their final configuration. The function of the forced distribution is to encourage active decision making and comparison of the Q sample items to one another (Brown, 1980).
Figure 1
Sample Q Sort Distribution

The condition of instruction for this study was, “Sort the following counselor advocacy behaviors according to how important or unimportant they are to your career counseling work.” The two poles of the distribution were most important and most unimportant. Poles range from most to most so that the ends of the distribution represent the areas that hold the greatest degree of psychological significance to the participant, and the middle of the distribution represents items that hold relatively little meaning or are more neutral in importance (Watts & Stenner, 2012).
The Q sorts for this study were conducted both in person and via phone or video chat (i.e., Google Hangouts, Skype). Once informed consent was obtained, I facilitated the Q sorting procedure by reading the condition of instruction, observing the sorting process, and conducting the post-sort interview. Once each participant felt satisfied with his or her sort, the distribution of statements was recorded onto a response sheet for later data entry.
Post-Sort Interview
Immediately following the Q sort, I conducted a semistructured interview with each participant in order to gain a greater understanding of the meaning of the items and their placement, as well as his or her broader understanding of the topic at hand (Watts & Stenner, 2012). The information gathered during the interview is used when interpreting the final emergent factors. Items in the middle of the distribution are not neglected and are specifically asked about during the post-sort interview so that the researcher can gain an understanding of the entire Q sort for each participant. Although the interview data are crucial to a complete and rigorous factor interpretation and should be conducted with every participant in every Q study, the data analysis process is guided by the quantitative criteria for factor analysis and factor extraction. The qualitative interview data, as well as the demographic data, are meant to help the researcher better understand the results of the quantitative analysis.
Data Analysis
Data were entered into the PQMethod program (Schmolck, 2014) and Pearson product moment correlations were calculated for each set of Q sorts. Inspection of the correlation matrix revealed that all sorts (i.e., all participants) were positively correlated with one another, some of them significantly so. This indicated a high degree of consensus among the participants regarding the role of advocacy in career counseling, which was further explored through factor analysis.
I used centroid factor analysis and Watts and Stenner’s (2012) recommendation of beginning by extracting one factor for every six Q sorts. Centroid factor analysis is the method of choice among Q methodologists because it allows for a fuller exploration of the data than a principal components analysis (McKeown & Thomas, 2013; Watts & Stenner, 2012). Next, I calculated the significance level at p < .01, which was .516 for this 25-item Q sample.
The unrotated factor matrix revealed two factors with Eigenvalues near or above the commonly accepted cutoff of 1 according to the Kaiser-Guttman rule (Kaiser, 1970). Brown (1978) argued that although Eigenvalues often indicate factor strength or importance, they should not solely guide factor extraction in Q methodology since “the significance of Q factors is not defined objectively (i.e., statistically), but theoretically in terms of the social-psychological situation to which the emergent factors are functionally related” (p. 118). Since there currently is little empirical evidence of differing perspectives on advocacy among career counselors, two factors were retained for rotation.
In order to gain another perspective on the data, I used the Varimax procedure. I flagged those sorts that loaded significantly (i.e., at or above 0.516) onto only one factor after rotation. Four participants (2, 8, 9 and 17) loaded significantly onto both rotated factors and were therefore dropped from the study and excluded from further analysis (Brown, 1980; Watts & Stenner, 2012). Two rotated factors were retained, which accounted for 60% of the variance in perspectives on advocacy behaviors. Fifteen of the original 19 participants were retained in this factor solution.
Q methodology uses only orthogonal rotation techniques, meaning that all factors are zero-correlated. Even so, it is possible for factors to be significantly correlated but still justify retaining separate factors (Watts & Stenner, 2012). The two factors in this study are correlated at 0.71. This correlation indicates that the perspectives expressed by the two factor arrays share a point of view but are still distinguishable and worthy of exploration as long as the general degree of consensus is kept in mind (Watts & Stenner, 2012).
Constructing Factor Arrays
After the two rotated factors were identified, factor arrays were constructed in PQMethod. A factor array is a composite Q sort and the best possible estimate of the factor’s viewpoint using the 25 Q sample items. First, a factor weight was calculated for each of the 15 Q sorts that loaded onto a factor. Next, normalized factor scores (z scores) were calculated for each statement on each factor, which were finally converted into factor arrays (see Table 1). In Q methodology, unlike traditional factor analysis, attention is focused more on factor scores than factor loadings. Since factor scores are based on weighted averages, Q sorts with higher factor loadings contribute proportionally more to the final factor score for each item in a factor than those with relatively low factor loadings. Finally, factors were named by examining the distinguishing statements and interview data of participants that loaded onto the respective factors. Factor one was labeled focus on clients and factor two was labeled focus on multiple roles.
Factor Characteristics
Factor one was labeled focus on clients and accounted for 32% of the variance in perspectives on advocacy behaviors. It included nine participants. The demographic breakdown on this factor was: six females, three males; eight White individuals and one person who identified as multi-racial. The average age on this factor was about 51 (SD = 10.33), ranging from 37 to 66. Persons on this factor had on average 11 years of post-master’s counseling experience (SD = 8.6), ranging from one and a half to 31 years. Fifty-six percent of participants on this factor worked in 4-year colleges or universities, 33% in non-profit agencies, and one person worked at a community college.
Factor two was labeled focus on multiple roles and accounted for 28% of the variance in career counselors’ perspectives on advocacy behaviors. It included six participants. Five participants on this factor identified as female and one identified as male. Five persons were White; one was Black. The average age of participants on this factor was almost 35 (SD = 6.79), ranging from 29 to 48, and they had an average of just over seven years of post-master’s experience (SD = 3.76), ranging from three and a half to 14 years. Four worked in higher education, and two worked in non-profit settings.
Factor Interpretation
In the factor interpretation phase of data analysis, the researcher constructs a narrative for each factor by incorporating post-sort interview data with the factor arrays to communicate the rich point of view of each factor (Watts & Stenner, 2012). Each participant’s interview was considered only in conjunction with the other participants on the factor on which they loaded. I read post-sort interview transcripts, looking for shared perspectives and meaning, in order to understand each factor array and enrich each factor beyond the statements of the Q sample. Thus, the results are reported below in narrative form, incorporating direct quotes and paraphrased summaries from interview data, but structured around the corresponding factor arrays.
Table 1
Q Sample Statements, Factor Scores and Q Sort Values
|
No
|
Statement
|
Factor 1
|
Factor 2
|
|
|
Factor Score
|
QSV
|
Factor Score
|
QSV
|
| 1 |
Question intervention practices that appear inappropriate. |
0.09
|
1
|
0.54
|
1
|
| 2 |
Seek feedback regarding others’ perceptions of my advocacy efforts. |
-0.85
|
-2
|
-0.75
|
-1
|
| 3 |
Serve as a mediator between clients and institutions. |
-0.47
|
-1
|
-1.05
|
-2
|
| 4 |
Express views on proposed bills that will impact clients. |
-0.97
|
-2
|
-1.96
|
-4
|
| 5 |
Maintain open dialogue to ensure that advocacy efforts are consistent with group goals. |
-0.19
|
0
|
-0.05
|
0
|
| 6 |
Encourage clients to research the laws and policies that apply to them. |
-0.31
|
0
|
0.15
|
0
|
| 7 |
Collect data to show the need for change in institutions. |
-0.67
|
-2
|
-0.75
|
-2
|
| 8 |
Educate other professionals about the unique needs of my clients. |
0.87
|
1
|
0.86
|
2
|
| 9 |
Help clients develop needed skills. |
1.67
|
3
|
0.42
|
1
|
| 10 |
Assist clients in carrying out action plans. |
-1.31
|
3
|
1.06
|
2
|
| 11 |
Help clients overcome internalized negative stereotypes. |
1.02
|
2
|
0.89
|
2
|
| 12 |
Conduct assessments that are inclusive of community members’ perspectives. |
-1.31
|
-3
|
0.5
|
1
|
| 13 |
With allies, prepare convincing rationales for social change. |
-0.35
|
-1
|
-1.36
|
-3
|
| 14 |
Identify strengths and resources of clients. |
2.17
|
4
|
1.62
|
3
|
| 15 |
Get out of the office to educate people about how and where to get help. |
0.58
|
1
|
-0.47
|
-1
|
| 16 |
Teach colleagues to recognize sources of bias within institutions and agencies. |
-0.37
|
-1
|
-0.37
|
-1
|
| 17 |
Deal with resistance to change at the community/system level. |
-0.43
|
-1
|
-0.21
|
0
|
| 18 |
Collaborate with other professionals who are involved in disseminating public information. |
-0.33
|
0
|
-0.4
|
-1
|
| 19 |
Help clients identify the external barriers that affect their development. |
1.08
|
2
|
1.46
|
3
|
| 20 |
Use multiple sources of intervention, such as individual counseling, social advocacy and case management. |
-0.32
|
0
|
1.73
|
4
|
| 21 |
Train other counselors to develop multicultural knowledge and skills. |
0.15
|
1
|
0.19
|
0
|
| 22 |
Work to ensure that clients have access to the resources necessary to meet their needs. |
1.03
|
2
|
0.85
|
1
|
| 23 |
Work to change legislation and policy that negatively affects clients. |
-1.78
|
-4
|
-1.39
|
-3
|
| 24 |
Ask other counselors to think about what social change is. |
-0.25
|
0
|
-0.22
|
0
|
| 25 |
Communicate with my legislators regarding social issues that impact my clients. |
-1.45
|
-3
|
-1.28
|
-2
|
Note. Q sort values are -4 to 4 to correspond with the Q distribution (Figure 1) where 4 is most important
and -4 is most unimportant; QSV = Q Sort Value.
Results
Factor 1: Focus on Clients
For participants on the focus on clients factor, the most important advocacy behavior was to “identify client strengths and resources” (see Table 1). When speaking about this item, participants often discussed teaching clients self-advocacy skills, stating that this is a key way in which career counselors promote social justice. Identifying client strengths and resources was referred to as “the starting point,” “the bottom line” and even the very “definition of career counseling.” One participant said that counseling is about “empowering our clients or jobseekers, whatever we call them, to do advocacy on their own behalf and to tell their story.” In general, persons on this factor were most concerned with empowering individual clients; for example, “I would say, even when we’re doing group counseling and family counseling, ultimately it’s about helping the person in the one-to-one.” Similarly, one participant said, “Instead of fighting for the group in legislation or out in the community, I’m working with each individual to help them better advocate for themselves.” Interview data indicated that social justice was a strongly held value for persons on this factor, but they typically emphasized the need for balancing their views on social injustice with their clients’ objectives; they wanted to take care not to prioritize their own agendas over those of their clients.
Several participants on this factor perceived items related to legislation or policy change as among the least client-centered behaviors and therefore as the more unimportant advocacy behaviors in their career counseling work. Persons on this factor stated that advocacy at the systems level was neither a strength of theirs nor a preference. A few reported that there are other people in their offices or campuses whose job is to focus on policy or legislative change. There also was a level of skepticism about counselors’ power to influence social change. In regard to influencing legislative change in support of clients, one participant said, “I don’t think in my lifetime that is going to happen. Maybe someday it will. I’m just thinking about market change right now instead of legislative change.”
Interview data revealed that career counselors on this factor thought about advocacy in terms of leadership, both positively and negatively. One person felt that a lack of leadership was a barrier to career counselors doing more advocacy work. Another person indicated that leaders were the ones who publicly called for social change and that this was neither his personality nor approach to making change, preferring instead to act at the micro level. Finally, persons on this factor expressed that conversations about social change or social justice were seen as potentially divisive in their work settings. One White participant said the following:
There is a reluctance to do social justice work because—and it’s mostly White people—people really don’t understand what it means, or feel like they don’t have a right to do that, or feel like they might be overstepping. Talking about race or anything else, people are really nervous and they don’t want to offend or say something that might be wrong, so as a result they just don’t engage on that level or on that topic.
Factor 2: Focus on Multiple Roles
One distinguishing feature of the focus on multiple roles factor was the relatively high importance placed on using multiple sources of intervention (see Table 1). Participants described this as being all-encompassing of what a career counselor does and reflective of the multiple roles a career counselor may hold. One participant said, “You never know what the client is going to come in with,” arguing that career counselors have to be open to multiple sources of intervention by necessity. Another participant indicated that she wished she could rely more on multiple sources of intervention but that the specialized nature of her office constricted her ability to do so.
Participants on this factor cited a lack of awareness or skills as a barrier to their implementing more advocacy behaviors. They were quick to identify social justice as a natural concern of career counselors and one that career counselors are well qualified to address due to their ability to remain aware of personal, mental health and career-related concerns simultaneously. One participant said:
I don’t know if the profession of career counseling is really seen as being as great as it is in that most of us have counseling backgrounds and can really tackle the issues of career on a number of different levels.
In talking about the nature of career counseling, another participant said, “Social justice impacts work in so many ways. It would make sense for those external barriers to come into our conversations.”
Regarding collaborating with other professionals to prepare convincing rationales for social change, one participant stated that there are already enough rationales for social change; therefore, this advocacy behavior was seen as less important to her. Persons on this factor placed relatively higher importance on valuing feedback on advocacy efforts than did participants on factor one. One participant said she would like to seek feedback more often but had not thought of doing so in a while: “I did this more when I was in graduate school because you are thinking about your thinking all the time. As a practitioner, as long as social justice and advocacy are on my radar, that’s good.”
Discussion
Neither setting nor gender appeared to differentiate the factors, but age and years of post-master’s experience may have been distinguishing variables. Younger individuals and those with fewer years of post-master’s experience tended to load onto factor two. Factor one had an average age of 51 compared to 35 for factor two, and the average age for all study participants was 43. It is interesting to note that the four participants who loaded onto both factors and were therefore dropped from analysis had an average of just over two years of post-master’s counseling experience versus 11 for factor one and seven for factor two. It is possible that their more recent training regarding advocacy may account for some differences in perspective from those of more experienced counselors.
Participants on factor one (focus on clients) who emphasized the importance of individual clients tended to perceive it as more difficult to have conversations about social justice with their peers or supervisors. In contrast, participants on factor two (focus on multiple roles) were more likely to cite a lack of knowledge or skills regarding their reasons for not engaging in more advocacy behaviors beyond the client level. Factor arrays indicated that factor one participants viewed engaging at the community level as more important, whereas participants on factor two viewed conversations with colleagues and clients about social justice as more important to their work.
The broader view of persons on factor two regarding the career counselor’s role and their openness to acknowledging their own lack of awareness or skills may reflect a different kind of socialization around advocacy compared to persons on factor one. Career counselors who graduated from counseling programs prior to the emphasis on multicultural competence in the early 1990s or before the inclusion of social justice in the literature and CACREP standards in the first decade of the 21st century may have had limited exposure to thinking about contextual or social factors that impact client wellness. Persons on both factors, however, expressed interest in social justice and felt that the vast majority of advocacy behaviors were important.
In post-sort interviews, participants from both factors described a gradual shift in emphasis from a focus on the individual on the right hand (most important) side of the Q sort distribution to an emphasis on legislation on the left hand (most unimportant) side. For example, the statement identify strengths and resources of clients was one of the most important behaviors for nearly every participant. Likewise, the statement work to change legislation and policy that negatively affects clients was ranked among the most unimportant advocacy behaviors for both factors. Interestingly, the statement encourage clients to research the laws and policies that apply to them was a consensus statement with a Q sort value of 0, or the very middle of the distribution. Since this advocacy behavior is both client focused and presumably would provide clients with important self-advocacy skills, it is interesting that it was ranked lower than other items related to client self-advocacy. Some participants indicated that they considered this item a “passive” counselor behavior in that they might encourage clients to research laws but could not or would not follow up with clients on this task. One participant said she would like to encourage clients to research laws that apply to them but shared that she would first need to learn more about the laws that impact her clients in order to feel effective in using this intervention.
Participants were asked directly about potential barriers to advocacy and potential strengths of career counselors in promoting social justice. Responses are discussed below. The questions about strengths and barriers in the post-sort interview did not reference Q sample items, so participant responses are reported together below.
Barriers to Promoting Social Justice
In the post-sort interviews, lack of time was mentioned by nearly every participant as a barrier to implementing more advocacy in career counseling, and it often came in the form of little institutional support for engaging in advocacy. For example, participants indicated that while their supervisors would not stop them from doing advocacy work, they would not provide material support (e.g., time off, reduced case load) to do so. This finding is consistent with other literature that suggests that career counselors report a lack of institutional support for engaging in advocacy (Arthur et al., 2009).
Another major barrier to advocacy was a lack of skill or confidence in one’s ability as an advocate. Advocacy at the social/political level requires a unique set of skills (M. A. Lee, Smith, & Henry, 2013), which practitioners in the present study may or may not have learned during their counseling training. Pieterse, Evans, Risner-Butner, Collins, and Mason (2009) reviewed 54 syllabi from required multicultural courses in American Psychological Association (APA)- and CACREP-accredited programs and found that awareness and knowledge tended to be emphasized more than skill building or application of social justice advocacy. This seems to have been reflected in the responses from many participants in the present study.
Participants on both factors indicated that they held some negative associations to advocacy work, calling it “flag waving” or “yelling and screaming” about inequality or social issues. They expressed some concern about how they might be perceived by their peers if they were to engage in advocacy; however, involvement in this study seemed to provide participants with a new understanding of advocacy as something that happens at the individual as well as at the social level. Participants appeared to finish the data collection sessions with a more positive understanding of what advocacy is and could be.
Strengths of Career Counselors in Promoting Social Justice
In addition to discussing barriers to advocacy, participants were asked directly about strengths of career counselors in promoting social justice and were able to identify many. First and foremost, participants saw the ability to develop one-on-one relationships with clients as a strength. One participant nicely captured the essence of all responses in this area by stating, “The key thing is our work one-on-one with an individual to say that even though you’re in a bad place, you have strengths, you have resources, and you have value.” Participants indicated that social change happens through a process of empowering clients, instilling hope and seeing diversity as a strength of a client’s career identity. The ability to develop strong counseling relationships was attributed partially to participants’ counseling training and identity, as well as to their exposure to a broad range of client concerns due to the inseparable nature of work from all other aspects of clients’ lives (Herr & Niles, 1998; Tang, 2003).
Career counselors in this study served diverse populations and highly valued doing so. These participants described multicultural counseling skills and experience as central to competent career counseling and to advocacy. They felt that they possessed and valued multicultural competence, which bodes well for their potential to engage in competent and ethical advocacy work with additional training, experience and supervision (Crook, Stenger, & Gesselman, 2015; Vespia, Fitzpatrick, Fouad, Kantamneni, & Chen, 2010).
Finally, participants felt that career counseling is seen as more accessible than mental health counseling to some clients, giving career counselors unique insight into clients’ social and personal worlds. Participants reported having a broad perspective on their clients’ lives and therefore unique opportunities to advocate for social justice. Relatedly, participants noted that the more concrete and tangible nature of career counseling and its outcomes (e.g., employment) may lead policymakers to be interested in hearing career counselors’ perspectives on social issues related to work. One participant noted that “there’s a huge conversation to be had around work and social justice” and that career counselors’ key strength “is empowering clients and the broader community to understand the role of work.”
Implications for Career Counselors, Counselor Educators, and Supervisors
Nearly all participants described the sorting process as thought provoking and indicated that social justice and advocacy were topics they appreciated the opportunity to think more about. There was a strong desire among some practitioners in this study to talk more openly with colleagues about social justice and its connection to career counseling, but a lingering hesitation as well. Therefore, one implication of the present study is that practitioners should begin to engage in discussions about this topic with colleagues and leaders in the profession. If there is a shared value for advocacy beyond the individual level, but time and skills are perceived as barriers, perhaps a larger conversation about the role of career counselors is timely. Career counselors may benefit from finding like-minded colleagues with whom to talk about social justice and advocacy. Support from peers may help practitioners strategize ways to question or challenge coworkers who may be practicing career counseling in ways that hinder social justice.
To move toward greater self-awareness and ethical advocacy, practitioners and career counseling leaders must ask themselves critical and self-reflexive questions about their roles and contributions in promoting social justice (McIlveen & Patton, 2006; Prilleltensky & Stead, 2012). Some authors have indicated there is an inherent tension in considering a social justice perspective and that starting such conversations can even lead to more questions than answers (Prilleltensky & Stead, 2012; Stead & Perry, 2012). Counselors should turn their communication skills and tolerance for ambiguity inward and toward one another in order to invite open and honest conversations about their role in promoting social justice for clients and communities. The participants in this study seem eager to do so, though leadership may be required to get the process started in a constructive and meaningful way.
Counselor educators and supervisors can provide counselors-in-training increased experience with systemic-level advocacy by integrating the ACA Advocacy Competencies and the Multicultural and Social Justice Counseling Competencies into all core coursework. Even though broaching issues of social justice has been reported as challenging and potentially risky, counselor educators should integrate such frameworks and competencies in active and experiential ways (Kiselica & Robinson, 2001; M. A. Lee et al., 2013; Lopez-Baez & Paylo, 2009; Manis, 2012). Singh and colleagues (2010) found that even self-identified social justice advocates struggled at times with initiating difficult conversations with colleagues; they argued that programs should do more to help counselors-in-training develop skills “to anticipate and address the inevitable interpersonal challenges inherent in advocacy work” (p. 141). Skills in leadership, teamwork and providing constructive feedback might be beneficial to prepare future counselors for addressing injustice. Furthermore, Crook and colleagues (2015) found that advocacy training via coursework or workshops is associated with higher levels of perceived advocacy competence among school counselors, lending more support in favor of multi-level training opportunities.
Limitations
The current study is one initial step in a much-needed body of research regarding advocacy practice in career counseling. It did not measure actual counselor engagement in advocacy, which is important to fully understand the current state of advocacy practice; rather, it measured perceived relative importance of advocacy behaviors. Researcher subjectivity may be considered a limitation of this study, as researcher decisions influenced the construction of the Q sample, the factor analysis and the interpretation of the emergent factors. By integrating feedback from two expert reviewers during construction of the Q sample, I minimized the potential for bias at the design stage. Factor interpretation is open to the researcher’s unique lens and also may be considered a limitation, but if it is done well, interpretation in Q methodology should be constrained by the factor array and interview data. Although generalizability is not a goal of Q methodology, the sample size in this study is small and therefore limits the scope of the findings.
Suggestions for Future Research and Conclusion
Advocacy is central to career counseling’s relevance in the 21st century (Arthur et al., 2009; Blustein, McWhirter, & Perry, 2005; McMahon, Arthur, & Collins, 2008a), yet due to the complexity and personal nature of this work, more research is required if we are to engage in advocacy competently, ethically and effectively. There appears to be interest among career counselors in gaining additional skills and knowledge regarding advocacy, so future research could include analyzing the effects of a training curriculum on perceptions of and engagement with advocacy. Outcome research could also be beneficial to understand whether career counselors who engage in high levels of advocacy report different client outcomes than those who do not. Finally, research with directors of career counseling departments could be helpful to understand what, if any, changes to career counselors’ roles are possible if career counselors are interested in doing more advocacy work. Understanding the perspectives of these leaders could help further the conversation regarding the ideals of social justice and the reality of expectations and demands faced by career counseling offices and agencies.
This research study is among the first to capture U.S. career counselors’ perspectives on a range of advocacy behaviors rather than attitudes about social justice in general. It adds empirical support to the notion that additional conversations and training around advocacy are wanted and needed among practicing career counselors. Stead (2013) wrote that knowledge becomes accepted through discourse; it is hoped that the knowledge this study produces will add to the social justice discourse in career counseling and move the profession toward a more integrated understanding of how career counselors view the advocate role and how they can work toward making social justice a reality.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The author conducted this research with the assistance of grants awarded by the National Career Development Association, the North Carolina Career Development Association, and the Southern Association for Counselor Education and Supervision.
References
American Counseling Association. (2014). 2014 ACA Code of Ethics. Alexandria, VA: Author. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/Resources/aca-code-of-ethics.pdf
Arthur, N., Collins, S., Marshall, C., & McMahon, M. (2013). Social justice competencies and career development practices. Canadian Journal of Counselling and Psychotherapy, 47, 136–154.
Arthur, N., Collins, S., McMahon, M., & Marshall, C. (2009). Career practitioners’ views of social justice and barriers for practice. Canadian Journal of Career Development, 8, 22–31.
Blustein, D. L. (2006). The psychology of working. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Blustein, D. L., McWhirter, E. H., & Perry, J. C. (2005). An emancipatory communitarian approach to vocational development theory, research, and practice. The Counseling Psychologist, 33, 141–179. doi:10.1177/0011000004272268
Brown, S. R. (1978). The importance of factors in Q methodology: Statistical and theoretical considerations. Operant Subjectivity, 1, 117–124.
Brown, S. R. (1980). Political subjectivity: Applications of Q methodology in political science. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor. (2016a). Charting the labor market: Data from the Current Population Survey (CPS). Retrieved from http://www.bls.gov/web/empsit/cps_charts.pdf
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor. (2016b). The employment situation – May 2016. Retrieved from http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf
Chope, R. C. (2010). Applying the ACA advocacy competencies in employment counseling. In M. J. Ratts, R. L. Toporek, & J. A. Lewis (Eds.), ACA advocacy competencies: A social justice framework for counselors (pp. 225–236). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Cook, E. P., Heppner, M. J., & O’Brien, K. M. (2005). Multicultural and gender influences in women’s career development: An ecological perspective. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 33, 165–179. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1912.2005.tb00014.x
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2009). 2009 standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/2009-Standards.pdf
Crook, T. M., Stenger, S., & Gesselman, A. (2015). Exploring perceptions of social justice advocacy competence among school counselors. Journal of Counselor Leadership and Advocacy, 2, 65–79.
