Oct 14, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 4
Ashley J. Blount, Dalena Dillman Taylor, Glenn W. Lambie, Arami Nika Anwell
Wellness is an integral component of the counseling profession and is included in ethical codes, suggestions for practice and codes of conduct throughout the helping professions. Limited researchers have examined wellness in counseling supervision and, more specifically, clinical mental health supervisors’ experiences with their supervisees’ levels of wellness. Therefore, the purpose of this phenomenological qualitative research was to investigate experienced clinical supervisors’ (N = 6) perceptions of their supervisees’ wellness. Five emergent themes from the data included: (a) intentionality, (b) self-care, (c) humanness, (d) support, and (e) wellness identity. As counselors are at risk of burnout and unwellness because of the nature of their job (e.g., frequent encounters with difficult and challenging client life occurrences), research and education about wellness practices in the supervisory population are warranted.
Keywords: supervision, wellness, unwellness, phenomenological qualitative research, helping professions
Wellness is an integral component of the counseling profession (Myers & Sweeney, 2004; Witmer, 1985) and is included in ethical codes, suggestions for practice and codes of conduct throughout the helping professions of counseling, psychology and social work (American Counseling Association [ACA], 2014; American Psychological Association [APA], 2010; National Association of Social Workers [NASW], 2008). Yet, individuals in the helping professions do not necessarily practice wellness or operate from a wellness paradigm, even though counselors are susceptible to becoming unwell because of the nature of their job (Lawson, 2007; Skovholt, 2001). As a helping professional, proximity to human suffering and trauma, difficult life experiences and additional occupational hazards (e.g., high caseloads) make careers like counseling costly for helpers (Sadler-Gerhardt & Stevenson, 2011). Further, helpers may be vulnerable to experiencing burnout because of their ability (and necessity because of their career) to care for others (Sadler-Gerhardt & Stevenson, 2011). Compassion fatigue, vicarious traumatization and other illness-enhancing issues often coincide with burnout, increasing the propensity for therapists to become unwell (Lambie, 2007; Puig et al., 2012). Extended periods of stress also can lead to helping professionals’ impairment and burnout and can negatively impact quality of client services (Lambie, 2007). Furthermore, counselors who are unwell have the potential of acting unethically and may in turn harm their clients (Lawson, 2007). Thus, it is imperative that helping professionals’ wellness be examined.
More specifically, counseling professionals are required to follow guidelines that support a wellness paradigm. ACA (2014) states that counselors should monitor themselves “for signs of impairment from their own physical, mental, or emotional problems” (Standard C.2.g.). In addition, counselors are instructed to monitor themselves and others for signs of impairment and “refrain from offering or providing professional services when such impairment is likely to harm a client or others” (ACA, 2014, F.5.b.). The Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP; 2015) supports counselors having a wellness orientation and a focus on prevention (Section II.5.a.) and that counselors promote wellness, optimal functioning and growth in clients (Section II.2.e.). Thus, prevention of impairment and a wellness focus are intertwined throughout the standards of the counseling profession. Consequently, it is unethical for counseling professionals to operate while personally or professionally impaired.
Wellness and Supervision in Counseling
In the following section, the importance of wellness and potential impacts of unwellness in the counseling profession will be discussed. Specifically, stressors contributing to impairment will be highlighted. In addition, supervision within a counseling context and general information regarding the supervisory experience will be reviewed.
Wellness and the Counseling Profession
The counseling profession was founded on a wellness philosophy, with holistic wellness including personal characteristics, such as nutritional wellness, physical wellness, stress management and self-care (Puig et al., 2012), and other realms including spiritual, occupational and intellectual well-being (Myers & Sweeney, 2008). According to Carl Rogers (1961), personal characteristics influence counselors’ ability to help others. For instance, individual wellness may influence how knowledgeable, self-aware and skillful supervisees are in relation to working with clients (Lambie & Blount, 2016). Counselors who are well are more likely to be helpful to their clients (Lawson & Myers, 2011; Venart, Vassos, & Pitcher-Heft, 2007), and counselors’ mental health and wellness impacts the quality of services clients receive (Roach & Young, 2007). Therefore, counselor preparation programs and supervisors should discuss wellness and areas in which impairment could arise when training students to become counselors and supervisors (Roach & Young, 2007). Though wellness is a core aspect of counselor training and preparation, many practicing counselors report their colleagues to be stressed (33.29%), distressed (12.24%) and impaired (4.05%; Lawson, 2007).
Individuals who are attracted to and enter into helping fields often appear to have severe adjustment and personality issues, and these individuals may range from students entering into programs to faculty members employed by institutions (Witmer & Young, 1996). In addition, counselors are often remiss about taking their own advice about wellness (Cummins, Massey, & Jones, 2007) and frequently preach wellness to their clients but do not practice wellness personally (Myers, Mobley, & Booth, 2003). Many counselors do not see their own impairment or are unwilling to take the steps to get help (Kottler, 2010), supporting the importance of supervisors identifying and addressing their supervisees’ impairment. Consequently, counselors seeing clients in agency settings, private practices and other settings may experience stressors that are influencing their wellness and, in parallel, the wellness of their clients.
With the counseling profession having a wellness undertone, counselors are expected to promote well-being in their clients and model appropriate wellness lifestyles. Nevertheless, counselors experience job stressors that impact their abilities to be effective helping professionals (Puig et al., 2012). Counselors face several stressors within their career such as managed care, financial limitations, high caseloads, severe mental disorders in clientele and lack of support (O’Halloran & Linton, 2000). Other factors impacting counselors and mental health professionals include: (a) compassion fatigue (Perkins & Sprang, 2012), (b) unhappy workplace relationships (Lambie, 2007), (c) vicarious trauma (Trippany, White Kress, & Wilcoxon, 2004), and (d) general fatigue (Lambie, 2007). Moreover, these systemic factors contribute to increased likelihood for counselors to experience burnout and impairment, impacting their clients’ therapeutic outcomes (Puig et al., 2012). Furthermore, counselors may not disclose their impairment because of denial, shame, professional priorities, lack of responsibility and fear of reprisal (Kottler & Hazler, 1996).
Counselor impairment occurs when counselors ignore, minimize and dismiss their personal needs for health, self-care, balance and wellness (Lawson, Venart, Hazler, & Kottler, 2007). Lawson and colleagues (2007) stated counselors need awareness of their personal wellness and should work to maintain their wellness. In addition, ACA (2014) states that counselors are responsible for seeking help if they are impaired and that it is the duty of colleagues and supervisors to recognize professional impairment and take appropriate action (Standard C.2.g.). Thus, counselors and supervisors are responsible for not only maintaining their personal wellness, but are also responsible for monitoring the wellness or impairment of their colleagues. One of the platforms for monitoring counselor wellness is supervision.
Supervision
ACA (2014) stipulates that supervision involves a process of monitoring “client welfare and supervisee clinical performance and professional development” (Standard F.1.a.). Supervision is an integral component of the counseling profession, involving a relationship in which an experienced professional facilitates the development of therapeutic competence in another (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014). Furthermore, supervision is fundamental in developing and evaluating counselors’: (a) skills (Borders, 1993), (b) wellness (Lenz, Sangganjanavanich, Balkin, Oliver, & Smith, 2012), and (c) development into competent and effective counselors (Swank, Lambie, & Witta, 2012). Clinical supervisors are tasked with evaluating their supervisees’ effectiveness in addition to their level of wellness (Puig et al., 2012). Consequently, stressors, such as personal and cultural issues, addictions, burnout, and other counseling-related occupational challenges, may negatively influence supervisees’ wellness and ability to be effective helping professionals.
Supervision “provides a means to impart necessary skills; to socialize novices into particular profession’s values and ethics; to protect clients; and finally, to monitor supervisees’ readiness to be admitted to the profession” (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014, p. 5). Supervisors have the unique opportunity to operate from a wellness paradigm, socialize their supervisees to wellness practices, monitor supervisee wellness, and gauge how supervisees’ wellness influences client outcomes (Lambie & Blount, 2016). As a result, supervisors who operate from a wellness paradigm and evaluate their supervisees’ wellness may influence the wellness of supervisees’ clients by encouraging positive client outcomes (Lawson, 2007; Lenz & Smith, 2010). As such, supervisee and supervisor wellness is an important component of counselor preparation programs and clinical supervision (Lenz et al., 2012).
Counselor educators (Wester, Trepal, & Myers, 2009), clinical supervisors (Lenz & Smith, 2010; Storlie & Smith, 2012), counselors-in-training (Myers & Sweeney, 2004; Smith, Robinson, & Young, 2007), and licensed counselors (Lawson, 2007; Myers et al., 2003) face challenges in obtaining optimal well-being (e.g., high caseloads, proximity to client trauma, empathizing with students and clients). Supervisors play an integral role in counselor trainee development and can model appropriate wellness behaviors for their supervisees. Furthermore, supervisors have the unique opportunity to work closely with their supervisees and provide an in-depth look at how emerging counselors are learning about wellness behaviors, partaking in wellness actions and promoting wellness in their clients. Nevertheless, no available research has examined experienced clinical supervisors’ perceptions of their supervisees’ wellness. Because clinical supervisors have a close relationship with their supervisees, their perceptions of their supervisees’ wellness can provide important information for the counseling profession. Therefore, the following research question guided our investigation: What are clinical mental health supervisors’ experiences with their supervisees’ wellness?
Methodology
Identifying themes related to clinical supervisors’ experiences of their supervisees’ wellness provides insights for both supervisors and supervisees. The researchers followed a psychological phenomenological methodology (Creswell, 2013a; Moustakas, 1994), allowing for both the meaning (themes) and the essence (experience) of the participants to be examined. In phenomenological research, researchers attempt to identify the essence of participants’ experiences surrounding a phenomenon. By developing interview questions and using an interview protocol technique (Creswell, 2013b), the researchers petitioned participants’ (i.e., clinical supervisors) direct and conscious experiences (Hays & Wood, 2011) to assess their perceptions of their supervisees’ wellness (see Table 1). The following section includes discussion on: (a) epoche and bracketing, (b) participants, (c) procedure, (d) qualitative data analysis and (e) trustworthiness.
Epoche
The first course of action in phenomenological analysis is called epoche (Patton, 2015); therefore, the research team members are described with some of their potential biases. The research team consisted of two counselor educators, a counselor education doctoral candidate, and a counseling master’s student (one man and three women), all of whom identify as Caucasian. All of the researchers were affiliated with the same institution, a large, public, CACREP-accredited university located in the Southeastern United States. In addition, biases relating to the effectiveness of supervisory styles were discussed, and bracketing throughout the data analysis was implemented in order to minimize bias and allow for participant perspectives to be at the forefront. Participant experiences were documented in personal interviews and in the form of collaborative discussions.
Participants
The participants consisted of clinical supervisors who were purposefully selected from a Department of Health and Human Services counseling professional list from a large, southeastern state. Initial criteria for participation in the investigation included: (a) being clinical supervisors for 10 or more years and (b) being in an active supervisory role (i.e., providing supervision). Twenty-six participants initially responded, with 17 individuals meeting the necessary requirements for participation. The final sample consisted of six clinical supervisors, based on individuals who agreed to participate.
Criterion were established to support interviewing only “experienced” supervisors (i.e., supervisors with extensive supervision experience) and participants’ mean number of years of experience as clinical mental health supervisors was 21.2 years. Four of the experienced supervisors identified as female and two identified as male, and their ages ranged from 49 years to 63 years (M = 56.5 SD = 4.93). In addition, four of the participants identified as Caucasian (n = 4), one participant identified as Hispanic (n = 1), and one participant identified as Other (n = 1; i.e., chose not to disclose). The participants represented the following theoretical approaches: humanistic/Rogerian (n = 3), integrative/eclectic (n = 2) and cognitive-behavioral (n = 1). Primary supervision models for the clinical supervisors included: eclectic/integrative (n = 4), person-centered (n = 1) and solution focused (n = 1). The participants served as clinical supervisors at six different mental health agencies throughout a large southeastern state, supporting transferability of the findings.
In reference to wellness, the participants were asked to evaluate their level of wellness prior to participating in the interview process. Specifically, participants were asked to define what wellness meant for them as well as elaborate on the specific areas they felt influenced their wellness. Participants then rated on a 5-point Likert scale their level of overall wellness (i.e., 1 indicating very low wellness, 5 indicating very high wellness). Four of the six participants rated their overall wellness as 5 (very high wellness), while the remaining two individuals rated their overall wellness as 3 (average wellness) and 4 (high wellness) respectively. Thus, the participants reported having average to high levels of personal wellness.
Procedure
Before conducting the investigation, Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval was obtained. Following IRB approval, the researchers employed purposeful sampling (Hays & Wood, 2011) to recruit participants by accessing a public listing of all mental health practitioners in a southeastern state in the United States. The Department of Health and Human Services counseling professional list was utilized, which included e-mail addresses, telephone numbers and mailing addresses of potential participants. Twenty-six participants met the initial response criteria (i.e., 10 or more years of supervisory experience). Snowballing also was used to recruit additional participants (i.e., asking participants for a name of an individual who might fit the study criteria). However, of the 26 participants, 17 supervisors responded with complete general demographic questionnaires and sufficient number of years as supervisors (i.e., minimum of 10 years). Six individuals fit the final purposive sampling criteria for participating in the investigation (e.g., had over 10 years of clinical mental health supervisory experience, still practicing as supervisors in diverse agencies, and having a complete general demographic form).
The first round of data collection was essential in confirming the eligibility of the participants (e.g., completion of the general demographic questionnaire and informed consent form). The demographic questionnaire consisted of questions about personal wellness, ethnicity, theoretical orientation, age, gender and primary population served. Following completion of the initial documents, individual interviews were scheduled. The second round of data collection involved face-to-face or Skype interviews with each participant, where participants were asked the general research question: What are your experiences with your supervisees’ wellness? The researchers also had nine supporting interview questions, which were developed through a rigorous process involving: (a) researchers’ development of an initial question blueprint derived from the literature reviewed for the study, (b) experts’ review and modification of the initial questions, and (c) an initial pilot group testing the questions. The experts were comprised of educators with experience in conducting qualitative research, experience providing supervision and familiarity with the wellness paradigm.
The interview protocol included instructions for the interviewer, research questions, probes to follow the research questions (if needed), space for recording comments, and space for reflective comments to ensure all interviews followed the same procedure (Creswell, 2013a). The general interview questions were developed to aid in addressing the overall question of supervisors’ perceptions of their supervisees’ wellness and all individual interviews were audio recorded and then transcribed. The final list of interview questions is presented in Table 1. The researchers conducted all interviews individually, and to support the effectiveness of gathering the participants’ experiences, member checking was implemented (Creswell, 2013a). Specifically, all participants were e-mailed a copy of their interview transcription, along with a statement of themes and interpretation of the interview’s meaning. All participants (N = 6) responded to member checking and stated that their transcribed interview was accurate and agreed with the themes derived from their interviews.
Table 1
Interview Question Protocol
|
Data and Rationale
|
Draft Interview Questions
|
Prompts and Elicitations
|
| Values (gaining perceptions) |
1. What does wellness mean to you? |
Wellness, health, well-being |
| Beliefs, Values (learning expectations, perceptions) |
2. What influences wellness in counselors? |
Counselor-specific wellness |
| Values (gaining perceptions) |
3. What is the most important aspect of wellness? |
Crucial component(s) |
| Values, (gaining perceptions, opinions) |
4. Is wellness the same or different for everyone? |
Wellness looks like . . . individualized |
| Experiences, Values (what influences clients) |
5. Does wellness influence your supervisees’ client(s)? |
Wellness impacts clients, or supervisees’ clients |
| Experiences, Values (gaining information on standards of wellness and if they are being upheld) |
6. Do you feel your supervisees uphold to standards of wellness in the counseling field? |
Meeting standards, CACREP, ACA Ethics |
| Beliefs, Experiences (expectations of supervisors, experiences) |
7. What does unwellness in counseling supervisees look like? |
Depiction of unwellness |
| Beliefs, Experiences (expectations, experiences of seasoned counselors) |
8. What does unwellness in counselors-in-the field look like? |
Unwellness “picture” |
| Values, Beliefs (gaining other information relating to wellness) |
9. Is there anything else you would like to tell me about wellness? |
Personal wellness philosophy |
| Note: Draft Interview Questions were used in all participant interviews. |
Data Analysis
The researchers followed Creswell’s (2013a) suggested eight steps in conducting phenomenological research: (a) determining that the research problem could best be examined via a phenomenological approach (e.g., discussed the phenomenon of wellness and its relation to the counseling field and in the supervision of counselors); (b) identifying the phenomenon of interest (wellness); (c) bracketing personal experiences with the phenomenon; (d) collecting data from a purposeful sample; (e) asking participants interview questions that focused on gathering data relating to their personal experiences of the phenomenon; (f) analyzing data for significant statements (horizontalization; Moustakas, 1994) and developing clusters of meaning; (g) developing textural and structural descriptions from the meaning units; and (h) deriving an overall essence. In order to maintain organization, the researchers implemented color-coding of statements by selecting one color for initial significant statements or codes (e.g., step f), another color for textural descriptions (e.g., what participants experienced in step g) and a final color to represent structural descriptions (e.g., how participants experienced the phenomenon in step g) of the data (Creswell, 2013a). Finally, the researchers determined an overall essence (step h) based on the structural descriptions of the participants’ interview transcriptions. Following individual coding (i.e., steps f, g, and h), the researchers discussed their initial results and discrepancies, evaluating these discrepancies until reaching consensus.
Trustworthiness
The researchers established trustworthiness by bracketing researcher bias, implementing written epochs, triangulating data, implementing member checking, and providing a thick description of data (Creswell, 2013a; Hays & Wood, 2011). Coinciding with Denzin and Lincoln (2005), the researchers triangulated data collection using (a) a general demographic questionnaire, (b) semi-structured interviews and (c) open-ended research questions. Epochs allowed the researchers to increase their awareness on any biases present and set aside their personal beliefs. Member checking was employed in order to confirm the themes were consistent with the participants’ experiences. As such, participants were provided the opportunity to voice any concerns or discrepancies in their interview transcripts and in their derived meaning statements. The participants indicated no discrepancies or concerns. A thick description (detailed account of participants’ experiences; Lincoln & Guba, 1985) of the data was supported by the participants’ statements and derived themes. In addition, an external auditor was used to evaluate the overall themes and essence of the interviews and to mitigate researcher bias. The external auditor examined the transcripts separate from the other research members in order to evaluate the effectiveness of the derived themes and participant experiences.
Results
Following audio recording and transcription of the participant interviews, the researchers examined the participants’ responses and generated narratives of the emergent phenomena. As a result, themes of supervisees’ wellness from the clinical mental health supervisors’ experiences were derived and included: (a) intentionality, (b) self-care, (c) humanness, (d) support and (e) wellness identity. The themes are discussed in detail below.