Dean, J. K. (2009). Quantifying social justice advocacy competency: Development of the social justice advocacy scale
(Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from http://scholarworks.gsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=10
39&context=cps_diss
Fickling, M. J., & Gonzalez, L. M. (2016). Linking multicultural counseling and social justice through advocacy. Journal of Counselor Leadership and Advocacy. doi:10.1080/2326716X.2015.1124814
Herr, E. L., & Niles, S. G. (1998). Career: Social action on behalf of purpose, productivity, and hope. In C. C. Lee & G. R. Walz (Eds.), Social action: A mandate for counselors (pp. 117–136). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Kaiser, H. F. (1970). A second generation little jiffy. Psychometrika, 35, 401–415. doi:10.1007/BF02291817
Kiselica, M. S., & Robinson, M. (2001). Bringing advocacy counseling to life: The history, issues, and human dramas of social justice work in counseling. Journal of Counseling & Development, 79, 387–397. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2001.tb01985.x
Lee, C. C., & Hipolito-Delgado, C. P. (2007). Introduction: Counselors as agents of social justice. In C. C. Lee
(Ed.), Counseling for social justice (2nd ed., pp. xiii–xxviii). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Lee, M. A., Smith, T. J., & Henry, R. G. (2013). Power politics: Advocacy to activism in social justice counseling. Journal for Social Action in Counseling and Psychology, 5, 70–94. Retrieved from http://www.psysr.org/jsacp/Lee-V5n3-13_70-94.pdf
Lewis, J. A., Arnold, M. S., House, R., & Toporek, R. L. (2002). ACA advocacy competencies. American Counseling Association. Retrieved from https://www.counseling.org/docs/default-source/competencies/advocacy_competencies.pdf?sfvrsn=9
Lopez-Baez, S. I., & Paylo, M. J. (2009). Social justice advocacy: Community collaboration and systems advocacy. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87, 276–283. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2009.tb00107.x
Manis, A. A. (2012). A review of the literature on promoting cultural competence and social justice agency among students and counselor trainees: Piecing the evidence together to advance pedagogy and research. The Professional Counselor, 2, 48–57. doi:10.15241/aam.2.1.48
McIlveen, P., & Patton, W. (2006). A critical reflection on career development. International Journal for Educational and Vocational Guidance, 6, 15–27. doi:10.1007/s10775-006-0005-1
McKeown, B., & Thomas, D. B. (2013). Q methodology (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
McMahon, M., Arthur, N., & Collins, S. (2008a). Social justice and career development: Looking back, looking forward. Australian Journal of Career Development, 17, 21–29. doi:10.1177/103841620801700205
McMahon, M., Arthur, N., & Collins, S. (2008b). Social justice and career development: Views and experiences of Australian career development practitioners. Australian Journal of Career Development, 17(3), 15–25. doi:10.1177/103841620801700305
Milner, A., Page, A., & LaMontagne, A. D. (2013). Long-term unemployment and suicide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 8, e51333. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051333
National Career Development Association. (2009). Minimum competencies for multicultural career counseling and development. Retrieved from http://ncda.org/aws/NCDA/pt/sp/guidelines
Niles, S. G., Amundson, N. E., & Neault, R. A. (2010). Career flow: A hope-centered approach to career development. Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Paul, K. I., & Moser, K. (2009). Unemployment impairs mental health: Meta-analyses. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 74, 264–282. doi:10.1016/j.jvb.2009.01.001
Pieterse, A. L., Evans, S. A., Risner-Butner, A., Collins, N. M., & Mason, L. B. (2009). Multicultural competence and social justice training in counseling psychology and counselor education: A review and analysis of a sample of multicultural course syllabi. The Counseling Psychologist, 37, 93–115. doi:10.1177/0011000008319986
Pope, M., Briddick, W. C., & Wilson, F. (2013). The historical importance of social justice in the founding of the National Career Development Association. The Career Development Quarterly, 61, 368–373.
doi:10.1002/j.2161-0045.2013.00063.x
Pope, M., & Pangelinan, J. S. (2010). Using the ACA advocacy competencies in career counseling. In M. J. Ratts, R. L. Toporek, & J. A. Lewis (Eds.), ACA advocacy competencies: A social justice framework for counselors (pp. 209–223). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Prilleltensky, I., & Stead, G. B. (2012). Critical psychology and career development: Unpacking the adjust–challenge dilemma. Journal of Career Development, 39, 321–340. doi:10.1177/0894845310384403
Ratts, M. J., Lewis, J. A., & Toporek, R. L. (2010). Advocacy and social justice: A helping paradigm for the 21st century. In M. J. Ratts, R. L. Toporek, & J. A. Lewis (Eds.), ACA advocacy competencies: A social justice framework for counselors (pp. 3–10). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Ratts, M. J., Singh, A. A., Nassar-McMillan, S., Butler, S. K., & McCullough, J. R. (2015). Multicultural and social justice counseling competencies. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/knowledge-center/competencies
Sampson, J. P., Jr., Dozier, V. C., & Colvin, G. P. (2011). Translating career theory to practice: The risk of unintentional social injustice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 326–337.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00097.x
Savickas, M. L. (1997). Career adaptability: An integrative construct for life-span, life-space theory. The Career Development Quarterly, 45, 247–259. doi:10.1002/j.2161-0045.1997.tb00469.x
Schmolck, P. (2014). PQMethod 2.35 with PQROT 2.0 [Computer software and manual]. Retrieved from
http://schmolck.userweb.mwn.de/qmethod
Singh, A. A., Urbano, A., Haston, M., & McMahan, E. (2010). School counselors’ strategies for social justice change: A grounded theory of what works in the real world. Professional School Counseling, 13, 135–145. doi:10.5330/PSC.n.2010-13.135
Stead, G. S. (2013). Social constructionist thought and working. In D. L. Blustein (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of the psychology of working (pp. 37–48). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Stead, G. B., & Perry, J. C. (2012). Toward critical psychology perspectives of work-based transitions. Journal of Career Development, 39, 315–320. doi:10.1177/0894845311405661
Tang, M. (2003). Career counseling in the future: Constructing, collaborating, advocating. The Career Development Quarterly, 52, 61–69. doi:10.1002/j.2161-0045.2003.tb00628.x
Toporek, R. L., Lewis, J. A., & Crethar, H. C. (2009). Promoting systemic change through the ACA advocacy competencies. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87, 260–268. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2009.tb00105.x
Vespia, K. M., Fitzpatrick, M. E., Fouad, N. A., Kantamneni, N., & Chen, Y.-L. (2010). Multicultural career counseling: A national survey of competencies and practices. The Career Development Quarterly, 59, 54–71. doi:10.1002/j.2161-0045.2010.tb00130.x
Watts, S., & Stenner, P. (2012). Doing q methodological research: Theory, method and interpretation. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Webler, T., Danielson, S., & Tuler, S. (2009). Using Q method to reveal social perspectives in environmental research.
Greenfield, MA: Social and Environmental Research Institute. Retrieved from
http://seri-us.org/sites/default/files/Qprimer.pdf
Melissa J. Fickling, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of Memphis. Correspondence can be addressed to Melissa J. Fickling, University of Memphis, Ball Hall 100, Memphis, TN 38152, mfckling@memphis.edu.
May 19, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 2
Daniel T. Sciarra, Holly J. Seirup, Elizabeth Sposato
Over the past few decades there has been a dramatic paradigm shift in both focus and attitude among postsecondary institutions regarding the importance of student persistence, retention and academic success (Hu, 2011; Kuh, Kinzie, Buckley, Bridges, & Hayek, 2007), in contrast to the past where an institution’s prestige was tied to its ability to exclude students (Coley & Coley, 2010). U.S. News and World Report solidified this sea change, as its report of college rankings now includes retention and graduation rates as a measure of institutional quality (Morse, 2015). In addition, colleges and universities are under increased pressure from public policymakers to improve retention and graduation rates (Hossler, Ziskin, & Gross, 2009). The matter of college graduation rates and persistence has in fact taken on national prominence. In a speech at the University of Texas at Austin, President Obama (2010) commented that over a third of America’s college students and over half of our minority students don’t earn a degree even after six years. So we don’t just need to open the doors of college to more Americans; we need to make sure they stick with it through graduation. (Obama, 2010, para. 34)
The importance of completing a college degree has been magnified because of the high correlation with economic self-sufficiency and responsible citizenship (Kuh, Cruce, Shoup, Kinzie, & Gonyea, 2008). In this regard, the college degree has come to replace the high school diploma.
Students, parents, high school counselors and college counselors expend much time and energy on the college admissions process with high expectations that the student will be successful and persist (Seirup & Rose, 2011). Yet, the statistics regarding college persistence are surprisingly low, while the cost of attrition to the student, the college and the community is quite high. Forty-one percent of students who begin their college careers at a four-year college will not graduate within six years (U.S. Department of Education, 2013), while 35% will drop out completely (Tinto, 2004). The costs associated with students dropping out of college are sobering and impact multiple stakeholders who would potentially benefit from individuals who persisted and graduated from college. The American Institutes for Research (2010) found that the cost of students dropping out of their first year of college is more than nine billion dollars in state and federal funds. For individual students, the average debt is currently $29,000. More problematic is that those who drop out do not have the requisite economic and employment opportunities needed to repay those loans and therefore are four times more likely to default (Casselman, 2012). There also are the additional costs associated to the colleges and universities that need to provide redundant and remedial courses. Amos (2006) found that it costs $1.4 billion to provide remedial education to students who have recently completed high school. Finally, there are the costs to individuals who leave college without achieving their goals and are thus robbed of important opportunities to learn and benefit from that education after college (Hossler et al., 2009).
Prior Research on College Persistence
Based on the seminal work of authors such as Tinto (1975, 1987, 1993), Astin (1984, 1993), Kuh (2007), and Hu (2011), colleges and universities have begun to study factors that impact college persistence and, consequently, to develop and initiate programs to support student success, transition and persistence/retention. Tinto (1975) is perhaps the most recognized for work regarding college persistence. His original model focused on the impact of students’ academic and social integration on the decision to persist but was later revised to focus more on the issues of separation from the home environment and culture, transition from high school to college, and incorporation into the campus community (Tinto, 1987). Tinto (1993) introduced a model of student departure where he addressed the fact that different groups of students (e.g., first generation, at-risk, adults) and different institutions (e.g., public, private, residential) required different retention programs and support services to support student persistence. For example, pre-entry attributes such as family background, skills and abilities, and prior schooling are included in this latest model, yet the main focus of the model is student integration and engagement at the postsecondary institution. Tinto (1993) found that students enter college with certain traits, experiences and intentions that are subsequently and continually modified and reformulated as a result of interactions between the individual and members of the institution’s academic and social systems.
Astin (1993) found that student persistence was positively linked to involvement in academic and social activities along with interaction with faculty and peers. Kuh et al. (2007) found that most persistence and retention models included the following variables: (a) student background characteristics including pre-college academic and other experiences; (b) structural characteristics of institutions such as mission, size and selectivity; (c) interactions with faculty, staff members, and peers; (d) student perceptions of the learning environment; and (e) the quality of effort students devote to educational activities. Pascarella and Terenzini (2005) found the main variables that impact college persistence were: (a) academic performance as measured by grades, particularly those in the first semester/year; (b) academic support programs (e.g., developmental studies, remedial programs, supplemental instruction, instruction in non-academic support skills such as study skills and time management, first-year seminars, academic advising, counseling, and undergraduate research programs); (c) financial aid (the impact and importance of grants, scholarships, and loans and how these things often impact a student’s decision and need to work by reducing the economic obstacles one may face when deciding to persist); (d) interaction with faculty (the perception that faculty are available outside of the classroom positively impacts student persistence); (e) interaction with peers; (f) residence (overall, living on campus positively impacts persistence); (g) learning communities that promote both academic and social interaction; (h) academic major; and (i) social interaction in the form of extracurricular and social involvement. Pascarella and Terenzini (2005) further noted that the degree of integration into campus social systems had positive net effects on persistence and ultimately degree attainment, while involvement in extracurricular activities and the extent and quality of students’ peer interactions were particularly influential.
Current literature on college persistence continues to be based upon the work and models of Tinto, Astin and Kuh but has also focused on the impact of race and ethnicity (Arbona & Nora, 2007; Lundberg & Schreiner, 2004), finding that key variables on persistence are consistent with prior research. Lundberg and Schreiner (2004) found that “satisfying relationships with faculty members and frequent interaction with faculty members, especially those that encouraged students to work harder were strong predictors of learning across every racial group” (p. 559). Arbona and Nora (2007) supported prior findings that academic integration and engagement are significant predictors of persistence for Hispanic students as well.
Currently, a public outcry exists for colleges and universities to be more accountable in supporting students’ persistence to graduation (Nelson, 2012; U.S. Department of Education, 2006). The response to this outcry and the research on college persistence and academic success has been the implementation of initiatives to support students’ transitions from high school to college. These initiatives appear to focus on pre-admission/pre-college attributes such as family background, socioeconomic status and academic performance measured by high school GPA, SAT and ACT scores. Examples of such initiatives include enhanced orientation programs, freshman seminars, living-learning communities and housing options. The resulting outcome data from the successful implementation of these types of support initiatives have yielded increases in retention rates (Barefoot, 2004). Higher education institutions have therefore come to realize the important role the first year, and even the first few weeks, of college may play in a student’s decision to persist.
The above review indicates a clear identification of factors on the college level that impact persistence. Little is known, however, about whether these factors on the high school level can impact college persistence. If such factors could be identified, then counselors who work with pre-college adolescents could increase a student’s chances of persisting in college by developing and strengthening these factors.
While in the academic realm it seems clear that the intensity of the high school curriculum and GPA are predictive of academic success in college (Adelman, 2006; Kuh, et.al., 2008; Sciarra, 2010; Sciarra & Whitson, 2007; Trusty & Niles, 2003), less is known about the predictive effect upon persistence of other high school experiences and skills such as engagement in extracurricular activities, interaction with faculty, amount of time spent studying and doing homework, time doing paid and volunteer work, and the amount of social and academic support. Research (e.g., Kuh, 2007) has shown these factors in college to have a relationship to persistence; yet little if any research has shown whether such factors in high school are predictive of college persistence. This study seeks to answer the following question: Do the same factors at the college level that have a relationship to persistence also have a predictive value for persistence when measured at the high school level?
Method
The study used data from the three waves of ELS (U.S. Department of Education, 2008). ELS included a base year of 10th graders in 2002 followed by two subsequent waves that took place in 2004 and 2006. The base year of ELS comprised a nationally representative probability sample of 15,362 10th graders. A second wave of data in 2004 came from the same base-year participants in their senior year, and a third wave in 2006 came 2 years after scheduled graduation (Sciarra & Ambrosino, 2011). The base year of ELS employed a two-stage sample selection process. Schools were chosen with probability proportional to school size, and size was a composite measure based on school enrollment by race and ethnicity. There were 1,221 eligible public, Catholic and other private schools. Of these, 752 agreed to participate and were asked to provide sophomore enrollment lists. To deal with non-response bias, ELS conducted analyses in conjunction with weighting adjustment to reduce but not completely eliminate all bias. In the second step of sample selection, 26 students were selected from these lists using a stratified systematic sampling of students selected on a flow basis (Ingels et al., 2007). To provide non-academic data, participants completed paper-and-pencil, self-administered questionnaires usually done in the school setting. The ELS Web site provides actual copies of the questionnaires.
Participants
Participants included students who participated in all three waves (2002, 2004 and 2006) of ELS (U.S. Department of Education, 2008) and who enrolled in either a two-year or four-year institution upon graduation from high school. The enrollment condition was necessary since the study is an investigation into those who persisted in college versus those who did not. This resulted in a final N of 7,271. Participants also included sophomore math and English teachers. The student participants were 54% female and 46% male. Their ethnic identification was 1% Native American, 5% Asian, 15% African American, 13% Latino, 62% White, and 4% Multiracial. Since not all of the originally selected schools participated in the study’s three waves, the data were weighted to adjust for this and for probabilities that were unequal in the selection of schools and students (Ingels, Pratt, Rogers, Siegel, & Stutts, 2005). There are two main steps in the weighting process. First is the calculation of unadjusted weights as the inverse of the probabilities of selection; second, these weights are adjusted to compensate for non-response (Curtin, Ingels, Wu, & Heuer, 2002) and result in a relative weight derived by dividing the panel weight of the data base by the average weight of the sample.
Variables
The study employed a total of nine predictor variables, seven categorical and two interval.
Categorical variables. Four of the categorical variables were yes/no questions, two of which were teacher-reported. Both the student’s math and English teachers were asked: “Does this student talk with you outside of class about school work, plans for after high school or personal matters?” ELS limits its survey to only the math and English teachers. Another yes/no question included asking the students if they had gone to the school counselor for college entrance information, and the fourth asked the students whether they had performed any unpaid, volunteer, community service work during the past two years. The remaining three variables were the result of categorizing the number of hours spent weekly working at a job, doing homework and performing extracurricular activities. As regards to hours worked at a job, the original 10-category variable was collapsed into four categories: “none,” “low” (1 to 10 hours per week), “moderate” (11 to 20 hours per week), and “high” (21 or more hours per week). Hours spent weekly doing homework in or out of school were categorized as “very low” (none to less than 1 hour), “low” (1 to 6 hours), “moderate” (7 to 15 hours), and “high” (16 or more hours). Time spent weekly in extracurricular activities was categorized as “none,” “low” (less than 1 hour to 4 hours), “moderate” (5 to 14 hours), and “high” (15 or more hours). The two teacher-reported variables were from sophomore year, while the rest were asked of students in their senior year.
Interval variables. Created from individual items in the database, the study employed two composite, interval variables: academic and social support. These variables were selected based upon the research of Pascarella and Terenzini (2005), Kuh (2007), and Hu (2011) who identified these constructs as being integral to a student’s success in higher education. The academic support variable was composed of three Likert-scaled items: (1) “Among your close friends, how important is it to them that they study?”; (2) “Among your close friends, how important is it that they finish high school?”; and (3) “Among your close friends, how important is it that they continue their education past high school?” Cronbach’s alpha for the academic support scale was .72. The social support variable was also composed of three Likert-scaled items: (1) “Among your close friends, how important is it that they get together with friends?”; (2) “Among your close friends, how important is it that they go to parties?”; and (3) “How important is it to you to have strong friendships in your life?” Cronbach’s alpha for the social support scale was .49. All questions were asked of students in their sophomore year of high school and had three choices for answers: (1) not important, (2) somewhat important and (3) very important. Higher scores represented greater socialization.
Criterion variable. The criterion variable measured student status 2 years after scheduled graduation and had three categories: (1) leaver (enrolled after high school but not enrolled in January of 2006), (2) still enrolled in a two-year institution, and (3) still enrolled in a four-year institution. This same criterion variable with four categories was used in a previous study (Sciarra & Ambrosino, 2011).
Data Analysis
Since the criterion variable has three categories (leaver, still enrolled in a two-year institution, still enrolled in a four-year institution), the appropriate method for analysis is a multinomial logistic regression (MLR; Norusis, 2004). The MLR models the relationship between a categorical criterion variable and predictor variables (Menard, 2010; Norusis, 2004; Pampel, 2000). In MLR, the effect size results from the odds ratios for each predictor. Odds ratios are ratios of the probability of being in a particular group compared to being in the baseline or reference group (Sciarra & Ambrosino, 2011). In the present analysis, the reference group was the first category (leaver), to which the other groups were compared along the predictor variables. Unlike linear regression, MLR employs categorical variables and cannot rely on traditional transformation methods to deal with missing data. The SPSS default position was employed, which excludes all cases with missing values on any of the independent variables. The analysis, more theory-testing than exploratory, utilized the forced entry method where all predictors are entered at the same time into the regression equation. In large data sets, there is a danger of overdispersion. To check for this, a dispersion parameter was calculated by dividing the Pearson chi square goodness of fit by the degrees of freedom, which equaled 1.23. While any parameter greater than 1 indicates the presence of overdispersion, only a parameter approaching or greater than 2 suggests a problem (Field, 2009).
Results
The original MLR model had nine predictor variables (academic support, social support, talks with math teacher outside of class, talks with English teacher outside of class, has gone to counselor for college entrance information, performed volunteer/community service work, number of hours spent weekly on working, homework and extracurricular activities). From the sample of 7,271 who participated in all three waves (2002, 2004 and 2006) of ELS (U.S. Department of Education, 2008) and who enrolled in either a two-year or four-year institution upon graduation from high school, academic support [χ2 (2, 3148) =.90, ρ=.64], social support [χ2 (2, 3148) =.59, ρ=.74], talks with English teacher outside of class [χ2 (2, 3148) =1.14, ρ=.57] , has gone to counselor for college entrance information [χ2 (2, 3148) =1.44, ρ=.49], performed community/volunteer service [χ2 (2, 3148) =.63, ρ=.73], and number of hours worked [χ2 (6, 3148) =4.64, ρ=.59] were not significant and therefore were excluded from subsequent analyses.
The revised model included the three remaining variables whose correlations were .066 (hours spent on homework and talks with math teacher outside of class), .00 (number of hours spent on extracurricular activities and talks with math teacher outside of class, and .01 (number of hours spent on homework and number of hours spent on extracurricular activities). Low correlations along with low standard errors (ranging from .06 to .18) among the independents suggest the absence of multicollinearity. Tests for multicollinearity revealed tolerances values and various inflations factors to hover around 1.0, and the highest condition index was 7.9. All observations reveal low risk of multicollinearity (Cohen, Cohen, West, & Aiken, 2013).
For the MLR examining the effects of the three predictor variables, the likelihood ratio test for the overall model revealed that the model was significantly better than the intercept-only model [χ2 (14, 7271) = 594.63, p < .000]. In other words, the null hypothesis (that the regression coefficients of the independent variables are zero) was rejected. Both the Hosmer-Lemeshow test (Hosmer & Lemeshow, 2000) for model deviance [χ2 (48)=59.87, p < .117] and the goodness of fit test [χ2 (48)=58.53, p < .142] failed to reject the null hypothesis, implying that the model’s estimates fit the data at an acceptable level. Furthermore, the likelihood ratio test for individual effects showed that all of the predictor variables were significantly related to the categories of the criterion variable: talks with math teacher, χ2 (2) = 14.94, p < .001; hours of homework, χ2 (6) = 13.50, p < .05; and hours of extracurricular activities, χ2 (6) = 533.65, p < .000. Regarding effect size, the Nagelkerke R2 (Norusis, 2004) in the overall model was .086, considered a medium effect size (Sink & Stroh, 2006). Therefore, the independent variables included in the model explained 8.6% of the variability in college persistence.
Table 1
MLR Parameter Estimates and the Effects of the Predictor Variables Upon Postsecondary Education Status.
|
Still Enrolled in Two-Year Institution
|
Still Enrolled in Four-Year Institution
|
| VARIABLE |
β
|
Odds
|
β
|
Odds
|
| Talks with Math Teacher Outside of ClassNoYes |
.04
|
1.04
|
.21*** |
1.24
|
| Hours Spent Weekly on HomeworkVery LowLowModerateHigh |
.13
.20
.16
|
.88
1.23
1.17
|
.08.24.18 |
1.08
1.27
1.20
|
| Hours Spent Weekly on Extracurricular ActivityNoneLowModerateHigh |
-.25*
-.12
-.01
|
.78
.86
.99
|
-1.6***-.58***-.15 |
.20
.56
.86
|
Note. Leaver is the reference category for the dependent variable. The comparison categories for the predictor variables were talking to the math teacher outside of class, high (16 or more) number of hours per week on homework, and high (15 or more) number of hours spent in extracurricular activities. AM software (American Institutes for Research, 2003) was used to calculate adjusted standard errors for sampling design effects. Nagelkerke R2 = .09. * p ≤ .05; ** p ≤ .01; *** p ≤ .001.
Table 1 gives the parameter estimates from the MLR that analyzed the effects of the predictor variables on postsecondary education status and presents two nonredundant logits since our criterion variable (postsecondary status) has three possible values: leaver, still enrolled in a two-year institution, and still enrolled in a four-year institution. When comparing those still enrolled in a two-year institution to those no longer enrolled, the only parameter estimate that was significantly different from zero was time spent in extracurricular activities. Those students with no extracurricular activities (β=-.25) compared to those with a high number extracurricular activities (15 or more hours per week) were less likely to still be enrolled in a two-year institution. When examining the second logit (those still enrolled in a four-year institution compared to those no longer enrolled in any postsecondary institution), two predictors were significant: talks to the math teacher outside of class and time spent in extracurricular activities. Those students who spoke with their math teacher outside of class increased their chances of still being enrolled in a four-year institution rather than being in the leaver group by a factor of 1.24. The parameters for homework were not significant. In regards to the number of weekly hours in extracurricular activities, the parameters for none and low (1–4) hours were significant. Those students who spent either no or a low number of hours in extracurricular activities compared to those with a high number of hours (15 or more) were less likely to still be enrolled in a four-year institution. The difference between a moderate number (5–14) and a high number (15+) of hours spent in extracurricular activities was not significant.
Discussion
Based on previous research about factors in college related to persistence, this study hypothesized nine criterion variables on the high school level to predict college persistence. The hypothetical question guiding this study was: Would the same variables on the college level known to influence persistence predict persistence when measured at the high school level? Three of these nine variables were significant in the overall model: talks with math teacher outside of class, number of hours spent weekly on homework, and number of hours spent weekly on extracurricular activities. Six of the nine variables were not significant: academic support, social support, talks with English teacher outside of class, has gone to counselor for college entrance information, performed community/volunteer service, and number of hours worked. As a result, our original model was replaced with a more parsimonious model of three predictor variables. Furthermore, number of hours spent weekly on homework, while significant in the overall model, was not a strong enough predictor to distinguish those who persisted in two-year colleges from those who left or to distinguish those who persisted in four-year colleges from those who left. In the end, the two predictors strong enough to differentiate among the three groups were: talks with math teacher outside of class and number of hours spent in extracurricular activities.
Some of the predictor variables, like academic support and social support, were composite variables of just three Likert-scaled student-reported items. Thus, the reliability of these is questionable and may explain their lack of predictive value. Previous research (Kuh et al., 2008; Pascarella & Terenzini, 2005) has shown that college students with both academic and social support have a greater chance of persisting. Related to academic support, however, is seeking out and talking with professors outside of class. College students who interact with professors outside of class have a greater chance of persisting. The results of the present study indicate that high school students who spoke with their math teacher (not the English teacher) outside of class had a greater chance of persisting in a four-year college, but not necessarily in a two-year college. This result is not surprising as it was hypothesized that high school students who speak with their teachers outside of class would have a greater likelihood of doing so on the college level and, in turn, a greater likelihood of persisting in college. What may be surprising is that the predictive value lies particularly with the math teacher. The predictive value of the math curriculum upon completion of the baccalaureate degree has been well established (Adelman, 1999, 2006; Trusty & Niles, 2003). Thus, based on previous research, one might argue that students taking math more seriously in high school will have a greater chance of persisting in a four-year college, and one indication of such seriousness is speaking with the teacher outside of class. This is not to say that speaking with other teachers is unimportant, but it may be that such communication has less of an effect upon college persistence and completion of a four-year degree. Many students find math difficult, especially the more advanced courses. Some students may have the self-confidence to approach math teachers, and these attributes contribute to their persistence in college. The average student, however, may not feel so comfortable. If students are able to overcome the intimidation of difficult and challenging subject matter by approaching their teacher either to seek help for material that is confusing and not understood or desiring further work, they will find fewer obstacles in approaching other teachers or professors. Without wishing to sound overly simplistic, it may be stated: If you can speak with a teacher whose subject matter you find difficult and challenging, you might be able to speak with anyone. It fosters a help-seeking quality that may very well contribute to persistence in college. A history of speaking with the high school math teacher outside of class may make it less intimidating to speak with university professors once the students arrive at a four-year institution.