Intentionality
Intentionality was defined as the supervisor purposefully utilizing supervisory techniques and behaviors that elicit self-awareness and understanding in their supervisees (i.e., both of self and of their clients). The process of intentionality involved the supervisor actively engaging supervisees in discussions about wellness as well as actively modeling for the supervisees. Within the interviews, supervisors alluded to a parallel process that occurred between the supervisor–supervisee and supervisee–client dyads. When the supervisor intentionally modeled appropriate wellness between self and supervisee, the supervisee could then implement similar wellness activities between self and client. Reflecting on the process of supervisory modeling, Supervisor #1 stated:
The supervisor . . . has a lot . . . a lot of influence . . . checking in, what are you doing to take care of yourself? You seem really stressed, what is your wellness plan? What is your stress management? How do you detach yourself and unplug yourself from your responsibilities with your clients at work . . . to take care of you?
As depicted, the supervisor intentionally asked the supervisee questions relating to personal wellness and started a conversation about supervisees separating themselves from their work life. Supervisor #2 confirmed the importance of modeling as evidenced by the statement, “you can’t preach to someone to do something if you are not doing it yourself.” In other words, the supervisor alluded to the idea that supervisors must model appropriate professional and personal behaviors to their supervisees. Additionally, the supervisors discussed the impact of a trickledown effect (e.g., parallel process): how the supervisor approaches supervisees in turn affects how supervisees approach their clients. For instance, if the supervisor exhibited signs of burnout, then the behaviors would directly impact their relationship and understanding of the supervisee, which would indirectly impact their supervisee’s clients. Supervisor #3 noted that the wellness of supervisees influenced client wellness by saying “Oh, I can definitely see when my supervisees are unwell and how that directly influences their work with clients. It’s like they’re (supervisees) not on top of their game . . . like they’re not as effective with clients.” Furthermore, supervisors noted the use of direct interventions to help supervisees gain increased self-awareness after recognizing supervisees’ potential unwellness. Supervisor #5 stated in reference to a conversation with a supervisee, “I want you to be in the field to better help people by helping yourself and looking at your own issues.” Thus, supervisors need to be intentional when helping supervisees become more effective and more well in both their personal and professional lives.
Self-Care
Self-care was defined as the necessity of taking care of one’s self in order to be a better asset to supervisees and clients. The self-care theme supported the idea that “you cannot give away that which you do not possess” (Bratton, Landreth, Kellam, & Blackard, 2006, p. 15), which is consistent in the counseling and other helping professional literature (Lawson, 2007). In other words, we must take care of ourselves before we are able to care for others. Self-care is delineated from the theme of intentionality in this investigation in that supervisors reflected the importance of their own self-awareness to gauge wellness, especially to alleviate the potential for burnout. For example, Supervisor #4 stated, “If I’m not well, I can’t really help someone else get well.” Whereas the theme of intentionality reflects encouraging supervisees’ self-awareness, the self-care theme notes the importance of supervisors being self-aware and the specific actions supervisors felt they and their supervisees could take to promote self-care in their own lives. As Supervisor #6 said, “it’s an incredible field and it can be a very, very draining field if you aren’t careful, if you don’t take care of yourself.” Through the supervisors’ process of reflection and recognition, they were able to respond with care and compassion to their supervisees. However, as Supervisor #5 indicated when reflecting on counselor and supervisor burnout,
[It] happens to every single counselor, they’re going to experience compassion fatigue at some point in their career because it is a burnout job, and so to recognize . . . the signs . . . sometimes it takes someone else to point it out to us.
It is crucial to take care of oneself in counseling and be open to feedback from others who may see our behaviors from an objective standpoint. Furthermore, the supervisors noted the critical impact of taking care of themselves through activities outside of the workplace and leaving client and supervisee concerns at work. For example, Supervisor #3 noted:
I feel you need to take care of yourself, you need to do stuff for you . . . I’m clear to sit down with all of them [supervisees] and say . . .what are you going to . . . do good for yourself today . . . what are you going to do for you?
By creating differentiation between personal and professional life, supervisors and supervisees are able to rejuvenate, leading to better care for supervisees as Supervisor #1 indicated:
I do feel there are many ways to go about it . . . there’s a whole mindfulness movement, and yoga . . . animals . . . those are all ways we can go ahead and keep ourselves well. I think play is a component of keeping yourself well and . . . there are different definitions of play, but I would define it as when you’re so involved in doing something that you lose track of time. That could be art activities . . . dancing, doing something fun with your dog . . . playing games . . . being involved in something where time stands still and you’re totally in the moment. . . . I think that’s another key piece of really staying well.
As a result, the self-care theme involves supervisors identifying and implementing strategies to keep themselves well, as well as supervisees engaging in activities to support their own self-care journeys. Similar to other wellness research in the helping professions (Lawson, 2007; Myers & Sweeney, 2005b; Skovholt, 2001), self-care is paramount to supporting personal wellness, as well as having the capacity to promote wellness in others—supervisors with supervisees and in parallel, supervisees with clients.
Humanness
Humanness was defined as the supervisors’ and supervisees’ culture, history, background and the influences of previous life experiences on the therapeutic relationship. Our past actions, memories and families of origin influence our worldview and current functioning. As Supervisor #3 noted, “I define wellness on a personal level, it has to do with me and my personhood, it is unique and is based on my wants and needs.” In reference to the influence of individuals’ history and background, Supervisor #2 stated, “for myself definitely it was pretty much the way I grew up . . . it depends on the population, it depends on where they were raised. . . . There’s just too many dependent variables for it.” At times, supervisors noted that these factors lead to unintentional blindness between and within the dyad (i.e., supervisor–supervisee, supervisee–client). Supervisor #3 noted that “we all have biases, we all have prejudices on some level. Are you willing to acknowledge that you are struggling with this, but I am willing to work on this, willing to go to workshops or go into therapy?” Without reflection or self-awareness, supervisors and supervisees are susceptible to similar roadblocks and “stuckness” as their clients. For instance, Supervisor #4 noted the influence of current life events impacting her overall wellness:
I think to add to that, it is the nature of our human experience. . . . we are going to go through phases in our lives where things are affected to the point to where you would say this aspect of my life is not well right now.
Thus, supervisors perceive both their humanness (e.g., backgrounds and cultures) and their supervisees’ humanness qualities as influential to the therapeutic relationship and important in supervisees’ actions in counseling situations as well as personal settings (Lambie, 2006).
Support
Support was defined as leaning on and connecting with others (e.g., peer-to-peer, colleagues, friends, partners). Supervisors emphasized the importance of both themselves and their supervisees developing and maintaining significant relationships within the context of their job and outside the work setting. Supervisor #6 reflected that “support is integral to . . . overall wellness and, being that we are social creatures . . . support [is] really important for us.” Relationships at work can be crucial for processing tough client cases and personal issues that appear to be encroaching upon work with clients. For example, Supervisor #3 emphasized, “I think there has to be a support system of counselors who have been in the field . . . and having your own therapist.” At the same time, social relationships outside work are equally important. Similar to self-care and intentionality, separating personal life and professional life aids the supervisor and supervisee in leaving client cases at work and enjoying life beyond the role as a counselor. Within the literature, the influence of support aids supervisors and supervisees in achieving wellness and minimizing the likelihood of counselor burnout (Lambie, 2007; Lee, Cho, Kissinger, & Ogle, 2010).
Wellness Identity
Wellness identity was defined as the supervisors and supervisees operating from a wellness platform. Supervisors noted the necessity of holding this wellness platform in the forefront of conversations with students, other supervisors, and other therapists and counselors. As Supervisor #3 reflected,
We practice a strengths-based model and we see that the wellness model is depicted much, much more not only in the literature but also in the things that come about. . . . I’d rather see research in wellness rather than case research in defects.
Through attaching wellness to one’s identity as a counselor, supervisors and supervisees are compelled to continuous self-reflection on how external factors impact their work with supervisees and clients. Supervisor #1 stated “wellness is who we are, if we find ourselves straying, we probably need to re-evaluate things.” Furthermore, supervisors indicated in their interviews that wellness is an important topic for counselors and counselor educators to reflect upon and teach and discuss with students and supervisees. For instance, Supervisor #2 stated in relation to the idea of a wellness identity: “It comes from the teaching that one receives in the classroom. . . . I think that the issues have really brought it to the forefront and it has allowed us to teach wellness and to talk about it. I think teaching is the driving force.”
As shown in the wellness identity theme, all of the supervisors supported the idea that having a wellness base from which helpers operate is important. Additionally, the participants noted the importance of an open dialogue on wellness between supervisors and supervisees and, coinciding with Granello (2013) and Roach and Young (2007), stressed the idea that as a supervisor, wellness education can play a key role in promoting healthy helping professionals.
Discussion
The results from this study provided the data to answer the research question: What are clinical mental health supervisors’ experiences with their supervisees’ wellness? Experienced supervisors (e.g., 10 or more years of supervisory experience) discussed areas that influenced their wellness as well as their supervisees’ wellness. Furthermore, several themes that supported an essence of supervisee wellness (Hays & Wood, 2011; Moustakas, 1994) were derived. In interviewing the supervisors, the themes of (a) intentionality, (b) self-care, (c) humanness, (d) support and (e) wellness identity were derived from the data analysis. From the results of this study, implications for clinical supervisors and counselor educators, limitations of the research investigation, and areas for future research were derived.
Implications for Clinical Supervisors and Counselor Educators
The counseling field is grounded in holistic wellness (Myers & Sweeney, 2004). Therefore, our findings reflected the theme that wellness is important to the counseling profession and in supporting supervisors’ and supervisees’ overall growth. Scholars in the helping fields (Keyes, 2002, 2007; Myers, Sweeney, & Witmer, 2000) and professional guidelines (ACA, 2014; CACREP, 2015) support the necessity of a wellness focus, identifying that a lack of a wellness focus may lead to unwellness and burnout (Bakker, Demerouti, Taris, Schaufeli, & Schreurs, 2003). Thus, creating and maintaining a wellness identity in supervision can aid in supporting holistic wellness in supervisees. In addition, self-care can be important for counselors, as they are not immune to difficult experiences and life events faced by their clients (Venart et al., 2007). Supervisor #6 noted that burnout was an inevitable part of working as a counselor and, similarly, researchers have identified that burnout can influence counselors’ work with their clients (Lambie, 2007; Puig et al., 2012). Thus, wellness provides the foundation of helping professionals’ work with clients (Venart et al., 2007), and exploration of counselor burnout and other negative consequences of counselor unwellness warrants attention.
The clinical supervisors in our investigation indicated a need for counselor educators to be more intentional in their focus and inclusion of wellness with the therapeutic relationship. In order to mitigate the effects of burnout and unwellness in supervisees, a wellness course or a wellness plan for counselors-in-training over the duration of their preparation program is suggested to support counselor educators in preparing future clinicians with a mindset of reflection, process and activities to enhance wellness. By implementing a wellness focus throughout preparation programs, supervisees can learn about the positive and negative influence of their wellness choices, as well as the effects their wellness may have on their colleagues and clients. Furthermore, wellness plans could be implemented throughout the program to promote wellness awareness in supervisees. Classroom discussions and wellness groups could also aid in supporting students in their wellness growth and development throughout their program while providing counselors-in-training with the tools to share their knowledge and promote wellness in others.
Supervisors also can mitigate the effects of unwellness by continuously evaluating their current levels of functioning through formal assessments such as the Five Factor Wellness Inventory (5F-Wel; Myers & Sweeney, 2005a), or the Helping Professional Wellness Discrepancy Questionnaire (HWPDS; Blount & Lambie, in press) or informal assessments such as wellness journaling or implementing wellness plans. Supervisors also may choose to include wellness in their supervision sessions by assessing pre- and post-wellness levels in supervisees, operating from a wellness-supervision paradigm (e.g., the Integrative Wellness Model; Blount & Mullen, 2015; Wellness Model of Supervision; Lenz & Smith, 2010), having educational discussions on the holistic components of wellness, and modeling appropriate wellness behaviors. Thus, there are numerous actions supervisors can take to promote individual wellness, include wellness in their supervision, and promote wellness in their supervisees.
Supervision is crucial to counselor development (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014). CACREP (2015) Standards and licensure requirements emphasize the importance of supervision throughout trainees’ growth and establishment as a professional counselor. ACA (2014) emphasizes additional professional development and supervision throughout counselors’ careers, stating that counselors should “regularly pursue continuing education activities including both counseling and supervision topics and skills” (Standard F.2.a.). Even though the field of counseling is grounded in a wellness paradigm (ACA, 2014; CACREP, 2015), the process of supervision does not always support a wellness focus, as supervisors do not model wellness for their supervisees or stress the importance of counselor well-being. According to the supervisors in our investigation, wellness should be integrated and discussed within the supervision realm. Further, clients are more likely to benefit from a well counselor (Lawson, 2007) and as such, counselor educators and supervisors face the challenge of promoting effective, well therapists-in-training. The wellness process, however, typically occurs in a negative trickledown method (e.g., burned out supervisors modeling inappropriate wellness behavior for trainees who in return model inappropriate wellness for clients).
Counselor educators can break the cycle of negatively modeling wellness by incorporating wellness throughout the trainees’ experience in their preparation programs and by modeling wellness and self-care. Through the wellness paradigm, counselor educators can begin to change the thought process of trainees’ own reluctance to engage in self-care and work to change the “do as I say” mentality (i.e., telling clients or trainees to be well when we are not well ourselves), which is present throughout the helping professions (Lawson, 2007; Witmer & Young, 1996). Based on our results, the counseling profession should embrace the belief that “you cannot give away that which you do not possess” (Bratton et al., 2006; p. 238). By adapting a wellness framework, the benefits of the wellness paradigm at the beginning of trainees’ careers is significant, impacting other counselors and clients that enter into their path in a positive way.
Expanding beyond supervisors, therapists-in-training and practitioners, wellness practices can be influential on a larger scale. Counseling and counselor education programs, as well as respective professional organizations, can use wellness philosophies and practices to promote self-care in their members. In addition, organizations can support strong wellness identities in their helping professionals by upholding their ethical standards, promoting wellness-related actions, and educating new professionals on the importance of practicing wellness in their personal and professional lives. As voiced by many of the supervisors interviewed in our study, professional organizations can support their members by encouraging wellness identities and offering platforms for individuals to form relationships with other practitioners in the field. Practitioners can use the connections to exchange wellness ideas and practices, and offer support as professionals. Finally, supervisors can be integral in promoting their supervisees’ wellness throughout the career, supporting the services they provide to diverse clients.
Limitations
We followed steps to support the trustworthiness of the data; however, some limitations are noted. Given that the first author is invested in the wellness approach to counseling, researcher bias may have occurred. However, the research team implemented steps to mitigate the role of bias. For instance, researcher bias was bracketed at the forefront of the interviews and an external auditor reviewed interviews to note themes separate from the research team. As with all qualitative research, the results from our study are not generalizable. Nevertheless, the six clinical mental health supervisors worked in six different mental health agencies, supporting the transferability of the findings (Yardley, 2008). In addition, the sample size for the investigation met the criteria outlined for qualitative analyses (5–25 participants; Polkinghorne, 1989), yet all of the participants volunteered for participation and may have had a greater interest in wellness than those who did not volunteer. Finally, even with a small sample size (N = 6), the researchers believed that saturation of the themes occurred by implementing rigorous data analytic procedures (i.e., coding for themes and essence) and reaching an inability to glean new information from the coding (Guest, Bunce, & Johnson, 2006).
Areas for Future Research
In relation to future research endeavors, participants in this study emphasized the importance of wellness-related research in counseling. Given that the counseling field is grounded in a wellness model (Myers & Sweeney, 2005b; Witmer, 1985) and that limited studies on wellness are available, quantitative and/or qualitative studies examining the overall effect of wellness within the supervisory relationship are needed. Further, researchers might assess the degree to which supervisors or supervisees actually engage in wellness behaviors. As with most qualitative studies, our findings reflect a starting point for quantitative research, focusing on the identified themes across supervisors and supervisees. Future researchers could examine the parallel process between (a) educator and student and (b) supervisor and supervisee that takes place when trusting and safe relationships are established (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014). Furthermore, future researchers could assess differences in supervisors or supervision styles in supervisors with formal supervision courses versus no formal experience; or similar studies with supervisors who have participated in a wellness course versus those who have not. In addition, future research could focus on client outcomes when one party (i.e., counselor) models appropriate wellness and a different counselor does not model these qualities. Future researchers are also encouraged to assess the effect of the five identified themes on client outcomes and/or student progress within counselor education programs.
In summary, “it is not possible to give to others what you do not possess” (Corey, 2000, p. 29); therefore, we must take care of ourselves before we are fully capable to help others. As such, it is important to bring wellness to the forefront of clinical supervision and remain engaged in promoting personal wellness and the wellness of others. Thus, assessing and evaluating wellness in all supervisors and supervisees (counselors) is integral in providing quality supervision and efficacious counseling services and protecting client welfare. By increasing awareness on wellness themes, such as self-care, support, wellness identity, and humanness, along with operating intentionality, clinical supervisors can support their supervisees in achieving greater levels of wellness.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
American Counseling Association. (2014). 2014 ACA code of ethics. Alexandria, VA: Author.
American Psychological Association. (2010). Ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct. Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/ethics/code/index.aspx
Bakker, A. B., Demerouti, E., Taris, T. W., Schaufeli, W. B., & Schreurs, P. J. G. (2003). A multigroup analysis of the Job Demands–Resources Model in four home care organizations. International Journal of Stress Management, 10, 16–38. doi:10.1037/1072-5245.10.1.16
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2014). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Blount, A. J., & Lambie, G. W. (in press). The helping professional wellness discrepancy scale: Development and validation. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development.
Blount, A. J., & Mullen, P. R. (2015). Development of the integrative wellness model: Supervising counselors-in-training. The Professional Counselor, 5, 100–113. doi:10.15241/ajb.5.1.100
Borders, L. D. (1993). Learning to think like a supervisor. The Clinical Supervisor, 10, 135–148.
doi:10.1300/J001v10n02_09
Bratton, S. C., Landreth, G. L., Kellam, T., & Blackard, S. R. (2006). Child-parent relationship therapy (CPRT) treat-ment manual: A 10-session filial therapy model for training parents. New York, NY: Routledge.
Corey, G. (2000). Theory and practice of group counseling (5th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/ Thompson Learning.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2015). CACREP 2016 standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/2016-CACREP-Standards.pdf
Creswell, J. W. (2013a). Qualitative inquiry & research design: Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Creswell, J. W. (2013b). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Cummins, P. N., Massey, L., & Jones, A. (2007). Keeping ourselves well: Strategies for promoting and main-taining counselor wellness. The Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 46, 35–49.
doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2007.tb00024.x
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). The Sage handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Granello, P. F. (2013). Wellness counseling. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Guest, G., Bunce, A., & Johnson, L. (2006). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data satur-ation and variability. Field Methods, 18, 59–82. doi:10.1177/1525822X05279903
Hays, D. G., & Wood, C. (2011). Infusing qualitative traditions in counseling research designs. Journal of Coun-seling & Development, 89, 288–295. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00091.x
Keyes, C. L. M. (2002). The mental health continuum: From languishing to flourishing in life. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 43, 207–222.