The relationship between homework, extracurricular activities and college persistence merits some discussion. As mentioned previously, hours spent doing homework in high school were significant in the overall model of college persistence, but not strong enough to significantly differentiate those who persisted from those who did not. On the other hand, the number of hours spent in extracurricular activities was significant on both the four-year and two-year college levels. The relative lack of significance for homework is a surprising result, as studies show that college grades are related to hours spent doing homework and significantly impact persistence (Pascarella & Terenzini, 2005). Why then is homework not a significant predictor on the high school level? Kuh et al. (2007) found that 47% of high school students study 3 hours a week or less and receive predominantly A and B grades, and academic engagement declines in a linear fashion over the 4 years. This, taken into conjunction with extracurricular activities may explain why the latter is more important than the former. Research (Astin, 1993; Kuh et al., 2008; Pascarella & Terenzini, 2005) has shown that integration (i.e., a feeling of connectedness and belonging) is one of the strongest predictors of persistence on the college level. Participation in extracurricular activities is one of the many ways, if not the most effective way, students become integrated into the school environment. The present study shows that those involved in zero or low (1–4 hours weekly) number of hours of extracurricular activities were less likely to persist in a four-year institution. It can be suggested, then, that those who participated in a moderate (5–14 hours) and high (15+) number of hours in high school activities would more likely participate in clubs and activities on the college level, which may, in turn, foster their sense of belonging and integration in the college environment. This was somewhat less true for those who persisted in a two-year institution, where only those who had zero extracurricular activities were less likely to persist. It may be that since many two-year institutions are commuter schools, integration via participation in extracurricular activities may have a less important role in persistence. Among those who attend four-year colleges, the pathway to persistence initially may be through feeling part of something (e.g., a club, an activity, a sport), which fosters a sense of integration and consequential feelings of contentment. Rare are the students who like doing homework. More common, however, might be students who will do homework because they like the school environment, want to stay and do not want to be dismissed for academic reasons. In other words, the pathway to persistence may be through extracurricular activities.
Implications for Counseling Practice
Implications for School Counselors
School counselors are intricately involved in postsecondary planning and, in many schools, diligently work toward getting their students into the college of their choice (American School Counselor Association [ASCA], 2005b). One of the nine predictive variables in our initial model that was related to the school counselor, “gone to counselor for college entrance information,” was not significant. Getting information from a counselor regarding college entrance requirements is transactional, and although it may assist a student with getting into college, it would not necessarily impact their persistence. Furthermore, this variable focuses on one aspect of the school counselor’s complex role and not on the broader roles school counselors perform that can impact college persistence. The National Standards of ASCA (1997; Campbell & Dahir, 1997), the ASCA National Model (2003, 2005a), and the Transforming School Counseling Initiative (Education Trust, 1997) have contributed to determining the role of the school counselor as more proactive in maximizing the academic development of students. The results of our study imply that school counselors can influence factors related to persistence, namely extracurricular activities and talking with teachers outside of class. The ASCA National Model (ASCA, 2005a) focuses on the school counselor’s role and responsibility to promote the development of students in the academic, career, and personal and social domains. Specifically, the school counselor could support and encourage students to engage in extracurricular activities and to interact/talk with teachers outside of class, which would be proactive measures under the ASCA model and also increase the chances of college persistence. Those who develop a sense of belonging (Adler, 1964) through extracurricular activities in high school will be more equipped to replicate this effort on the college level. School counselors have always tried to promote school bonding by connecting students to clubs and organizations commensurate with their interests. This study shows that they can invigorate their efforts with the added knowledge that it may make a difference in whether a student persists or not on the college level.
A second implication for school counselors concerns the predictive value of talking to the math teacher outside of class. Speaking with a teacher outside of class, especially if it involves material not understood, can be challenging for many students. It requires assertiveness and self-confidence and, in spite of encouragement by counselors, many students may fail to make such efforts. This study implies that school counselors should develop and maintain efforts at facilitating student interactions with teachers outside of class. Most teachers are dedicated professionals and want to help students succeed. School counselors know both the teachers and the students and therefore are in a unique position to broker relationships between the two. Comprehensive school counseling programs emphasize collaboration between the professional school counselor and other educators in order to promote academic achievement (ASCA, 2005b). If students can develop facility during high school for talking with teachers outside of class and seeking help for material they do not understand, this study shows that doing so may make a difference in their ability to persist on the college level. The first year of college can be intimidating for many students, and their help-seeking capacities for academic challenges can make a big difference in their becoming comfortable and engaged in college life. Therefore, school counselors should not tire in their efforts to promote a healthy interaction between students and teachers, especially with a teacher whose subject matter students might find challenging. For many students, this may be the math teacher, which may explain why the present study found that talking to a high school math teacher outside of class positively predicted persistence in college.
Implications for Community and Mental Health Counselors
Often encouraged by the school, many parents whose children are struggling seek counseling services in the community. Poor academic performance can result in a variety of mental health problems, including learned helplessness, low self-esteem and poor self-efficacy (McLeod, Uemura, & Rohrman, 2012; Needham, Crosnoe, & Muller, 2004). A counselor’s advocacy with the school becomes a significant part of the treatment plan because these students often get lost in the system (Holcomb-McCoy & Bryan, 2010). With the parents’ permission, counselors can attend pupil personnel team meetings and talk with the school counselors and teachers. As mentioned several times, the interactions with teachers are an important predictor for college persistence. The first author works with many adolescents who attend large urban schools and struggle with math. He will often suggest talking to the teacher and getting extra help, a suggestion that is often unceremoniously dismissed. In some cases, through counseling and the use of role-plays, students can gain the necessary assertiveness and self-confidence to approach their teachers and discuss difficult subject matter. In other cases, students will continue to resist. After discussing the idea with the student, the counselor can call the school counselor and even the teacher to effectuate greater interactions with the students. More important than who initiates the interaction is the comfort level a student achieves from talking and meeting with teachers outside of class with the hope of receiving tutoring and mentoring (Bryan et al., 2012). With both the adolescent’s and parents’ permission, the senior author has often called teachers to discuss a struggling student’s performance and alert them to the student’s difficulty in asking for help. The phone call usually ends with an agreement that the teacher will reach out to the student. While it may be rare for the college professor to reach out, students who have had the experience of talking with teachers in high school about challenges in the classroom may be more likely to initiate such interactions on the college campus.
Implications for College Student Development Counselors
Recently, there have been calls for stronger links between secondary schools and institutions of higher education (Adams, 2013; Brock, 2010; Lautz, Hawkins, & Perez, 2005). In fact, President Obama’s 2014 budget included grants for high schools to partner with higher education, business and non-profit groups to develop programs to prepare students for college and the workplace (Adams, 2013.) While strides have been made in the development of programs to support early college, dual enrollment programs, various articulation agreements and the integration of offering college level courses in high schools (Adams, 2013; Allen & Murphy, 2008; Fowler & Luna, 2009; Lautz, Hawkins, & Perez, 2005), these programs are mostly academic and do not address the social, non-academic and engagement issues proven to impact persistence (Pascarella & Terenzini, 2005). Thus, it would seem that promoting increased communication and collaboration between school and college student development counselors might provide the needed link for those working directly with students outside of the classrooms at all grade levels. For example, the University of Buffalo has responded by developing a program that includes advisory boards made up of school counselors, hosting the local school counselor association meeting and trainings on campus, and connecting with school counselor education programs (Bernstein, 2003).
Our results suggest the need to promote the importance of students’ involvement in extracurricular activities as well as the interaction with faculty—particularly the math teachers. College student development counselors need to seek out opportunities to meet with high school students not only to recruit them to their respective schools, but to work with the school counselors and the students themselves to assist and encourage students in developing these important skills. Admissions counselors often have that very important initial contact with students and can build into their presentation a simple yet meaningful assessment to identify students who may not have the skills identified as positively impacting persistence. One implication from the present study would be to ask students about the number of hours spent in extracurricular activities and how well they know their teachers (particularly their math teacher). Such questions could give an indication as to how developed those skills are at the moment and identify those students who need additional assistance. Professional development for teachers might also assist in increasing their understanding of the important and future consequences of interaction with their students as it relates to college persistence. Again, if college counselors can promote the interaction between teachers and students on the high school level, it may pave the way for these same students to interact and seek out help more easily from their college professors.
Limitations and Future Research
First, data-based research limits the investigator to items in the data base. The academic and social support variables, known to have a significant effect at the college level upon persistence, were composed of items that made these variables equivocal to the kind of support experienced in college. More reliable measures of academic and social support are needed to properly assess their predictive value on the high school level in regards to persistence. Secondly, the study is longitudinal and relies on data collected over a period of 4 years. As is the case with many longitudinal studies, not all ELS base-year participants were available several years later for the second follow-up, a year and a half after scheduled graduation from high school. Studies using continuous variables can rely on transformation methods available in statistical programs to replace missing data. However, this was not an option for the present study because it employed mostly categorical variables and causes the study to have missing cases, which reduces its randomness and generalizability. Thirdly, in the Discussion section, reference was made to the path toward college persistence and the special significance extracurricular activities might play in that pathway. Logistic regression can measure the significance and strength of individual predictors but cannot determine whether there is a significant difference among the predictors. Future studies, using path analysis, can shed more light on our findings that were achieved through simple regression and determine more specifically the path toward college persistence and the strength of relationship among various predictors.
Conclusion
This study investigated variables at the high school level that predict college persistence. Persistence was the dependent variable and measured by those who were still enrolled in a postsecondary institution a year and a half after graduation from high school. From the variables on the college level known to have a relationship to persistence, this study measured those same variables on the high school level to see if they predicted persistence in either a two-year or four-year institution. Six of the nine variables from the original model were not significant: academic support, social support, talks with English teacher outside of class, has gone to counselor for college entrance information, performed community/volunteer service, and number of hours worked. Two variables were strong enough to distinguish those who persisted from those who left: hours of extracurricular activities and talking with math teachers outside of class. The study discussed the implications for school, college student development and community mental health counselors in regards to the significance of these two variables.
Persistence is a major concern today among colleges. Implications of this study reveal how counselors can contribute to enhancing persistence by examining the relationship between factors on the high school level and persistence. The results of this study indicate that much more research needs to be done on this topic. Only a small number of our originally hypothesized predictors were supported as having a relationship to college persistence. Homework, talking to the math teacher and extracurricular activities contributed to about 9% of the variance, indicating that high school persistence is explained by many more factors other than the ones found significant in this study. This study, however, is a first attempt at investigating how counselors working with high school youth might contribute to enhancing persistence on the college level. The authors hope that the findings that indicate the significance of some and the lack of significance of other variables will spur further interest in this topic. More so than attending college, graduating from college has become a major challenge today. If counselors can help construct a more solid foundation for persistence at the secondary school level, colleges will be in a better position to graduate qualified members for increasingly sophisticated and academically challenging work environments.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest or funding contributions for the development of this manuscript.
References
Adams, C. (2013). Obama calls for innovation in high school and higher ed. Education Week. Retrieved from http://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/college_bound/2013/02/obama_calls_
for_innovation_in_high_school_and_higher_ed.html
Adelman, C. (1999). Answers in the tool box: Academic intensity, attendance patterns, and bachelor’s degree attainment. U.S. Department of Education, Office of Educational Research and Improvement. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office.
Adelman, C. (2006). The toolbox revisited: Paths to degree completion from high school through college. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
Adler, A. (1964). Social interest: A challenge to mankind. New York, NY: Capricorn.
Allen, L., & Murphy, L. (2008). Leveraging postsecondary partners to build a college-going culture: Tools for high school/postsecondary partnerships. Boston, MA: Jobs for the Future.
American Institutes for Research. (2003). AM statistical software. Retrieved May 3, 2014 from http://am.air.org
American Institutes for Research. (2010). College dropouts cost cash-strapped states billions. Retrieved from http://www.air.org/news/press-release/college-dropouts-cost-cash-strapped-states-billions
American School Counselor Association. (1997). Executive summary: The national standards for school counseling programs. Alexandria, VA: Author.
American School Counselor Association. (2003). American school counselor association national model: A framework for school counseling programs. Alexandria, VA: Author.
American School Counselor Association. (2005a). The ASCA national model: A framework for school counseling programs (2nd ed.). Alexandria, VA: Author.
American School Counselor Association. (2005b). The professional school counselor and comprehensive school counseling programs. Alexandria, VA: Author.
Amos, J. (2006). Paying double: United States spends over $1.4 billion annually on remedial education for recent high school graduates. Alliance for Excellent Education, 6, 16. Retrieved from http://all4ed.org/articles/paying-double-united-states-spends-over-1-4-billion-annually-on-remedial-education-for-recent-high-school-graduates/
Arbona, C., & Nora, A. (2007). The influence of academic and environmental factors on Hispanic college degree attainment. Review of Higher Education, 30, 247–269. doi:10.1353/rhe.2007.0001
Astin, A. W. (1984). Student involvement: A developmental theory for higher education. Journal of College Student Personnel, 25, 297–308.
Astin, A. W. (1993). What matters in college? Four critical years revisited. San Francisco, CA: Jossey Bass.
Barefoot, B. O. (2004). Higher education’s revolving door: Confronting the problem of student drop out in U.S. college and universities. Open Learning, 19, 9–18. doi:10.1080/0268051042000177818
Bernstein, F. (2003). Good neighbors: Tips for colleges to enhance school-counselor relations. Journal of College Admission, 181, 30–31.
Brock, T. (2010. Young adults and higher education: Barriers and breakthrough to success. The Future of Children, 20, 109–132.
Bryan, J., Moore-Thomas, C., Gaenzle, S., Kim, J., Lin, C.-H., & Na, G. (2012). The effects of school bonding on high school seniors’ academic achievement. Journal of Counseling & Development, 90, 467–480.
Campbell, C. A., & Dahir, C. A. (1997). Sharing the vision: The national standards for school counseling programs. Alexandria, VA: American School Counselor Association.
Casselman, B.(2012, November 22). The cost of dropping out. Millions struggling with high college debt and no degree. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved from http://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424127887324595904578117400943472068
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2013). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Coley, C., & Coley, T. (2010). Retention and student success: Staying on track with early intervention strategies. Malvern, PA: Sunguard Higher Education.
Curtin, T. R., Ingels, S. J., Wu, S., & Heuer, R. (2002). National Education Longitudinal Study of 1988: Base-year to fourth follow-up data file user’s manual (NCES 2002–323). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics.
Education Trust. (1997). Working definition of school counseling. Washington, DC: Author.
Field, A. (2009). Discovering statistics using SPSS (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Fowler, M., & Luna, G. (2009). High school and college partnerships: Credit-based transition
programs. American Secondary Education, 38, 62–76.
Holcomb-McCoy, C., & Bryan, J. (2010). Advocacy and empowerment in parent consultation: Implications for theory and practice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 88, 259–268.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2010.tb00021.x
Hosmer, D. W., & Lemeshow, S. (2000). Applied logistic regression. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. doi:10.1002/0471722146.scard
Hossler, D., Ziskin, M., & Gross, J. (2009 January–February). Getting serious about institutional performance in student retention. Wiley InterScience, About Campus: Hoboken, NJ.
Hu, S. (2011). Reconsidering the relationship between student engagement and persistence in college. Innovative Higher Education, 36, 97–106. doi:10.1007/s10755-010-9158-4
Ingels, S. J., Pratt, D. J., Rogers, J. E., Siegel, P. H., & Stutts, E. S. (2005). Education Longitudinal Study of 2002: Base-year to first follow-up data file documentation (NCES 2006–344). U.S. Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics.
Ingels, S. J., Pratt, D. J., Wilson, D., Burns, L. J., Currivan, D., Rogers, J. E., & Hubbard-Bednasz, S. (2007). Education Longitudinal Study of 2002: Base-year to second follow-up data file documentation (NCES2008–347). U.S. Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics.
Kuh, G. D. (2007). What student engagement data tell us about college readiness. Peer Review, 9, 4–8.
Kuh, G. D., Cruce, T. M., Shoup, R., Kinzie, J., & Gonyea, R.M. (2008). Unmasking the effects of student engagement on first-year college grades and persistence. The Journal of Higher Education, 79, 540–563.
Kuh, G. D., Kinzie, J., Buckley, J. A., Bridges, B. K., & Hayek, J. C. (2007). Piecing together the student success puzzle: Research, propositions, and recommendations. ASHE Higher Education Report, 32. San Francisco, CA: Jossey Bass.
Lautz, J., Hawkins, D., & Perez, A.B. (2005). The high school visit: Providing college counseling and building crucial K–16 links among students, counselors and admission officers. Journal of College Admission, 188, 6–15.
Lundberg, C. A., & Schreiner, L. A. (2004). Quality and frequency of faculty-student interaction as predictors of learning: An analysis by student race/ethnicity. Journal of College Student Development, 45, 549–565. doi:10.1353/csd.2004.0061
McLeod, J. D., Uemura, R., & Rohrman, S. (2012). Adolescent mental health, behavior problems, and academic achievement. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 53, 482–497.
Menard, S. (2010). Logistic regression. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Morse, R., & Brooks, E. (2015). Best colleges ranking criteria and weights. US News and World Report. Retrieved from http://www.usnews.com/education/best-colleges/articles/ranking-criteria-and-weights
Needham, B. L., Crosnoe, R., & Muller, C. (2004). Academic failure in secondary schools: The inter-related role of health problems and educational context. Social Problems, 51, 569–586.
Nelson, L. A. (2012, April 12). Last rites for graduation rate. Inside Higher Ed. Retrieved from http://www.insidehighered.com/news/2012/04/12/education-department-changing-graduation-rate-measurements.
Norusis, M. J. (2004). SPSS 13.0 Advanced statistical procedures companion. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Obama, B. (2010). Remarks by the President on higher education and the economy at the University of Texas at Austin. Retrieved from https://www.whitehouse.gov/the-press-office/2010/08/09/remarks-president-higher-education-and-economy-university-texas-austin
Pampel, F. C. (2000). Logistic regression: A primer. Sage University Papers Series on Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences, 07–132. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Pascarella, E. T., & Terenzini, P. T. (2005). How college affects students: A third decade of research (Vol. 2). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass Higher & Adult Education.
Sciarra, D. T. (2010). Predictive factors in math course-taking in high school. Professional School Counseling, 13, 196–207.
Sciarra, D. T., & Ambrosino, K.E. (2011). Post-secondary expectations and educational attainment. Professional School Counseling, 14, 231–241.
Sciarra, D. T., & Whitson, M. L. (2007). Predictive factors in post-secondary education attainment among Latinos. Professional School Counseling, 10, 307–316.
Seirup, H., & Rose, S. (2011). Exploring the effects of hope on GPA and retention among college undergraduate students on academic probation. Education Research International, 2011, 1–7. doi:10.1155/2011/381429
Sink, C. A., & Stroh, H. R. (2006). Practical significance: The use of effect sizes in school counseling research. Professional School Counseling, 9, 401–411.
Tinto, V. (1975). Dropout from higher education: A theoretical synthesis of recent research. Review of Educational Research, 45, 89–125. doi:10.3102/00346543045001089
Tinto, V. (1987). Leaving college: Rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Tinto, V. (1994-. Leaving college: Rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition (2nd ed.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Tinto, V. (2004). Student retention and graduation: Facing the truth, living with the consequences. Washington, DC: The Pell Institute for the Study of Opportunity in Higher Education.
Trusty, J., & Niles, S. G. (2003). High-school math courses and completion of the Bachelor’s degree. Professional School Counseling, 7, 99–107.
U.S. Department of Education. (2006). A test of leadership: Charting the future of U.S. higher education, ED-06-C0-0013. Washington, DC: Author.
U.S. Department of Education. (2008). Educational longitudinal study: 2002/04/06 data files and electronic codebook system, base-year, first follow-up, second follow-up with high school transcripts. NCES 2008–346. Washington, DC: Author.
U.S. Department of Education. (2013). The condition of education 2013: Institutional retention and graduation rates for undergraduate students. NCES 2013–037. Washington, DC: Author.
Daniel T. Sciarra, NCC, is a Professor at Hofstra University. Holly J. Seirup is an Associate Professor at Hofstra University. Elizabeth Sposato is Assistant Director of Career Services at New York Institute of Technology. Correspondence can be addressed to Daniel Sciarra, 160 Hagedorn Hall, Hofstra University, Hempstead, NY 11549, daniel.t.sciarra@hofstra.edu.
Mar 24, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 1
Melissa Luke, J. Scott Hinkle, Wendi Schweiger, Donna Henderson
Mental health research supports the notion that better care management is achieved when people receive education, training and support to carry out the role of informal caregivers (World Fellowship for Schizophrenia and Allied Disorders, 2006). Although the prevalence of mental disorders in Africa is a significant health problem (Jenkins et al., 2010), treatment remains a low priority (Bird et al., 2011; Jacob et al., 2007), placed at the bottom of the public health care agenda. Mental health patients of all ages and their families are too often invisible, voiceless and living at the margins of society, and they are rarely mobilized to advocate for themselves (Saraceno et al., 2007). In Africa, mental health receives less attention due to a plethora of problems with communicable diseases and malnutrition (Gureje & Alem, 2000). Moreover, the contribution of mental distress to morbidity, as well as mortality, largely goes underappreciated (Jenkins et al., 2010).
Skeen, Lund, Kleintjes, Flisher, and the MHaPP Research Programme Consortium (2010) have reported: “Mental health is a crucial public health and development issue in sub-Saharan Africa” (p. 624). At least half of all African countries have no community-based mental health services, and almost as many have no integration of mental health into primary care or training facilities for primary care staff in the treatment of mental health (World Health Organization [WHO], 2005). In low-income countries like Malawi, essential psychotropic medications are not available, and resources for mental health training and care are largely lacking (Becker & Kleinman, 2013; WHO, 2004). Challenging the negative perception of mental disorders, reducing their prevalence and providing adequate care are essential policy goals for most of Africa (Gureje & Alem, 2000), a continent where widespread stigma and discrimination, human rights abuses and poverty are the hallmarks of mental health care (Lund, 2010).
In Africa, alternative explanations for mental distress, such as bewitchment, taboos and the belief that it runs in families, reduce the chances of access to mental health care (Bird et al., 2011; Wright, Common, Kauye, & Chiwandira, 2014). Moreover, attitudes about mental illness are strongly influenced by traditional beliefs (e.g., supernatural causes) and remedies. Public education that dispels notions that mental disorders are incurable and nonresponsive to typical care is needed (Gureje & Alem, 2000) as well as an effective strategy to decrease stigma (Bird et al., 2011). To accomplish these goals, governments, as well as nongovernmental organizations, need to bring community mental health services to scale (Hinkle, 2014; Patel, 2013; Patel et al., 2007). In 2006, Murthy reported that a global community mental health blueprint does not exist in order to achieve mental health access, and that national community workforce strategies need to be linked to each country’s unique situation. Relatedly, Hinkle (2012a, 2014), among others, has advocated for a radical shift in the way mental disorders are managed, including increasing the numbers of trained community-based workers who can be effectively utilized via informal non-health care sectors, as well as formal health care systems (Bradshaw, Mairs, & Richards, 2006; Gulbenkian Global Mental Health Platform, 2013; Petersen et al., 2009; Saraceno et al., 2007).
About 70% of African countries spend less than 1% of their budgets on mental health, with most of these monies going toward large psychiatric hospitals rather than cost-effective, community-based care (WHO, 2005). Mental health services are basically focused on emergency management (Petersen et al., 2009), with minimum long-term planning within the community. Resources for assisting people with mental stress, distress and disorders are insufficient, constrained, fragmented, inequitably distributed and ineffectively implemented (Becker & Kleinman, 2013; Chen et al., 2004; Gulbenkian Global Mental Health Platform, 2013; Hinkle, 2014; Hinkle & Saxena, 2006; Jenkins et al., 2010; Saraceno et al., 2007), especially in low-income African countries like Malawi, where there is a clear link between the lack of human resources and population ill health (Hinkle, 2014). Unfortunately, mental health services continue to be inequitably distributed, with lower-income countries having fewer mental health resources than higher-income countries (Coups, Gaba, & Orleans, 2004; Demyttenaere et al., 2004; Hinkle, 2014; WHO, 2005), as well as inefficient use of and decentralization of existing resources (Petersen et al., 2009). In summary, one of the major barriers to increased mental health care is the lack of people trained to provide care (Saraceno et al., 2007).
Historically, developing and promoting population-based mental health services at the grassroots level has been a difficult task (Hinkle, 2014). In less-developed countries like Malawi, 75–85% of people with mental disorders have received no treatment in the 12 months preceding a clinical interview, and this statistic does not account for the countless subthreshold cases (Demyttenaere et al., 2004; WHO, 2010a, 2010b). Furthermore, when people with mental disorders are identified, there is often no adequate resource to refer them to (Petersen et al., 2009).
Hinkle (2014) has reported the following:
Most mental disorders are highly prevalent in all societies, remain largely undetected and untreated, and result in a substantial burden to families and communities. Although many mental disorders can be mitigated or are avoidable, they continue to be overlooked by the international community and produce significant economic and social hardship. (p. 2)
Existing mental health care in Africa is under-resourced and overburdened (Bradshaw et al., 2006), with enormous gaps between the degree of mental suffering and the number of people receiving care (Becker & Kleinman, 2013; Hinkle, 2014; Saraceno et al., 2007; Weissman et al., 1997; Weissman et al., 1994; Weissman et al., 1996; WHO, 2010a, 2010b).
Chorwe-Sungani, Shangase, and Chilinda (2014), as well as Pence (2009), have indicated that mental health problems in Malawi “are often not identified and treated, because health professionals do not believe they are sufficiently competent to provide mental health care” (Chorwe-Sungani et al., 2014, p. 35). Unfortunately, mental health professionals might not have the “requisite public health skills for effective national advocacy” regarding mental health (Jenkins et al., 2010, p. 232). The numbers of primary care and specialist mental health workers are in general decline because of training costs and migration from frontier or rural settings to urban areas, and from low-income countries like Malawi to higher-income countries (Jenkins et al., 2010). In general, collaborations between mental health organizations and health agencies are weak (Gureje & Alem, 2000).
Low salaries and poor working conditions, as well as lack of training and recognition, are major demotivating factors for existing health workers’ involvement in mental health care (Bach, 2004; Manafa et al., 2009). Higher salaries in the private sector have resulted in few incentives for health care workers to work in rural areas where most people live in low-income countries (Saraceno et al., 2007). Overreliance on medical solutions to address psychosocial issues has a disempowering impact on communities (Jain & Jadhav, 2009), including their schools.