Keyes, C. L. M. (2007). Promoting and protecting mental health as flourishing: A complementary strategy for improving national mental health. American Psychologist, 62(2), 95–108. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.62.2.95
Kottler, J. A. (2010). On being a therapist (4th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Kottler, J. A., & Hazler, R. J. (1996). Impaired counselors: The dark side brought into light. The Journal of Human-istic Counseling, 34(3), 98–107. doi:10.1002/j.2164-4683.1996.tb00334.x
Lambie, G. W. (2006). Burnout prevention: A humanistic perspective and structured group supervision activity. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 45, 32–44. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2006.tb00003.x
Lambie, G. W. (2007). The contribution of ego development level to burnout in school counselors: Implica-
tions for professional school counseling. Journal of Counseling & Development, 85, 82–88. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2007.tb00447.x
Lambie, G. W., & Blount, A. J. (2016). Tailoring supervision to the supervisee’s developmental level. In K.
Jordan (Ed.), Couple, marriage and family therapy supervision (pp. 71–86). New York, NY: Spring Publishing.
Lawson, G. (2007). Counselor wellness and impairment: A national survey. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 46, 20–34. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2007.tb00023.x
Lawson, G., & Myers, J. E. (2011). Wellness, professional quality of life, and career-sustaining behaviors: What keeps us well? Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 163–171. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00074.x
Lawson, G., Venart, E., Hazler, R. J., & Kottler, J. A. (2007). Toward a culture of counselor wellness. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 46, 5–19. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2007.tb00022.x
Lee, S. M., Cho, S. H., Kissinger, D., & Ogle, N. T. (2010). A typology of burnout in professional counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 88, 131–138. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2010.tb00001.x
Lenz, A. S., Sangganjanavanich, V. F., Balkin, R. S., Oliver, M., & Smith, R. L. (2012). Wellness model of super-vision: A comparative analysis. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 207–221.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00015.x
Lenz, A. S., & Smith, R. L. (2010). Integrating wellness concepts within a clinical supervision model. The Clinical Supervisor, 29, 228–245. doi:10.1080/07325223.2010.518511
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Myers, J. E., Mobley, A. K., & Booth, C. S. (2003). Wellness of counseling students: Practicing what we preach. Counselor Education and Supervision, 42, 264–274. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2003.tb01818.x
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2004). The indivisible self: An evidence-based model of wellness. (Reprint.). The Journal of Individual Psychology, 61, 269–279.
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2005a). The five factor wellness inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Mindgarden.
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (Eds.). (2005b). Counseling for wellness: Theory, research, and practice. Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2008). Wellness counseling: The evidence base for practice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 86, 482–493. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2008.tb00536.x
Myers, J. E., Sweeney, T. J., & Witmer, J. M. (2000). The Wheel of Wellness counseling for wellness: A holistic
model for treatment planning. Journal of Counseling & Development, 78, 251–266.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2000.tb01906.x
National Association of Social Workers. (2008). Code of ethics of the National Association of Social Workers. Wash-ington, DC: Author. https://www.socialworkers.org/pubs/code/code.asp
O’Halloran, T. M., & Linton, J. M. (2000). Stress on the job: Self-care resources for counselors. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 22, 354–364.
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research and evaluation methods (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Perkins, E. B., & Sprang, G. (2012). Results from the Pro-QOL-IV for substance abuse counselors working with offenders. International Journal of Mental Health Addiction, 11, 199–213. doi:10.1007/s11469-012-9412-3
Polkinghorne, D. E. (1989). Phenomenological research methods. In R. S. Valle & S. Halling (Eds.), Existential-phenomenological perspectives in psychology (pp. 41–60). New York, NY: Plenum Press.
Puig, A., Baggs, A., Mixon, K., Park, Y. M., Kim, B. Y., & Lee, S. M. (2012). Relationship between job burnout and personal wellness in mental health professionals. Journal of Employment Counseling, 49, 98–109. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1920.2012.00010.x
Roach, L. F., & Young, M. E. (2007). Do counselor education programs promote wellness in their students? Counselor Education & Supervision, 47, 29–45. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2007.tb00036.x
Rogers, C. R. (1961). On becoming a person: A therapist’s view of psychotherapy. New York, NY: Houghton Mifflin.
Sadler-Gerhardt, C. J., & Stevenson, D. L. (2011). When it all hits the fan: Helping counselors build resilience and avoid burnout. Ideas and Research You Can Use: VISTAS 2012, 1, 1–8. https://www.counseling.org/resources/library/vistas/vistas12/Article_24.pdf
Skovholt, T. M. (2001). The resilient practitioner: Burnout prevention and self-care strategies for counselors, therapists, teachers, and health professionals. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Smith, H. L., Robinson, E. H. M., III, & Young, M. E. (2007). The relationship among wellness, psychological distress, and social desirability of entering master’s-level counselor trainees. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 96–109. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2007.tb00041.x
Storlie, C. A., & Smith, C. K. (2012). The effects of a wellness intervention in supervision. The Clinical Supervisor, 31, 228–239. doi:10.1080/07325223.2013.732504
Swank, J. M., Lambie, G. W., & Witta, E. L. (2012). An exploratory investigation of the Counseling Competen-cies Scale: A measure of counseling skills, dispositions, and behaviors. Counselor Education and Super-vision, 51, 189–206. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00014.x
Trippany, R. L., White Kress, V. E., & Wilcoxon, S. A. (2004). Preventing vicarious trauma: What counselors should know when working with trauma survivors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 82, 31–37. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2004.tb00283.x
Venart, E., Vassos, S., & Pitcher-Heft, H. (2007). What individual counselors can do to sustain wellness. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 46, 50–65. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2007.tb00025.x
Wester, K. L., Trepal, H. C., & Myers, J. E. (2009). Wellness of counselor educators: An initial look. The Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 48, 91–109. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2009.tb00070.x
Witmer, J. M. (1985). Pathways to personal growth. Muncie, IN: Accelerated Development.
Witmer, J. M., & Young, M. E. (1996). Preventing counselor impairment: A wellness approach. Journal of Human-istic Counseling, 34, 141–155. doi:10.1002/j.2164-4683.1996.tb00338.x
Yardley, L. (2008). Demonstrating validity in qualitative psychology. In J. A. Smith (Ed.), Qualitative psychology: A practical guide to research methods (pp. 235–251). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Ashley J. Blount, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at the University of Nebraska Omaha. Dalena Dillman Taylor is an Assistant Professor at the University of Central Florida. Glenn W. Lambie, NCC, is a Professor at the University of Central Florida. Arami Nika Anwell is a recent graduate of the University of Central Florida. Correspondence can be addressed to Ashley Blount, 6001 Dodge Street, RH 101E, Omaha, NE 68182, ablount@unomaha.edu.
Feb 9, 2015 | Article, Volume 5 - Issue 1
Ashley J. Blount, Patrick R. Mullen
Supervision is an integral component of counselor development with the objective of ensuring safe and effective counseling for clients. Wellness also is an important element of counseling and often labeled as the cornerstone of the counseling profession. Literature on supervision contains few models that have a wellness focus or component; however, wellness is fundamental to counseling and the training of counselors, and is primary in developmental, strengths-based counseling. The purpose of this article is to introduce an integrative wellness model for counseling supervision that incorporates existing models of supervision, matching the developmental needs of counselors-in-training and theoretical tenets of wellness.
Keywords: supervision, wellness, counselors-in-training, integrative wellness model, developmental
The practice of counseling is rich with challenges that impact counselor wellness (Kottler, 2010; Maslach, 2003). Consequently, counselors with poor wellness may not produce optimal services for the clients they serve (Lawson, 2007). Furthermore, wellness is regarded as a cornerstone in developmental, strengths-based approaches to counseling (Lawson, 2007; Lawson & Myers, 2011; Myers & Sweeney, 2005, 2008; Witmer, 1985; Witmer & Young, 1996) and is an important consideration when training counselors (Lenz & Smith, 2010; Roach & Young, 2007). Therefore, a focus on methods by which counselor educators can prepare counseling trainees to obtain and maintain wellness is necessary.
Clinical supervision is an integral component of counselor training and involves a relationship in which an expert (e.g., supervisor) facilitates the development of counseling competence in a trainee (Loganbill, Hardy, & Delworth, 1982). Supervision is a requirement of master’s-level counseling training programs and is a part of developing and evaluating counseling students’ skills (Borders, 1992), level of wellness (Lenz, Sangganjanavanich, Balkin, Oliver, & Smith, 2012), readiness for change (Aten, Strain, & Gillespie, 2008; Prochaska & DiClemente, 1982) and overall development into effective counselors (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014). Supervisors use pedagogical methods and theories of supervision to assess and evaluate trainees with the goal of enhancing their counseling competence (American Counseling Association [ACA], 2014; Bernard & Goodyear, 2014). The method or theory of supervision relates to the interaction between counselor educators and counseling trainees and is isomorphic to a counselor using a theory with a client.
The number of supervision theories and methods has increased over recent years. In addition, integrated supervision models have been established with a focus on specific trainee groups (e.g., Carlson & Lambie, 2012; Lambie & Sias, 2009) or specific purposes (e.g., Luke & Bernard, 2006; Ober, Granello, & Henfield, 2009). These integrated models combine the theoretical tenets of key models with the goal of formulating a new perspective for clinical training that adapts to the needs of the supervisee or context. Lenz and Smith (2010) and Roscoe (2009) suggested that the construct of wellness needs further clarification and articulation as a method of supervision. Currently, a single model of supervision with a wellness perspective is available (see Lenz & Smith, 2010). However, it does not specifically apply to master’s-level counselors-in-training (CITs) or focus on the wellness constructs highlighted in the proposed integrative wellness model (IWM). Therefore, this manuscript serves to review relevant literature on supervision and wellness, introduce the IWM, and present implications regarding its implementation and evaluation.
Supervision
ACA (2014), the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP; 2009), and the Association for Counselor Education and Supervision (ACES; 2011) have articulated standards for best practices in supervision. For example, ACES’ (2011) Standards for Best Practices Guidelines highlights 12 categories as integral components of the supervision process. The categories include responsibilities of supervisors and suggestions for actions to be taken in order to ensure best practices in supervision. The ACA Code of Ethics (2014) states that supervision involves a process of monitoring “client welfare and supervisee performance and professional development” (Standard F.1.a). Furthermore, supervision can be used as a tool to provide supervisees with necessary knowledge, skills and ethical guidelines to provide safe and effective counseling services (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014).
Supervision has two central purposes: to foster supervisees’ personal and professional development and to protect clients (Vespia, Heckman-Stone, & Delworth, 2002). Supervisors work to ensure client welfare by monitoring and evaluating supervisee behavior, which serves as a gatekeeping tool for the counseling profession (Robiner, Fuhrman, Ristvedt, Bobbit, & Schirvar, 1994). Thus, supervisors protect the counseling profession and clients receiving counseling services by providing psychoeducation, modeling appropriate counselor behavior, and evaluating supervisees’ counseling skills and other professional behaviors. In order to do this, supervisors and supervisees must have a strong supervisory relationship that supports positive supervision outcomes (Rønnestad & Skovholt, 2003).
Supervision is a distinct intervention (Borders, 1992) that is separate from teaching, counseling and consultation. Supervision is unique in that it is comprised of multifaceted (e.g., teacher, counselor and consultant) roles that occur at different times throughout the supervision process (Bernard, 1997). Bernard’s (1979, 1997) discrimination model (DM) of supervision is an educational perspective positing that supervisors can match the needs of supervisees with a supervisor role and supervision focus. The DM is situation specific, meaning that supervisors can change roles throughout the supervision session based on their goal for supervisee interaction (Bernard, 1997). Therefore, supervisees require different roles and levels of support from their supervisors at different times throughout the supervision process, which can be determined by a process of assessment and matching of supervisee needs.
According to Worthen and McNeill (1996), supervision varies according to the developmental level of trainees. Beginning supervisees need more support and structure than intermediate or advanced supervisees (Borders, 1990). Additionally, supervisors working with beginning supervisees must pay more attention to student skills and aid in the development of self-awareness. With intermediate supervisees, supervision may focus on personal development, more advanced case conceptualizations of clients and operating within a specific counseling theory (McNeill, Stoltenberg, & Pierce, 1985). Advanced supervisees work on more complex issues of personal development, parallel processes or a replication of the therapeutic relationship in a variety of settings (e.g., counseling, supervision; Ekstein & Wallerstein, 1972), and advanced responses and reactions to clients (Williams, Judge, Hill, & Hoffman, 1997). Consequently, supervision progresses from beginning stages to advanced stages for supervisees, with a developmental framework central to the process. Supervision is tailored to the specific developmental level of a supervisee, and tasks are personalized for needs at specific times throughout the supervision process. Developmental stages in supervision have been identified as key processes that counselor trainees undergo (e.g., Rønnestad & Skovholt, 2003; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2012), a conceptualization that necessitates a supervision model that aids supervisees in a developmental fashion.
Recent models of supervision represent trends toward integrative and empirically based supervision modalities (e.g., Bernard & Goodyear, 2014; Lambie & Sias, 2009). The current integrated model of supervision draws from the theoretical tenets of the DM (Bernard, 1979, 1997), matching supervisee developmental needs (Lambie & Sias, 2009; Loganbill et al., 1982; Stoltenberg, 1981) and wellness constructs (Lenz et al., 2012; Myers, Sweeney, & Witmer, 1998). Wellness is a conscious, thoughtful process that requires increased awareness of choices that are being made toward optimal human functioning and a more satisfying lifestyle (Johnson, 1986; Swarbrick, 1997). As such, the IWM includes wellness undertones in order to support optimal supervisee functioning. This article presents the IWM’s theoretical tenets, implementation and methods for supervisee evaluation. In addition, a case study is presented to demonstrate the IWM’s application in clinical supervision.
Theoretical Tenets Integrated Into the IWM of Supervision
The DM (Bernard, 1979, 1997) is considered “one of the most accessible models of clinical supervision” (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014, p. 52) and includes the following three supervisor roles: teacher, counselor and consultant. In the teacher role, the supervisor imparts knowledge to the supervisee and serves an educational function. The counselor role involves the supervisor aiding the supervisee in increasing self-awareness, enhancing reflectivity, and working through interpersonal and intrapersonal conflicts. Lastly, the consultant role provides opportunities for supervisors and supervisees to have discussions on a balanced level (Bernard, 1979). The three roles are used throughout the supervision process to promote supervisee learning, growth and development.
The DM of supervision is situation specific in that supervisors enact different roles throughout the supervision session based on the observed need of the supervisee (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014). As needs arise in supervision, the supervisor decides which role is best suited for the issue or concern. This process requires the supervisor to identify or assess a need and to make a decision regarding the appropriate role (i.e., teacher, counselor or consultant) to facilitate appropriate supervision. Furthermore, the use of supervisory roles is fluid, with its ebb and flow contingent upon the supervisee needs or issues. For example, if a supervisee is struggling with how to review informed consent, a supervisor can use the teacher role to educate the student on how to proceed, and then address the supervisee’s anxiety about seeing his or her first client using the counseling role. The DM roles are integrated into the IWM, and supervisors alternate between roles to match supervisee needs throughout the supervision process.
Developmental Tenets
The authors of developmental models have suggested that counseling trainees progress in a structured and sequential fashion through stages of development that increase in complexity and integration (e.g., Blocher, 1983; Loganbill et al., 1982; Stoltenberg, 1981; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2010). In early experiences, supervisees engage in rigid thinking, have high anxiety and dependence on the supervisor, and express low confidence in their abilities (Borders & Brown, 2005; Rønnestad, & Skovholt, 2003; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2012). Moreover, supervisees have limited understanding of their own abilities and view their supervisor as an expert (Borders & Brown, 2005; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2010). Struggles between independency and autonomy, as well as bouts of self-doubt, occur during the middle stages of counselor development (Borders & Brown, 2005; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2010). In addition, counselors experience decreased anxiety paired with an increase in case conceptualization, skill development and crystallization of theoretical orientation (Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2010). Thinking becomes more flexible and there is an increased understanding of unique client qualities and traits (Borders & Brown, 2005). The later stages of counselor development are marked by increased stability and focus on clinical skill development and professional growth, which promotes a flexibility and adaptability that allows for trainees to overcome setbacks with minimal discouragement (Stoltenberg & McNeill, 1997). Furthermore, supervisees focus on more complex information and diverse perspectives as they learn to conceptualize clients more effectively (Borders & Brown, 2005).
In summary, supervisees’ movement through the developmental stages is marked by individualized supervision needs. Structured, concrete feedback and information are desired in early supervision experiences (Bernard, 1997; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2010). The middle stages have a general focus on processing the interpersonal reactions in which supervisees engage, and supervisors provide support to help supervisees increase their awareness of transference and countertransference (Borders & Brown, 2005; Stoltenberg, 1981). Toward the later stages of supervision, supervisees seek collaborative relationships with supervisors. This collaboration provides supervisees with more freedom and autonomy, which allows them to progress through the stages as they begin to self-identify the focus of their supervision (Borders & Brown, 2005).
Similar to the IWM, models of supervision that are development-focused derive from Hunt’s (1971) matching model that suggests a person–environment fit (Stoltenberg, McNeill, & Crethar, 1994). The matching model advocates that the developmental level of supervisees should be matched with environmental or contextual structures to enhance the opportunity for learning (Lambie & Sias, 2009). Specifically, the developmental models account for trainees’ needs specific to their experience level and contextual environment, with the goal of matching interventions to support movement into more advanced developmental levels (Bernard & Goodyear, 2014; Stoltenberg & McNeill, 2012). The IWM derives its developmental perspective from the unique levels trainees experience during supervision and the cycling and recycling of stages that occurs (Loganbill et al., 1982).
Wellness and Unwellness
Wellness is a topic that has received much attention in counseling literature (Hattie, Myers, & Sweeney, 2004), including several perspectives on how to define wellness (Keyes, 1998). Dunn (1967) is considered the architect of the wellness crusade and described wellness as an integration of spirit, body and mind. The World Health Organization (1968) defined health as more than the absence of disease and emphasized a wellness quality, which includes mental, social and physical well-being. Cohen (1991) described wellness as an idealistic state that individuals strive to attain, and as something that is situated along a continuum (i.e., people experience bouts of wellness and unwellness). Witmer and Sweeney (1992) depicted wellness as interconnectedness between health characteristics, life tasks (spirituality, love, work, friendship, self), and life forces (family, community, religion, education). Additionally, Roscoe (2009) depicted wellness as a holistic paradigm that includes physical, emotional, social, occupational, spiritual, intellectual and environmental components. Witmer and Granello (2005) stated that the counseling profession is distinctively suited to promoting health and wellness with a developmental approach and, coincidentally, supervision could serve as a tool to promote wellness in supervisees as well as in clients receiving counseling services.
Smith, Robinson, and Young (2007) found that counselor wellness is negatively influenced by increased exposure to psychological distress. Furthermore, research has shown that counselors face stress because of the nature of their job (Cummins, Massey, & Jones, 2007). Increased stress and anxiety associated with counseling may have deleterious effects on counselor wellness, and supervisors and supervisees who are unwell may adversely impact their clients. In addition, Lawson and Myers (2011) suggested that increasing counselors’ wellness could lead to increased compassion satisfaction and aid counselors in avoiding compassion fatigue and burnout. Thus, supervisee and supervisor wellness should be an important component of counselor training and supervision. The IWM makes counselor wellness a focus of the supervision process.