Furthermore, primary health care providers cannot adequately intervene with the numbers of mental health cases confronting communities, and medicine has not yet developed sufficient answers for chronic mental health and lifestyle problems (Swartz, 1998). Depending exclusively on medicine to deliver mental health care services risks an overreliance on a medical model and its medications, and less reliance on psychosocial interventions and influences, such as talking with people and problem solving (Patel, 2002; Petersen, 1999), especially for school children. Ten percent of children are considered to have mental health problems, but pediatricians are not generally equipped to provide effective treatment (Chisholm et al., 2000; Craft, 2005). The evidence reveals significant psychopathology among sub-Saharan children, with one in seven children and adolescents experiencing significant difficulties. The most common mental health problems among this age group include depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder and behavior issues.
In addition to a general lack of mental health workers (Chorwe-Sungani et al., 2014), one psychiatrist served the entire country of Malawi (Chorwe-Sungani et al., 2014), only 2.5 psychiatric nurses were available for every 100,000 people (WHO, 2005), and only one psychiatric unit was available, but not always open or at full capacity. A variety of settings must be used in Malawi, and not all of them are within formal health care. For far too long, the concentration has been on an overburdened medical system and not on the development of local community mental health care (Becker & Kleinman, 2013; Hinkle, 2014; Patel, 2013). For a review of the global impact of untreated mental health problems, see Hinkle (2014).
Recognizing the importance of community and family support and using general lay workers equipped with fundamental mental health skills can have positive outcomes (Gureje & Alem, 2000; Saraceno et al., 2007; Swartz, 1998). Saraceno et al. (2007) have reported, “Non-formal community resources will need to be recognized and mobilized to ensure access to care” (p. 1172). Likewise, in low- to middle-income countries, community workers are often the first line of contact with the health care system (Anand & Bärnighausen, 2004; Hinkle, 2014; Hongoro & McPake, 2004).
Communities in developing countries have historically lacked opportunities for mental health training, skill development and capacity building (Abarquez & Murshed, 2004). However, Hinkle (2014) also has indicated that “long years of training are not necessary for learning how to provide fundamental help for people who are emotionally distressed” (p. 4). International health care organizations have demonstrated a need to develop innovative uses of informal mental health assistants and facilitators to establish community mental health services (Hinkle, 2014; Warne & McAndrew, 2004). Hinkle (2006, 2009, 2014) and Eaton and colleagues (Eaton, 2013; Eaton et al., 2011) have indicated that if the gap in mental health services is to be closed, it must include the use of non-specialists to deliver care. Such non-specialized workers should receive Mental Health Facilitator training in order to identify mental stress, distress and disorders; provide fundamental care; monitor helping strategies; and make appropriate referrals (Becker & Kleinman, 2013; Hinkle, 2014; Hinkle, Kutcher, & Chehil, 2006; Hinkle & Schweiger, 2012; Jorm, 2012; Saraceno et al., 2007). According to Hinkle (2014), the “data speaks loudly to the need for accessible, effective and equitable global mental health care. However, a common barrier to mental health care is a lack of providers who have the necessary competencies to address basic community psychosocial needs” (p. 5).
Informal community mental health care is characterized by community members without formal education or training in mental health providing much-needed services. MHF training has been used to bridge the gap between formal and informal mental health care (Hinkle et al., 2006). Murthy (2006) has indicated that informal community care, including self-care, is critical. Moreover, promotion of community mental health increases understanding of mental health problems and decreases mistrust of people suffering from mental health concerns (Kabir, Iliyasu, Abubakar, & Aliyu, 2004; Wright et al., 2014).
Simply put, community workers are a large untapped volunteer resource for people suffering from problems associated with poor mental health (Hinkle, 2014; Hoff, Hallisey, & Hoff, 2009), and data have shown that the delivery of psychosocial-type interventions in non-specialized care settings is feasible (WHO, 2010a, 2010b). Hinkle (2014) has reported that “enhancing basic community mental health services, both informally and formally, is a viable way to assist the never-served” (p. 4). He elaborated that the “MHF program is part of a grassroots implementation trend that has already begun in communities around the globe” (p. 4). In straightforward terms, the demand for the strategic increasing of community mental health services in low-resource settings (Wright et al., 2014) needs to be simplified, locally contextualized, available where people live, affordable and sustainable (Patel, 2013). This plan includes offering services to school children and their families. Wright et al. (2014) have reported that “brief structured psychotherapies, delivered by non-specialist health workers, have been successfully trialed” (p. 156), but the benefits have not necessarily translated into everyday practice. However, this paper reports on one such translation.
Overview of the Mental Health Facilitator Curriculum and Training
The National Board for Certified Counselors (NBCC) International developed the MHF curriculum as well as an implementation method that is making a global impact (Hinkle, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2010a, 2010b, 2012a, 2012b, 2012c, 2013a, 2013b, 2014; Hinkle & Henderson, 2007; Hinkle & Schweiger, 2012). The MHF training program addresses the need for population-based mental health training that can be adapted to reflect the social, cultural, economic and political realities of any country (Hinkle, 2014). Hinkle (2014) described the MHF program as follows:
The MHF training program draws on a variety of competencies derived from related disciplines, including but not limited to psychiatry, psychology, social work, psychiatric nursing, and counseling. Because MHF training is transdisciplinary, traditional professional helping silos are not reinforced; skills and competencies are linked instead to population-based mental health needs rather than professional ideologies. Thus, individuals with MHF training (MHFs) can effectively identify and meet community mental health needs in a standardized manner, regardless of where these needs are manifested and how they are interpreted. Mental health and the process of facilitating it is based on developing community relationships that promote a state of well-being, enabling individuals to realize their abilities, cope with the normal and less-than-normal stresses of life, work productively, and make a contribution to their communities. (p. 6)
The MHF training program has been taught in 25 countries and augments specialized mental health services, where they exist, by functioning within the community to provide targeted assistance, referral and follow-up monitoring (Paredes, Schweiger, Hinkle, Kutcher, & Chehil, 2008). The MHF curriculum consists of information ranging from basic mental health knowledge to specific, local, culturally relevant, first-contact approaches to helping, including mental health advocacy, monitoring, and referral, all of which meet local population needs and respect human dignity (Hinkle, 2014). Nonclinical forms of mental health care such as emotional support or strategic problem solving utilized within the community and schools are emphasized.
Mental health training programs must have a practical component in order to become successful (Saraceno et al., 2007). Accordingly, Hinkle (2014) has stated, “the MHF program is designed to be flexible so local experts can modify components of the training to reflect the realities of their situation; so consumers and policymakers ensure that MHF trainings provide culturally relevant services to the local population” (p. 6). Such a contextual approach connects the MHF program to the principle that mental health care is a combination of universally applicable and context-specific knowledge and skills (Furtos, 2013; Hinkle, 2012a; Paredes et al., 2008; Swartz, 1998).
The diverse backgrounds of MHF trainees enhance the possibilities of addressing gaps in local mental health care. This factor in turn assists local educators, policymakers, service providers and volunteers to meet mental health needs without costly infrastructural investments. Local, contextualized MHF training further facilitates the development and delivery of school- and community-based care consistent with WHO recommendations for addressing the gap in mental health services (Hinkle, 2014), especially among school children.
More specifically, the fundamental features of the MHF curriculum include first-responder forms of community mental health care such as basic assessment, social support and referral. The standard training consists of approximately 30 hours, and a brief one-day version is available (Hinkle & Henderson, 2007). The curriculum includes a focus on the universality of mental stress and distress, as well as mental disorders (Desjarlais, Eisenberg, Good, & Kleinman, 1995; Hinkle & Henderson, 2007), basic helping skills, community mental health services, and advocacy, in addition to specified interventions such as suicide mitigation and responses to child maltreatment. Hinkle (2014) has indicated: “In general, MHFs are taught that negative and unhealthy assumptions about life and living contribute to additional mental and emotional stress” (p. 9). Investing in mental health, cost-effective interventions, the impact of mental disorders on families, and barriers to mental health care also are included. Hinkle and Henderson’s (2007) curriculum also encompasses understanding perspectives regarding feelings, effective communication (e.g., listen, listen, listen) and using questions effectively in the helping process, as well as how to assess problems, identify mental health issues and provide support (e.g., assess, identify, support, refer).
Hinkle (2014) has reported that MHF “trainees concentrate on the abilities, needs and preferences that all people possess and how these are integrated in various cultures,” as well as “how to solve problems and set goals with people experiencing difficulty coping with life” (p. 11). Similarly, trainees learn specific information about basic mental disorders (e.g., anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, depression and mania, psychosis and schizophrenia, substance abuse and dependence, intellectual disability, autism, epilepsy).
In view of the vast burden of mental disorders in low- and middle-income countries, as well as the lack of resources for such care in these countries, more research and services are desperately needed (MacLachlan, Nyirenda, & Nyando, 1995; Saxena, Maulik, Sharan, Levav, & Saraceno, 2004). The MHF curriculum has been applied in public schools in Malawi, prompting an initial investigation of its effectiveness.
Method
Design
An applied ethnographic research design (Pelto, 2013) was selected to explore how MHF stakeholders in the schools experienced the program in Malawi. As a constructivist research tradition, ethnography explores cultural patterns within a group (Hays & Wood, 2011). Accordingly, it has been argued that ethnographic methods can enhance education-related research conducted within multicultural communities, as well as provide a contextual understanding of diversity; consequently, ethnography has been purported as effective in giving a voice to those who have been underrepresented in research (Quimby, 2006).
Several steps were taken to strengthen the methodological rigor of this study, specifically efforts to increase trustworthiness through establishing credibility, dependability, transferability and confirmability (Lincoln & Guba, 1985). To demonstrate the credibility or believability of the current findings, we used prolonged community engagement and triangulation (Hays & Singh, 2012). Two of the four researchers were involved in data collection through interviews and focus groups over a five-day period, and a three-person coding team (one author and two advanced doctoral students) were employed for the analysis. As another form of triangulation, and consistent with past research, those involved in data collection and analysis intentionally maintained different degrees of familiarity with the MHF program itself, the research methodology and the related literature (Goodrich, Hrovat, & Luke, 2014). To demonstrate dependability, or consistency of study results, researchers kept detailed accounts of the data collection and analysis processes undertaken, including the steps used to collapse codes, reduce data and represent relationships between themes. To address transferability, or how well findings apply to other students and educators, the researchers used purposeful maximum variance sampling to solicit participants across differing MHF stakeholder groups and used persistent observation while collecting data until saturation was reached (Hays & Singh, 2012). Lastly, to address confirmability or assurance that findings reflect the participants in the study, the researchers utilized prolonged engagement with research participants, bracketing and participant member checking as part of data analysis. Finally, thick description was used when reporting the findings (Lincoln & Guba, 1985).
Participants
Participants in this study were working and living in three different regions of Malawi (i.e., Lilongwe, Michinji and Salima) and included various stakeholders—five MHF master trainers, twelve MHF trainers, seven MHFs, seven MHF beneficiaries and nine MHF community member stakeholders, who included parents, school personnel and government officials. Twenty-four participants were males and sixteen were females; seven of the participants were children or adolescents. Researchers did not ask participants to identify their ages in order to be culturally responsive to customs in Malawi.
Master trainers are the highest level of trainers in the MHF program. They are required to have a minimum of a master’s degree in a mental health field and significant teaching experience, or they can be included in the Malawi program if they have significant experience with the MHF program. Master trainers are required to take part in additional training, which includes a teaching demonstration and receiving feedback on their subject matter knowledge and interactive skills. In addition, in order to be fully vested in the MHF program, they are required to take part in a co-training exercise. All master trainers were highly placed administrators in the Malawian Ministry of Education or were upper-level staff at an institution dedicated to working with youth and the school system.
MHF trainers have a bachelor’s degree or its equivalent in a mental health-related field, experience as trainers, and are required to attend additional instruction that includes a teaching skills demonstration. MHF trainers in the current study were teachers, guidance teachers and head teachers
(Malawian reference to school principals) who worked in schools participating in the MHF program.
Lastly, MHFs have been instructed in the full MHF curriculum and completed all curriculum requirements. MHF beneficiaries in this study were learners (Malawian reference to students) in schools that incorporated the MHF program. MHF community stakeholders were parents or village leaders who were familiar with the MHF program and able to discuss its effects on their children and communities.
Researcher Stance
In presenting ethnographic results, it is imperative to discuss the researchers’ characteristics due to their potential to influence data collection and analysis. One outside researcher had no prior experience with the MHF curriculum and was intentionally included in an effort to reduce researcher bias. All four researchers identified as Caucasian doctoral-level counseling professionals from the United States. Two female researchers identified as doctoral-level school counselor educators with previous experience working as school counselors, and two researchers (one male and one female) identified as employees of NBCC International (a division of NBCC). All four researchers had professional experiences focused on the development of counseling within an international context and shared an interest in better understanding how the MHF program impacted stakeholders in Malawi. Two of the researchers had previous professional relationships with the partnering organization in Malawi where the MHF training took place.
As part of the research development, all four researchers met to discuss their respective positions and how their experiences might impact beliefs and perceptions related to the study. Intentional efforts were made to bracket and triangulate perspectives throughout the research process for the purpose of identifying and mitigating biases that could interfere with the project (Hays & Singh, 2012).
Sampling and Data Collection
The sole inclusion criterion for the project was for participants to be MHF stakeholders in Malawi since each stakeholder group could provide a unique perspective. The researchers used purposeful sampling to identify potential participants in two different ways. Prior to leaving the United States, the research team contacted the partnering MHF organization in Malawi to discuss the project and make arrangements for the research visit. During these contacts, the partnering organization agreed to review their records of the MHF master trainers, MHF trainers and MHFs to identify potential participants. Additionally, the partnering organization worked with collaborating schools to solicit potential MHF beneficiary and MHF community member stakeholder participants. Convenience sampling was used based on participant availability at schools (both parents and children) and related organizations. One quarter of the participants (n = 10) were interviewed individually to encourage open dialogue. Three quarters of the participants (n = 30) took part in both individual interviews and focus groups. As noted above, the partnering MHF organization solicited participants for this project and scheduled potential participants during the five-day research visit. Potential participants were provided with information about the research and an informed consent or assent and asked if they would participate in an audiotaped interview about their experiences with the MHF program. As part of the signed consent, all participants were informed of the voluntary nature of this research and their right to withdraw from participation at any time.
All interviews and focus groups were conducted in person by one or two of the researchers using a semi-structured research protocol. Interviewees were selected by their availability and convenience. Focus groups were conducted at either a convenient administrative building or classrooms at MHF-participating schools. Each of the 10 interviews began with one of the researchers asking the following open, general question: “Can you please describe what it was like to train/provide/receive MHF services?” After this question, the researchers followed up with probes from the semi-structured research guide that consisted of five areas, including the first question, with follow-up questions (probes) for each area. Another example of a question later in the interview was the following: “What has surprised you about MHF services?” If time permitted, the researchers ended the interview with a question that allowed individual interviewees or focus groups to address anything not discussed in the five areas; for example: “Is there anything additional that you thought we would ask that we did not?” There were between six and nine potential probes that could follow each of the five areas. The following is an example of a probe following the initial question: “On a scale of 1 to 10, how satisfied were you with your MHF experience?” Probes also were open-ended, such as, “What might have made your experience with MHF implementation better?” Consistent with the institutional review board-approved research protocol, researchers tried to use probes from all five areas outlined, but consistent with qualitative research design, not all questions were asked of all participants in the same order. This flexible interview style has been used in past research, permitting researchers to probe and follow topics introduced by participants (see Goodrich et al., 2014).
Focus groups were used as a culturally responsive strategy to facilitate the sharing of multiple perspectives and to promote conversations about a topic which, given customs and cultural practices, might be more challenging to discuss in an individual interview (Bogdan & Biklen, 2006). Focus groups were scheduled based on the participants’ availability and generally delineated by stakeholder group (i.e., other MHF trainers, MHFs, MHF beneficiaries, and community stakeholders). The number of participants in each of 10 focus groups ranged from three to 12 participants, with an average of five per focus group. The total number of focus groups was dependent on the combined schedules of participants and the need to balance the overall schedule with the necessity of researcher travel to conduct interviews in locations most convenient and appropriate for the participants. The use of a semi-structured focus group research guide also allowed researchers to ask specific questions that focused on predetermined key topics related to the study, while also maintaining flexibility to follow up on topics that emerged from participants. Similarly, the 10 focus groups all began with the question, “As you reflect on your own experiences as MHF stakeholders, what is significant?” and then proceeded with probes based on the semi-structured research guide. Both interviews and focus groups were audiotaped in their entirety and conducted in English. Individual interviews averaged 35 minutes, ranging from approximately 20–60 minutes in length. Focus groups averaged 50 minutes, with a range of approximately 30–75 minutes. All individual interviews and focus groups were transcribed verbatim by a team of transcriptionists associated with the study.
Data Analysis
Data analysis began on site in Malawi during the data collection process, with the on-site researchers debriefing about patterns and themes as well as their reflections at the end of each day of data collection. After interviews and focus groups were transcribed, the outside researcher created a consensus coding procedure (Hays & Singh, 2012) similar to that used in past studies (Goodrich et al., 2014; Luke & Goodrich, 2013) in which she and two advanced doctoral students trained in ethnographic research each performed the initial coding independently. The process began with each coding team member reading and rereading the data to become familiar with the content and then conducting initial coding using constant comparative methods (Bogdan & Biklen, 2006). Therefore, throughout the initial stage of the analysis, all three coders used line-by-line open coding (e.g., Fassinger, 2005) and compared codes within and across transcripts. This process ensured triangulation, as three different individuals viewed all data.
Although the coding team moved back and forth between the coding stages, the second stage of coding involved the coding team meeting weekly during the coding process. Consensus meetings were conducted using a modified Miles and Huberman (1994) approach to discuss the emergent codes, clarify questions and identify key quotes and reflections on the data, as well as refine the next steps in the research process. Once all transcripts were coded and discussed, the third coding stage began. During the third stage, axial coding was utilized to group and collapse the initial codes, and to form larger categories or themes (Bogdan & Biklen, 2006). The final step of analysis involved developing operational definitions for each theme (Hays & Singh, 2012) and soliciting feedback through peer debriefing and member checking. The feedback received through both peer debriefing and member checking was considered and incorporated into the findings.
Results
In general, the results revealed that the 40 MHF participants in Malawi all agreed that the MHF program was valuable. Participants unanimously noted appreciation for the MHF program and the vital educational role it served in their communities. For example, one adult participant noted, “I am very satisfied with [the] MHF program: It’s a 10 [on a scale of 1–10, with 10 being the best].” Participants also described what made the MHF program implementation successful, with one adult participant stating, “MHF is contributing positively, not only to the access of education, but [to] the quality of education.” Additionally, participants reported that there would be negative consequences should the MHF program discontinue. Illustrating the significance of the MHF program and his appreciation for it, another adult participant stated, “It is our prayer that this program should continue. I know sometimes resources are limited, but I know God is going to help us.”
More specifically, four interrelated themes emerged to illustrate the MHF participants’ appreciative beliefs about and experiences with the MHF program. The first theme, Malawian cultural history and context, served as grounding for three additional themes: resources and needs, processes and outcomes. Participants explained how these themes interacted with and influenced each other.
MHF Themes
Malawian cultural history and context. One adult participant described how the MHF program was culturally congruent as follows:
There is a culture of working together. . . . This program . . . has some of the components such as stress, distress, disorders . . . it helps people to identify the signs and symptoms which show that this person is stressed [or] distressed. . . . African culture says, “We are because you are,” meaning that we belong to each other . . . meaning that if you see a person showing signs of sadness, you must quickly go in and help.
Another adult participant echoed the idea that the MHF program was interacting within the unique Malawian educational context by saying, “We have packed classes. . . . It’s very difficult for a teacher to reach out. . . . Together with the MHF program and the training of teachers . . . they can respond.” Still another adult participant explained that before the MHF trainings,
they [teachers] didn’t know that a learner goes through a lot of experiences, right from their homes and on their way to school. . . . They have experiences that need MHF. So the teacher is now aware of handling the learner as a human being, as somebody . . . that is available for their assistance.
Participants also described how the MHF program was adapted to contextual needs in Malawi. One adult participant noted the realism in the MHF training, saying, “Everything that we do and say in trainings, or everything around [the] MHF program, is based on real-life issues.” One of the strongest features of the MHF program is its adaptability to cultural contexts. MHF clubs were created in Malawian schools by guidance teachers, teachers, and administrators who had completed MHF training. The clubs are a place where MHFs teach mental health skills to learners and provide a safe place for learners to talk about school and family concerns. Several of the clubs have organized performances for other students and the community using song and dance, an important contextual part of Malawian culture, to illustrate common concerns and the use of MHF skills in addressing these matters.
Participants also discussed specific cultural meanings and social practices as well as context-specific activities within the schools and communities where MHF was implemented. A focus group of learners described the activities they did in their MHF club, and one learner began by saying:
My poem is based on [a] true story of my friend who [was] . . . always stressed when we had class, wasn’t concentrating, always feeling down . . . so, I tried to ask him what his problem was and then I went to a teacher. . . . The patron helped him . . . and now he is doing pretty well. . . . I tried to give him . . . some tips how he could manage stress on his own, like telling him to sometimes listen to some music, do some physical exercises . . . and then after that . . . I referred him to the teacher.
Another learner described a story he developed based on MHF content. He explained that he had a friend who had failed a test and who was worried about going home and telling his father, whom he believed would be angry. The learner stated that he referred his friend to a teacher who successfully met with the parents and his friend about the test score.
Resources and needs. Bird et al. (2011) have shared that African health workers believe that mental health resources are desperately lacking. Participants discussed examples of invested individuals and MHF programming, and articulated specific ideas about the materials and adaptations desired for the MHF program in the future. One adult participant spoke about MHFs as an asset, saying, “MHFs are creative, [and] like [using a] curriculum that is more simplified [the MHF curriculum is now offered in 1-day formats for communities and schools].” Participants also described the receptivity of people and educational communities as a significant resource. For example, one adult participant said, “The schools are very interested and communities are eager to be involved. They are open to . . . MHF.” Another adult participant described something similar within the community, saying, “So far, we
engaged the traditional leaders in communities to say there’s this program. . . . We have talked to them and I think they would be interested in the training . . . because this time we talked to the chiefs.” Expanding on this idea, another adult participant noted,
I am sure this program is even extending [beyond] the learners. Even the parents also benefit from the program. Because we can tell the learner, and the learner goes to their parent. But if the parent has no idea about it, it would be so difficult. So, also looking at even the parent and community should be synthesized . . . so they know actually what we mean when we talk about mental health. . . . The teachers, the learners and the parents . . . join together [and] they will be able to assist the learner.
Participants also described how their experience of the MHF program was influenced by the need for more tangible resources (e.g., materials, personnel, transportation). One adult participant reported,
Because the whole program is . . . 19 modules, we ask the office to at least produce one for the school so that we can have it in the building. . . . We have loaded them all on our computers, but access isn’t possible by every teacher.
In addition, many participants expressed a desire for the MHF program to incorporate transportation as one of the provided services, to improve communication between MHFs, and to increase dissemination of MHF information. For example, an adult participant suggested, “If other zones [regions or geographic districts] also [had] mental health facilitation, that could assist [with] ideas.” Another adult participant commented similarly, “More and more teachers are getting [MHF] and it’s very helpful. Maybe to travel to see one another or meet, to talk about what we are each doing—that would be good.” Adult participants explained the purpose of travel for MHF collaboration, stating that it would be helpful if the schools involved with MHF could meet at both the district and regional levels to share ideas and that this would benefit not only those involved, but also those outside of the program’s current involvement.
Additionally, even though all MHF participants expressed a desire for more MHF programming, participants described how less tangible resources and needs (e.g., mental health and education status, service demands and credentials) influenced their experience of MHF. For example, an adult participant noted that language fluency was one such resource that could expand access to the MHF trainings, commenting, “The other thing that I think you should know in order for your project to benefit . . . you [MHF program] should learn our language . . . so that you can communicate with those village headmen because most of them do not speak English.” (The MHF curriculum has been translated into 11 languages, including Swahili.)
Several participants also explained the importance of religious institutions in Malawi, offering recommendations for their involvement in MHF service delivery. One adult participant said, “You should take it [to] religious institutions because they understand there [are] some religious beliefs which prohibit children from going to school. So, by targeting these religious institutions you can easily reach the minds of the young ones.”
Processes. Participants distinguished various MHF-related processes as those consisting of psychoeducational helping, those linked to larger community development efforts, and those focused on specific strategies for spreading the MHF message more broadly. One child participant said, “In the MHF club we learn about how we can . . . advise our friends or how we can . . . [have] good behavior.” A second child participant added, “We are supposed to talk, to show people who are drinking or smoking to stop this bad behavior.” A third child participant offered, “We learn more about having good friends who have good behavior.”
Participants also noted additional educational processes related to MHF. One adult participant stated, “So, the program is developing leadership. It is helping people to grow as individuals and helping society to grow, and when it comes to the learners the program has . . . increased . . . access to education.” Another adult participant described the processes of MHF service delivery as follows: “They [beneficiaries] feel as if they are in control because they are decision makers. We just listen, we just guide and they come up with the decision . . . because we cannot make decision[s] for them.” Yet another adult participant described MHF activities, including the ability to make referrals, in the following way: “. . . helping people individually [and] referring people to other sources of assistance. I can do that, because I know . . . many systems that can offer assistance.”
Relatedly, participants also discussed MHF efforts that were incorporated into educational communities. One child participant described the community process of singing and sharing MHF messages as follows: “I feel good . . . when . . . we sing songs. Songs are more about what MHF [is], so people can remember what we sing and if people drink or smoke they can stop because of the song.” Other child participants demonstrated something similar, singing an MHF song they had created and performed. One child participant described how social role modeling was an important process in MHF service delivery, saying, “You become a model to other people and because of that, even those people that we talk to, those people that we teach . . . become recognized in the communities.” Other adult participants described how the MHF program used relational implementation processes, stating, “The MHF program addresses critical thinking, good planning . . . in addition to mental health because now we are looking at the whole person.”
Lastly, participants described the importance of the use of technology when it came to marketing strategies for the MHF program. One adult participant described how “t-shirts with anti-suicide messages” could be produced to serve two aims, indicating that “learners would feel a sense of belonging” and they could “spread the MHF messages to others.” Another adult participant described how communication of the MHF message was important by saying, “We share information about the availability of MHF now by word of mouth, but it could be broken down by different media, like using radio or TV programs.” Another adult participant offered the following perspective on MHF results:
[People] are able to discuss . . . mental health whereas before they could not. Some topics weren’t discussed, now they air [them] out. . . . This [is a] very important topic, because once you air [it] out on the radio and in the media or in the newspaper, the ability to discuss [mental health] spreads.