Supervision literature contains few supervision models that include wellness components and/or focus on wellness as a key aspect of the supervision experience (e.g., Lenz et al., 2012; Lenz & Smith, 2010). Nevertheless, the paradigm of wellness has emerged in the field of counseling and is primary in developmental, strengths-based counseling (Lenz & Smith, 2010; Myers & Sweeney, 2005). The CACREP 2009 Standards note the importance of wellness for counseling students and counselor educators by promoting human functioning, wellness and health through advocacy, prevention and education. To illustrate, the CACREP 2009 Standards include suggestions of facilitating optimal development and wellness, incorporating orientations to wellness in counseling goals, and using wellness approaches to work with a plethora of populations. The overall goal of wellness counseling is to support wellness in clients (Granello & Witmer, 2013). However, if supervisees seeing clients are unwell, how efficient are they in promoting wellness in others? In order to support development of wellness in supervisees, the IWM incorporates the five wellness domains of creative, coping, physical, essential and social (Myers, Luecht, & Sweeney, 2004) by implementing the use of the Five Factor Wellness Evaluation of Lifestyle (5F-Wel; Myers et al., 2004). In addition, supervisees can use a starfish template (Echterling et al., 2002) to gauge their own wellness and prioritize the constructs that influence their personal and professional levels of wellness and unwellness, as well as create plans to increase their overall wellness.
Implementing the IWM
The IWM was created to offer an integrative method of supervision that is concise and easy to facilitate. Specifically, the IWM consists of several processes, including supervisory relationship development, evaluation of developmental phase, allocation of supervision need, and assessment and matching of wellness intervention. The following section outlines each process.
Supervisory Relationship Development
Rapport building and relationship development between supervisor and supervisee constitute a critical step in supervision (Hird, Cavalieri, Dulko, Felice, & Ho, 2001). Similar to counseling, establishing a strong, trusting supervisory relationship is essential because the relationship is an integral component of the supervision experience (Borders & Brown, 2005; Rønnestad & Skovholt, 1993). During initial sessions, supervisors describe the process of the IWM to supervisees in order to maintain open, transparent communication and to promote a safe environment for supervisees to learn, share emotions and feelings, and develop counseling skills. It is hoped that modeling appropriate professional behaviors and setting up supervision sessions to promote a trusting environment will aid in the overall development of counseling supervisees and matriculate into their normal routines as professional counselors. As with counseling, supervisors can promote a strong relationship with supervisees by focusing on the core conditions of empathy, genuineness and unconditional positive regard (Rogers, 1957). Open communication and supervisor authenticity are just two examples of processes that help develop a sound supervisor–supervisee relationship.
Evaluation of Developmental Phase
Supervisee development is an important consideration in the IWM. The IWM divides supervisee development into three phases that consist of distinct developmental characteristics. Similar to Stoltenberg and McNeill’s (2010) suggestion and other integrative models (e.g., Carlson & Lambie, 2012; Young, Lambie, Hutchinson, & Thurston-Dyer, 2011), the phases in the IWM are hierarchical in nature, with the highest phase (phase three) being ideal for developed supervisees. In addition, the IWM acknowledges the preclinical experiences (e.g., lay helper; Rønnestad, & Skovholt, 2003) of supervisees as valuable and relevant to their development. In the IWM, it is important to acknowledge and address the experiences that supervisees have had prior to their work as counselors because they may impact perceptions and expectations.
For example, supervisors can facilitate activities to promote awareness of how supervisees influence counseling sessions. To illustrate, supervisees may participate in activities highlighting culture, family-of-origin, character strengths and bias, and evaluate how those factors may influence their counseling skills, views of clients and interactions with clients, peers and supervisors. One example of a technique that can generate conversation on the aforementioned areas is the genogram (Lim & Nakamoto, 2008). Supervisees can use the genogram to map out their family history, life influences and path to becoming a counselor during a supervision session. Ultimately, the genogram can be used as a tool to assess where supervisees are developmentally and what might have contributed to their worldview and presence as counselors. With any technique used during the supervision process, the goal of increasing awareness is emphasized. Furthermore, supervisees can implement these activities for use with their own clients. Ultimately, supervisors work to facilitate supervisee progression toward being more self-actualized, self-aware counselors. Table 1 provides descriptions of awareness of well-being, developmental characteristics, supervisory descriptors and supervision considerations for each developmental phase.
Table 1
IWM Phases of Supervisee Development
|
Awareness of Well-being
|
Developmental Characteristics
|
Supervisory Descriptors
|
Supervision Considerations
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Phase 1 |
|
Low awareness |
Low independenceIncreased anxietyFollows the lead of others
Low self-efficacy |
SupportiveEducationalStructured |
Live supervisionFeedbackPsychoeducation
Modeling |
| Phase 2 |
|
Pursuit of awareness |
Seeking independenceModerate anxietyMakes attempts to lead
Modest self-efficacy |
Generating awarenessCelebrating successesChallenging |
Advanced skill feedbackChallenge awareness |
| Phase 3 |
|
Increased awareness |
Mostly independentNominal anxietyLeads others
Moderate–high self-efficacy |
Increased mutualityCollaborative |
Active listeningConsultation |
One way supervisors seek to assess supervisees’ developmental phase is through active inquiry. Similar to Young and colleagues’ (2011) recommendations, the assessment of supervisees’ developmental phase is achieved through the use of questioning, reflecting, active listening and challenging incongruences. In addition, direct and intentional questions are used to target specific topics. For example, a supervisor seeking to assess the wellness of a supervisee might ask, “How are you feeling?” and then if there is incongruence, the supervisor might state, “You’re saying that you feel ‘fine,’ but you appear to be anxious tonight.” Based on supervisee reaction, the supervisor can judge the level of awareness the trainee has into his or her own well-being. Additionally, supervisors might want to ask about specific issues such as planned interventions, diagnostic interpretations or theoretical orientation. For example, a supervisor might ask, “How do you plan to assess for suicide?” Then, based on the trainee’s reaction (e.g., asking for help, giving a tentative answer or giving a confident answer) the supervisor can determine his or her developmental phase.
Supervisors also can assess supervisee developmental phase through evaluation. By observing a supervisee in a number of settings (e.g., counseling, triadic supervision, group supervision), supervisors can gauge where he or she is developmentally. Furthermore, observing the supervisee’s counseling skills, professional behaviors and dispositions (Swank, Lambie, & Witta, 2012) can provide increased insight into what phase the supervisee is experiencing at that particular point in time.
Allocation of Supervision Need
The allocation of supervision need is the next process in the IWM of supervision. The supervisor assesses the developmental phase of the supervisee and then provides a supervision intervention (contextual or educational) with the goal of supporting and/or challenging the supervisee (Lambie & Sias, 2009). Phase one of supervisee development is marked by high anxiety, low self-efficacy, decreased awareness of wellness and poor initiative. The supervision environment is one of structure with prescribed activities. Activities to support growth in phase one include live supervision, critical feedback, education on relevant issues, and modeling of behavior and skill.
Gaining insight into trainee wellness also is critical. Supervisors can use insight-oriented activities such as scrapbook journaling, which allows supervisees to gain awareness through the use of multiple media such as photos, music, quotes and poems in the journaling process (Bradley, Whisenhunt, Adamson, & Kress, 2013), or openly discussing the supervisee’s current state of wellness to help foster an increased awareness of it. Supervisees in this developmental phase can be encouraged to explore the five wellness domains (creative self, coping self, social self, essential self, physical self) and begin increasing awareness of their current level of wellness. An example of an activity for assessing supervisee wellness is the starfish technique, which is adapted from Echterling and colleagues’ (2002) sea star balancing exercise. Within this technique, supervisees receive a picture of a five-armed starfish marked with the five wellness constructs (creative, coping, physical, essential, social; Hattie et al., 2004; Myers et al., 2004) and are asked to evaluate the areas that influence or contribute to their overall wellness. Following this, supervisors and supervisees can pursue a discussion regarding the constructs. After the discussion, supervisees redraw the starfish with arm lengths representing the amount of influence that each construct has on their overall wellness or change the constructs into things that they feel better represent their personal wellness. Figure 1 is an example of a supervisee’s initial starfish. Figure 2 is the redrawn wellness starfish based on prioritizing or changing the wellness constructs; this supervisee’s redrawn starfish prioritizes social, physical and creative aspects. In contrast, nutritional and emotional constructs are depicted as smaller arms, indicating areas for growth or a potential imbalance.
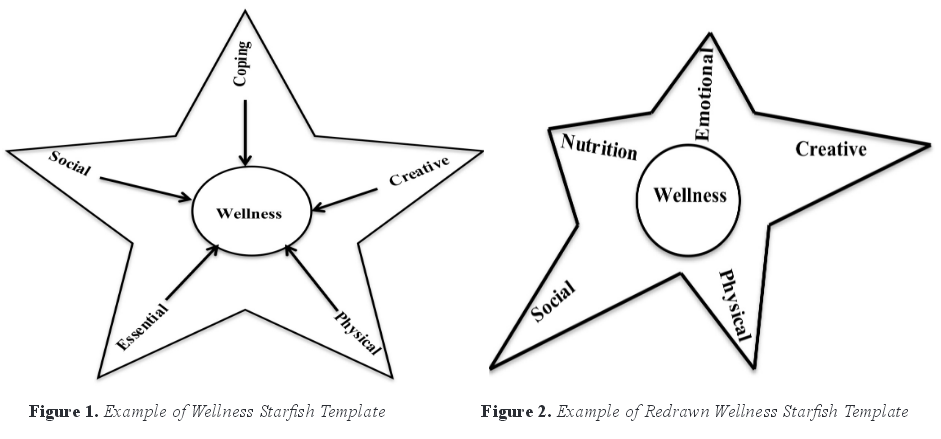
Supervisees’ progression to higher levels of development is facilitated through educational and reflective interventions that their supervisors deliver. Phase two of supervisee development is marked by increased autonomy and self-efficacy, decreased anxiety, and attempts to lead or take initiatives. The context of supervision is less concrete and structured but still supportive and encouraging. Supervisees may seek independence, as well as reassurance that they are correct when working through challenges (Borders & Brown, 2005). Supervisors can provide feedback on advanced skills, challenge supervisee awareness and foster opportunities for supervisees to take risks (i.e., challenge, support; Lambie & Sias, 2009). Supervisees in phase two have an increased awareness of their well-being but may be reluctant to integrate support strategies. Therefore, supervisors may integrate activities, assignments or challenges to enhance supervisees’ wellness. For example, supervisors can have supervisees create wellness plans or discuss current wellness plans. Thus, the supervisor can hold the supervisee accountable for personal well-being.
Supervisees in phase three exhibit high autonomy and self-efficacy, low anxiety, and greater efforts to lead (Borders & Brown, 2005). The supervision environment is less structured and the supervisor assumes a consultative role. In addition, the supervisee may serve as a leader by supporting less developed peers. Interventions at this level take the form of consulting on tough cases, working through unresolved issues and providing guidance on advanced skills. Furthermore, supervisees have higher awareness of their wellness and its implications on their work with clients. Finally, supervisees in this phase seek to minimize negative well-being and may need encouragement to overcome this challenge.
Assessment and Matching of Wellness Interventions
Evaluation is a key component of the supervision process (Borders & Brown, 2005) and therefore, wellness, supervisee skill level and supervisor role are assessed in the IWM. A key feature of the IWM is the emphasis on promoting supervisee wellness. Therefore, the IWM emphasizes the evaluation of supervisees and matching of wellness interventions. Furthermore, it is important to assess supervisees’ counseling skills throughout the supervision process to provide formative and summative feedback.
The IWM utilizes the five factors of the indivisible self model (Myers & Sweeney, 2004, 2005) as points of assessment. Furthermore, the development of personal well-being is dependent upon education of wellness, self-assessment, goal planning and progress evaluation (Granello, 2000; Myers, Sweeney, & Witmer, 2000). Therefore, the IWM utilizes these aspects of wellness development as a modality for enhancing supervisee well-being. Supervisees are viewed from a positive, strengths-based perspective in the IWM and thus, activities in supervision should highlight positive attributes, increase understanding of supervisees’ level of wellness and promote knowledge of holistic wellness. Wellness plans (WPs) and the starfish activity are used to assess supervisee wellness by promoting communication and self-awareness in the supervision session. Furthermore, both evaluations are valuable self-assessment measures for supervisees and allow for initial wellness goal setting. WPs should be developed during early supervision sessions and used as a check-in mechanism for formative wellness feedback. Concurrently, the starfish assessment can be used early on to gauge initial wellness and areas for wellness growth.
Progress evaluation is assessed with the 5F-Wel (Myers et al., 2004), a model used to consider factors contributing to healthy lifestyles. The 5F-Wel is a frequently used assessment of wellness and is based on the creative, coping, essential, physical and spiritual self components of the indivisible self model (Myers et al., 2004; Myers & Sweeney, 2005). Supervisees take this assessment during the initial and final sessions to assess their wellness. Myers and Sweeney (2005) have reported the internal consistency of the 5F-Wel as ranging from .89 to .96.
Supervisee counseling skills should be evaluated using a standardized assessment tool. For example, the Counselor Competency Scale (CCS; Swank et al., 2012) can be used as a formative (e.g., midterm or weekly) and summative (e.g., end of semester) assessment of supervisee competencies. In addition, the CCS examines whether supervisees have the knowledge, self-awareness and counseling skills to progress to additional advanced clinical practicum or internship experiences. The CCS assesses supervisee development of skill, professional behavior and professional disposition (Swank et al., 2012). Therefore, supervisors can utilize the CCS to match and support supervisees’ growth by taking on appropriate roles (i.e., teacher, counselor, consultant) to enhance work on specific developmental issues.
Evaluation allows supervisors to monitor supervisee development of career-sustaining mechanisms that enhance well-being, as well as counseling skills, dispositions and professional behaviors. Specifically, the goals of supervisee development are to increase or maintain level of wellness and increase or maintain counseling skills by the end of the supervision process. However, if a supervisee does not improve well-being, the WP should be reevaluated and a remediation plan set so that the supervisee continues to work toward increased wellness. Similarly, if a student does not meet the minimal counseling skill requirements, a remediation plan can be created to support the student’s continued development.
Matching. Supervisors gain a picture of where counseling trainees are developmentally based on the assessment and evaluation process. Then supervisors can match supervisee developmental levels (of skill and wellness) by assuming the appropriate role (i.e., counselor, teacher, consultant) and using the role to provide the appropriate level of support for each trainee. This process allows for individualization of the supervision process and for supervisors to tailor specific events, techniques and learning experiences to the needs of their supervisees. Furthermore, matching supervisee developmental needs and gauging levels of awareness and anxiety allows for appropriate discussions during supervision. Discussing wellness during the latter part of supervision is appropriate for beginning counselors who may be anxious about their skills and work with clients (Borders, 1990) and may not absorb information about their wellness. Each supervisee is an individual, and as a result, it is important to make sure that the supervisee is ready to hear wellness feedback during the supervision session.
IWM: Goals, Strengths and Limitations
The overall goals of the IWM of supervision are for supervisees to increase their wellness, progress through developmental stages and gain counseling skills required to be effective counselors. Additionally, supervisors using the IWM can aid supervisees in increasing wellness awareness via completion of wellness-related assessments (e.g., WPs and starfish technique). Furthermore, supervisors can work to increase supervisees’ self-awareness and professional awareness of counseling issues such as multicultural wellness concerns, the therapeutic alliance, becoming a reflective practitioner, and positive, strengths-based approaches of counseling under the IWM framework.
The IWM is innovative in that it is one of a few supervision models to contain a wellness component. Additionally, the IWM tenets (i.e., wellness, discrimination, development) are empirically supported on individual levels. Furthermore, the IWM includes techniques and assessments for promoting open communication relating to supervisee wellness and counseling skills, and therefore supports supervisory relationships and greater self-awareness, and ultimately allows supervisors to encourage and promote wellness.
As with all models of supervision, the IWM has limitations. Specifically, the IWM may not be applicable to advanced counselors and supervisees. The IWM includes three developmental phases, which are applicable to CITs. In addition, the model may not be as beneficial to supervisees who already have a balanced wellness plan or practice wellness, because the wellness component may be repetitive for such individuals. Additionally, all aspects of the IWM might not be effective or appropriate across all multicultural groups (i.e., races, ethnicities, genders, religions). For example, in relation to wellness, supervisees may not adhere to a holistic paradigm or believe in certain wellness constructs. Lastly, the IWM is in its infancy and empirical evidence directly associated with the integrative prototype does not exist. Nevertheless, supervisors using the IWM can tailor the wellness, developmental and role-matching components to meet specific supervisee needs. The following case study depicts the use of the IWM with a counseling supervisee.
Case Study
Kayla is a 25-year-old female master’s-level counseling student taking her first practicum course. She is excited about the idea of putting the skills she has learned during her program into practice with clients. However, Kayla also is anxious about seeing her first clients and often questions whether she will be able to remember everything she is supposed to do. People tell her she will be fine; however, Kayla questions whether she will actually be able to help her clients.
In addition to the practicum course, Kayla is taking three other graduate courses. She has a full-time job and is in a steady relationship. Family is very important to her, but since beginning her graduate program, she has been unable to find enough time to spend with friends and family. Kayla feels the pull between these areas of her life and struggles to find a balance between family, school, work and her partner.
Kayla is in phase one (i.e., high anxiety); therefore, her supervisor assumes the counselor and teacher roles most often, to match Kayla developmentally. This choice of roles allows Kayla to receive appropriate levels of support and structure to help ease anxiety. During this phase, the supervisor introduces a WP to Kayla and has her complete the 5F-Wel and starfish activity. After discussing the supervisory process and explaining the IWM, Kayla and the supervisor have a conversation about the areas influencing her overall wellness. Based on her starfish results, Kayla is encouraged to develop a WP that coincides with the areas depicted on the starfish, emphasizing those that she wishes to develop further. Additionally, the 5F-Wel provides a baseline of well-being to use in future sessions. Along with the wellness focus, the supervisor explains how imbalance or unwellness influences counselors and, in turn, how it can influence clients.
Initial supervision sessions will continue to provide Kayla with appropriate levels of support and psychoeducation so that she will be able to transition from low awareness to a greater sense of counseling skill awareness and increased mindfulness regarding her overall wellness. If the supervisor and supervisee are able to establish a strong working relationship, it is expected that Kayla will eventually move developmentally into phase two, where she will continue to gain insight into her counseling and wellness, begin to increase her autonomy, and work on increasing self-efficacy.
Implications for Counseling
The IWM integrates developmental and DM supervision tenets with domains of wellness. A supervision model that incorporates wellness is a logical fit in counseling and counselor education, where programs can and should address personal development through wellness strategies for CITs (Roach & Young, 2007). Furthermore, the IWM supports the idea that wellness is important. According to White and Franzoni (1990), CITs often show higher psychological disturbances than the general population. Cummins, Massey, and Jones (2007) highlighted the fact that counselors and CITs often struggle to take their own advice about wellness in their personal lives. Thus, while counseling is theoretically and historically a wellness-oriented field, many counselors are unwell and failing to practice what they preach (Lawson, Venart, Hazler, & Kottler, 2007; Myers & Sweeney, 2005). Implementing the IWM can aid in supporting overall wellness in supervisees as well as educating CITs to practice wellness with their clients and with themselves.