Outcomes. It is of note that participants only identified positive outcomes of the MHF program, without any negative impacts. Participants described the positive global impact by saying, “Every time, every year the MHF training comes and goes, it leaves [the] facilitator, it leaves the community, it leaves the learner, and even the teachers better off than they were before.” Another adult participant described the change of perspective provided through the MHF program as follows: “It’s an eye opener. . . . It’s really a new way of thinking.”
Participants also identified manifestation of MHF-related growth and development as personal change, community welfare and larger systemic influences. One child participant described the personal impact as follows: “Personally I have benefitted a lot, because [MHF] touches what I go through on a daily basis.” In addition, an adult participant reported, “In my family there is a big improvement. I do respect other people’s views and even have to promote my decision-making skills.” Another adult participant described a similar change:
I’ve got two children who are in the [MHF] club. . . . Previously, the boy was very, very, very troublesome. But I’ve . . . noticed some changes in . . . him and I’ve never heard about any fight against his friends up to now, so I was wondering what is happening to this child now that he has changed. . . . I came to understand that . . . it is because of this program, the Mental Health Facilitator.
Likewise, a participant described the community benefit when he offered, “The whole school is changing because they are . . . teaching [MHF]. . . . Children as a group . . . are changing. . . . There’s no violence . . . as it was before.” Still another adult participant described the community outcomes in the following way: “One of the teachers was telling me [that] now [learners] trust him even more than their own parents.” Participants identified how the MHF program has been able to shift some community inequities as well. For example, one adult participant indicated the following:
They [MHFs] are able to identify people’s problems at the early stage and they are able to give them personal data and some assistance [so] that these people might be healthy. . . . What happens [when people drop out of school] you find out . . . in fact there are more girls [dropping out] than boys . . . because of stressful situations that they have at home or . . . in the schools. So [MHF] programs have [provided] assistance [in] ways [so] teachers can give some guidance.
At times, participants distinguished direct from indirect outcomes. One adult participant offered the following example of direct impact: “The teachers [and] the learners are directly able to understand and know how to handle . . . life challenges.”
Discussion
Participants in this study expressed engagement in and appreciation for the MHF program in Malawi schools. Interview responses indicated similarities between the interconnectedness encouraged in the training and the strong interpersonal relationships within the local culture. Participants also recognized the adaptability of the curriculum and credited the MHF program with dealing with real issues. Indeed, they discussed the ways that the MHF training transformed them and provided examples of the influence that the school MHF clubs had on teachers and students. One goal of the MHF program involves culturally appropriate, grassroots efforts to address mental health concerns in resource-poor countries. Based on the comments delivered by the participants, we have initial evidence of meeting that goal in Malawi.
The appropriateness of the research method used in this study provides an important implication. The focus groups allowed researchers to uncover a depth of description about the impact of the MHF project. Had the investigation proceeded with a survey instrument or a more structured interview, the results likely would have been limited. With an ethnographic design, more was uncovered about not only the similarities of the MHF participants’ experiences, but also their particular voices and variations on these similarities. Thus, the applied research design (Pelto, 2013) allowed for a constructivist investigation that provided a contextual understanding of the participants in Malawi and their experiences with MHF.
A further implication involves an unforeseen benefit of the MHF curriculum. Participants in this study reported a community of helpers. They credited the MHF training with providing a platform for a shared language and a common desire to support students, families and communities. Furthermore, they discussed how that language and mission have a ripple or multiplier effect that extends the benefits of the MHF curriculum to strengthen various groups.
Participants in this study confirmed that the mission of the MHF training in Malawi’s schools was fulfilled—members of a community can learn to help each other. The findings of this study suggest positive results from a compressed training period designed to prepare participants to adapt basic mental health responding skills and knowledge to their community. Current responses to the lack of mental health resources would be augmented significantly by supporting this type of community and school peer assistance preparation, an economical answer to a persistent need for mental health care.
Participants learned the MHF concepts and integrated the information into their daily living. Their explanations incorporated the terms (e.g., “stress, distress, disorder”) and the phrases (e.g., “We just listen, we just guide”). The limits of what an MHF can do also were reported as follows: “. . . helping people individually, referring people to other resources of assistance. I can do that.” Participants have written songs about mental health and have become role models and leaders in schools and the community since the completion of the MHF training. They demonstrated improvements in their confidence levels and competence in the information they shared; it seems reasonable to acknowledge these improvements as evidence of the positive impact the project has had on their knowledge and skills, as well as their influence on the people they encounter. This study outcome reflects a multiplier effect with which the project was designed. Therefore, based on these interviews and the resultant themes, we conclude that the participants in the MHF program in Malawi exemplify the ideals of the project.
The Study and General Limitations
Although this study used maximum variation sampling to identify a diverse group of MHF stakeholders, all participants were ultimately self-selected. Therefore, it is possible that the experiences of participants agreeing to be part of the study might reflect something outside the scope of this study and as of yet not identified (Bogdan & Biklen, 2006). Additionally, as all interviews were conducted in English, the design may have privileged participants with more formal education. Accordingly, the convenience sample may not be representative of the perspectives of all MHF stakeholders in Malawi. Also, cross-cultural research can present unique challenges (Goodrich et al., 2014); therefore, it is conceivable that the level of comfort and openness of participants, as well as decisions about the content shared, may have been different had the two researchers who collected data not been Caucasian American women. Although the research team included an independent member not affiliated with NBCC-I or the MHF program in Malawi, it is possible that the positionality of the research team influenced the participants’ reported experiences. That said, as noted elsewhere, intentional efforts were undertaken to strengthen the trustworthiness of the study; however, as with results of any single qualitative study, findings should be interpreted with caution (Kline, 2008).
Participants were proud of the designation of being an MHF and saw themselves as assets to their communities, schools and families. But they also pointed out barriers to expansion of the MHF program and shared solutions to some of their concerns. Population-based mental health risk management helps reduce vulnerabilities to stress (see Bradshaw et al., 2006). However, Hinkle (2014) has pointed out the following limitation:
For the MHF program to proliferate, it will take not only training, education and implementation in often less than optimal working conditions, but also savvy negotiation of often poorly managed political systems that experience some level of corruption and inability to impact the universal stigma that plagues mental illness. (p. 12)
The efforts to give mental health the prominence it deserves in Africa in general, and in Malawi in particular, will continue to be a political as well as an intervention-related battle (Dawes, 1986) that needs budgets and services that are adequately translated from policies (Bird et al., 2011).
Although the MHF program in Malawi appears to have positive outcomes to date, political support will be needed to realize the program’s full potential impact on mental health care (Saraceno et al., 2007). As long as mortality rather than morbidity is the basis for funding for any health problem, mental health will consistently receive less attention (i.e., less funding and fewer services; Bird et al., 2011). Thus, identifying the various levers and entry points (Jenkins et al., 2010) is critical to the sustainability of programs like MHF, in Malawi and elsewhere. Jenkins and colleagues (2010) have reported that mental health “recognition by international donors and the African Union of the importance of mental health to the [sub-Saharan] region would be extremely helpful in eliciting and pooling resources for this crucially underfunded area” (p. 233). Moreover, it is important that mental health policies (Gureje & Alem, 2000) and population-based mental health training not sit on the proverbial shelf gathering dust. Hinkle (2014) has reported that “unfortunately, not even the laudable efforts of the WHO or United Nations have been able to bring countries that are in desperate need of basic mental health care together effectively,” which “underscores the need for urgent development of grassroots community mental health programs” (p. 12).
Unfortunately, we did not collect specific data as to how many guidance teachers and head teachers participated in the study. Future researchers could find that differences among these two groups of teachers exist.
Conclusion
The MHF program is community-based training that includes basic, universally applicable and context-specific skills. All 40 adult and child MHF stakeholders in Malawi suggested that the MHF program had a positive impact in their lives, schools and communities. Participants’ identification of four interrelated themes—the responsiveness to the Malawian cultural history and context, the availability and limitations of resources, the processes involved in the implementation of the MHF program, and the varied outcomes—begin to illustrate the ways in which the MHF program has been incorporated into school and community contexts, and identify participants’ beliefs about what might be necessary to strengthen and expand the MHF program in this country. Because the MHF program was originally developed to address the unmet mental health needs of individuals in an international context, and trainings have been conducted in 25 countries to date, studies such as this, as well as future quantitative research, can be conducted elsewhere to better understand the ways in which the program is meeting its objectives and to identify the types of support that could be provided to MHFs and human services-related advocacy efforts around the world (Hinkle, 2014; Lee, 2012).
Mental health resource allocations are often haphazard in African countries (Lund & Flisher, 2006); however, Patel et al. (2007) have indicated that the evidence supports the cost-effectiveness of mental health intervention, and the current study reports this potential in the schools in Malawi. Mental health cost-effectiveness also is reflected by a select number of other sub-Saharan countries (e.g., Tanzania, Kenya) that have integrated mental health into basic health service delivery and have set an admirable example of systematic implementation of community mental health service delivery (Jenkins et al., 2010). Community caregiving for mental stress, distress and disorders is often uncompensated and has tremendous public health value, since such caregiving can offset expensive services and assist shorthanded healthcare professionals (Viana et al., 2013). This reality has been demonstrated thus far in the schools in Malawi.
Future Directions in Malawi
More traditional healers should be incorporated into mental health services in Malawi (MacLachlan et al., 1995), a perspective that is reflected by some of the participants’ comments. Integrating traditional health care (i.e., indigenous healers) can impact people in ways that Western approaches do not (Gureje & Alem, 2000; Swartz, 2006). Community mental health care should take into account the beliefs of those being served, and both traditional and more modern progressive strategies need to be integrated. Tropical tolerance, or entertaining competing explanations of mental illness, is imperative when Westerners are assisting with the implementation of intervention programs (MacLachlan et al., 1995), using the emic, or worldview of the person, approach.
In Africa, a large proportion of the population does not receive mental health services for four basic reasons—first, few services are available (resources and needs); second, when services are sought out they are inadequate (outcomes); third, people often prefer self-care and traditional healers (processes); and lastly, stigma leads people to hide their mental health problems (processes and outcomes; Bird et al., 2011). These reasons are all relevant to school children and communities in that mental health can no longer be ignored as a building block of population health as well as social, educational and economic development (Lund, 2010). This study demonstrates that the MHF program addresses many of these concerns and is making at least a modest impact in Malawi. It would be short-sighted not to acknowledge that mental health problems are related to poverty, marginalization, social disadvantage, reductions in economic productivity and the interruption of educational processes (Alonso, Chatterji, He, & Kessler, 2013; Baingana & Bos, 2006; Bird et al., 2011; Breslau et al., 2013; Friedman & Thomas, 2009; Hinkle, 2014; Patel et al., 1997). These factors are even more worrisome in countries like Malawi that have seen poverty levels rise in recent years (Mattes, 2008). Although the MHF strategy is clearly challenged by these factors, the program has demonstrated an impact on Malawian school children that cannot be denied.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The author reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Abarquez, I., & Murshed, Z. (2004). Field practitioner’s handbook. Bangkok, Thailand: Asian Disaster Preparedness Center.
Alonso, J., Chatterji, S., He, Y., & Kessler, R. C. (2013). Burdens of mental disorders: The approach of the World Mental Health (WMH) surveys. In J. Alonso, S. Chatterji, & Y. He (Eds.), The burdens of mental disorders: Global perspectives from the WHO World Mental Health surveys (pp. 1–6). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Anand, S., & Bärnighausen, T. (2004). Human resources and health outcomes: Cross-country econometric study. The Lancet, 364, 1603–1609.
Bach, S. (2004). Migration patterns of physicians and nurses: Still the same story? Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 82, 624–625.
Baingana, F. K., & Bos, E. R. (2006). Changing patterns of disease and mortality in sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence for disease control priorities. In D. T. Jamison, R. G. Feachem, M. W. Makgoba, E. R. Bos. F. K. Baingana, K. J. Hofman, & K. O. Rogo (Eds.), Disease and mortality in sub-Saharan Africa (2nd ed., pp. 1–10). Washington, DC: World Bank.
Becker, A. E., & Kleinman, A. (2013). Mental health and the global agenda. New England Journal of Medicine, 369, 66–73. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1110827
Bird, P., Omar, M., Doku, V., Lund, C., Nsereko, J. R., Mwanza, J., & the MHaPP Research Programme Consortium. (2011). Increasing the priority of mental health in Africa: Findings from qualitative research in Ghana, South Africa, Uganda and Zambia. Health Policy and Planning, 26, 357–365. doi:10.1093/heapol/czq078
Bogdan, R. C., & Biklen, S. K. (2006). Qualitative research for education: An introduction to theories and methods (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson.
Bradshaw, T., Mairs, H., & Richards, D. (2006). Developing mental health education for health volunteers in a township in South Africa. Primary Health Care Research and Development, 7, 95–105. doi:10.1191/1463423606pc282oa
Breslau, J., Lee, S., Tsang, A., Lane, M. C., Aguilar-Gaxiola, S., Alonso, J., . . . Williams, D. R. (2013). Associations between mental disorders and early termination of education. In J. Alonso, S. Chatterji, & Y. He (Eds.), The burdens of mental disorders: Global perspectives from the WHO World Mental Health surveys (pp. 56–65). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Chen, L., Evans, T., Anand, S., Boufford, J. I., Brown, H., Chowdhury, M., . . . Wibulpolprasert, S. (2004). Human resources for health: Overcoming the crisis. The Lancet, 364, 1984–1990.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17482-5
Chisholm, D., Sekar, K., Kumar, K. K., Saeed, K., James, S., . . . & Murthy, R. S. (2000). Integration of mental health care into primary care. British Journal of Psychiatry, 176, 581–588. doi:10.1192/bjp.176.6.581
Chorwe-Sungani, G., Shangase, N., & Chilinda, I. (2014). Care of patients in Malawi who have HIV/AIDS and mental health problems. Mental Health Practice, 17, 35–39.
Coups, E. J., Gaba, A., & Orleans, C. T. (2004). Physician screening for multiple behavioral health risk factors. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 27, 34–41. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2004.04.021
Craft, A. (2005). What are the priorities for child health in 2004? Child: Care, Health and Development, 31, 1–2. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2214.2005.00491.x
Dawes, A. R. L. (1986). The notion of relevant psychology with particular reference to Africanist pragmatic initiatives. Psychology in Society, 5, 28–48.
Demyttenaere, K., Bruffaerts, R., Posada-Villa, J., Gasquet, I., Kovess, V., Lepine, J. P., . . . Chatterji, S. (2004). Prevalence, severity, and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Journal of the American Medical Association, 291, 2581–2590. doi:10.1001/jama.291.21.2581
Desjarlais, R., Eisenberg, L., Good, B., & Kleinman, A. (1995). World mental health: Problems and priorities in low-income countries. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Eaton, J. (2013, October). Document two. In J. M. C. de Almeida (Chair), Innovation in mental health care delivery and service organization. Symposium conducted at the International Forum on Innovation in Mental Health, Gulbenkian Global Mental Health Platform, Lisbon, Portugal.
Eaton, J., McCay, L., Semrau, M., Chatterjee, S., Baingana, F., Araya, R., . . . Saxena, S. (2011). Scale up of services for mental health in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet, 378, 1592–1603. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60891-X
Fassinger, R. E. (2005). Paradigms, praxis, problems, and promise: Grounded theory in counselling psychology research. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52, 156–166.
Friedman, J., & Thomas, D. (2009). Psychological health before, during, and after an economic crisis: Results from Indonesia, 1993–2000. World Bank Economic Review, 23, 57–76. doi:10.1093/wber/lhn013
Furtos, J. (2013, May). Globalization and mental health: The weight of the world, the size of the sky. In C. I. Cohen & K. Thompson (Chairs), Envisioning a new psychiatry: Radical perspectives. Presidential symposium conducted at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, San Francisco, CA.
Goodrich, K. M., Hrovat, A., & Luke, M. (2014). Professional identity, practice, and development of Kenyan teacher-counsellors: An ethnography. Journal of Counselor Leadership & Advocacy, 1, 44–66.
doi:10.1080/2326716X.2014.886976
Gulbenkian Global Mental Health Platform. (2013). Integrating mental and physical health, promoting social inclusion, humanizing mental health care. Retrieved from http://www.gulbenkianmhplatform.com
Gureje, O., & Alem, A. (2000). Mental health policy development in Africa. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 78, 475–482.
Hays, D. G., & Singh, A. A. (2012). Qualitative inquiry in clinical and educational settings. New York, NY: Guilford.
Hays, D. G., & Wood, C. (2011). Infusing qualitative traditions in counseling research designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 288–295. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00091.x
Hinkle, J. S. (2006, October). MHF town meeting: Ideas/questions. Presentation at the NBCC Global Mental Health Congress, New Delhi, India.
Hinkle, J. S. (2007, June). The mental health facilitator training: Ongoing developments. Presentation at the 12th International Counseling Conference, Shanghai, China.
Hinkle, J. S. (2009, July). Mental health facilitation: The challenge and a strategy. Keynote address at the Association for Multicultural Counseling and Development/Association for Counselor Education and Supervision 2nd Annual Conference on Culturally Competent Disaster Response, Gaborone, Botswana.
Hinkle, J. S. (2010a). International disaster counseling: Today’s reflections, tomorrow’s needs. In J. Webber & J. B. Mascari (Eds.), Terrorism, trauma, and tragedies: A counselor’s guide to preparing and responding (3rd ed., pp. 179–184). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Hinkle, J. S. (2010b, August). Mental health facilitation: A global challenge and workable strategy. Manuscript presented at the Biennial Conference-Workshop of the Association of Psychological and Educational Counselors of Asia-Pacific, Penang, Malaysia.
Hinkle, J. S. (2012a, May). Mental health facilitation: A global strategy. Manuscript presented at the Biennial
Conference-Workshop of the Association of Psychological and Educational Counselors of Asia-Pacific,
Tokyo, Japan.
Hinkle, J. S. (2012b). The Mental Health Facilitator program: Optimizing global emotional health one country at a time. Retrieved from http://www.revistaenfoquehumanistico.com/#!Scott Hinkle/c1lbz
Hinkle, J. S. (2012c, October). Population-based mental health facilitation (MHF): A strategy that works. Manuscript presented at the Seventh World Conference on the Promotion of Mental Health and the Prevention of Mental and Behavioural Disorders, Perth, Australia.
Hinkle, J. S. (2013a, February). Population-based mental health facilitation (MHF): Community empowerment and a vision that works. Manuscript presented at the conference of the North Carolina Counseling Association, Greensboro, NC.
Hinkle, J. S. (2013b, November). La salud mental en e mundo. Presentation at the Old Dominion University Counseling Institute, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Hinkle, J. S. (2014). Population-based mental health facilitation (MHF): A grassroots strategy that works. The Professional Counselor, 4, 1–18. doi:10.15241/jsh.4.1.1
Hinkle, J. S., & Henderson, D. (2007). Mental health facilitation. Greensboro, NC: National Board for Certified Counselors-International.
Hinkle, J. S., Kutcher, S. P., & Chehil, S. (2006, October). Mental health facilitator: Curriculum development. Presentation at the NBCC International Global Mental Health Congress, New Delhi, India.
Hinkle, J. S., & Saxena, S. (2006, October). ATLAS: Mapping international mental health care. Presentation at the NBCC International Global Mental Health Congress, New Delhi, India.
Hinkle, J. S., & Schweiger, W. (2012, September). Mental health facilitation around the world. Manuscript presented at HOLAS Second Counseling Conference of the Americas, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Hoff, L. A., Hallisey B. J., & Hoff, M. (2009). People in crisis: Clinical and diversity perspectives (6th ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Hongoro, C., & McPake, B. (2004). How to bridge the gap in human resources for health. The Lancet, 364,
1451–1456.
Jacob, K. S., Sharan, P., Mirza, I., Garrido-Cumbrera, M., Seedat, S., Mari, J. J., . . . Saxena, S. (2007). Mental health systems in countries: Where are we now? The Lancet, 370, 1061–1077.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61241-0
Jain, S., & Jadhav, S. (2009). Pills that swallow policy: Clinical ethnography of a community mental health program in Northern India. Transcultural Psychiatry, 46, 60–85. doi:10.1177/1363461509102287
Jenkins, R., Baingana, F., Belkin, G., Borowitz, M., Daly, A., Francis., P., . . . Sadiq, S. (2010). Mental health and the development agenda in sub-Saharan Africa. Psychiatric Services, 61, 229–234.
Jorm, A. F. (2012). Mental health literacy: Empowering the community to take action for better mental health. American Psychologist, 67, 231–243.
Kabir, M., Iliyasu, Z., Abubakar, I. S., & Aliyu, M. H. (2004). Perception and beliefs about mental illness among adults in Karfi village, northern Nigeria. BMC International Health and Human Rights, 4, 3. doi:10.1186/1472-698X-4-3
Kline, W. B. (2008). Developing and submitting credible qualitative manuscripts. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 210–217. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2008.tb00052.x
Lee, C. C. (2012). Social justice as the fifth force in counseling. In C. Y. Chang, C. A. Barrio Minton, A. L. Dixon, J. E. Myers, & T. J. Sweeney (Eds.), Professional counseling excellence through leadership and advocacy
(pp. 109–120). New York, NY: Routledge.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Luke, M., & Goodrich, K. M. (2013). Investigating the LGBTQ Responsive Model of Group Supervision. The Journal for Specialists in Group Work, 38, 121–145. doi:10.1080/01933922.2013.775207.
Lund, C. (2010). Mental health in Africa: Findings from the mental health and poverty project. International Review of Psychiatry, 22, 547–549. doi:10.3109/09540261.2010.535809
Lund, C., & Flisher, A. J. (2006). Norms for mental health services in South Africa. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 41, 587–594. doi:10.1007/s00127-006-0057-z
MacLachlan, M., Nyirenda, T., & Nyando, C. (1995). Attributions for admission to Zomba Mental Hospital: Implications for the development of mental health services in Malawi. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 41, 79–87.
Manafa, O., McAuliffe, E., Maseko, F., Bowie, C., MacLachlan, M., & Normand, C. (2009). Retention of health workers in Malawi: Perspectives of health workers and district management. Human Resources for Health, 7, 65–73. doi:10.1186/1478-4491-7-65
Mattes, R. (2008). The material and political bases of lived poverty in Africa: Insights from the Afrobarometer (Working paper no. 98). Cape Town, South Africa: Afrobarometer.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Murthy, R. S. (Ed.). (2006). Mental health by the people. Bangalore, India: People’s Action for Mental Health.
Paredes, D., Schweiger, W., Hinkle, J. S., Kutcher, S., & Chehil, S. (2008). The mental health facilitator program: An approach to meet global mental health care needs. Temas Selectos en Orientación Psicológica, 3, 73–80.
Patel, V. (2002). Where there is no psychiatrist. London, United Kingdom: Gaskell.
Patel, V. (2013, October). Integrating mental health care in priority health programs: Addressing a grand challenge in global mental health. Manuscript presented at the International Forum on Innovation in Mental Health, Gulbenkian Global Mental Health Platform, Lisbon, Portugal.
Patel, V., Araya, R., Chatterjee, S., Chisholm, D., Cohen, A., DeSilva, M., . . . van Ommeren, M. (2007). Treatment and prevention of mental disorders in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet, 370, 991–1005. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61240-9
Patel, V., Todd, C., Winston, M., Gwanzura, F., Simunyu, E., Acuda, W., & Mann, A. (1997). Common mental disorders in primary care in Harare, Zimbabwe: Associations and risk factors. British Journal of Psychiatry, 171, 60–64. doi:10.1192/bjp.171.1.60
Pelto, P. J. (2013). Applied ethnography: Guidelines for field research. Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press.
Pence, B. W. (2009). The impact of mental health and traumatic life experiences on antiretroviral treatment outcomes for people living with HIV/AIDS. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 63, 636–640. doi:10.1093/jac/dkp006
Petersen, I. (1999). Training for transformation: Reorientating primary health care nurses for the provision of mental health care in South Africa. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 30, 907–915.
doi:10.1046/j.1365-2648.1999.01166.x
Petersen, I., Bhana, A., Campbell-Hall, V., Mjadu, S., Lund, C., Kleintjies, S. . . . Mental Health and Poverty Research Programme Consortium. (2009). Planning for district mental health services in South Africa: A situational analysis of a rural district site. Health Policy and Planning, 24, 140–150.
doi:10.1093/heapol/czn049
Quimby, E. (2006). Ethnography’s role in assisting mental health research and clinical practice. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62, 859–879. doi:10.1002/jclp.20277
Saraceno, B., van Ommeren, M., Batniji, R., Cohen, A., Gureje, O., Mahoney, J., . . . Underhill, C. (2007). Barriers to improvement of mental health services in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet, 370, 1164–1174. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61263-X
Saxena, S., Maulik, P. K., Sharan, P., Levav, I., & Saraceno, B. (2004). Mental health research on low- and
middle-income countries in indexed journals: A preliminary assessment. The Journal of Mental Health
Policy and Economics, 7, 127–131.
Skeen, S., Lund, C., Kleintjes, S., Flisher, A., & the MHaPP Research Programme Consortium. (2010). Meeting the millennium development goals in sub-Saharan Africa: What about mental health? International Review of Psychiatry, 22, 624–631. doi:10.3109/09540261.2010.535509
Swartz, L. (1998). Culture and mental health: A southern African view. Cape Town, South Africa: Oxford University Press.
Viana, M. C., Gruber, M. J., Shahly, V., de Jonge, P., He, Y., Hinkov, H., & Kessler, R. C. (2013). Family burden associated with mental and physical disorders. In J. Alonso, S. Chatterji, & Y. He (Eds.), The burdens of mental disorders: Global perspectives from the WHO World Mental Health surveys (pp. 122–135). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Warne, T., & McAndrew, S. (2004). The mental health assistant practitioner: An oxymoron? Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, 11, 179–184. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2850.2003.00704.x
Weissman, M. M., Bland, R. C., Canino, G. J., Faravelli, C., Greenwald, S., Hwu, H. G., . . . Yeh, E. K. (1997). The cross-national epidemiology of panic disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 54, 305–309.
Weissman, M. M., Bland, R. C., Canino, G. J., Greenwald, S., Hwu, H. G., Lee, C. K, . . . Yeh, E. K. (1994). The cross-national epidemiology of obsessive compulsive disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 55
(Suppl. 3), 5–10.
Weissman, M. M., Bland, R. C., Canino, G. J., Greenwald, S., Lee, C. K., Newman, S. C., . . . Wickramaratne, P. J. (1996). The cross-national epidemiology of social phobia: A preliminary report. International Clinical Psychopharmacology, 11 (Suppl. 3), 9–14.
World Fellowship for Schizophrenia and Allied Disorders. (2006). Families as partners in care. Retrieved from
http://www.world-schizophrenia.org/activities/fpc/index.html
World Health Organization. (2004). Atlas: Country resources for neurological disorders. Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
World Health Organization. (2005). Mental health atlas. Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
World Health Organization. (2010a). Mental health and development: Targeting people with mental health conditions as a vulnerable group. Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
World Health Organization. (2010b). mhGAP intervention guide for mental, neurological and substance use disorders in non-specialized health settings. Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
Wright, J., Common, S., Kauye, F., & Chiwandira, C. (2014). Integrating community mental health within
primary care in southern Malawi: A pilot educational intervention to enhance the role of health
surveillance assistants. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 60, 155–161. doi:10.1177/0020764012471924
Melissa Luke, NCC, is an Associate Professor at Syracuse University. J. Scott Hinkle, NCC, is the Editor of The Professional Counselor. Wendi Schweiger, NCC, is Vice President at NBCC International, Greensboro, NC. Donna Henderson, NCC, is a Professor at Wake Forest University. Equal authorship is intended. This article is dedicated to Professor Kenneth Hamwaka, Executive Director of the Guidance, Counselling and Youth Development Centre for Africa and Vice Chancellor of the Africa University of Guidance, Counselling and Youth Development. Correspondence can be addressed to Scott Hinkle, 3 Terrace Way, Greensboro, NC 27403, hinkle@nbcc.org.
Mar 24, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 1
Chad M. Yates, Courtney M. Holmes, Jane C. Coe Smith, Tiffany Nielson
Implementing continuous feedback loops between clients and counselors has been found to have significant impact on the effectiveness of counseling (Shimokawa, Lambert, & Smart, 2010). Feedback informed treatment (FIT) systems are beneficial to counselors and clients as they provide clinicians with a wide array of client information such as which clients are plateauing in treatment, deteriorating or at risk for dropping out (Lambert, 2010; Lambert, Hansen, & Finch, 2001). Access to this type of information is imperative because counselors have been shown to have poor predictive validity in determining if clients are deteriorating during the counseling process (Hannan et al., 2005). Furthermore, recent efforts by researchers show that FIT systems based inside university counseling centers have beneficial training features that positively impact the professional development of counseling students (Reese, Norsworthy, & Rowlands, 2009; Yates, 2012). To date, however, few resources exist on how to infuse FIT systems into counselor education curriculum and training programs.
This article addresses the current lack of information regarding the implementation of a FIT system within counselor education curricula by discussing: (1) an overview and implementation of a FIT system; (2) a comprehensive review of the psychometric properties of three main FIT systems; (3) benefits that the use of FIT systems hold for counselors-in-training; and (4) how the infusion of FIT systems within a counseling curriculum can help assess student learning outcomes.
Overview and Implementation of a FIT System
FIT systems are continual assessment procedures that include weekly feedback about a client’s current symptomology and perceptions of the therapeutic process in relation to previous counseling session scores. These systems also can include other information such as self-reported suicidal ideation, reported substance use, or other specific responses (e.g., current rating of depressive symptomology). FIT systems compare clients’ current session scores to previous session scores and provide a recovery trajectory, often graphed, that can help counselors track the progress made through the course of treatment (Lambert, 2010). Some examples of a FIT system include the Outcome Questionnaire (OQ-45.2; Lambert et al., 1996), Session Rating Scale (SRS; Miller, Duncan, & Johnson, 2000), Outcome Rating Scale (ORS; Miller & Duncan, 2000), and the Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms (CCAPS; Locke et al., 2011), all of which are described in this article.
Variety exists regarding how FIT systems are used within the counseling field. These variations include the selected measure or test, frequency of measurement, type of feedback given to counselors and whether or not feedback is shared with clients on a routine basis. Although some deviations exist, all feedback systems contain consistent procedures that are commonly employed when utilizing a system during practice (Lambert, Hansen, & Harmon, 2010). The first procedure in a FIT system includes the routine measurement of a client’s symptomology or distress during each session. This frequency of once-per-session is important as it allows counselors to receive direct, continuous feedback on how the client is progressing or regressing throughout treatment. Research has demonstrated that counselors who receive regular client feedback have clients that stay in treatment longer (Shimokawa et al., 2010); thus, the feedback loop provided by a FIT system is crucial in supporting clients through the therapeutic process.
The second procedure of a FIT system includes showcasing the results of the client’s symptomology or distress level in a concise and usable way. Counselors who treat several clients benefit from accessible and comprehensive feedback forms. This ease of access is important because counselors may be more likely to buy in to the use of feedback systems if they can use them in a time-effective manner.
The last procedure of FIT systems includes the adjustment of counseling approaches based upon the results of the feedback. Although research in this area is limited, some studies have observed that feedback systems do alter the progression of treatment. Lambert (2010) suggested that receiving feedback on what is working is apt to positively influence a counselor to continue these behaviors. Yates (2012) found that continuous feedback sets benchmarks of performance for both the client and the counselor, which slowly alters treatment approaches. If the goal of counseling is to decrease symptomology or increase functioning, frequently observing objective progress toward these goals using a FIT system can help increase the potential for clients to achieve these goals through targeted intervention.
Description of Three FIT Systems
Several well-validated, reliable, repeated feedback instruments exist. These instruments vary by length and scope of assessment, but all are engineered to deliver routine feedback to counselors regarding client progress. Below is a review of three of the most common FIT systems utilized in clinical practice.
The OQ Measures System
The OQ Measures System uses the Outcome Questionnaire 45.2 (OQ-45.2; Lambert et al., 1996), a popular symptomology measure that gauges a client’s current distress levels over three domains: symptomatic distress, interpersonal relations and social roles. Hatfield and Ogles (2004) listed the OQ 45.2 as the third most frequently used self-report outcome measure for adults in the United States. The OQ 45.2 has 45 items and is rated on a 5-point Likert scale. Scores range between 0 and 180; higher scores suggest higher rates of disturbance. The OQ 45.2 takes approximately 5–6 minutes to complete and the results are analyzed using the OQ Analyst software provided by the test developers. The OQ 45.2 can be delivered by paper and pencil versions or computer assisted administration via laptop, kiosk, or personal digital assistant (PDA). Electronic administration of the OQ 45.2 allows for seamless administration, scoring and feedback to both counselor and client.
Internal consistency for the OQ 45.2 is α = 0.93 and test-retest reliability is r = 0.84. The OQ 45.2 demonstrated convergent validity with the General Severity Index (GSI) of the Symptom Checklist 90-Revised (SCL-90-R; Derogatis, 1983; r = .78, n = 115). The Outcome Questionnaire System has five additional outcome measures: (1) the Outcome Questionnaire 30 (OQ-30); (2) the Severe Outcome Questionnaire (SOQ), which captures outcome data for more severe presenting concerns, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia; (3) the Youth Outcome Questionnaire (YOQ), which assesses outcomes in children between 13 and 18 years of age; (4) the Youth Outcome Questionnaire 30, which is a brief version of the full YOQ; and (5) the Outcome Questionnaire 10 (OQ-10), which is used as a brief screening instrument for psychological symptoms (Lambert et al., 2010).
The Partners for Change Outcome Management System (PCOMS)
The Partners for Change Outcome Management System (PCOMS) uses two instruments, the Outcome Rating Scale (ORS; Miller & Duncan, 2000) that measures the client’s session outcome, and the Session Rating Scale (SRS; Miller et al., 2000) that measures the client’s perception of the therapeutic alliance. The ORS and SRS were designed to be brief in response to the heavy time demands placed upon counselors. Administration of the ORS includes handing the client a copy of the ORS on a sheet of letter sized paper; the client then draws a hash mark on four distinct 10-centimeter lines that indicate how he or she felt over the last week on the following scales: individually (personal well-being), interpersonally (family and close relationships), socially (work, school and friendships), and overall (general sense of well-being).
The administration of the SRS includes four similar 10-centimeter lines that evaluate the relationship between the client and counselor. The four lines represent relationship, goals and topics, approach or methods, and overall (the sense that the session went all right for me today; Miller et al., 2000). Scoring of both instruments includes measuring the location of the client’s hash mark and assigning a numerical value based on its location along the 10-centimeter line. Measurement flows from left to right, indicating higher-level responses the further right the hash mark is placed. A total score is computed by adding each subscale together. Total scores are graphed along a line plot. Miller and Duncan (2000) used the reliable change index formula (RCI) to establish a clinical cut-off score of 25 and a reliable change index score of 5 points for the ORS. The SRS has a cut-off score of 36, which suggests that total scores below 36 indicate ruptures in the working alliance.
The ORS demonstrated strong internal reliability estimates (α = 0.87-.096), a test-retest score of r = 0.60, and moderate convergent validity with measures like the OQ 45.2 (r = 0.59), which it was created to resemble (Miller & Duncan, 2000; Miller, Duncan, Brown, Sparks, & Claud, 2003). The SRS had an internal reliability estimate of α = 0.88, test-retest reliability of r = 0.74, and showed convergent validity when correlated with similar measures of the working alliance such as the Helping Alliance Questionnaire–II (HAQ–II; Duncan et al., 2003; Luborsky et al., 1996). The developers of the ORS and SRS have also created Web-based administration features that allow clients to use both instruments online using a pointer instead of a pencil or pen. The Web-based administration also calculates the totals for the instruments and graphs them.
The Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms (CCAPS)
The CCAPS was designed as a semi-brief continuous measure that assesses symptomology unique to college-aged adults (Locke et al., 2011). When developed, the CCAPS was designed to be effective in assessing college students’ concerns across a diverse range of college campuses. The CCAPS has two separate versions, the CCAPS-62 and a shorter version, the CCAPS-34. The CCAPS-62 has 62 test items across eight subscales that measure: depression, generalized anxiety, social anxiety, academic distress, eating concerns, family distress, hostility and substance abuse. The CCAPS-34 has 34 test items across seven of the scales found on the CCAPS-62, excluding family distress. Additionally, the substance use scale on the CCAPS-62 is renamed the Alcohol Use Scale on the CCAPS-32 (Locke et al., 2011). Clients respond on a 5-point Likert scale with responses that range from not at all like me to extremely like me. On both measures clients are instructed to answer each question based upon their functioning over the last 2 weeks. The CCAPS measures include a total score scale titled the Distress Index that measures the amount of general distress experienced over the previous 2 weeks (Center for Collegiate Mental Health, 2012). The measures were designed so that repeated administration would allow counselors to compare each session’s scores to previous scores, and to a large norm group (N = 59,606) of clients completing the CCAPS at university counseling centers across the United States (Center for Collegiate Mental Health, 2012).
The CCAPS norming works by comparing clients’ scores to a percentile score of other clients who have taken the measure. For instance, a client’s score of 80 on the depressive symptoms scale indicates that he or she falls within the 80th percentile of the norm population’s depressive symptoms score range. Because the CCAPS measures utilize such a large norm base, the developers have integrated the instruments into the Titanium Schedule ™, an Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system. The developers also offer the instruments for use in an Excel scoring format, along with other counseling scheduling software programs. The developers of the CCAPS use RCI formulas to provide upward and downward arrows next to the reported score on each scale. Downward arrows indicate the client’s current score is significantly different than previous sessions’ scores and suggests progress during counseling. An upward arrow would suggest a worsening of symptomology. Cut-off scores vary across scales and can be referenced in the CCAPS 2012 Technical Manual (Center for Collegiate Mental Health, 2012).
Test-retest estimates at 2 weeks for the CCAPS-62 and CCAPS-34 scales range between r = 0.75–0.91 (Center for Collegiate Mental Health, 2012). The CCAPS-34 also demonstrated a good internal consistency that ranged between α = 0.76–0.89 (Locke et al., 2012). The measures also demonstrated adequate convergent validity compared to similar measures. A full illustration of the measures’ convergent validity can be found in the CCAPS 2012 Technical Manual (Center for Collegiate Mental Health, 2012).
Benefits for Counselors-in-Training
The benefits of FIT systems are multifaceted and can positively impact the growth and development of student counselors (Reese, Norsworthy, et al., 2009; Schmidt, 2014; Yates, 2012). Within counselor training laboratories, feedback systems have shown promise in facilitating the growth and development of beginning counselors (Reese, Usher, et al., 2009), and the incorporation of FIT systems into supervision and training experiences has been widely supported (Schmidt, 2014; Worthen & Lambert, 2007; Yates, 2012).
One such benefit is that counseling students’ self-efficacy improved when they saw evidence of their clients’ improvement (Reese, Usher, et al., 2009). A FIT system allows for the documentation of a client’s progress and when counseling students observed their clients making such progress, their self-efficacy improved regarding their skill and ability as counselors. Additionally, the FIT system allowed the counselor trainees to observe their effectiveness during session, and more importantly, helped them alter their interventions when clients deteriorated or plateaued during treatment. Counselor education practicum students who implemented a FIT system through client treatment reported that having weekly observations of their client’s progress helped them to isolate effective and non-effective techniques they had used during session (Yates, 2012). Additionally, practicum counseling students have indicated several components of FIT feedback forms were useful, including the visual orientation (e.g., graphs) to clients’ shifts in symptomology. This visual attenuation to client change allowed counselors-in-training to be more alert to how clients are actually faring in between sessions and how they could tailor their approach, particularly regarding crisis situations (Yates, 2012).
Another benefit discovered from the above study was that counseling students felt as if consistent use of a FIT system lowered their anxiety and relieved some uncertainty regarding their work with clients (Yates, 2012). It is developmentally appropriate for beginning counselors to struggle with low tolerance for ambiguity and the need for a highly structured learning environment when they begin their experiential practicums and internships (Bernard & Goodyear, 2013). The FIT system allows for a structured format to use within the counseling session that helps to ease new counselors’ anxiety and discomfort with ambiguity.
Additionally, by bringing the weekly feedback into counseling sessions, practicum students were able to clarify instances when the feedback was discrepant from how the client presented during session (Yates, 2012). This discrepancy between what the client reported on the measure and how they presented in session was often fertile ground for discussion. Counseling students believed bringing these discrepancies to a client’s attention deepened the therapeutic alliance because the counselor was taking time to fully understand the client (Yates, 2012).
Several positive benefits are added to the clinical supervision of counseling students. One such benefit is that clinical supervisors found weekly objective reports of their supervisees helpful in providing evidence of a client’s progress during session that was not solely based upon their supervisees’ self-report. This is crucial because relying on self-report as a sole method of supervision can be an insufficient way to gain information about the complexities of the therapeutic process (Bernard & Goodyear, 2013). Supervisors and practicum students both reported that the FIT system frequently brought to their attention potential concerns with clients that they had missed (Yates, 2012). A final benefit is that supervisees who utilized a FIT system during supervision had significantly higher satisfaction levels of supervision and stronger supervisory alliances than students who did not utilize a FIT system (Grossl, Reese, Norsworthy, & Hopkins, 2014; Reese, Usher, et al., 2009).
Benefits for Clients
Several benefits exist for counseling clients when FIT systems are utilized in the therapeutic process. The sharing of objective progress information with clients has been found to be perceived as helpful and a generally positive experience by clients (Martin, Hess, Ain, Nelson, & Locke, 2012). Surveying clients using a FIT system, Martin et al. (2012) found that 74.5% of clients found it “convenient” to complete the instrument during each session. Approximately 46% of the clients endorsed that they had a “somewhat positive” experience using the feedback system, while 20% of clients reported a “very positive” experience. Hawkins, Lambert, Vermeersch, Slade, and Tuttle (2004) found that providing feedback to both clients and counselors significantly increased the clients’ therapeutic improvement in the counseling process when compared to counselors who received feedback independently. A meta-analysis of several research studies, including Hawkins et al. (2004), found effect sizes of clinical efficacy related to providing per-session feedback ranged from 0.34 to 0.92 (Shimokawa et al., 2010). These investigations found more substantial improvement in clients whose counselors received consistent client feedback when compared with counselors who received no client feedback regarding the therapeutic process and symptomology. These data also showed that consistent feedback provision to clients resulted in an overall prevention of premature treatment termination (Lambert, 2010).
Utilization of FIT Systems for Counseling Curriculum and Student Learning Outcome Assessment
The formal assessment of graduate counseling student learning has increased over the past decade. The most recent update of the national standards from the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) included the requirement for all accredited programs to systematically track students at multiple points with multiple measures of student learning (CACREP, 2015, Section 4, A, B, C, D, E). Specifically, “counselor education programs conduct formative and summative evaluations of the student’s counseling performance and ability to integrate and apply knowledge throughout the practicum and internship” (CACREP, 2015, Section 4.E). The use of continuous client feedback within counselor education is one way to address such assessment requirements (Schmidt, 2014).
Counseling master’s programs impact students on both personal and professional levels (Warden & Benshoff, 2012), and part of this impact stems from ongoing and meaningful evaluation of student development. The development of counselors-in-training during experiential courses entails assessment of a myriad of counseling competencies (e.g., counseling microskills, case conceptualization, understanding of theory, ethical decision-making and ability to form a therapeutic relationship with clients; Haberstroh, Duffey, Marble, & Ivers, 2014). As per CACREP standards, counseling students will receive feedback during and after their practicum and internship experiences. This feedback typically comes from both the supervising counselor on site, as well as the academic department supervisor.
Additionally, “supervisors need to help their supervisees develop the ability to make effective decisions regarding the most appropriate clinical treatment” (Owen, Tao, & Rodolfa, 2005, p. 68). One suggested avenue for developing such skills is client feedback using FIT systems. The benefit of direct client feedback on the counseling process has been well documented (Minami et al., 2009), and this process can also be useful to student practice and training. Counseling students can greatly benefit from the use of client feedback throughout their training programs (Reese, Usher, et al., 2009). In this way, counselors-in-training learn to acknowledge client feedback as an important part of the counseling process, allowing them to adjust their practice to help each client on an individual basis. Allowing for a multi-layered feedback model wherein the counselor-in-training can receive feedback from the client, site supervisor and academic department supervisor has the potential to maximize student learning and growth.
Providing students feedback for growth through formal supervision is one of the hallmarks of counseling programs (Bernard & Goodyear, 2013). However, a more recent focus throughout higher education is the necessity of assessment of student learning outcomes (CACREP, 2015). This assessment can include “systematic evaluation of students’ academic, clinical, and interpersonal progress as guideposts for program improvement” (Haberstroh et al., 2014, p. 28). As such, evaluating student work within the experiential courses (e.g., practicum and internship) is becoming increasingly important.
FIT systems provide specific and detailed client feedback regarding clients’ experiences within therapy. Having access to documented client outcomes and progress throughout the counseling relationship can provide an additional layer of information regarding student growth and skill development. For instance, if a student consistently has clients who drop out or show no improvement over time, those outcomes could represent a problem or unaddressed issue for the counselor-in-training. Conversely, if a student has clients who report positive outcomes over time, that data could show clinical understanding and positive skill development.
Student learning outcomes can be assessed in a myriad of ways (e.g., FIT systems, supervisor evaluations, student self-assessment and exams; Haberstroh et al., 2014). Incorporating multiple layers of feedback for counseling students allows for maximization of learning through practicum and internships and offers a concrete way to document and measure student outcomes.
An Example: Case Study
Students grow and develop through a wide variety of methods, including feedback from professors, supervisors and clients (Bernard & Goodyear, 2013). Implementing a FIT system into experiential classes in counseling programs allows for the incorporation of structured, consistent and reliable feedback. We use a case example here to illustrate the benefits of such implementation. Within the case study, each CACREP Student Learning Outcome that is met through the implementation of the FIT system is documented.
A counselor educator is the instructor of an internship class where students have a variety of internship placements. This instructor decides to have students implement a FIT system that will allow them to track client progress and the strength of the working alliance. The OQ 45.2 and the SRS measures were chosen because they allow students to track client outcomes and the counseling relationship and are easy to administer, score and interpret. In the beginning of the semester, the instructor provides a syllabus to the students where the following expectations are listed: (1) students will have their clients fill out the OQ 45.2 and the SRS during every session with each client; (2) students will learn to discuss and process the results from the OQ 45.2 and SRS in each session with the client; and (3) students will bring all compiled information from the measures to weekly supervision. By incorporating two FIT systems and the subsequent requirements, the course is meeting over 10 CACREP (2015) learning outcome assessment components within Sections 2 and 3, Professional Counseling Identity (Counseling and Helping Relationships, Assessment and Testing), and Professional Practice.
A student, Sara, begins seeing a client at an outpatient mental health clinic who has been diagnosed with major depressive disorder; the client’s symptoms include suicidal ideation, anhedonia and extreme hopelessness. Sara’s initial response includes anxiety due to the fact that she has never worked with someone who has active suicidal ideation or such an extreme presentation of depressed affect. Sara’s supervisor spends time discussing how she will use the FIT systems in her work with the client and reminds her about the necessities of safety assessment.
In her initial sessions with her client, Sara incorporates the OQ 45.2 and the SRS into her sessions as discussed with her supervisor (CACREP Section 2.8.E; 2.8.K). However, after a few sessions, she does not yet feel confident in her work with this client. Sara feels constantly overwhelmed by the depth of her client’s depression and is worried about addressing the suicidal ideation. Her instructor is able to use the weekly OQ 45.2 and SRS forms as a consistent baseline and guide for her work with this client and to help Sara develop a treatment plan that is specifically tailored for her client based upon the client’s symptomology (CACREP Section 2.5.H, 2.8.L). Using the visual outputs and compiled graphs of weekly data, Sara is able to see small changes that may or may not be taking place for the client regarding his depressive symptoms and overall feelings and experiences in his life. Sara’s instructor guides her to discuss these changes with the client and explore in more detail the client’s experiences within these symptoms (CACREP Section 2.5.G). By using this data with the client, Sara will be better able to help the client develop appropriate and measureable goals and outcomes for the therapeutic process (CACREP Section 2.5.I). Additionally, as a new counselor, such an assessment tool provides Sara with structure and guidance as to the important topics to explore with clients throughout sessions. For example, by using some of the specific content on the OQ 45.2 (e.g., I have thoughts of ending my life, I feel no interest in things, I feel annoyed by people who criticize my drinking, and I feel worthless), she can train herself to assess for suicidal ideation and overall diagnostic criteria (CACREP Section 2.7.C).
Additionally, Sara is receiving feedback from the client by using the SRS measure within session. In using this additional FIT measure, Sara can begin to gauge her personal approach to counseling with this client and receive imperative feedback that will help her grow as a counselor (CACREP, Section 2.5.F). This avenue provides an active dialogue between client and counselor about the work they are doing together and if they are working on the pieces that are important to the client. Her instructor is able to provide both formative and summative feedback on her overall process with the client using his outcomes as a guide to her effectiveness as a clinician (CACREP, Section 3.C). Implementing a FIT system allows for the process of feedback provision to have concrete markers and structure, ultimately allowing for a student counselor to grow in his or her ability to become self-reflective about his or her own practice.
Implications for Counselor Education
The main implications of the integration of FIT systems into counselor education are threefold: (1) developmentally appropriate interventions to support supervisee/trainee clinical growth; (2) intentional measurement of CACREP Student Learning Outcomes; and (3) specific attention to client care and therapeutic outcomes. There are a variety of FIT systems being utilized, and while they vary in scope, length, and targets of assessment, each has a brief administration time and can be repeated frequently for current client status and treatment outcome measurement. With intentionality and dedication, counselor education programs can work to implement the utilization of these types of assessment throughout counselor trainee coursework (Schmidt, 2014).
FIT systems lend themselves to positive benefits for training competent emerging counselors. Evaluating a beginning counselor’s clinical understanding and skills are a key component of assessing overall learning outcomes. When counselors-in-training receive frequent feedback on their clients’ current functioning or session outcomes, they are given the opportunity to bring concrete information to supervision, decide on treatment modifications as indicated, and openly discuss the report with clients as part of treatment. Gathering data on a client’s experience in treatment brings valuable information to the training process. Indications of challenges or strengths with regard to facilitating a therapeutic relationship can be addressed and positive change supported through supervision and skill development. Additionally, by learning the process of ongoing assessment and therapeutic process management, counselor trainees are meeting many of the CACREP Student Learning Outcomes. The integration of FIT systems into client care supports a wide variety of clinical skill sets such as understanding of clinical assessment, managing a therapeutic relationship and treatment planning/altering based on client needs.
Finally, therapy clients also benefit through the use of FIT. Clinicians who receive weekly feedback on per-session client progress consistently show improved effectiveness and have clients who prematurely terminate counseling less often (Lambert, 2010; Shimokawa et al., 2010). In addition to client and counselor benefit, supervisors also have been shown to utilize FIT systems to their advantage. One of the most important responsibilities of a clinical supervisor is to manage and maintain a high level of client care (Bernard & Goodyear, 2013). Incorporation of a structured, validated assessment, such as a FIT system, allows for intentional oversight of the client–counselor relationship and clinical process that is taking place between supervisees and their clients. Overall, the integration of FIT systems into counselor education would provide programs with a myriad of benefits including the ability to meet student, client and educator needs simultaneously.
Conclusion
FIT systems provide initial and ongoing data related to a client’s psychological and behavioral functioning across a variety of concerns. They have been developed and used as a continual assessment procedure to provide a frequent and continuous self-report by clients. FIT systems have been used effectively to provide vital mental health information within a counseling session. The unique features of FIT systems include the potential for recurrent, routine measure of a client’s symptomatology, easily accessible and usable data for counselor and client, and assistance in setting benchmarks and altering treatment strategies to improve a client’s functioning. With intentionality, counselor educator programs can use FIT systems to meet multiple needs across their curriculums including more advanced supervision practices, CACREP Student Learning Outcome Measurement, and better overall client care.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The author reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2013). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Merrill.
Center for Collegiate Mental Health. (2012). CCAPS 2012 technical manual. University Park: Pennsylvania State
University.
The Council for Accreditation of Counseling Related Academic Programs (CACREP). (2015). 2016 accreditation standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/for-programs/2016-cacrep-standards
Derogatis, L. R. (1983). The SCL-90: Administration, scoring, and procedures for the SCL-90. Baltimore, MD: Clinical
Psychometric Research.
Duncan, B. L., Miller, S. D., Sparks, J. A., Claud, D. A., Reynolds, L. R., Brown, J., & Johnson, L. D. (2003). The Session Rating Scale: Preliminary psychometric properties of a “working” alliance measure. Journal of Brief Therapy, 3, 3–12.
Grossl, A. B., Reese, R. J., Norsworthy, L. A., & Hopkins, N. B. (2014). Client feedback data in supervision: Effects on supervision and outcome. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 8, 182–188.
Haberstroh, S., Duffey, T., Marble, E., & Ivers, N. N. (2014). Assessing student-learning outcomes within a counselor education program: Philosophy, policy, and praxis. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 5, 28–38. doi:10.1177/2150137814527756
Hannan, C., Lambert, M. J., Harmon, C., Nielsen, S. L., Smart, D. W., Shimokawa, K., & Sutton, S. W. (2005). A lab test and algorithms for identifying clients at risk for treatment failure. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 61, 155–163.