In relation to developmental matching and DM roles, counseling supervisors using the IWM have the following theoretical issues (e.g., Bernard, 1997; Myers et al., 2004; Myers & Sweeney, 2005) to facilitate: supervisee change, skill development, increased self-awareness and increased professional development. The IWM is a holistic, strengths-based model that focuses on supervisee development, matching supervisee needs through supervisor role changing, and wellness to promote knowledgeable, well and effective counseling supervisees.
Conclusion
The IWM is designed to integrate wellness, developmental stages and role matching to allow supervisors to encourage holistic wellness through supervision. Wellness has a positive relationship with counselors’ increased use of career-sustaining mechanisms and increased professional quality of life (Lawson, 2007; Lawson & Myers, 2011). Likewise, increased professional quality of life has been shown to make a positive contribution to counselors’ self-efficacy and counseling service delivery (Mullen, 2014). Therefore, it is logical to promote wellness and career-sustaining behaviors throughout the supervision process.
In summary, the IWM offers a new, integrated model of supervision for use with CITs. Supervisors using the IWM have the unique opportunity to operate from a wellness paradigm, familiarize their supervisees with wellness practices, and monitor supervisees’ wellness and how their wellness influences their client outcomes, while simultaneously supporting supervisee growth, counseling skill development and awareness of professional dispositions.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of
interest or funding contributions for
the development of this manuscript.
References
American Counseling Association. (2014). ACA code of ethics. Alexandria, VA: Author.
Association for Counselor Education and Supervision. (2011). Best practices in clinical supervision. Retrieved from http://www.acesonline.net/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/ACES-Best-Practices-in-clinical-supervision-document-FINAL.pdf
Aten, J. D., Strain, J. D., & Gillespie, R. E. (2008). A transtheoretical model of clinical supervision. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 2, 1–9. doi:10.1037/1931-3918.2.1.1
Bernard, J. M. (1979). Supervisor training: A discrimination model. Counselor Education and Supervision, 19, 60–68. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.1979.tb00906.x
Bernard, J. M. (1997). The discrimination model. In C. E. Watkins (Ed.), Handbook of psychotherapy supervision (pp. 310–327). New York, NY: Wiley.
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (2014). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Blocher, D. H. (1983). Toward a cognitive developmental approach to counseling supervision. The Counseling Psychologist, 11, 27–34. doi:10.1177/0011000083111006
Borders, L. D. (1990). Developmental changes during supervisees’ first practicum. The Clinical Supervisor, 8, 157–167. doi:10.1300/J001v08n02_12
Borders, L. D. (1992). Learning to think like a supervisor. The Clinical Supervisor, 10, 135–148. doi:10.1300/J001v10n02_09
Borders, L. D., & Brown, L. L. (2005). The new handbook of counseling supervision. New York, NY: Routledge.
Bradley, N., Whisenhunt, J., Adamson, N., & Kress, V. E. (2013). Creative approaches for promoting counselor self-care. Journal of Creativity in Mental Health, 8, 456–469. doi:10.1080/15401383.2013.844656
Carlson, R. G., & Lambie, G. W. (2012). Systemic-developmental supervision: A clinical supervisory approach for family counseling student interns. The Family Journal, 20, 29–36. doi:10.1177/1066480711419809
Cohen, E. L. (1991). In pursuit of wellness. American Psychologist, 46, 404–408.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2009). 2009 standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/2009-Standards.pdf
Cummins, P. N., Massey, L., & Jones, A. (2007). Keeping ourselves well: Strategies for promoting and maintaining counselor wellness. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 46, 35–49. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2007.tb00024.x
Dunn, H. L. (1967). High-level wellness. Arlington, VA: Beatty.
Echterling, L. G., Cowan, E., Evans, W. F., Staton, A. R., Viere, G., & McKee, J. (2002). Thriving!: A manual for students in the helping professions. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Ekstein, R., & Wallerstein, R. S. (1972). The teaching and learning of psychotherapy (2nd ed.). New York, NY: International Universities Press.
Granello, P. (2000). Integrating wellness work into mental health private practice. Journal of Psychotherapy in Independent Practice, 1, 3–16. doi:10.1300/J288v01n01_02
Granello, P. F., & Witmer, J. M. (2013). Theoretical models for wellness counseling. In P. F. Granello (Ed.), Wellness counseling (pp. 29–36). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Hattie, J. A., Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2004). A factor structure of wellness: Theory, assessment, analysis, and practice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 82, 354–364. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2004.tb00321.x
Hird, J. S., Cavalieri, C. E., Dulko, J. P., Felice, A. A. D., & Ho, T. A. (2001). Visions and realities: Supervisee perspectives of multicultural supervision. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 29, 114–130. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1912.2001.tb00509.x
Hunt, D. E. (1971). Matching models in education: The coordination of teaching methods with student characteristics. Toronto, Canada: Ontario Institute for Studies in Education.
Johnson, J. A. (1986). Wellness: A context for living. Thorofare, NJ: Slack.
Keyes, C. L. M. (1998). Social well-being. Social Psychology Quarterly, 61, 121–140.
Kottler, J. A. (2010). On being a therapist (4th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Lambie, G. W., & Sias, S. M. (2009). An integrative psychological developmental model of supervision for professional school counselors-in-training. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87, 349–356. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2009.tb00116.x
Lawson, G. (2007). Counselor wellness and impairment: A national survey. The Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 46, 20–34.
Lawson, G., & Myers, J. E. (2011). Wellness, professional quality of life, and career-sustaining behaviors: What keeps us well? Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 163–171. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00074.x
Lawson, G., Venart, E., Hazler, R. J., & Kottler, J. A. (2007). Toward a culture of counselor wellness. The Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 46, 5–19. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2007.tb00022.x
Lenz, A. S., Sangganjanavanich, V. F., Balkin, R. S., Oliver, M., & Smith, R. L. (2012). Wellness model of supervision: A comparative analysis. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 207–221. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00015.x
Lenz, A. S., & Smith, R. L. (2010). Integrating wellness concepts within a clinical supervision model. The Clinical Supervisor, 29, 228–245. doi:10.1080/07325223.2020.518511
Lim, S.-L., & Nakamoto, T. (2008). Genograms: Use in therapy with Asian families with diverse cultural heritages. Contemporary Family Therapy: An International Journal, 30, 199–219. doi:10.1007/s10591-008-9070-6
Loganbill, C., Hardy, E., & Delworth, U. (1982). Supervision, a conceptual model. The Counseling Psychologist, 10, 3–42. doi:10.1177/0011000082101002
Luke, M., & Bernard, J. M. (2006). The school counseling supervision model: An extension of the discrimination model. Counselor Education and Supervision, 45, 282–295. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2006.tb00004.x
Maslach, C. (2003). Burnout: The cost of caring. Cambridge, MA: Malor Books.
McNeill, B. W., Stoltenberg, C. D., & Pierce, R. A. (1985). Supervisees’ perceptions of their development: A test of the counselor complexity model. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 32, 630–633. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.32.4.630
Mullen, P. R. (2014). The contribution of practicing school counselors’ self-efficacy and professional quality of life to their programmatic service delivery. (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL.
Myers, J. E., Luecht, R. M., & Sweeney, T. J. (2004). The factor structure of wellness: Reexamining theoretical and empirical models underlying the wellness evaluation of lifestyle (WEL) and the Five-Factor Wel. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 36, 194–208.
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2004). The indivisible self: An evidence-based model of wellness. The Journal of Individual Psychology, 60, 234–244.
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2005). The indivisible self: An evidence-based model of wellness. (Reprint.). The Journal of Individual Psychology, 61, 269–279.
Myers, J. E., & Sweeney, T. J. (2008). Wellness counseling: The evidence base for practice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 86, 482–493.
Myers, J. E., Sweeney, T. J., & Witmer, J. M. (1998). The wellness evaluation of lifestyle. Palo Alto, CA: Mind Garden.
Myers, J. E., Sweeney, T. J., & Witmer, J. M. (2000). The wheel of wellness counseling for wellness: A holistic model for treatment planning. Journal of Counseling & Development, 78, 251–266. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2000.tb01906.x
Ober, A. M., Granello, D. H., & Henfield, M. S. (2009). A synergistic model to enhance multicultural competence in supervision. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48, 204–221. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2009.tb00075.x
Prochaska, J. O., & DiClemente, C. C. (1982). Transtheoretical therapy: Toward a more integrative model of change. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research & Practice, 19, 276–288. doi:10.1037/h0088437
Roach, L. F., & Young, M. E. (2007). Do counselor education programs promote wellness in their students? Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 29–45. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2007.tb00036.x
Robiner, W. N., Fuhrman, M., Ristvedt, S., Bobbitt, B., & Schirvar, J. (1994). The Minnesota Supervisory Inventory (MSI): Development, psychometric characteristics, and supervisory evaluation issues. The Clinical Psychologist, 47(4), 4–17.
Rogers, C. R. (1957). The necessary and sufficient conditions of therapeutic personality change. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 21, 95–103. doi:10.1037/h0045357
Rønnestad, M. H., & Skovholt, T. M. (1993). Supervision of beginning and advanced graduate students of counseling and psychotherapy. Journal of Counseling & Development, 71, 396–405. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1993.tb02655.x
Rønnestad, M. H., & Skovholt, T. M. (2003). The journey of the counselor and therapist: Research findings and perspectives on professional development. Journal of Career Development, 30, 5–44.
Roscoe, L. J. (2009). Wellness: A review of theory and measurement for counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 87, 216–226. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2009.tb00570.x
Smith, H. L., Robinson, E. H. M., III, & Young, M. E. (2007). The relationship among wellness, psychological distress, and social desirability of entering master’s-level counselor trainees. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47, 96–109. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2007.tb00041.x
Stoltenberg, C. D. (1981). Approaching supervision from a developmental perspective: The counselor complexity model. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 28, 59–65.
Stoltenberg, C. D., & McNeill, B. W. (1997). Clinical supervision from a developmental perspective: Research and practice. In C. E. Watkins, Jr. (Ed.), Handbook of psychotherapy supervision (pp. 184–202). New York, NY: Wiley.
Stoltenberg, C. D., & McNeill, B. W. (2010). IDM supervision: An integrative developmental model of supervision (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Stoltenberg, C. D., & McNeill, B. W. (2012). Supervision: Research, models, and competence. In N. A. Fouad (Ed.), APA handbook of counseling psychology: Vol. 1. Theories, research, and methods (pp. 295–327). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Stoltenberg, C. D., McNeill, B. W., & Crethar, H. C. (1994). Changes in supervision as counselors and therapists gain experience: A review. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 25, 416–449. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.25.4.416
Swank, J. M., Lambie, G. W., & Witta, E. L. (2012). An exploratory investigation of the counseling competencies Scale: A measure of counseling skills, dispositions, and behaviors. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51, 189–206. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00014.x
Swarbrick, M. (1997). A wellness model for clients. Mental Health Special Interest Section Quarterly, 20, 1–4.
Vespia, K. M., Heckman-Stone, C., & Delworth, U. (2002). Describing and facilitating effective supervision behavior in counseling trainees. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training, 39, 56–65. doi:10.1037/0033-3204.39.1.56
White, P. E., & Franzoni, J. B. (1990). A multidimensional analysis of the mental health of graduate counselors in training. Counselor Education and Supervision, 29, 258–267. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6978.1990.tb01165.x
Williams, E. N., Judge, A. B., Hill, C. E., & Hoffman, M. A. (1997). Experiences of novice therapists in prepracticum: Trainees’, clients’, and supervisors’ perceptions of therapists’ personal reactions and management strategies. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 44, 390–399. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.44.4.390
Witmer, J. M. (1985). Pathways to personal growth. Muncie, IN: Accelerated Development.
Witmer, J. M., & Granello, P. F. (2005). Wellness in counselor education and supervision. In J. E. Myers & T. J. Sweeney (Eds.), Counseling for wellness: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 261–272). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
Witmer, J. M., & Sweeney, T. J. (1992). A holistic model for wellness and prevention over the life span. Journal of Counseling & Development, 71, 140–148. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1992.tb02189.x
Witmer, J. M., & Young, M. E. (1996). Preventing counselor impairment: A wellness approach. The Journal of Humanistic Education and Development, 34, 141–155. doi:10.1002/j.2164-4683.1996.tb00338.x
World Health Organization. (1968). Constitution of the World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
Worthen, V., & McNeill, B. W. (1996). A phenomenological investigation of “good” supervision events. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 43, 25–34. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.43.1.25
Young, T. L., Lambie, G. W., Hutchinson, T., & Thurston-Dyer, J. (2011). The integration of reflectivity in developmental supervision: Implications for clinical supervisors. The Clinical Supervisor, 30, 1–18. doi:10.1080/07325223.2011.532019
Ashley J. Blount, NCC, is a doctoral student at the University of Central Florida. Patrick R. Mullen, NCC, is an Assistant Professor at East Carolina University. Correspondence can be addressed to Ashley J. Blount, The Department of Child, Family, and Community Sciences, University of Central Florida, P.O. Box 161250, Orlando, Florida, 32816-1250, ashleyjwindt@gmail.com.
Sep 7, 2014 | Article, Volume 1 - Issue 3
E. Heather Thompson, Melodie H. Frick, Shannon Trice-Black
Counselors-in-training face the challenges of balancing academic, professional, and personal obligations. Many counselors-in-training, however, report a lack of instruction regarding personal wellness and prevention of personal counselor burnout. The present study used CQR methodology with 14 counseling graduate students to investigate counselor-in-training perceptions of self-care, burnout, and supervision practices related to promoting counselor resilience. The majority of participants in this study perceived that they experienced some degree of burnout in their experiences as counselors-in-training. Findings from this study highlight the importance of the role of supervision in promoting resilience as a protective factor against burnout among counselors-in-training and provide information for counselor supervisors about wellness and burnout prevention within supervision practice
Keywords: counselors-in-training, wellness, burnout, supervision, resilience
Professional counselors, due to often overwhelming needs of clients and heavy caseloads, are at high risk for burnout. Research indicates that burnout among mental health practitioners is a common phenomenon (Jenaro, Flores, & Arias, 2007). Burnout is often experienced as “a state of physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion caused by long-term involvement in emotionally demanding situations” (Gilliland & James, 2001, p. 610). Self-care and recognition of burnout symptoms are necessary for counselors to effectively care for their clients as well as themselves. Counselors struggling with burnout can experience diminished morale, job dissatisfaction (Koeske & Kelly, 1995), negative self-concept, and loss of concern for clients (Rosenberg & Pace, 2006). Clients working with counselors experiencing burnout are at serious risk, as they may not receive proper care and attention to often severe and complicated problems.
The potential hazards for counselor distress in practicum and internship are many. Counselors-in-training often begin their professional journeys with a certain degree of idealism and unrealistic expectations about their roles. Many assume that hard work and efforts will translate to meaningful work with clients who are eager to change and who are appreciative of the counselor’s efforts (Leiter, 1991). However, clients often have complex problems that are not always easily rectified and which contribute to diminished job-related self-efficacy for beginning counselors (Jenaro et al., 2007). In addition, counselor trainees often experience difficulties as they balance their own personal growth as counselors while working with clients with immense struggles and needs (Skovholt, 2001). Furthermore, elusive measures for success in counseling can undermine a new counselor’s sense of professional competence (Kestnbaum, 1984; Skovholt, Grier, & Hanson, 2001). Client progress is often difficult to concretely monitor and define. The “readiness gap,” or the lack of reciprocity of attentiveness, giving, and responsibility between the counselor-in-training and the client, are an additional job-related stressor that may increase the likelihood of burnout (Kestnbaum, 1984; Skovholt et al., 2001; Truchot, Keirsebilck, & Meyer, 2000).
Counselors-in-training are exposed to emotionally demanding stories (Canfield, 2005) and situations which may come as a surprise to them and challenge their ideas about humanity. The emotional demands of counseling entail “constant empathy and one-way caring” (Skovholt et al., 2001, p. 170) which may further drain a counselor’s reservoir of resilience. Yet, mental health practitioners have a tendency to present themselves as caregivers who are less vulnerable to emotional distress, thereby hindering their ability to focus on their own needs and concerns (Barnett, Baker, Elman, & Schoener, 2007; Sherman, 1996). Counselors who do not recognize and address their diminished capacity when stressed are likely to be operating with impaired professional competence, which violates ethical responsibilities to do no harm.
Counselor supervision is designed to facilitate the ethical, academic, personal, and professional development of counselors-in-training (CACREP, 2009). Bolstering counselor resilience in an effort to prevent burnout is one aspect of facilitating ethical, personal, and professional development. Supervisors who work closely with counselors-in-training during their practicum and internship can promote the hardiness and sustainability of counselors-in-training by helping them learn to self-assess in order to recognize personal needs and assert themselves accordingly. This may include learning to say “no” to the demands that exceed their capacity or learning to actively create and maintain rejuvenating relationships and interests outside of counseling (Skovholt et al., 2001). Supervisors also can teach and model self-care and positive coping strategies for stress, which may influence supervisees’ practice of self-care (Aten, Madson, Rice, & Chamberlain, 2008). In an effort to bolster counselor resilience, supervisors can facilitate counselor self-understanding about overextending oneself to prove professional competency to achieve a sense of self-worth (Rosenburg & Pace, 2006). Supervisors can help counselors-in-training come to terms with the need for immediate positive reinforcement related to work or employment, which is limited in the counseling profession as change rarely occurs quickly (Skovholt et al., 2001). Counselor resiliency also may be bolstered by helping counselors-in-training establish realistic measures of success and focus on the aspects of counseling that they can control such as their knowledge and ability to create strong therapeutic alliances rather than client outcomes. In sum, distressing issues in counseling, warning signs of burnout, and coping strategies for dealing with stress should be discussed and the seeds of self-care should be planted so they may grow and hopefully sustain counselors-in-training over the course of their careers.
Method
The purpose of this exploratory study was to investigate counselor-in-training perceptions of self-care, burnout, and supervision practices related to promoting counselor resilience. The primary research questions that guided this qualitative study included: (a) What are master’s-level counselors-in-training’s perceptions of counselor burnout? (b) What are the perceptions of self-care among master’s-level counselors-in-training? (c) What, if anything, have master’s-level counselors-in-training learned about counselor burnout in their supervision experiences? And (d) what, if anything, have master’s level counselors-in-training learned about self-care in their supervision experiences?
The consensual qualitative research method (CQR) was used to explore the supervision experiences of master’s-level counselors-in-training. CQR works from a constructivist-post-positivist paradigm that uses open-ended semi-structured interviews to collect data from individuals, and reaches consensus on domains, core ideas, and cross-analyses by using a research team and an external auditor (Hill, Knox, Thompson, Williams, Hess, & Ladany, 2005; Ponterotto, 2005). Using the CQR method, the research team examined commonalities and arrived at a consensus of themes within and across participants’ descriptions of the promotion of self-care and burnout prevention within their supervision experiences (Hill et al., 2005; Hill, Thompson, & Nutt Williams, 1997).
Participants
Interviewees. CQR methodologists recommend a sample size of 8–15 participants (Hill et al., 2005). The participants in this sample included 14 individuals; 13 females and 1 male, who were graduate students in master’s-level counseling programs and enrolled in practicum or internship courses. The participants attended one of three universities in the United States (one in the Midwest and two in the Southeast). The sample consisted of 10 participants in school counseling programs and 4 participants in clinical mental health counseling programs. Thirteen participants identified as Caucasian, and one participant identified as Hispanic. The ages of participants ranged from 24 to 52 years of age (mean = 28).