Hatfield, D., & Ogles, B. M. (2004). The use of outcome measures by psychologists in clinical practice.
Professional Psychology: Research & Practice, 35, 485–491. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.35.5.485
Hawkins, E. J., Lambert, M. J., Vermeersch, D. A., Slade, K. L., & Tuttle, K. C. (2004). The therapeutic effects of providing patient progress information to therapists and patients. Psychotherapy Research, 14, 308–327. doi:10.1093/ptr/kph027
Lambert, M. J. (2010). Prevention of treatment failure: The use of measuring, monitoring, & feedback in clinical practice.
Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Lambert, M. J., Hansen, N. B., & Finch, A. E. (2001). Patient-focused research: Using patient outcome data to enhance treatment effects. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 69, 159–172.
Lambert, M. J., Hansen, N. B., & Harmon, S. C. (2010). Outcome Questionnaire system (The OQ system): Development and practical applications in healthcare settings. In M. Barkham, G. Hardy, & J. Mellor-Clark (Eds.), Developing and delivering practice-based evidence: A guide for the psychological therapies (pp. 141–154). New York, NY: Wiley-Blackwell.
Lambert, M. J., Hansen, N. B., Umphress, V., Lunnen, K., Okiishi, J., Burlingame, G. M., & Reisinger, C. (1996). Administration and scoring manual for the OQ 45.2. Stevenson, MD: American Professional Credentialing Services.
Locke, B. D., Buzolitz, J. S., Lei, P. W., Boswell, J. F., McAleavey, A. A., Sevig, T. D., Dowis, J. D. & Hayes, J.
(2011). Development of the Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms-62 (CCAPS-62).
Journal of Counseling Psychology, 58, 97–109.
Locke, B. D., McAleavey, A. A., Zhao, Y., Lei, P., Hayes, J. A., Castonguay, L. G., Li, H., Tate, R., & Lin, Y. (2012). Development and initial validation of the Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms-34 (CCAPS-34). Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 45, 151–169. doi:10.1177/0748175611432642
Luborsky, L., Barber, J. P., Siqueland, L., Johnson, S., Najavits, L. M., Frank, A., & Daley, D. (1996). The Helping
Alliance Questionnaire (HAQ–II): Psychometric properties. The Journal of Psychotherapy Practice and
Research, 5, 260–271.
Martin, J. L., Hess, T. R., Ain, S. C., Nelson, D. L., & Locke, B. D. (2012). Collecting multidimensional client data using repeated measures: Experiences of clients and counselors using the CCAPS-34. Journal of College Counseling, 15, 247–261. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1882.2012.00019.x
Miller, S., & Duncan, B. (2000). The outcome rating scale. Chicago, IL: International Center for Clinical Excellence.
Miller, S., Duncan, B., & Johnson, L. (2000). The session rating scale. Chicago, IL: International Center for Clinical
Excellence.
Miller, S. D., Duncan, B. L., Brown, J., Sparks, J. A., & Claud, D. A. (2003). The Outcome Rating Scale: A
preliminary study of the reliability, validity, and feasibility of a brief visual analog measure. Journal of
Brief Therapy, 2, 91–100.
Minami, T., Davies, D. R., Tierney, S. C., Bettmann, J. E., McAward, S. M., Averill, L. A., & Wampold, B. E. (2009). Preliminary evidence on the effectiveness of psychological treatments delivered at a university counseling center. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 56, 309–320.
Owen, J., Tao, K. W., & Rodolfa, E. R. (2005). Supervising counseling center trainees in the era of evidence-based practice. Journal of College Student Psychotherapy, 20, 66–77.
Reese, R. J., Norsworthy, L. A., & Rowlands, S. R. (2009). Does a continuous feedback system improve psychotherapy outcome? Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training, 46, 418–431.
doi:10.1037/a0017901
Reese, R. J., Usher, E. L., Bowman, D. C., Norsworthy, L. A., Halstead, J. L., Rowlands, S. R., & Chisolm, R.
R. (2009). Using client feedback in psychotherapy training: An analysis of its influence on supervision
and counselor self-efficacy. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 3, 157–168.
doi:10.1037/a0015673
Schmidt, C. D. (2014). Integrating continuous client feedback into counselor education. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 6, 60–71. doi:10.7729/62.1094
Shimokawa, K., Lambert, M. J., & Smart, D. W. (2010). Enhancing treatment outcome of patients at risk of treatment failure: Meta-analytic and mega-analytic review of a psychotherapy quality assurance system. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 78, 298–311. doi:10.1037/a0019247
Warden, S. P., & Benshoff, J. M. (2012). Testing the engagement theory of program quality in CACREP-accredited counselor education programs. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 127–140.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00009.x
Worthen, V. E., & Lambert, M. J. (2007). Outcome oriented supervision: Advantages of adding systematic
client tracking to supportive consultations. Counselling & Psychotherapy Research, 7, 48 –53.
doi:10.1080/14733140601140873
Yates, C. M. (2012). The use of per session clinical assessment with clients in a mental health delivery system: An
investigation into how clinical mental health counseling practicum students and practicum instructors use
routine client progress feedback (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Kent State University, Kent, Ohio.
Chad M. Yates is an Assistant Professor at Idaho State University. Courtney M. Holmes, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at Virginia Commonwealth University. Jane C. Coe Smith is an Assistant Professor at Idaho State University. Tiffany Nielson is an Assistant Professor at the University of Illinois at Springfield. Correspondence can be addressed to Chad M. Yates, 921 South 8th Ave, Stop 8120, Pocatello, Idaho, 83201, yatechad@isu.edu.
Mar 23, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 1
Ellen W. Armbruster, David C. Witherington
The attachment work of John Bowlby (1988) affords clinicians and researchers the opportunity to view psychopathology as relationally based, rather than as unique to the individual to whom a specific label has been given. Anxiety is a particularly fitting place to focus this type of investigation since understanding the meaning and function of anxiety within the context of human development lies at the center of attachment theory. Bowlby integrated the time-honored notion that the early child-caregiver bond is critical to the child’s survival and well-being into his knowledge of scientific facts and meaning and provided an interpersonal understanding of healthy as well as pathological development. Bowlby’s thoughts, flowing as they did from psychoanalysis and object relations, revolutionized the analytic world by removing dysfunction from the center of the individual and placing it in the space between interacting humans. Through the use of instruments designed to measure attachment style, early bonding memories and five different types of anxiety, this study utilizes Bowlby’s viewpoint as a springboard from which to examine the correlations between adults’ perception of their past and present relational experiences and their current levels of anxiety.
Relationship of Attachment and Bonding to Anxiety Disorders
There is a sizeable body of research suggesting a relationship between anxiety and attachment or bonding experiences (e.g., Cassidy, Lichtenstein-Phelps, Sibrava, Thomas, & Borkovec, 2009; Cavedo & Parker, 1994; Chorpita & Barlow, 1998; Eng & Heimberg, 2006; Eng, Heimberg, Hart, Schneier, & Liebowitz, 2001; Manicavasagar, Silove, Wagner, & Hadzi-Pavlovic, 1999; Marazziti et al., 2007; Meites, Ingram, & Siegle, 2012; O’Connor & Elklit, 2008; Pacchierotti et al., 2002; Parker, 1979; Renaud, 2008; Seganfredo et al., 2009; Turgeon, O’Connor, Marchand, & Freeston, 2002). We will first review the literature explicating the anxiety–attachment paradigm and then consider research that has looked at anxiety and bonding, before turning to the studies that have incorporated measures of both attachment and bonding in an examination of individuals with specific anxiety states.
Anxiety and Attachment
Substantial investigation has considered anxiety-attachment associations. Potential links have been found between generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and attachment, with indications that increasing perceptions of difficult early attachment experiences are tied to a risk for GAD (Cassidy et al., 2009). Furthermore, investigation has shown individuals with GAD to report less secure parental attachment, less trust, increased difficulty with communication, and more alienation than individuals without the disorder (Eng & Heimberg, 2006). In other work, participants with panic disorder (PD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder were found to have higher levels of preoccupied attachment style, and participants without these conditions had higher levels of secure attachment (Marazziti et al., 2007). Social anxiety also has been considered in light of adult attachment, and individuals with an anxious-preoccupied attachment style have reported higher levels of social fear and avoidance than participants with a secure attachment style (Eng et al., 2001).
Attachment anxiety and avoidance have been connected to increased symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in veterans (Renaud, 2008). However, the vast majority of participants in Renaud’s (2008) study reported a preference for attachment avoidance (either fearful or dismissing), and PTSD symptoms were higher among these individuals. In young adults, secure attachment has been associated with fewer PTSD symptoms; however, dismissing and fearful attachment preferences have been tied to a higher number of PTSD symptoms (O’Connor & Elklit, 2008). Associations of this nature may indicate that secure attachment offers potential protection against the development of PTSD, whereas dismissing and fearful attachment may increase risk (O’Connor & Elklit, 2008).
Anxiety and Bonding
A noteworthy number of studies have looked at the relationship between anxiety and bonding. For instance, associations have been demonstrated between both PD and GAD and the condition of affectionless control (lack of attunement and overprotection) by parents (Chorpita & Barlow, 1998). In other research (Chambless, Gillis, Tran, & Stekettee, 1996), people with PD or OCD also most commonly perceived their parents’ style of caregiving to fall within the affectionless control category. In addition, individuals who rated their mothers most highly on the overprotection scale experienced the earliest onset of anxiety disorders.
Associations have been found between mother overprotection and PD in men and between father overprotection and PD in women (Seganfredo et al., 2009), and a relationship has been noted between perception of parental overprotection and adult symptoms of separation anxiety (Manicavasagar et al., 1999). Furthermore, in a study matching participants diagnosed with PD and healthy controls, individuals with PD reported lower parental care than those without the disorder (Pacchierotti et al., 2002). A relationship also has been demonstrated between low parental care and generalized fear among a large sample of undergraduates (Meites et al., 2012). Other researchers have conceded that the development of GAD may be related to unfavorable parental behavior (Silove, Parker, Hadzi-Pavlovic, Manicavasagar, & Blaszczynski, 1991). However, they also suggested the alternative possibility that maternal overprotection could be a response to early signs of anxiety in people with PD.
Early bonding memories and obsessionality have been shown to be related as well. Positive correlations were noted between obsessionality and parental overprotection for both males and females, and between obsessionality and maternal care in females; however, negative correlations were found between obsessionality and parental care in males (Cavedo & Parker 1994). In other work, outpatients with OCD or PD remembered their parents as being more overprotective than did a control group of non-anxious participants, leading researchers to the conclusion that parental overprotection may increase the risk that children will develop anxiety disorders (Turgeon et al., 2002). However, in another study investigating the link between early bonding memories and obsessive-compulsive behaviors in a non-clinical population, researchers concluded that low parental care may represent a risk for emotional suffering in adulthood, but does not predict a specific psychiatric disorder (Mancini, D’Olimpio, Prunetti, Didonna, & Del Genio, 2000).
The relationship between early bonding memories and agoraphobia or social phobia also has been assessed (Parker, 1979). Parker (1979) found that people with agoraphobia reported their mothers to be less caring than did participants in the control group, but differed in no other way. Individuals with social phobia reported both their mothers and fathers to be less caring and more overprotective than did the control group individuals.
Anxiety, Attachment and Bonding
Despite substantial evidence of correlation between adult attachment and anxiety and between early bonding memories and anxiety, fewer empirical studies explicitly differentiate between adult attachment and parental bonding constructs, or consider both in relation to specific anxiety types. Here, we will review studies that have investigated the association between anxiety and both adult attachment and parental bonding.
Myhr, Sookman, and Pinard (2004) examined adult attachment and early parental bonding memories in a sample of individuals with OCD or depression. More relationship anxiety was evident among participants with OCD or depression and more dependency discomfort (avoidance) was seen in participants with depression and in unmarried participants with OCD. With regard to early bonding memories, individuals with OCD did not differ from controls, and there was no clear correlation between adult attachment and early bonding memories. The researchers suggested two potential reasons for this finding: (a) the bonding instrument they were using may not have measured relational elements necessary for adult attachment security; or (b) the responses may have reflected a bias based on attachment security or specific diagnosis.
Ghafoori, Hierholzer, Howsepian, and Boardman (2008) investigated the protective value of adult attachment, parental bonding and divine love in adjustment to trauma experienced in the military. They found that current PTSD symptoms in veterans who participated in the study negatively correlated with secure attachment and positively correlated with insecure attachment. However, no significant relationship emerged between current PTSD symptoms and early childhood bonding memories. Findings did indicate that adult attachment style contributes to the severity of PTSD and that perceived parental care moderates that relationship (i.e., since parental care negatively correlated with insecure attachment).
Yarbro, Mahaffey, Abramowitz, and Kashdan (2013) used online self-report measures to explore the relationship between memories of low care in early child–caregiver relationships and reports of obsessive beliefs in a sample of undergraduate college students. Their findings indicated significant associations between the two variables, lending support to the idea that there is a relationship between obsessive beliefs and affectionless and neglectful parenting (Yarbro et al., 2013). The researchers also considered whether attachment anxiety or avoidance may mediate this relationship. Through the use of hierarchical regression models, they demonstrated that attachment anxiety may serve as a partial mediator of the relationship between memories of low care and self-reported obsessive beliefs, but that attachment avoidance did not function in this way (Yarbro et al., 2013).
As well as providing additional support in favor of the relationship between attachment, bonding and anxiety, the Myhr et al. (2004), Ghafoori et al. (2008) and Yarbro et al. (2013) studies lead us to consider a further possibility. We offer the idea that adult attachment and parental bonding may address qualitatively distinct aspects of human interaction, especially when considered in light of different types of anxiety. The work of the aforementioned authors highlights the need to investigate adult attachment and parental bonding as distinct yet potentially interdependent constructs that illuminate, from different viewpoints, the intricacies of interpersonal connection.
Constructs of Adult Attachment and Parental Bonding
The construct of adult attachment may be understood as resolving to two primary dimensions: model of self and model of others (Bartholomew & Horowitz, 1991). In Bartholomew and Horowitz’s (1991) work, the degree of positivity an individual experiences with regard to his or her representation of self meets the degree of positivity that person experiences with regard to his or her representation of others to yield four potential patterns of preference in relationships. Those who have a positive view of themselves and of others are at ease in intimate and in autonomous situations and have a secure style of attachment. Individuals with a preoccupied style of attachment have a negative view of self, but see others in a positive light; they look to their intimate relationships for fulfillment and validation. The fearful style of attachment involves a wish for closeness that remains unfulfilled due to fears of rejection, whereas the dismissing style is typified by denial that intimacy with others is needed or desired. According to Bartholomew and Horowitz’s (1991) model, the fearful style reflects a negative view of self (undeserving of the love and support of others), as well as a negative view of others, whereas the dismissing style reflects a positive view of self (minimizing the awareness of needs or distress) and a negative view of others.
The construct of parental bonding and its classificatory scheme also can be understood as resolving to two primary dimensions: (perceived) parental care and (perceived) parental overprotection (Parker, Tupling, & Brown, 1979). The dimensions are presumed to contribute to the bond that develops between a parent and a child early in life and, when considered together, result in four potential bonding experiences. Optimal bonding is said to occur when parental care (emotional warmth and acceptance) is high and overprotection (psychological control and intrusion) is low; whereas affectionate constraint refers to bonding in which parents are highly overprotective of their children while exhibiting some caring behaviors toward them (Gladstone & Parker, 2005). When parental care and overprotection are both low, the parent–child bond that develops may be weak or absent, and when care is low (emotional coldness and rejection) and overprotection is high, affectionless control typifies the bonding relationship.
Although the constructs of adult attachment and parental bonding tap into the nature of relationship quality, each construct views human connection from a different vantage point. Whereas Bartholomew and Horowitz’s (1991) four-category adult attachment model considers individuals’ perceptions of their current close relationships with peers, Parker et al.’s (1979) conceptualization of parental bonding involves recollections of early relationships with caregivers. That is, the attachment construct targets the manner in which people perceive their own worth and that of others in the context of current relationships; the bonding construct, however, targets a present-day characterization of past caregiver style. Rather than addressing the perception of one’s upbringing, adult attachment focuses on a current sense of worth and the expectation of how others will respond in relationship. Parental bonding, in contrast, focuses upon memories of early child–caregiver interactions and the sense of how one was treated by one’s caregivers.
In consideration of the distinctions between the adult attachment and parental bonding constructs, we may view the assessment of adult attachment as eliciting a general sense of how one fits into current relationships and the assessment of parental bonding as specific to the memory of past child–caregiver interactions. In other words, adult attachment and parental bonding, while certainly interrelated in that both tap into the quality of relationships individuals form with others, nonetheless do not actually target the same general conceptualization of relationship quality, but are instead distinct constructs that capture slightly different aspects of human interaction from divergent points of view.
Purpose of the Study and Predictions
This study, in light of the relative paucity of research involving single-sample assessments of our constructs of interest, was designed to address more systematically the interconnections that may exist between adult attachment, memories of early parental bonding experiences and various forms of anxiety. To accomplish this, we specifically targeted adults’ reports of early interactions with caregivers, as well as their present interpersonal approach in relation to five different types of self-reported anxiety: obsessive-compulsive behavior, panic symptomatology, experience of worry and generalized anxiety, post-trauma symptomatology, and experience of social anxiety.
Predictions for the study flowed from our premise that adult attachment and parental bonding are interconnected but separate aspects of relational experience. Although Myhr et al. (2004) found no significant correlation between attachment and early bonding memories, the authors suggested potential reasons for this finding, including instrument limitations and attachment or diagnosis biases of the participants. Taking into account this explanation and our premise that the attachment and bonding constructs, while interrelated, capture relationship quality from different vantage points, we first conjectured that we would find a low to moderate relationship between these two variables.
With respect to relationships among adult attachment and anxiety, since the preponderance of the literature (Cassidy et al., 2009; Eng & Heimberg, 2006; Eng et al., 2001; Ghafoori et al., 2008; Marazziti et al., 2007; Myhr et al., 2004; O’Connor & Elklit, 2008; Renaud, 2008) indicates associations between self-reports of adult attachment style and self-reports of anxiety, we predicted that the tendency toward each of several different anxiety types would negatively correlate with secure attachment style and positively correlate with the insecure styles of attachment, and that these associations would be strong.
With respect to relationships between parental bonding and anxiety, some of the literature indicates a clear association (Chambless et al., 1996; Chorpita & Barlow, 1998; Pacchierotti et al., 2002; Parker, 1979; Turgeon et al., 2002; Yarbro et al., 2013), whereas other investigations have yielded mixed results (Cavedo & Parker, 1994; Ghafoori et al., 2008; Mancini et al., 2000; Manicavasagar et al., 1999; Myhr et al., 2004; Parker, 1979; Silove et al., 1991). Given these inconsistencies and our assumption of adult attachment and parental bonding as measuring distinct aspects of relational quality, we anticipated fewer significant correlations between parental bonding and different forms of anxiety. Nevertheless, where significant correlations arose, we predicted positive correlations between anxiety and the overprotection dimension of parental bonding and negative correlations between anxiety and the care dimension.
Method
Participants
Participants for the study were 201 undergraduate psychology students (152 female, 48 male, with one person not reporting gender) at a university located in the Southwestern United States. Latino/Hispanic participants comprised 36.8% of the sample and Caucasian participants comprised 49.8%. The remaining participants reported race or ethnicity as African American (3%), Asian (2%), Native American (2%), Pacific Islander (.5%), or Other (6%). Participants’ ages ranged from 17 to 50 years, with a mean of 19.86 (SD = 3.78).
Procedures
Approval for the study was granted by the Institutional Review Board at our university. Participants were recruited through a Web-based recruitment system and their participation was an optional part of their psychology course requirement. A description of the study and the dates and times during which data collection would take place were posted on the Web site and participants signed up for the test period that was convenient for them. As participants arrived at the testing location, they were greeted by the test administrator and seated around a table. After informed consent was explained and a questionnaire packet provided, participants were allowed up to 1.5 hours to complete the surveys. A maximum of 25 participants were permitted to sign up for each test period.
Variables and Instrumentation
Relationship Scales Questionnaire. To index adult attachment, we used the Relationship Scales Questionnaire (RSQ; Griffin & Bartholomew, 1994). The RSQ consists of 30 items and asks participants to rate, on a 5-point scale, how well each of the items fits their perception of the style they use in their close relationships. Individuals are scored on each of four attachment patterns: secure, fearful, preoccupied, and dismissing. Internal consistencies for the RSQ range from .41 for secure attachment to .71 for dismissing attachment. Although these alpha values may appear low, it is a natural result of combining two orthogonal dimensions, including model of self and model of others. It also is important to note that test–retest reliability may be inferred from the data on internal consistency, since the RSQ indexes attachment using a dimensional approach (Griffin & Bartholomew, 1994). A psychometric examination of the RSQ in a French population demonstrated good construct validity, test–retest reliability and internal consistency (Guédeney, Fermanian, & Bifulco, 2010). We chose the RSQ for its widespread application in counseling and other mental health venues to study attachment as it relates to topics such as parental bonding and anxiety (Ghafoori et al., 2008; Yarbro et al., 2013), perfectionism (Chen, Hewitt, & Flett, 2015), interpersonal sensitivity (Otani et al., 2014), and problematic substance use (Massey, Compton, & Kaslow, 2014).
Parental Bonding Instrument. To index parental bonding, we used the Parental Bonding Instrument (PBI) developed by Parker et al. (1979). The instrument consists of 25 items, including 12 parental care items and 13 parental overprotection items, and asks participants to rate on a 4-point scale how they remember their primary caregiver. A test–retest reliability study yielded a Pearson correlation coefficient for the care scale of .761 and a Pearson correlation coefficient for the overprotection scale of .628 (Parker et al., 1979). A comparison of the psychometric properties of the PBI and another measure of parenting behavior demonstrated that the PBI may be more stable over time (Safford, Alloy, & Pieracci, 2007), and a Persian version showed high internal consistency and test–retest reliability (Behzadi & Parker, 2015). We chose the PBI for its long history of utilization in the study of familial relationships. It continues to be a frequently employed instrument in the investigation of caregiver–offspring interactions in the context of problems such as anxiety (Meites et al., 2012; Seganfredo et al., 2009), pathological gambling (Villalta, Arévalo, Valdepérez, Pascual, & Pérez de los Cobos, 2015), intermittent explosive disorder (Lee, Meyerhoff, & Coccaro, 2014) and suicidality (Goschin, Briggs, Blanco-Lutzen, Cohen, & Galynker, 2013).
Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory-Revised. To assess tendency toward obsessive-compulsive behavior, we used the Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory-Revised (OCI-R; Foa et al., 2002). This questionnaire consists of 18 items and asks participants to rate, on a 5-point scale, how much each item has bothered them in the last month. In their examination of the psychometric properties of the OCI-R, Foa et al. (2002) demonstrated that test–retest reliability ranged from .74 to .91 for individuals with OCD, and from .57 to .87 for non-anxious controls. In a recent psychometric examination, the OCI-R was shown to be valid, reliable and diagnostically sensitive (Wootton et al., 2015). The OCI-R also demonstrated good validity and reliability in an older adult population (Calamari et al., 2014).
Panic Disorder Severity Scale-Self Report. To assess tendency toward panic symptoms, we used the Panic Disorder Severity Scale-Self Report (PDSS-SR; Houck, Speigel, Shear, & Rucci, 2002). The PDSS-SR consists of seven questions rated on a 5-point scale. The questions explore the presence and degree of panic in the lives of participants. Test–retest reliability was shown by Shear et al. (2001) to be satisfactory, with a Pearson correlation coefficient of .71. More recently, a psychometric evaluation of the self-report and clinician-administered versions of the PDSS indicated adequate or promising reliability and validity for each form (Wuyek, Antony, & McCabe, 2011). An examination of the Spanish version of the PDSS-SR demonstrated that the psychometric properties were comparable to those of other versions of this instrument (Santacana et al., 2014).
Penn State Worry Questionnaire. To assess tendency toward worry and generalized anxiety, we used the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ; Meyer, Miller, Metzger, & Borkovec, 1990). This measure consists of 16 items and asks participants to rate, on a 5-point scale, how characteristic each item is of them. Meyer et al. (1990) found the PSWQ to possess high internal consistency and good test–retest reliability (r[45] = .92, p < .001) in clinical as well as in non-clinical samples, with alpha coefficients ranging from .88 to .95 for both groups. More recent examinations of the PSWQ have indicated that the instrument is psychometrically sound in African American populations (DeLapp, Chapman, & Williams, 2015), in online administrations of the Hungarian version (Pajkossy, Simor, Szendi, & Racsmány, 2015) and among older adults (Wuthrich, Johnco, & Knight, 2014). The PSWQ continues to be used to index worry in the study of therapeutic concerns such as psychological inflexibility (Ruiz, 2014), negative mood (Dash & Davey, 2012), and distress tolerance (Macatee, Capron, Guthrie, Schmidt, & Cougle, 2015).
PTSD Checklist-Civilian Version. To assess tendency toward post-trauma symptoms, we used the PTSD Checklist-Civilian Version (PCL-C; Weathers, Litz, Herman, Huska, & Kean, 1993). The PCL-C consists of 17 items asking participants to rate, on a 5-point scale, how often each item has bothered them in the last month. Weathers et al. (1993) studied veterans in their original research on the psychometric properties of the PCL and found that test–retest reliability was .96 over a period of 2 to 3 days. Recent investigation of the psychometric properties of the PCL-C indicated continued high internal consistency and high test–retest reliability in a non-clinical population; in addition, convergent and discriminant validity were satisfactory when compared to other assessments of PTSD (Conybeare, Behar, Solomon, Newman, & Borkovec, 2012).
Social Interaction Anxiety Scale. To assess tendency toward social anxiety, we used the Social Interaction Anxiety Scale (SIAS; Mattick & Clarke, 1998). The SIAS consists of 20 items. This questionnaire asks participants to rate, on a 5-point scale, how characteristic each item is of them. In their examination of the psychometric properties of the SIAS, Mattick and Clark (1998) found the alpha coefficient for test–retest reliability to be .92 at both 4 weeks (range 3–5 weeks) and 12 weeks (range 11–13 weeks). More recently, the SIAS has been evaluated in several settings and formats, including the Internet (Hedman et al., 2010; Hirai, Vernon, Clum, & Skidmore, 2011) and in a shortened version (Fergus, Valentiner, Kim, & McGrath, 2014) with consistently adequate results. The SIAS continues to be used to index social anxiety in the study of mental health related topics such as participation in Alcoholics Anonymous (Moser, Turk, & Glover, 2015) and efficacy of cognitive-behavioral group therapy versus group psychotherapy (Bjornsson et al., 2011).
Data Analyses
Scoring. Scores and, when relevant, sub-scores were calculated for each instrument. Although the PBI can yield specific categories of parental bonding (i.e., optimal bonding or affectionless control), for the purposes of our study each dimension of this instrument (care and overprotection) was scored continuously. Like the PBI, the RSQ may be employed categorically; we elected, instead, to utilize the multi-item nature of the RSQ to permit participants to express their attachment preferences on a continuous scale so that overall attachment preferences would incorporate aspects of each of the four attachment patterns (Griffin & Bartholomew, 1994). This approach allowed us to develop a correlation matrix that included continuous scores not only for the PBI and RSQ, but also for each of the anxiety indices utilized. Data analysis also involved the calculation of Pearson’s r for the relationships between RSQ and PBI scores, between RSQ scores and scores on each of the five anxiety indices we used, and between PBI scores and scores on each of the five anxiety indices.
Reliability of scores. Reliability coefficients were calculated for each of the instruments utilized, including the subscales of the PBI, the RSQ, and the OCI-R. Cronbach’s alpha for the instruments ranged from .420 for the secure subscale of the RSQ to .938 for the PSWQ (see Tables 1 and 2). Due to the low reliability for several of the scales, all observed correlations were disattenuated (corrected to account for measurement error) using the following equation (Osborne, 2003):
The reliability coefficients are represented by r11 and r22, while r12 is the observed correlation and r*12 is the disattenuated correlation. Disattenuated correlations are listed in parentheses below the observed correlations in Tables 1 and 2.
Significance level and magnitude of correlations. In order to reduce the risk of a Type I Error in this study, a more stringent alpha level was adopted: only correlations that were significant at p < .01 were considered, while correlations significant at p < .05 were disregarded.
Correlation coefficients of 0 to .3 were considered to be of small magnitude, whereas correlation coefficients of .4 to .7 were considered to be of moderate magnitude, and correlation coefficients of .8 or greater were considered to be of high magnitude.
With respect to correlations between RSQ scores and ratings on each of the five self-report measures of anxiety (OCI-R, PDSS-SR, PSWQ, PCL-C, and SIAS), higher scores for the RSQ’s secure attachment preference negatively correlated with higher scores on all five self-report measures of anxiety (p < .01). The disattenuated correlation between scores for the RSQ’s secure attachment preference and ratings on the SIAS was of high magnitude (r = -.805), while the magnitudes of the disattenuated correlations for scores for the RSQ’s secure attachment preference and scores on the other anxiety indices were all moderate (secure attachment–obsessive-compulsive, r = -.642; secure attachment–panic, r = -.467; secure attachment–worry, r = -.567; secure attachment–post-trauma, r = -.622). Higher scores for the RSQ’s preoccupied and fearful attachment preferences positively correlated with higher scores on every type of anxiety indexed (p < .01), with all disattenuated correlations nearing or reaching moderate magnitude. Dismissing attachment style was not correlated with scores for any type of anxiety assessed in this study.
With respect to correlations between PBI scores and ratings on each of the five self-report measures of anxiety (OCI-R, PDSS-SR, PSWQ, PCL-C, and SIAS), neither PBI’s care nor overprotection dimension correlated with obsessive-compulsive symptoms, panic, or worry. However, higher scores on the PBI care dimension negatively correlated with higher scores for post-trauma and social anxiety symptoms (p < .01), and higher scores on PBI’s overprotection dimension positively correlated with higher scores for post-trauma and social anxiety (p < .01). All correlations were of small magnitude (care–post-trauma, r = -.276; care–social anxiety, r = -.317; overprotection–post-trauma, r = .220; overprotection–social anxiety, r = .220).
Discussion
This study examined the relationship between participant reports of adult attachment style, early bonding interactions with caregivers, and five different anxiety types. Results of the study supported our predictions of (a) a low to moderate relationship between adult attachment and parental bonding, (b) strong negative correlations between a secure attachment preference and all types of anxiety, (c) strong positive correlations between preoccupied and fearful attachment preferences and all types of anxiety, and (d) fewer significant correlations between early bonding memories and different anxiety types. With regard to this last prediction, only two types of anxiety (post-traumatic and social) were negatively associated with the care dimension of bonding and positively associated with the overprotection dimension; the other anxiety types were not correlated with either bonding dimension. Contrary to prediction, dismissing attachment did not correlate with any anxiety type or with either the care or overprotection dimension of parental bonding.
The positive correlation we found between secure attachment and early memories of high care and low overprotection contrasts with the absence of significant correlation in Myhr et al.’s (2004)
results, but is in keeping with our assumption that adult attachment and parental bonding constructs are distinct, as well as interrelated (hence our prediction of a low to moderate relationship). Also noteworthy was the absence of significant correlation between dismissing attachment style and both the care and overprotection scales of the PBI. Since insecure attachment is considered to result from relationship experiences that do not support the optimal development of a child (Bowlby, 1988), it is interesting that only fearful and preoccupied attachment preferences were correlated with less-than-optimal caregiving (lower care scores and higher overprotection scores).
Further explanation for this result may lie in the inherent qualities of the dismissing attachment pattern. Bartholomew (1993) suggested that dismissing attachment is characterized by a denial of the need for close relationships and George, Kaplan, and Main (1996) posited that individuals with a dismissing attachment state of mind often idealize their caregivers. Participants with a dismissing attachment style may have failed to report less-than-optimal caregiving, because they did not feel close to their caregivers and were thus unaware of their caregivers’ deficiencies or even dismissed unpleasant early bonding memories. In addition, the absence of significant correlation between dismissing attachment and total scores for all types of anxiety indexed in our sample suggests that individuals with a dismissing attachment style may experience a lower level of the subjectively disagreeable physiological reactivity that is often present alongside anxiety. If so, this may help explain the decreased reporting of anxiety and unpleasant early bonding memories among individuals who reported a preference for the dismissing attachment pattern.
As expected, lower correlations emerged between memories of early parental bonding (both care and overprotection) and different types of anxiety than those observed between anxiety and the secure, preoccupied, and fearful styles of adult attachment. Neither the care nor the overprotection dimension of bonding significantly correlated with total obsessive-compulsive symptoms, panic symptoms or generalized anxiety symptoms, which is partly consistent with Manicavasagar et al. (1999), who determined that PD may not be correlated with parental overprotection. Congruent with Parker’s (1979) investigation, which found that people with social phobia reported decreased care and increased overprotection in their caregivers, our results revealed significant correlations between parental bonding and anxiety only with respect to post-trauma and social anxiety symptomatology, and these correlations were of low magnitude.
Given that our study revealed associations between early bonding memories and experiences of both post-trauma and social anxiety, but not the other types of anxiety indexed, it is necessary to consider a possible etiology for this finding. Since our sample consisted of undergraduate psychology students, we thought it likely that many of our participants might be young people who were away from their homes and families for the first time and could be experiencing fear about their new social environment and possibly even feel traumatized by the separation from their caregivers. Indeed, our thinking is supported by the work of Manicavasagar et al. (1999), which indicated a potential association between the perception of parental overprotection and adult symptoms of separation anxiety.
Although results were consistent with predictions of lower correlations between parental bonding and anxiety than between attachment and anxiety, our findings diverged from the work of several other researchers. For example, Silove et al. (1991), Cavedo and Parker (1994), and Turgeon et al. (2002) found significant correlations between various types of anxiety and early bonding memories. It is possible that the lack of significant correlation in our sample between early bonding memories
and obsessive-compulsive, panic or generalized anxiety symptoms may indicate that people with these types of anxiety remembered fewer adverse early bonding experiences as a means of self-soothing during a difficult time (i.e., first experience living away from home). Even though these individuals did not report enough positive or negative experiences with caregivers to result in care
or overprotection correlations, they may have been unconsciously attempting to calm (or neutralize) their anxiety by remembering their early experiences in a more favorable light.
Treatment Implications of Attachment Style and Early Bonding Memories
Given the findings of our study, we believe that awareness of client attachment style may enhance therapeutic outcome in the treatment of anxiety conditions. For example, anxiety in individuals with secure attachment may be due to recent trauma rather than to long-term pathology, and the counselor’s role will be to help these individuals traverse their current obstacles and regain previous effectual functioning (Pistole, 1989). On the other hand, fearful clients may need extra time to form an attachment to their counselors and to use them as a “secure base” from which to explore the world in
a less anxious way. Anxious individuals with a preoccupied style of attachment may have difficulty managing their emotional responses and counselors may find it helpful to respond with empathic listening, rather than becoming frustrated by emotional behavior (Pistole, 1989). Individuals with a dismissing attachment style may deny anxiety, as well as any desire or need for closeness, and the counselor may find it necessary to confront the dismissal of important relationships (including the therapeutic bond) and the denial of emotions like anxiety (Pistole, 1989).
Awareness of clients’ early bonding memories may also inform therapeutic intervention when working with anxious individuals. In this study, post-trauma and social anxiety symptoms correlated with memories of early bonding, and understanding these connections may be meaningful in the treatment of anxiety. Young adults, who are potentially living away from their families of origin for the first time, may be particularly susceptible to post-trauma and social anxiety and may seek counseling for their concerns. A therapeutic understanding that these anxiety symptoms may be related to a less-than-optimal early environment, triggered by the uncertainties of being away from home, could result in treatment that is more relevant and individualized to the situation. Although medication may be appropriate for some clients contending with these circumstances, in other instances it could be especially beneficial to approach the treatment from the perspective of understanding the early family environment.
In contrast to post-trauma and social anxiety symptoms, obsessive-compulsive, panic and generalized anxiety symptoms were not correlated with early bonding memories. This may indicate that these conditions have fewer roots originating within the family, and the use of medications to control these particular anxiety symptoms may be appropriate. Despite the apparent lack of association between these three types of anxiety and early bonding memories, however, we suggest that involvement in counseling simultaneous to the use of any medication may increase the efficacy of treatment by providing a safe place for clients to discuss their concerns and consider solutions to the difficulties they encounter as a result of their anxiety conditions.
Considering the findings of this study, it is fair to assume that those counselors who bear in mind client attachment style and early bonding memories will provide a potentially more successful treatment for clients with anxiety conditions. The idea that attachment and bonding are related but distinct and separate constructs has the potential to broaden counselors’ conceptualization of the manner in which relational involvement may impact anxiety and therefore contribute to enhanced treatment efficacy. Ideally, treatment of anxious clients will include an individualized approach that takes into account the manner and style in which each person forms attachments to others and with regard for the relationship between the type of anxiety being treated and memories of the early child–caregiver bond.
Limitations and Future Directions
The choice to focus our investigation on a non-clinical population is consistent with the method of several studies concerning this literature (e.g., Eng et al., 2001; Mancini et al., 2000; Meites et al., 2012; O’Connor & Elklit, 2008; Yarbro et al., 2013). Nevertheless, the use of a non-clinical undergraduate sample may have resulted in more limited variation within anxiety states, creating a potential restriction of scores. Clearly, a clinical sample of individuals with previously diagnosed anxiety disorders is necessary to substantiate the non-clinical findings of this study. In addition, our sample’s overrepresentation of women relative to men may be considered a limitation in that the associations between attachment, bonding, and anxiety could vary according to gender.
We also suggest that ongoing investigation of anxiety and attachment incorporate the use of instruments that do not require participants to discern their own degree of relational capacity. For example, the Adult Attachment Interview (George et al., 1996) provides a method for assessing attachment state of mind through unconscious processes. The dismissing attachment style, which itself merits further study, could be illuminated through the use of an instrument such as this. In addition to this concern, several of the instruments we elected to use were older measures. Although they continue to be utilized for investigatory purposes in the mental health field, their age may have bearing upon the data they yield, particularly since several of the instruments have not been re-normed or validated with current populations.
Finally, although Latino participants comprised nearly 37% of our sample, we advocate that future study of attachment, bonding and anxiety include a specific focus on multicultural populations. There may well be differences in the ways individuals from varied backgrounds experience anxiety and this should be investigated. People who have recently immigrated, for example, may experience change of this magnitude as stressful and anxiety provoking. Understanding the role of attachment and early bonding relationships in this population ultimately may provide information to support individuals, families and children who transition from their original culture into a new one.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported that the research was supported
in part by UNM’s Regent’s Fellowship Award and
Research Project and Travel Grant.
References
Bartholomew, K. (1993). From childhood to adult relationships: Attachment theory and research. In S. W. Duck (Ed.), Understanding relationship processes 2: Learning about relationships (pp. 30–62). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Bartholomew, K., & Horowitz, L. M. (1991). Attachment styles among young adults: A test of a four-category model. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61, 226–244. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.61.2.226
Behzadi, B., & Parker, G. (2015). A Persian version of the Parental Bonding Instrument: Factor structure and psychometric properties. Psychiatry Research, 225, 580–587. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2014.11.042
Bjornsson, A. S., Bidwell, L. C., Brosse, A. L., Carey, G., Hauser, M., Mackiewicz Seghete, K. L., . . . & Craighead, W. E. (2011). Cognitive–behavioral group therapy versus group psychotherapy for social anxiety disorder among college students: A randomized controlled trial. Depression and Anxiety, 28, 1034–1042.
doi:10.1002/da.20877
Bowlby, J. (1988). A secure base: Parent-child attachment and healthy human development. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Calamari, J. E., Woodard, J. L., Armstrong, K. M., Molino, A., Pontarelli, N. K., Socha, J., & Longley, S. L. (2014).
Assessing older adults’ obsessive-compulsive disorder symptoms: Psychometric characteristics of
the Obsessive Compulsive Inventory-Revised. Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, 3,
124–131. doi:10.1016/j.jocrd.2014.03.002
Cassidy, J., Lichtenstein-Phelps, J., Sibrava, N. J., Thomas, C. L., Jr., & Borkovec, T. D. (2009). Generalized anxiety disorder: Connections with self-reported attachment. Behavior Therapy, 40, 23–38.
doi:10.1016/j.beth.2007.12.004
Cavedo, L. C., & Parker, G. (1994). Parental Bonding Instrument: Exploring for links between scores and obsessionality. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 29, 78–82.
Chambless, D. L., Gillis, M. M., Tran, G. Q., & Steketee, G. S. (1996). Parental bonding reports of clients with obsessive-compulsive disorder and agoraphobia. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 3(2), 77–85.
Chen, C., Hewitt, P. L., & Flett, G. L. (2015). Preoccupied attachment, need to belong, shame, and interpersonal perfectionism: An investigation of the perfectionism social disconnection model. Personality and Individual Differences, 76, 177–182. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2014.12.001
Chorpita, B. F., & Barlow, D. H. (1998). The development of anxiety: The role of control in the early environment. Psychological Bulletin, 124, 3–21. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.124.1.3
Conybeare, D., Behar, E., Solomon, A., Newman, M. G., & Borkovec, T. D. (2012). The PTSD Checklist—Civilian Version: Reliability, validity, and factor structure in a nonclinical sample. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 68, 699–713. doi:10.1002/jclp.21845
Dash, S. R., & Davey, G. C. L. (2012). An experimental investigation of the role of negative mood in worry: The role of appraisals that facilitate systematic information processing. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 43, 823–831. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2011.12.002
DeLapp, R. C. T., Chapman, L. K., & Williams, M. T. (2015). Psychometric properties of a brief version of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire in African Americans and European Americans. Psychological Assessment. doi:10.1037/pas0000208
Eng, W., & Heimberg, R. G. (2006). Interpersonal correlates of generalized anxiety disorder: Self versus other perception. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 20, 380–387. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2005.02.005
Eng, W., Heimberg, R. G., Hart, T. A., Schneier, F. R., & Liebowitz, M. R. (2001). Attachment in individuals with social anxiety disorder: The relationship among adult attachment styles, social anxiety, and depression. Emotion, 1, 365–380. doi:10.1037/1528-3542.1.4.365
Fergus, T. A., Valentiner, D. P., Kim, H.-S., & McGrath, P. B. (2014). The Social Interaction Anxiety Scale (SIAS) and the Social Phobia Scale (SPS): A comparison of two short-form versions. Psychological Assessment, 26, 1281–1291. doi:10.1037/a0037313
Foa, E. B., Huppert, J. D., Leiberg, S., Langner, R., Kichic, R., Hajcak, G., & Salkovskis, P. M. (2002). The Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory: Development and validation of a short version. Psychological Assessment, 14, 485–496. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.14.4.485
George, C., Kaplan, N., & Main, M. (1996). Adult Attachment Interview. Unpublished manuscript, Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley (3rd ed.).
Ghafoori, B., Hierholzer, R. W., Howsepian, B., & Boardman, A. (2008). The role of adult attachment, parental bonding, and spiritual love in the adjustment to military trauma. Journal of Trauma & Dissociation, 9, 85–106. doi:10.1080/15299730802073726
Gladstone, G. L., & Parker, G. B. (2005). The role of parenting in the development of psychopathology: An overview of research using the Parental Bonding Instrument. In J. L. Hudson & R. M. Rapee (Eds.), Psychopathology and the family (pp. 21–33). New York, NY: Elsevier Science.
doi:10.1016/B978-008044449-9/50003-4
Goschin, S., Briggs, J., Blanco-Lutzen, S., Cohen, L. J., & Galynker, I. (2013). Parental affectionless control and suicidality. Journal of Affective Disorders, 151, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.05.096
Griffin, D. W., & Bartholomew, K. (1994). The metaphysics of measurement: The case of adult attachment. In K. Bartholomew & D. Perlman (Eds.), Advances in personal relationships, Vol. 5: Attachment processes in adulthood (pp. 17–52). London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
Guédeney, N., Fermanian, J., & Bifulco, A. (2010). La version française du relationship scales questionnaire de
Bartholomew (RSQ, questionnaire des échelles de relation): Étude de validation du construit. L’Encéphale:
Revue de Psychiatrie Clinique Biologique et Thérapeutique, 36, 69–76. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2008.12.006
Hedman, E., Ljótsson, B., Rück, C., Furmark, T., Carlbring, P., Lindefors, N., & Andersson, G. (2010). Internet administration of self-report measures commonly used in research on social anxiety disorder: A psychometric evaluation. Computers in Human Behavior, 26, 736–740. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2010.01.010
Hirai, M., Vernon, L. L., Clum, G. A., & Skidmore, S. T. (2011). Psychometric properties and administration measurement invariance of social phobia symptom measures: Paper-pencil vs. internet administrations. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 33, 470–479. doi:10.1007/s10862-011-9257-2
Houck, P. R., Speigel, D. A., Shear, M. K., & Rucci, P. (2002). Reliability of the self-report version of the Panic Disorder Severity Scale. Depression and Anxiety, 15, 183–185. doi:10.1002/da.10049
Lee, R., Meyerhoff, J., & Coccaro, E. F. (2014). Intermittent explosive disorder and aversive parental care. Psychiatry Research, 220, 477–482. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2014.05.059
Macatee, R. J., Capron, D. W., Guthrie, W., Schmidt, N. B., & Cougle, J. R. (2015). Distress tolerance and pathological worry: Tests of incremental and prospective relationships. Behavior Therapy, 46, 449–462. doi:10.1016/j.beth.2015.03.003
Mancini, F., D’Olimpio, F., Prunetti, E., Didonna, F., & Del Genio, M. (2000). Parental bonding: Can obsessive symptoms and general distress be predicted by perceived rearing practices? Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 7, 201–208. doi:10.1002/1099-0879(200007)7:3
Manicavasagar, V., Silove, D., Wagner, R., & Hadzi-Pavlovic, D. (1999). Parental representations associated with adult separation anxiety and panic disorder-agoraphobia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 33, 422–428. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1614.1999.00566.x
Marazziti, D., Dell’Osso, B., Dell’Osso, M. C., Consoli, G., Del Debbio, A., Mungai, F., . . . & Dell’Osso, L. (2007). Romantic attachment in patients with mood and anxiety disorders. CNS Spectrums, 12, 751–756.
Massey, S. H., Compton, M. T., & Kaslow, N. J. (2014). Attachment security and problematic substance use in low-income, suicidal, African American women. The American Journal on Addictions, 23, 294–299. doi:10.1111/j.1521-0391.2014.12104.x
Mattick, R. P., & Clarke, J. C. (1998). Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 36, 455–470. doi:10.1016/S0005-7967(97)10031-6
Meites, T., Ingram, R. E., & Siegle, G. J. (2012). Unique and shared aspects of affective symptomatology: The role of parental bonding in depression and anxiety symptom profiles. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 36, 173–181. doi:10.1007/s10608-011-9426-3
Meyer, T. J., Miller, M. L., Metzger, R. L., & Borkovec, T. D. (1990). Development and validation of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 28, 487–495. doi:10.1016/0005-7967(90)90135-6
Moser, J. C., Turk, C. L., & Glover, J. G. (2015). The relationship between participation in Alcoholics Anonymous and social anxiety. Psi Chi Journal of Psychological Research, 20, 97–101. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/1710260749?accountid=10181.
Myhr, G., Sookman, D., & Pinard, G. (2004). Attachment security and parental bonding in adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder: A comparison with depressed out-patients and healthy controls. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 109, 447–456. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0047.2004.00271.x
O’Connor, M., & Elklit, A. (2008). Attachment styles, traumatic events, and PTSD: A cross-sectional investigation of adult attachment and trauma. Attachment and Human Development, 10, 59–71. doi:10.1080/14616730701868597
Osborne, J. W. (2003). Effect sizes and the disattenuation of correlation and regression coefficients: Lessons from educational psychology. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation, 8. Retrieved from http://pareonline.net/getvn.asp?v=8&n=11
Otani, K., Suzuki, A., Matsumoto, Y., Shibuya, N., Sadahiro, R., & Enokido, M. (2014). Correlations of interpersonal sensitivity with negative working models of the self and other: Evidence for link with attachment insecurity. Annals of General Psychiatry, 13. Retrieved from http://www.annals-general-psychiatry.com/content/13/1/5.
Pacchierotti, C., Bossini, L., Castrogiovanni, A., Pieraccini, F., Soreca, I., & Castrogiovanni, P. (2002). Attachment and panic disorder. Psychopathology, 35, 347–354.
Pajkossy, P., Simor, P., Szendi, I., & Racsmány, M. (2015). Hungarian validation of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ): Method effects and comparison of paper-pencil versus online administration. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 31, 159–165. doi:10.1027/1015-5759/a000221
Parker, G. (1979). Reported parental characteristics of agoraphobics and social phobics. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 135, 555–560. doi:10.1192/bjp.135.6.555
Parker, G., Tupling, H., & Brown, L. B. (1979). A Parental Bonding Instrument. British Journal of Medical Psychology, 52, 1–10. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8341.1979.tb02487.x
Pistole, C. (1989). Attachment: Implications for counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 68, 190–193. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1989.tb01355.x
Renaud, E. F. (2008). The attachment characteristics of combat veterans with PTSD. Traumatology, 14(3), 1–12. doi:10.1177/1534765608319085
Ruiz, F. J. (2014). The relationship between low levels of mindfulness skills and pathological worry: The mediating role of psychological inflexibility. Anales De Psicología, 30, 887–897. doi:10.6018/analesps.30.3.150651
Safford, S. M., Alloy, L. B., & Pieracci, A. (2007). A comparison of two measures of parental behavior. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 16, 375–384. doi:10.1007/s10826-006-9092-3
Santacana, M., Fullana, M. A., Bonillo, A., Morales, M., Montoro, M., Rosado, S., . . . & Bulbena, A. (2014). Psychometric properties of the Spanish self-report version of the Panic Disorder Severity Scale. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.04.007
Seganfredo, A. C. G., Torres, M., Salum, G. A., Blaya, C., Acosta, J., Eizirik, C., & Manfro, G. G. (2009). Gender differences in the associations between childhood trauma and parental bonding in panic disorder. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria, 31, 314–321. doi:10.1590/S1516-44462009005000005
Shear, M. K. (1996). Factors in the etiology and pathogenesis of panic disorder: Revisiting the attachment-separation paradigm. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 153(Suppl.), 125–136.
Shear, M. K., Rucci, P., Williams, J., Frank, E., Grochocinski, V., Vander Bilt, J., . . . & Wang, T. (2001). Reliability and validity of the Panic Disorder Severity Scale: Replication and extension. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 35, 293–296. doi:10.1016/S0022-3956(01)00028-0
Silove, D., Parker, G., Hadzi-Pavlovic, D., Manicavasagar, V., & Blaszczynski, A. (1991). Parental representations of patients with panic disorder and generalised anxiety disorder. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 835–841. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.6.835
Turgeon, L., O’Connor, K. P., Marchand, A., & Freeston, M. H. (2002). Recollections of parent-child relationships in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder and panic disorder with agoraphobia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 105, 310–316. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0447.2002.1188.x
Villalta, L., Arévalo, R., Valdepérez, A., Pascual, J. C., & Pérez de los Cobos, J. (2015). Parental bonding in subjects with pathological gambling disorder compared with healthy controls. Psychiatric Quarterly, 86, 61–67. doi:10.1007/s11126-014-9336-0
Weathers, F. W., Litz, B. T., Herman, D. S., Huska, J. A., & Kean, T. M. (1993). The PTSD Checklist: Reliability, validity, and diagnostic utility. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies, San Antonio, TX, October.
Wootton, B. M., Diefenbach, G. J., Bragdon, L. B., Steketee, G., Frost, R. O., & Tolin, D. F. (2015). A contemporary psychometric evaluation of the Obsessive Compulsive Inventory—Revised (OCI-R). Psychological Assessment, 27, 874–882. doi:10.1037/pas0000075
Wuthrich, V. M., Johnco, C., & Knight, A. (2014). Comparison of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ) and abbreviated version (PSWQ-A) in a clinical and non-clinical population of older adults. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 28, 657–663. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2014.07.005
Wuyek, L. A., Antony, M. M., & McCabe, R. E. (2011). Psychometric properties of the Panic Disorder Severity
Scale: Clinician-administered and self-report versions. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 18, 234–243.
doi:10.1002/cpp.703
Yarbro, J., Mahaffey, B., Abramowitz, J., & Kashdan, T. B. (2013). Recollections of parent-child relationships, attachment insecurity, and obsessive-compulsive beliefs. Personality and Individual Differences, 54, 355–360. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2012.10.003
Ellen W. Armbruster, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at Central Michigan University. David C. Witherington is an Associate Professor at the University of New Mexico. The authors also wish to acknowledge the contributions of David Olguin, Jay Parkes, Gene Coffield, and Jeffrey Katzman. Correspondence can be addressed to Ellen Armbruster, Education and Human Services Bldg. #353, Central Michigan University, Mt. Pleasant, MI 48859, armbr1ew@cmich.edu.

![]()