Researchers. An informed understanding of the researchers’ attempt to make meaning of participant narratives about supervision, counselor burnout, and self-care necessitates a discussion of potential biases. This research team consisted of three Caucasian female faculty members from three different graduate-level counseling programs. All three researchers are proficient in supervision practices and passionate about facilitating counselor growth and development through supervision. All members of the research team facilitate individual and group supervision for counselors-in-training in graduate programs. The three researchers adhere to varying degrees of humanistic, feminist, and constructivist theoretical leanings. All members of the research team believe that supervision is an appropriate venue for bolstering both personal and professional protective factors that may serve as buffers against counselor burnout. It also is worth noting that the three members of the research team believed they had experienced varying degrees of burnout over the course of their careers. The researchers acknowledge these shared biases and attempted to maintain objectivity with an awareness of their personal experiences with burnout, approaches to supervision, and beliefs regarding the importance of addressing protective factors, wellness and burnout prevention in supervision. This study also was influenced by an external auditor who is a former counselor educator with more than 20 years of experience in qualitative research methods and supervision practice. As colleagues in the field of counselor education and supervision, the research team and the auditor were able to openly and respectfully discuss their differing perspectives throughout the data analysis process, which permitted them to arrive at consensus without being stifled by power struggles.
Procedures for Data Collection
Criterion sampling was used to select participants in an intentional manner to understand specified counseling students’ experiences in supervision. Criteria for participation in this study included enrollment as a graduate student in a master’s-level counseling program and completion of a practicum experience or participation in a counseling internship in a school or mental health counseling agency. Researchers disseminated information about this study by email to master’s-level students in counseling programs at three different universities. Interested students were instructed to contact, by email or phone, a designated member of the research team, who was not a faculty member at their university. All participants were provided with an oral explanation of informed consent and all participants signed the informed consent documents. All procedures followed those established by the Institutional Review Board of the three universities associated with this study.
Within the research team, researchers were designated to conduct all communication, contact, and interviews with participants not affiliated with their respective universities, in order to foster a confidential and non-coercive environment for the participants. Interviews were conducted on one occasion, in person or via telephone, in a semi-structured format. Participants in both face-to-face and telephone interviews were invited to respond to questions from the standard interview protocol (see Appendix A) about their experiences and perceptions of supervision practices that addressed counselor self-care and burnout prevention. Participants were encouraged to elaborate on their perceptions and experiences in order to foster the emergence of a rich and thorough understanding. The transferability of this study was promoted by the rich, thick descriptions provided by an in-depth look at the experiences and perceptions of this sample of counselors-in-training. Interviews lasted approximately 50–70 minutes. The interview protocol was generated after a thorough review of the literature and lengthy discussions about researcher experiences as a supervisee and a supervisor. Follow-up surveys (see Appendix B) were administered electronically to participants six weeks after the interview to capture additional thoughts and experiences of the participants.
Data Analysis
All interviews were audio-taped and transcribed verbatim for data analysis. Transcripts were checked for accuracy by comparing them to the audio-recordings after the transcription process. Participant names were changed to pseudonyms to protect participant anonymity. Participants’ real names and contact information were only used for scheduling purposes. Information linking participants to their pseudonyms was not kept.
Coding of domains. Prior to beginning the data analysis process, researchers generated a general list of broad domain codes based on the interview protocol, a thorough understanding of the extant literature, and a review of the transcripts. Once consensus was achieved, each researcher independently coded blocks of data into each domain code for seven of the 14 cases. Next, as a team, the researchers worked together to generate consensus on the domain codes for the seven cases. The remaining cases were analyzed by pairs of the researchers. The third team member reviewed the work of the pair who generated the domain coding for the remaining seven cases. Throughout the coding process, domains were modified to best capture the data.
Abstracting the core ideas within each domain. Each researcher worked independently to capture the core idea for each domain by re-examining each transcript. Core ideas consisted of concise statements of the data that illuminated the essence of the participant’s expressed perspectives and experiences. As a group, the researchers discussed the wording of core ideas for each case until consensus was achieved.
Cross analysis. The researchers worked independently to identify commonalities of core ideas within domains across cases. Next, as a group, the research team worked to find consensus on the identified categories across cases. Aggregated core ideas were placed into categories and frequency labels were applied to indicate how general, typical, or variant the results were across cases. General frequencies refer to findings that are true for all but one of the cases (Hill et al., 2005). Typical frequencies refer to findings that are present in more than half of the cases. Variant frequencies refer to finding in at least two cases, but less than half.
Audit. An external auditor was invited to question the data analysis process and conclusions. She was not actively engaged in the conceptualization and implementation of this study, which gave the research team the benefit of having an objective perspective. The external auditor reviewed and offered suggestions about the generation of domains and core ideas, and the cross-case categories. Most feedback was given in writing. At times, feedback was discussed via telephone. The research team reviewed all auditor comments, looked for evidence supporting the suggested change, and made adjustments based on team member consensus.
Stability check. For the purpose of determining consistency, two of the 14 transcripts were randomly selected and set aside for cross-case analysis until after the remaining 12 transcripts were analyzed. This process indicated no significant changes in core domains and categories, which suggested consistency among the findings.
Results
A final consensus identified five domains: counselor burnout, counselor self-care, faculty supervision, site supervision, and improvements (see Table 1). Cross-case categories and subcategories were developed to capture the core ideas. Following CQR procedures (Hill et al., 1997, 2005), a general category represented all or all but one of the cases (n = 13–14); a typical category represented at least half of the cases (n = 7–12); and a variant category represented less than half but more than two of the cases (n = 3 – 6). Categories with fewer than three cases were excluded from further analysis. General categories were not identified from the data.
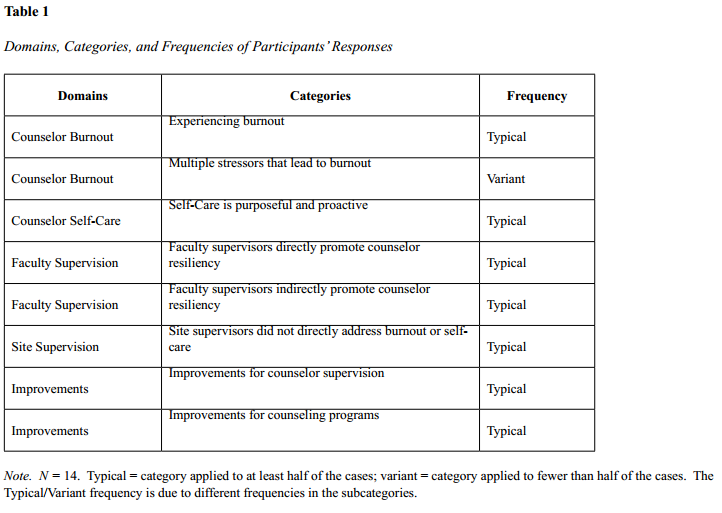
Counselor Burnout
Experiencing burnout. Most participants reported knowledge of or having experiences with burnout. Participants identified stressors leading to burnout as a loss of enthusiasm and compassion, the struggle to balance school, work, and personal responsibilities and relationships, and difficulty delineating and separating personal and professional boundaries.
Participants described counselor burnout as no longer having compassion or enthusiasm for counseling clients. One participant defined counselor burnout as, “it seems routine or [counselors] feel like they’ve dealt with so many situations over time that they’re just kind of losing some compassion for the field or the profession.” Another participant described counselor burnout as no longer seeing the unique qualities of individuals seen in counseling:
I wouldn’t see [clients] as individuals anymore…and that’s where I get so much of it coming at me, or so many clients coming at me, that they’re no longer an individual they’re just someone that’s sitting in front of me, and when they leave they write me a check….they are not people anymore, they’re clients.
Participants often discussed a continual struggle to balance personal and professional responsibilities. One participant described burnout as foregoing pleasurable activities to focus on work-related tasks:
I can tell when I am starting to get burned out when I am focusing so much on those things that I forgo all of those things that are fun for me. So I am not working out anymore, I am not reading for fun, and I am putting off hanging out with my friends because of my school work. There’s school work that maybe doesn’t have to get done at that moment, but if I don’t work on it I’m going to be thinking about it and not having fun.
Another participant described burnout as having a hard time balancing professional and personal responsibilities stating, “I think I don’t look forward to…working with…people. I’m just kind of glad when they don’t show up. And this kind of sense that I’m losing the battle to keep things in balance.”
Boundary issues were commonly cited by participants. Several participants reported that they struggled to be assertive, set limits, maintain realistic expectations, and not assume personal responsibility for client outcomes. One participant described taking ownership of a client’s outcome and wanting to meet all the needs of her clients:
I believe part of it is internalizing the problem on myself, feeling responsible. Maybe loosing sight of my counseling skills and feeling responsible for the situation. Or feeling helpless. Also, in school counseling there tends to be a larger load of students. And this is frustrating to not meet all the needs that are out there.
Participants reported experiences with burnout and multiple stressors that lead to burnout. Participants defined counselor burnout as a loss of compassion for clients, diminished enthusiasm, difficulty maintaining a life-work balance, and struggles to maintain boundaries.
Counselor Self-Care
Self-care is purposeful and proactive. Participants were asked to describe self-care for counselors and reported that self-care requires purposeful efforts to set time aside to engage in activities outside of work that replenish energy and confidence. Most participants identified having and relying on supportive people, such as family, friends, and significant others to help them cope with stressors. Participants also identified healthy eating and individualized activities such as exercise, reading, meditation, and watching movies as important aspects of their self-care. One participant described self-care as:
Anything that can help you reenergize and refill that bucket that’s being dipped into every day. If that’s going for a walk in the park…so be it. If that’s going to Starbucks…go do it….Or something that makes you feel good about yourself, something that makes you feel confident, or making someone else feel confident….Whatever it is, something that makes you feel good about yourself and knowing that you’re doing what you need to be doing.
Participants reported that self-care requires proactive efforts to consult with supervisors and colleagues; one of the first steps is recognizing when one needs consultation. One participant explained:
I think in our program, [the faculty] were very good about letting us know that if you can’t handle something, refer out, consult. Consult was the theme. And then if you feel you really can’t handle it before you get in over your head, make sure you refer out to someone you feel is qualified.
Participants described self-care as individualized and intentional, and included activities and supportive people outside of school or work settings that replenished their energy levels. Participants also discussed the importance of identifying when counselor self-care is necessary and seeking consultation for difficult client situations.
Faculty Supervision
Faculty supervisors directly promote counselor resiliency. More than half of the participants reported that faculty supervisors directly initiated conversations about self-care. A participant explained, “Every week when we meet for practicum, [the faculty supervisor] is very adamant, ‘is everyone taking care of themselves, is anyone having trouble?’ She is very open to listening to any kind of self-care situation we might have.” Similarly, another participant stated, “Our professors have told us about the importance of self-care and they have tried to help us understand which situations are likely to cause us the most stress and fatigue.” One participant identified preventive measures discussed in supervision:
In supervision, counselor burnout is addressed from the perspective of prevention. We develop personal wellness plans, and discuss how well we live by them during supervision….Self-care is addressed in the same conversation as counselor burnout. In supervision, the mantra is good self-care is vital to avoiding burnout.
Faculty supervisors indirectly promote counselor resiliency. Participants also reported that faculty supervisors indirectly addressed counselor self-care by being flexible and supportive of participants’ efforts with clients. Participants repeatedly expressed appreciation for supervisors who processed cases and provided positive feedback and practical suggestions. One participant explained, “I know that [my supervisor] is advocating for me, on my side, and allowing me to vent, and listening and offering advice if I need it….giving me positive feedback in a very uncomfortable time.”
Further, participants stated they appreciated supervisors who actively created a safe space for personal exploration. One participant explained:
[Supervision] was really a place for us to explore all of ourselves, holistically. The forum existed for us for that purpose. [The supervisors] hold the space for us to explore whatever needs to be explored. That was the great part about internship with the professor I had. He sort of created the space, and we took it. It took him allowing it, and us stepping into the space.
Modeling self-care also is an indirect means of addressing counselor burnout and self-care. Half of the participants reported that their faculty supervisors modeled self-care. For example, faculty supervisors demonstrated boundaries with personal and professional obligations, practiced meditation, performed musically, and exercised. Conversely, participants reported that a few supervisors demonstrated a lack of personal self-care by working overtime, sacrificing time with their families for job obligations, and/or having poor diet and exercise habits.
Participants reported that faculty supervisors directly and indirectly addressed counselor burnout and self-care in supervision. Supervisors who intentionally checked in with the supervisees and used specific techniques such as wellness plans were seen as directly affecting the participants’ perspective on counselor self-care. Supervisors who were present and available, created safe environments for supervision, provided positive feedback and suggestions, and modeled self-care were seen as indirectly addressing counselor self-care. Both direct and indirect means of addressing counselor burnout and self-care were seen as influential by participants.
Site Supervision
Site supervisors did not directly address burnout or self-care. Participants reported that site supervisors rarely initiated conversations about counselor burnout or self-care. One participant reported that counselor burnout was not addressed and as a result she felt a lack of support from the supervisor:
[Site Supervisors] don’t ask about burnout though. Every time I’m bringing it up, the answers I’m getting are ‘well, when you’re in grad school you don’t get a life.’ You know, yeah, I get that, but that’s not really true, so I get a lot of those responses, ‘well, you know, welcome to the club.’
One participant stated that her site supervisor did not specifically address counselor burnout or self-care, stating “I think that is less addressed in a school setting than it is in the mental health field….I think that because we see such a small picture of our students, I think it is not as predominantly addressed.” Some participants, however, reported that their site supervisors indirectly addressed self-care by modeling positive behaviors. One participant stated:
[My site supervisor] has either structured her day or her life in such a way that no one cuts into that time unless she allows it. In that sense, she’s great at modeling what’s important…She just made a choice….She was protective. She made her priorities. Her family was a priority. Her walk was a priority, getting a little activity. Other things, house chores, may have fallen by the wayside. She had a good sense of priorities, I thought. That was good to watch.
In summary, participants reported that counselor burnout and self-care were not directly addressed in site supervision. Indeed, some participants felt a lack of support when feeling overwhelmed by counseling duties, and that school sites may address burnout and self-care less than at mental health sites. At best, self-care was indirectly modeled by site supervisors with positive coping mechanisms.
Improvements for Counselor Supervision and Training
Improvements for counselor supervision. More than half of the participants reported wanting more understanding and empathy from their supervisors. One participant complained:
A lot of my class mates have a lot on their plates, like I do, and our supervisors don’t have as much on their plate as we do. And it seems like they don’t quite get where we are coming from. They are not balancing all the things that we are balancing….a lot of the responses you get demonstrate their lack of understanding.
Another participant suggested:
I think just hearing what the person is saying. If the person is saying, I need a break, just the flexibility. Not to expect miracles, and just remember how it felt when you were in training. Just be relatable to the supervisees and try to understand what they are going through, and their point of view. You don’t have to lower your expectations to understand where we’re at…and to be honest about your expectations…flexible, honest, and understanding. If [supervisors] are those three things, it’ll be great.
Participants also suggested having counselor burnout and self-care more thoroughly addressed in supervision, including more discussions on balancing personal and professional responsibilities, roles, and stressors. One participant explained:
What would be really helpful when the semester first begins is one-on-one time that is direct about ‘how are you approaching this internship in balance with the rest of your life?’ ‘What are any issues that it would be worthwhile for me to know about?’ How sweet for the supervisor to see you as a whole person. And then to put out the invitation: the door’s always open.
Improvements for counselor training programs. More than half of the participants wanted a comprehensive and developmentally appropriate approach to self-care interwoven throughout their counselor training, with actual practice of self-care skills rather than “face talk.” One participant commented:
Acknowledge the reality that a graduate-level program is going to be a challenge, talking about that on the front end….[faculty] can’t just say you need to have self-care and expect [students] to be able to take that to the next level if we don’t learn it in a graduate program….how much better would it be for us to have learned how to manage that while we were in our program and gotten practice and feedback about that, and then that is so important of a skill to transfer and teach to our clients.
Most of the participants suggested the inclusion of concrete approaches to counselor self-care. Participants provided examples such as preparing students for their work as counselors-in-training by giving them an overview of program expectations at the beginning of their programs, and providing students with self-care strategies to deal with the added stressors of graduate school such as handling administrative duties during internship, searching for employment prior to graduation, and preparing for comprehensive exams.
Discussion
Findings from this study highlight the importance of the role of supervision in promoting resilience as a protective factor against burnout among counselors-in-training. The majority of participants in this study perceived that they experienced some degree of burnout in their experiences as counselors-in-training. Participants’ perceptions of experiencing burnout are a particularly meaningful finding because it indicates that these counselors-in-training see themselves as over-taxed during their education and training. If, during their master’s programs, counselors-in-training are creating professional identities based on cognitive schemas for being a counselor, then perhaps these counselors-in-training have developed schemas for counseling that include a loss of compassion for clients, diminished enthusiasm for counseling, a lopsided balance of personal and professional responsibilities, and struggles to maintain boundaries. Counselors-in-training should be aware of these potential pitfalls as these counselors-in-training reported experiencing symptoms of burnout which were rarely addressed in supervision.
In contrast to recent literature, which suggests that counselor burnout is related to overcommitment to client outcomes (Kestnbaum, 1984; Leiter, 1991; Shovholt et al., 2001), many counselor trainees in this study did not perceive that their supervisors directly addressed their degree of personal commitment to their clients’ success in counseling. Similarly, emotional exhaustion is commonly identified as a potential hazard for burnout (Barnett et al., 2007); yet, few participants believed that their supervisors directly inquired about the degree of emotional investment in their clients. Finally, elusive measures of success in counseling are often indicated as a potential factor for burnout (Kestnbaum, 1984; Skovholt, et al., 2001). The vast majority of participants interviewed for this study did not perceive that these elusive measures of success were addressed in their supervision experiences. Supervisors who are interested in thwarting counselor burnout early in the training experiences of counselors may want to consider incorporating conversations about overcommitment to client outcomes, emotional exhaustion, degree of emotional investment, and elusive measures of success into their supervision with counselors-in-training. In an effort to promote more resilient schemas and expectations for counseling work, supervisors can take an active role in helping counselors-in-training understand the importance of awareness and protective factors to protect against a lack of compassion, enthusiasm, life-work balance, and professional boundaries, similar to the way a pilot is aware that a plane crash is possible and therefore employs purposeful and effective methods of prevention and protection.
Participants in this study conceptualized self-care as purposeful behavioral efforts. Proactive behavioral choices such as reaching out to support others are ways that many counselors engage in self-care. However, self-care cannot be solely limited to engagement in specific behaviors. Self-care also should include discussions about cognitive, emotional, and spiritual coping skills. Supervisors can help counselors-in-training create a personal framework for finding meaning in their work in order to promote hardiness, resilience, and the potential for transformation (Carswell, 2011). Because of the nature of counseling, it is necessary for counselors to be open and have the courage to be transformed. Growth and transformation are often perceived as scary and something to be avoided. Yet, growth and transformation can be embraced and understood as part of each counselor’s unique professional and personal process. Supervisors can normalize and validate these experiences and help counselors-in-training narrate their inspirations and incorporate their personal, spiritual, and philosophical frameworks in their counseling. In addition, supervisors can directly address misperceptions about counseling, which often include: “I can fix the problem,” “I am responsible for client outcomes,” “Caring more will make it better,” and “My clients will always appreciate me” (Carswell, 2011). While these approaches to supervision are personal in nature, counselors-in-training in this study reported an appreciation for time spent discussing how the personal informs the professional. This finding is consistent with Bernard & Goodyear’s (1998) model of supervision which emphasizes personal development as an essential part of supervision. Models for personal development in counselor education programs have been proposed by many professionals in the field of counseling (Myers, 1991; Myers & Williard, 2003; Witmer & Granello, 2005).
Counselors-in-training in this study reported an appreciation for supervision experiences in which their supervisors provided direct feedback and positive reinforcement. Counselors-in-training often experience performance anxiety and self-doubt (Aten et al., 2008). In an effort to diminish counselor-in-training anxiety, supervisors may provide additional structure and feedback in the early stages of supervision. Once the counselor-in-training becomes more secure, the supervisor may facilitate a supervisory relationship that promotes supervisee autonomy and higher-level thinking.
The majority of participants interviewed reported a desire for supervisors to place a greater emphasis on life-work balance and learning to cope with stress. These findings suggest the importance of counselor supervisors examining their level of expressed empathy and emphasis on preventive, as well as remedial, measures to ameliorate symptoms and stressors that lead to counselor burnout. Participants expressed a need to be more informed about additional stressors in graduate school such as administrative tasks in internship, preparing for comprehensive exams, and how to search for employment. These findings suggest the need for counselor educators and supervisors to examine how they indoctrinate counselors-in-training into training programs in order to help provide realistic expectations of work and personal sacrifice during graduate school and in the counseling field. Moreover, counselor educators and supervisors should strive to provide ongoing discussions on self-care throughout the program, specifically when students in internship are experiencing expanding roles between school, site placement, and searching for future employment. As mental health professionals, counselor educators and supervisors may also struggle with their own issues of burnout; thus, attentiveness to self-care also is recommended for those who teach and supervise counselors in training.
Limitations
Findings from this study will benefit counselor educators, supervisors, and counselors-in-training; however, some limitations exist. One limitation is the lack of diversity in the sample of participants. The majority of the participants identified as Caucasian females, which is representative of the high number of enrolled females in the counseling programs approached for this study. The purpose for this study, however, was not to generalize to all counselor trainees’ experiences, but rather to shed light on how counselor perceptions of burnout and self-care are being addressed, or not, in counselor supervision.
Participant bias and recall is a second limitation of this study. Recall is affected by a participant’s ability to describe events and may be influenced by emotions or misinterpretations. This limitation was addressed by triangulating sources, including a follow-up questionnaire, reinforcing internal stability with researcher consensus on domains, core ideas, and categories, and by using an auditor to evaluate analysis and prevent researcher biases.
Conclusion
Counselors should be holders of hope for their clients, but one cannot give away what one does not possess (Corey, 2000). Counselors who lack enthusiasm for their work and compassion for their clients are not only missing a critical element of their therapeutic work, but also may cause harm to their clients. Counseling is challenging and can tax even the most “well” counselors. A lack of life-work balance and boundaries can add to the already stressful nature of being a counselor. Discussions in supervision about the potential for emotional exhaustion, the counselor-in-training’s degree of emotional investment in client outcomes, elusive measures of success in counseling, coping skills for managing stress, meaning-making and sources of inspiration, and personalized self-care activities are several ways supervisors can promote counselor resilience and sustainability. Supervisors should discuss the definitions of burnout, how burnout is different from stress, how to identify early signs of burnout, and how to address burnout symptoms in order to promote wellness and prevent burnout in counselors-in-training. Counselor educators and supervisors have the privilege and responsibility of teaching counselors-in-training how to take care of themselves in addition to their clients.
References
Aten, J. D., Madson, M. B., Rice, A., & Chamberlain, A. K. (2008). Postdisaster supervision strategies for promoting supervisee self-care: Lessons learned from hurricane Katrina. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 2(2), 75–82. doi:10.1037/1931-3918.2.2.75
Barnett, J. E., Baker, E. K., Elman, N. S., & Schoener, G. R. (2007). In pursuit of wellness: The self-care imperative. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 38(6), 603–612. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.6.603
Bernard, J. M., & Goodyear, R. K. (1998). Fundamentals of clinical supervision (2nd ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) (2009). 2009 Standards. Retrieved from http://www.cacrep.org/ doc/2009%20standards %20with20cover.pdf
Canfield, J. (2005). Secondary traumatization, burnout, and vicarious traumatization: A review of the literature as it relates to therapists who treat trauma. Smith College Studies in Social Work, 75(2), 81–102. doi:10.1300 J497v75n02_06
Carswell, K. (2011, March). Lecture on combating compassion fatigue: Strategies for the long haul. Counseling Department, Western Carolina University, Cullowhee, NC.
Corey, G. (2000). Theory and practice of group counseling (5th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/Thompson Learning.
Hill, C. E., Knox, S., Thompson, S. J., Williams, E. N, Hess, S. A., & Ladany, N. (2005). Consensual qualitative research: An update. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 23(2), 196–205. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.52.2.196
Hill, C. E., Thompson, B. J., & Nutt Williams, E. (1997). A guide to conducting consensual qualitative research. The Counseling Psychologist, 25, 517–572. doi:10.1177/ 0011000097254001
Gilliland, B. E., & James, R. K. (2001). Crisis intervention strategies. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning.
Jenaro, C., Flores, N., & Arias, B. (2007). Burnout and coping in human service practitioners. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 38, 80–87. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.1.80
Koeske, G. F., & Kelly, T. (1995). The impact of overinvolvement on burnout and job satisfaction. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 65, 282–292. doi:10.1037/h0079622
Kestnbaum, J. D. (1984). Expectations for therapeutic growth: One factor in burnout. Social Casework: The Journal of Contemporary Social Work, 65, 374–377.
Leiter, M. (1991). The dream denied: Professional burnout and the constraints of human service organizations. Canadian Psychology, 32(4), 547–558. doi:10.1037/h0079040
Myers, J. E. (1991). Wellness as the paradigm for counseling and development. The possible future. Counselor Education and Supervision, 30, 183–193.
Myers, J. E., & Williard, K. (2003). Integrating spirituality into counselor preparation: A developmental, wellness approach. Counseling and Values, 47, 142–155.
Ponterotto, J. G. (2005). Qualitative research in counseling psychology: A primer on research paradigms and philosophy of science. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52(2), 126–136. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.52.2.196
Rosenberg, T., & Pace, M. (2006). Burnout among mental health professionals: Special considerations for the marriage and family therapist. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 32(1), 87–99. doi:10.1111/j.1752- 0606.2006.tb01590
Sherman, M. D. (1996). Distress and professional impairment due to mental health problems among psychotherapists. Clinical Psychology Review, 16, 299–315. doi:10.1016/0272- 7358(96)00016-5
Skovholt, T. M. (2001). The resilient practitioner: Burnout prevention and self-care strategies for counselors, therapists, teachers, and health professionals. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Skovolt, T. M., Grier, T. L., & Hanson, M. R. (2001). Career counseling for longevity: Self-care and burnout prevention strategies for counselor resilience. Journal of Career Development, 27(3), 167–176. doi:10.1177/089484530102700303
Truchot, D., Keirsebilck, L., & Meyer, S. (2000). Communal orientation may not buffer burnout. Psychological Reports, 86, 872–878. doi:10.2466/PR0.86.3.872-878
Witmer, J. M., & Granello, P. F. (2005). Wellness in counselor education and supervision. In J. E. Myers & T. J. Sweeney (Eds.), Counseling for wellness: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 342–361). Alexandria, VA: American Counseling Association.
E. Heather Thompson is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Counseling Western Carolina University. Melodie H. Frick is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Counseling at West Texas A & M University. Shannon Trice-Black is an Assistant Professor at the College of William and Mary. Correspondence can be addressed to Shannon Trice-Black, College of William and Mary, School of Education, PO Box 8795, Williamsburg, VA, 23187-8795, stblack@wm.edu.
Appendix A
Interview Protocol
1. What do you know about counselor burnout or how would you define counselor burnout?
2. What do you think are possible causes of counselor burnout?
3. As counselors we often are overloaded with administrative duties which may include treatment planning, session notes, and working on treatment teams. What has this experience been like for you?
4. Counseling requires a tremendous amount of empathy which can be emotionally exhausting. What are your experiences with empathy and emotional exhaustion? Can you give a specific example?
5. How do you distinguish between feeling tired and the early signs of burnout?
6. As counselors, we sometimes become overcommitted to clients who are not as ready, motivated, or willing to engage in the counseling process. Not all of our clients will succeed in the way that we want them to. How do you feel when your clients don’t grow in the way you want them to? How has this issue been addressed in supervision?
7. What is your perception of how your supervisors have dealt with stress?
8. How has counselor burnout been addressed in supervision?
prompt: asked about, evaluated, provided reading materials, and how often
9. How have specific issues related to burnout been addressed in supervision such as: (a) over-commitment to clients who seem less motivated to change, (b) emotional exhaustion, and (c) elusive measures of success?
10. How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor burnout?
prompt: asked about, evaluated, provided reading materials, modeled by supervisor
11. What do you know about self-care or how would you define self-care for counselors?
12. What are examples of self-care, specifically ones that you use as counselors-in-training?
13. How has counselor self-care been addressed in supervision?
14. Sometimes we have to say “no.” How would you characterize your ability to say “no?” What have you learned in supervision about setting personal and professional boundaries?
15. What, if any, discussions have you had in supervision about your social, emotional, spiritual, and/or physical wellbeing? What is a specific example?
16. How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor self-care?
prompt: asked about, provided reading materials, modeled by supervisor
17. How could your overall counselor training be improved in addressing counselor burnout and counselor self-care?
Appendix B
Follow-Up Questionnaire
How would you describe counselor burnout?
How has counselor burnout been addressed in supervision?
How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor burnout?
How would you describe self-care for counselors?
How has counselor self-care been addressed in supervision?
How could supervision be improved in addressing counselor self-care?
How could your overall counselor training be improved in addressing counselor burnout and counselor self-care?
Jul 2, 2014 | Article, Volume 4 - Issue 3
Saundra M. Tomlinson-Clarke, Colleen M. Georges
The 2013 publication of the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5) marked the reemergence of issues related to the appropriateness of diagnosis and the uses of the DSM-5 within the counseling profession. Concerns focus on the implications of the DSM-5 for counseling professionals whose professional identity is grounded in a prevention and wellness model, and the impact of the diagnostic process on counseling ethical practice. In this article, the authors explore the use of the DSM-5 in counseling training and practice. The authors also discuss integrating DSM-5 diagnosis into a counselor training framework while maintaining a wellness orientation. Multicultural and strength-based considerations are recommended when using the DSM-5 in counseling training and practice, while maintaining consistency with a philosophical orientation focused on development and wellness and delivering services that are indicative of a unified counseling professional identity.
Keywords: diagnosis, DSM-5, strengths, wellness, counselor training, multicultural
The history of the counseling profession dates back to the vocational guidance movement of the early 1900s. As society became increasingly industrialized, a need arose to improve individuals’ vocational choices (Whiteley, 1984). With a focus on helping people to resolve problems in living, the counseling profession has maintained an emphasis on growth, prevention and early intervention across the life span (Gladding, 2013). Counseling is defined as “a professional relationship that empowers diverse individuals, families, and groups to accomplish mental health, wellness, education, and career goals” (Kaplan, Tarvydas, & Gladding, 2013). According to Remley and Herlihy (2014), many problems and issues that people face are developmental in nature. A wellness orientation toward helping and help seeking and the use of holistic approaches to treatment distinguish professional counselors from other mental health professionals (Mellin, Hunt, & Nichols, 2011). A focus on normal development and positive lifestyles promotes counselor professional identity and unifies the counseling profession (Gale & Austin, 2003). Given its common historical roots of assisting individuals with educational, occupational and emotional well-being (Whiteley, 1984), the field of counseling psychology also “maintains a focus on facilitating personal and interpersonal functioning across the life span. . . [with] particular attention to emotional, social, vocational, educational, health-related, developmental, and organizational concerns” (Society of Counseling Psychology, American Psychological Association, Division 17, 2014). Therefore, counselors, counseling psychologists and counselor educators benefit from understanding the dynamics of human growth and development in developing responsive interventions for clients with mental health concerns (Ibrahim, 1991). Furthermore, in creating a shared vision for supporting counselors, services to clients and the counseling profession, “advocat[ing] for optimal human development by promoting prevention and wellness” was among the six critical themes identified at the Counselor Advocacy Leadership Conference (Kaplan & Gladding, 2011, p. 368).
With the publication of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association [APA], 2013), issues related to counselor professional identity, diagnosis and the use of the DSM-5 within the counseling profession have reemerged. Concerns focus on the implications of the DSM-5 for counseling professionals who advocate prevention and wellness, and the impact of the diagnostic process on counseling ethical practice (Kress, Hoffman, Adamson, & Eriksen, 2013). Also, multicultural and contextual considerations may be ignored when adhering to a medical model implied by the DSM system. Despite these criticisms, few models exist for integrating diagnosis using the DSM-5 into a wellness and prevention orientation, which is central to professional counseling training and practice. Our goal is to explore the use of the DSM-5 in counseling training and practice, and to suggest ways that DSM-5 diagnosis might be integrated into a counselor training framework while maintaining a wellness orientation.
DSM and Counseling Training
Distinguishing counseling from other mental health professions by a focus on human development, prevention and wellness does not exclude counseling professionals and trainees from acquiring an understanding of behavior across the adaptive-maladaptive continuum. In promoting a counselor professional identity, and reinforcing the consensus definition of professional counseling as empowering individuals, families and groups, teaching diagnosis using the DSM-5 to counseling trainees requires a cultural and contextual understanding of individuals and their concerns. Providing counseling trainees with learning experiences designed to foster knowledge and skills extends beyond exposure to the DSM-5 classification systems for categorizing behavior identified as disordered. Successfully integrating knowledge, skills and practices of diagnosis and the DSM-5 into counselor education involves a review of counselor common core curricular and professional practice (Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs [CACREP], 2009).
In the requirements for common core curricular experiences and demonstrated knowledge, CACREP (2009) requires that all counseling trainees learn about “the nature and needs of persons at all developmental levels and in multicultural contexts” (II.G.3, p. 10), including “theories for facilitating optimal development and wellness over the life span” (II.G.3.h, p. 10) and about “human behavior, including an understanding of developmental crises, disability, psychopathology, and situational and environmental factors that affect both normal and abnormal behavior” (II.G.3.f, p. 10). Furthermore, the standards for Addiction Counseling and Clinical Mental Health Counseling specifically require demonstrated “professional knowledge, skills, and practices” (CACREP, 2009, III, p. 17; p. 29), use of the current DSM and use of other diagnostic tools. Therefore, in addition to common core curricular experiences that develop knowledge and skills needed for “facilitating optimal development and wellness over the life span” (CACREP, 2009, II.G.3.h, p. 10), professional counselors must have diagnostic knowledge, skills and practices. This includes understanding “etiology, the diagnostic process and nomenclature, treatment, referral, and prevention of mental and emotional disorders” (CACREP, 2009, III.C.2, p. 30) and “the range of mental health service delivery” (III.C.5, p. 30). Specifically, CACREP (2009) standards require that counseling trainees must evidence knowledge, relevant skills and practices that include the following: knowledge of the use of the current edition of the DSM (i.e., DSM-5), an understanding of possible biases that might occur when using diagnostic tools with culturally diverse clients, knowledge of the correct use of diagnosis during a traumatic event, and the ability to differentiate “between diagnosis and developmentally appropriate reactions” to traumatic events (CACREP, 2009, III.L.3, p. 34). Moreover, in demonstrating knowledge, skills and practices of the diagnostic process, counseling trainees must understand the implications of diagnosis and treatment interventions. To this end, Kress et al. (2013) stressed the importance of weighing both the benefits and risks of diagnosis when working with clients.
DSM-5 and Counseling Practice
Despite goals of revising the diagnostic classification scheme to make it “more clinically valuable and more biologically valid” (Nemeroff et al., 2013, p. 2), and of acknowledging cultural variations in clients’ expressions of their concerns (Brown & Lewis-Fernández, 2011), the DSM-5 has been criticized from within and beyond the psychiatric community. Released in May 2013, the DSM-5 was met with controversy from mental health professionals and organizations representing their interest in providing effective clinical mental health services to clients (Washburn, 2013). Many viewed the DSM-5 as an extension of the traditional medical model of diagnosis. For example, Ladd (2013) criticized DSM diagnosis for (1) ignoring the therapeutic alliance as a critical aspect of treatment; (2) depending on “statistically acquired symptoms” and “specific rules and timelines” created by Task Force/Work Group professional experts (p. 2); and (3) gearing its usefulness toward “insurance companies, managed care agencies and other professionals in the health care system” (p. 3). The American Mental Health Counselors Association (AMHCA) DSM-5 Task Force (2012), among other groups, submitted feedback to improve the DSM-5 draft. Although the DSM provides a common language for presenting client problems (Hinkle, 1999), the language and assumptions associated with the criteria for diagnosis became the focus of criticism. Stressing the important distinction of “separating the art of mental health diagnosis and complying with the mental health diagnosis business,” Ladd (2013, p. 3) described the DSM as “the diagnostic instrument for the ‘mental health diagnosis business’ with categories and labels used as the language for insurance reimbursement, pharmaceutical treatment, and collaboration between experts” (p. 3).
Due to a growing need for quality mental health services, counseling professionals are providing services to clients presenting with a diverse range of concerns. Counselors are often required to diagnose clients’ problems using the DSM-5 (Miller & Prosek, 2013). DSM diagnosis is necessary for counselors to access managed care and insurance company reimbursements (Hinkle, 1999). However, a traditional use of the DSM may pathologize behavior and separate diagnosis from treatment interventions (Ivey & Ivey, 1999). Counselors faced with these ethical dilemmas may question their professional identity, the usefulness of a wellness orientation and the effectiveness of counseling-related tasks (McAuliffe & Eriksen, 1999; Mellin et al., 2011). Counselors’ challenge to adhere to a wellness orientation as the foundation of their professional identity may be further tested by other mental health professionals’ tendency to conceptualize health and illness using models of pathology and remediation (McAuliffe & Eriksen, 1999). These dilemmas in counseling practice are more likely to become problematic when counselors are not grounded in a strong professional identity. Gale and Austin (2003) encouraged counselors to embrace a wellness model rather than an illness or deficit model of help seeking and treatment planning. Counselor clinical judgment is critical to the diagnostic process. Notwithstanding criticisms of the DSM, Johnson (2013) asserted that diagnosis is directly related to the philosophical and theoretical orientations of the clinician. The medical model used in diagnosis negatively impacts clients’ willingness to seek help for their concerns, and also influences mental health professionals’ orientations toward deficit models (McAuliffe & Eriksen, 1999).
Important considerations for teaching the DSM are directly related to understanding the diagnostic process and implications for models of helping used to conceptualize counseling goals and interventions with clients. Given the focus on prevention, wellness and health across the life span, key questions arise when teaching the DSM-5 to counseling trainees from a traditional medical model that is “focused disproportionately on the physical aspects of illness” (Ingersoll, 2002, p. 115). A traditional disease model views the helper as the expert responsible for healing the client (McAuliffe & Eriksen, 1999). Brickman et al. (1982) viewed this model of helping as deficient in that the helper fosters dependency, which is antithetical to an empowering therapeutic relationship. Teaching the DSM-5 to counseling students requires an understanding of a developmental and wellness orientation. Models of helping must be philosophically and theoretically congruent with a professional counseling identity. To this end, counseling trainees must be challenged to examine their beliefs about seeking help and their view of a helper in the counseling relationship. Diagnosis and treatment should not be separate; rather, diagnosis should occur in conjunction with treatment (Ivey & Ivey, 1999). Viewing clients from a holistic perspective assumes that the greatest source of information lies within the client, not a manual or system of classifying disorders. Focusing on clients’ strengths rather than deficiencies helps to empower clients as part of their learning and development. Integrating multicultural and strength-based considerations as part of the diagnostic process helps to ensure that clients receive culturally responsive counseling interventions.
Integrating Multicultural and Strength-Based Considerations
Counselors, counseling psychologists and counselor educators have been instrumental in recognizing the role of culture and integrating multicultural perspectives in an attempt to understand behavior more fully (Pedersen, 1991; Sue, Sue, Sue, & Sue, 2014). Although racial-ethnic minority groups remained underrepresented in research examining psychopathology, African-American and Hispanic or Latino clients are more likely to be diagnosed, to receive diagnoses of greater severity and to experience less effective treatment outcomes than are White clients (Johnson, 2013; Sue & Sue, 2013). Consequently, multicultural counselor competencies are necessary to address counselors’ culturally biased assumptions and to increase counseling effectiveness in a society changing in culture and diversity (Arredondo et al., 1996; Pedersen, 1987, 2003; Sue, Arredondo, & McDavis, 1992; Sue et al., 1982; Sue & Sue, 2013). Multiculturalism integrates culturally specific and universal perspectives in explaining the dynamics of behavior and developing culturally responsive approaches to treatment. However, counselors may ignore multicultural considerations when adhering to a medical model implied by the DSM. Ivey and Ivey (1999) called on counseling professionals to apply multicultural perspectives when using the DSM. In advancing a contextual understanding of behavior and disorders, Sue et al. (2014) developed a multipath model using four dimensions (i.e., biological, psychological, social and sociocultural) to describe etiological explanations of abnormal behavior.
Social, cultural and economic considerations must be acknowledged when attempting to identify and classify behavior diagnosed as maladaptive. Sue et al. (2014) distinguished cultural universality from cultural relativity in describing behavior within a sociocultural context. Important cultural nuances may be misunderstood when viewed by others who are culturally dissimilar. The result is the labeling of culturally normal behavior as maladaptive. To this end, myths associated with abnormal behavior have led to the social construction of diagnostic categories, which have been cited as major criticisms of using the DSM. Among these faulty assumptions is the belief that abnormal behavior can be readily recognized, distinguished from normal behavior and therefore categorized according to a diagnostic classification scheme (Maddux, 2002; Sue et al., 2014). Maddux (2002) further stated that diagnostic categories used in making biased clinical judgments lead to culturally unresponsive treatment interventions. Inherent in this approach is the basis of the medical model, in which clients are more often treated for pathological behavior (McAuliffe & Eriksen, 1999).
A step toward more holistic diagnostic practices appeared in the DSM-5 in the form of dimensional rather than categorical assessments. These dimensional assessments of every categorical diagnosis were designed to assist counselors with diagnosis and treatment planning (Jones, 2012). Unlike previous versions of the DSM that used a categorical system, dimensional assessments view disorders on a continuum, representing varying degrees of a behavior (Sue et al., 2014). The dimensional assessment also allows counselors to consider individual differences and the influences of race and culture (Johnson, 2013). With the dimensional model, counselors are able to determine whether a diagnostic criterion is present and rate its severity (Brown & Lewis-Fernández, 2011). Viewing disorders on a continuum of behavior may decrease comorbidity; however, it also may affect clients’ accessibility to services by eliminating clients who might have formerly met the criteria for diagnosis or diagnosing clients with a disorder that would have been excluded based on the former criteria. Examples include autism spectrum disorder and depression resulting from bereavement, respectively. Given these changes, the effect of the DSM-5 on diagnosis may impact clients’ access to mental health services and create ethical dilemmas for counselors related to over- and undertreatment.
In addition to the dimensional assessments, the DSM-5 also contains disorders associated with cultural issues. Psychosocial factors are included by using V codes from the World Health Organization’s (WHO) International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM; WHO, 1979) and Z codes from the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10; WHO,1992), as well as three new terms: cultural syndrome, cultural idiom of distress and cultural explanation or perceived cause (Pomeroy & Anderson, 2013). Counselors must become familiar with the ICD-10-CM diagnostic codes, which will become the standard medical coding system in the United States beginning October 1, 2015. Inclusion of psychosocial factors evidences the relationship between psychosocial factors and mental health. Multicultural considerations in diagnosis allow mental health practitioners to understand cultural and individual characteristics that define identity and experience. These characteristics of a client’s identity are multiple and interlocking. The uniqueness that defines a client may be lost if group generalizations as represented by the DSM-5 are used as the only means of understanding a client’s experiences. Critical to understanding clients and their stories is the ability to conceptualize clients as individuals interacting within the sociocultural context in which they live. This also involves hearing clients’ stories from their perspective, using their own words.
The importance of cultural influences on mental health diagnosis also is demonstrated by the inclusion of the Cultural Formulation Interview (CFI; Pomeroy & Anderson, 2013). The CFI was developed to improve cross-cultural diagnostic assessment and was created from the Outline for Cultural Formulation (OCF) of the DSM-IV (Aggarwal, Nicasio, DeSilva, Boiler, & Lewis-Fernández, 2013). In keeping with multicultural competency models, the CFI provides a way for counselors to explore and understand clients’ experiences and worldviews, as well as clients’ cultural explanations and interpretations of their concerns. However, Aggarwal et al. (2013) cautioned that the overstandardization of the CFI may result in counselor and client barriers such as the following: a counselor misunderstanding the problem and the problem severity, a lack of conceptual relevance between the client’s concern and counseling interventions, and a counselor and client’s lack of acceptance and unwillingness to engage in the process. Counselors’ ability to develop authentic and caring relationships is essential to accurate diagnosis and relevant counseling interventions. When clients are viewed as unique and counselors understand their experiences, accurate diagnosis and ethical practice are ensured (Swartz-Kulstad & Martin, 1999).
Moving beyond an illness model toward a counselor-client collaborative wellness model begins with a process of engaging with the client, gathering the information needed for assessing the client and trusting in the therapeutic alliance to accomplish the goals of treatment (Ivey & Ivey, 1999). Contrary to the medical or illness model, in which the client’s weaknesses or deficiencies precipitate the diagnosis, treatment and policy decisions, the integration of a strength-based framework and counselor preparation ensures a holistic approach to assessment and treatment (Wright & Lopez, 2002). Working with clients from a holistic perspective requires knowledge and skills that preserve the integrity of the counseling profession by embracing multicultural and strength-based considerations. A framework adapted from positive psychology, defined as “the study of . . . what is ‘right’ about people––their positive attributes, psychological assets, and strengths” (Kobau et al., 2011, p. e1), assists in bolstering resilience and promoting mental health.
Strength-Based Approaches to Diagnosis
Character Strengths and Virtues
Character Strengths and Virtues: A Handbook and Classification (CSV; Peterson & Seligman, 2004), which its authors dub a “Manual of the Sanities” (p. 3) in the introductory chapter, was developed in part as a companion to the DSM that focuses on classifying what is right about people. It includes explicit criteria for character strengths and launched the development of several assessment tools that aid in diagnosing one’s strengths in the way that the DSM diagnoses one’s limitations. Character strengths are the foundation of strength-based approaches and provide a way to assess client functioning from a wellness orientation (O’Hanlon & Bertolino, 2012). The CSV distinguishes three conceptual levels: (1) virtues: core characteristics that moral and religious philosophers esteem; (2) character strengths: processes that define virtues; and (3) situational themes: practices that lead people to establish specific character strengths in certain situations.
Parallel to the DSM, the CSV outlines 10 specific criteria that must be satisfied to warrant inclusion as a character strength. Using these criteria, 24 character strengths were identified under the respective umbrellas of six core virtues: (1) wisdom and knowledge (creativity, curiosity, open-mindedness, love of learning, and perspective); (2) courage (bravery, persistence, integrity, and vitality); (3) humanity (love, kindness, and social intelligence); (4) justice (citizenship, fairness, and leadership); (5) temperance (forgiveness and mercy, humility and modesty, prudence, and self-regulation); and (6) transcendence (appreciation of beauty and excellence, gratitude, hope, humor, and spirituality). The CSV also broadly outlines strength assessment strategies, as well as interventions that further cultivate strengths. For example, counselors might assist clients in realizing or reaffirming their virtue of strength of courage by exploring the will to achieve goals while facing external or internal opposition (O’Hanlon & Bertolino, 2012). This exercise empowers clients and provides counselors with a positive rather than a negative assessment of client behavior. Similarly, the use of positive talk moves clients away from a perspective of deficiency and illness toward encouragement and motivation for change.
Using the CSV in conjunction with the DSM enables counselors to help their clients identify, take pride in and use their character strengths and virtues to enhance well-being in all areas of their lives. Gander, Proyer, Ruch and Wyss (2013) found that using one’s signature strengths in a different way lowered depression and boosted happiness for six months. Wood, Linley, Matlby, Kashdan and Hurling’s (2011) longitudinal study determined that using one’s strengths was correlated with well-being; decreased stress; and greater self-esteem, positive affect and vitality, with the effects still present at three-month and six-month follow-ups. Furthermore, the majority of positive counseling interventions focus on character strength interventions, which have been found to benefit both adults and children dealing with depression and anxiety (Rashid & Anjum, 2008; Seligman, Rashid, & Parks, 2006).
Client diagnosis and conceptualization using the DSM-5 may be incomplete if clinicians do not consider clients’ environmental resources, well-being and strengths (Snyder et al., 2003). Minor alterations to this diagnostic system could promote emphasis on positive functioning and provide information that could contribute to a more complete client picture and conceptualization. Recommendations for rescaling the Axis V Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) Scale of the DSM-IV-TR included creating a functioning baseline, with the current GAF level of 100 (absence of symptomatology) rescaled to a midpoint of 50. This would have encouraged practitioners to identify and use client strengths, with a GAF of 1 representing severely impaired functioning, 50 representing good health and 100 representing optimal functioning. Snyder et al. (2003) also suggested adding personal strengths and growth facilitators through three brief questions and four positive psychology assessments that measure hope, optimism, personal growth initiative and subjective well-being. Similarly, Magyar-Moe (2009) suggested using a seven-axis system of positive psychological assessment that included documenting positive and negative aspects of clients’ cultural identities, as well as clients’ personal strengths as facilitators of growth.
These exercises, based in positive well-being, are consistent with a wellness orientation of helping and should not be solely limited to clients’ growth and development. Counseling trainees and professional counselors benefit personally and professionally when functioning from a strength-based orientation. For example, based on findings from attribution theory, negative labels affect motivation for change (O’Hanlon & Bertolino, 2012). Therefore, O’Hanlon and Bertolino cautioned against using negative diagnostic labels that may communicate a belief that clients are unable to change. From this perspective, counselors must continually examine their own behavior and the subtle messages that clients might receive during counseling. Through strength-based exercises, counselors are encouraged to promote strengths and resilience as part of an ongoing reflective practice.
Conclusion
Teaching the process of diagnosis using the DSM-5 to counseling trainees is not an easy undertaking. Developed as a tool that promotes a language for use in the larger mental health system (Hinkle, 1999), the DSM is required learning for counseling trainees, and demonstrating professional knowledge, skills and practices is required for professional counselors. Teaching the basic vocabulary and criteria associated with disorders is only the first level of discussion. Effectively teaching diagnosis informed by multicultural and strength-based perspectives includes acknowledging the purpose and limitations of the DSM-5, and examining beliefs about helping, and the role and behavior of helpers. Counselors must explore the concept of normal behavior and their ability to identify abnormal behavior, as well as factors influencing growth and change.
Peterson (2013) stated, “we have developed a wonderful vocabulary that explains what goes wrong with folks and we have almost nothing to say about what can go right with folks” (p. 7). Teaching diagnosis and the DSM-5 integrated with multicultural and strength-based considerations helps counselors to understand what goes right with clients. Through this understanding, clients’ strengths, character and virtues become the support for growth and change within the counseling relationship. Rather than focusing on illness and deficiencies, counselors and clients acknowledge strengths and use them to assist clients in resolving problems in life. Informing the diagnostic process with multicultural and strength-based considerations fosters a holistic view of clients and reinforces counselor advocacy of optimal human functioning. Counselors must consider culture, context and strengths for the diagnostic process to be useful in working with clients from a wellness orientation (Adams & Quartiroli, 2010).
Furthermore, multicultural and strength-based practice considerations encourage reflection and counselor reflective practice, which challenge culturally biased assumptions that negatively affect counselor judgments about clients and the diagnostic process. As a result, counseling professionals do not view clients as confined and limited to a diagnosis; rather, they conceptualize clients as resilient and evolving (Adams & Quartiroli, 2010). Recognizing limitations and possibilities of the DSM-5, embracing a wellness and holistic orientation, and understanding clients from their cultural and situational contexts with a focus on strengths are critical factors that reduce ethical dilemmas and support the use of the DSM-5 in counseling training and practice (Adams & Quartiroli, 2010; Gale & Austin, 2003; McAuliffe & Eriksen, 1999). Integrating multicultural and strength-based considerations into counseling training and practice increases the likelihood that counselors will embrace a professional identity congruent with a wellness orientation when using the DSM-5 as a tool in the diagnostic process (Mannarino, Loughran, & Hamilton, 2007).
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The author reported no conflict of interest or funding contributions for the development of this manuscript.
References
Adams, J. R., & Quartiroli, A. (2010). Critical considerations of the diagnostic and statistical manual: Importance of the inclusion of cultural and contextual factors. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 49, 84–97. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1939.2010.tb00089.x
Aggarwal, N. K., Nicasio, A. V., DeSilva, R., Boiler, M., & Lewis-Fernández, R. (2013). Barriers to implementing the DSM-5 Cultural Formulation Interview: A qualitative study. Culture, Medicine, and Psychiatry, 37, 505–533. doi:10.1007/s11013-013-9325-z
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Arredondo, P., Toporek, R., Pack Brown, S., Jones, J., Locke, D. C., Sanchez, J., & Stadler, H. (1996). Operationalization of the multicultural counseling competencies. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 24, 42–78. doi:10.1002/j.2161-1912.1996.tb00288.x
Brickman, P., Rabinowitz, V. C., Karuza, J., Jr., Coates, D., Cohn, E., & Kidder, L. (1982). Models of helping and coping. American Psychologist, 37, 368–384.
Brown, R. J., & Lewis-Fernández, R. (2011). Culture and conversion disorder: Implications for the DSM-5. Psychiatry, 74, 187–206. doi:10.1521/psyc.2011.74.3.187
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2009). 2009 CACREP standards. Alexandria, VA: Author.
Gale, A. U., & Austin, B. D. (2003). Professionalism’s challenges to professional counselors’ collective identity. Journal of Counseling & Development, 81, 3–10. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2003.tb00219.x
Gander, F., Proyer, R. T., Ruch, W., & Wyss, T. (2013). Strength-based positive interventions: Further evidence for their potential in enhancing well-being and alleviating depression. Journal of Happiness Studies, 14, 1241–1259. doi:10.1007/s10902-012-9380-0
Gladding, S. T. (2013). Counseling: A comprehensive profession (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Hinkle, J. S. (1999). A voice from the trenches: A reaction to Ivey and Ivey (1998). Journal of Counseling & Development, 77, 474–483. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1999.tb02475.x
Ibrahim, F.A. (1991). Contribution of cultural worldview to generic counseling and development. Journal of Counseling & Development, 70, 13–19. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1991.tb01556.x
Ingersoll, R. E. (2002). An integral approach for teaching and practicing diagnosis. The Journal of Transpersonal Psychology, 34, 115–127.
Ivey, A. E., & Ivey, M. B. (1999). Toward a developmental diagnostic and statistical manual: The vitality of a contextual framework. Journal of Counseling & Development, 77, 484–490. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1999.tb02476.x
Johnson, R. (2013). Forensic and culturally responsive approach for the DSM-5: Just the FACTS. The Journal of Theory Construction & Testing, 17, 18–22.
Jones, K. D. (2012). Dimensional and cross-cutting assessment in the DSM-5. Journal of Counseling & Development, 90, 481–487. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2012.00059.x
Kaplan, D. M., & Gladding, S. T. (2011). A vision for the future of counseling: The 20/20 Principles for Unifying and Strengthening the Profession. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 367–372.
Kaplan, D. M., Tarvydas, V. M., & Gladding, S. T. (2013). 20/20: A vision for the future of counseling: The new consensus definition of counseling. Retrieved from http://www.counseling.org/docs/david-kaplan’s-files/consensus-definition-of-counseling.docx?sfvrsn=2
Kobau, R., Seligman, M. E. P., Peterson, C., Diener, E., Zack, M. M., Chapman, D., & Thompson, W. (2011). Mental health promotion in public health: Perspectives and strategies from positive psychology. American Journal of Public Health, 101, e1–e9. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2010.300083
Kress, V. E., Hoffman, R. M., Adamson, N., & Eriksen, K. (2013). Informed consent, confidentiality, and diagnosing: Ethical guidelines for counselor practice. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 35, 15–28.
Ladd, P. D. (2013). Knowledge vs. wisdom in DSM diagnosis: A person-centered perspective. In Ideas and research you can use: VISTAS 2013. Retrieved from http://www.counselingoutfitters.com/vistas/vistas13/Article_6.pdf
Maddux, J. E. (2002). Stopping the “madness”: Positive psychology and the deconstruction of the illness ideology and the DSM. In C. R. Snyder & S. J. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of Positive Psychology (pp.13–25). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Magyar-Moe, J. L. (2009). Therapist’s guide to positive psychological interventions. San Diego, CA: Elsevier Academic Press.
Mannarino, M. B., Loughran, M. J., & Hamilton, D. (2007, October). The professional counselor and the diagnostic process: Challenges and opportunities for education and training. Paper based on a program presented at the conference of the Association for Counselor Education and Supervision, Columbus, OH.
McAuliffe, G. J., & Eriksen, K. P. (1999). Toward a constructivist and developmental identity for the counseling profession: The context-phase-stage-style model. Journal of Counseling & Development, 77, 267–280. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1999.tb02450.x
Mellin, E. A., Hunt, B., & Nichols, L. M. (2011). Counselor professional identity: Findings and implications for counseling and interprofessional collaboration. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 140–147. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00071.x
Miller, R., & Prosek, E. A. (2013). Trends and implications of proposed changes to the DSM-5 for vulnerable populations. Journal of Counseling & Development, 91, 359–366. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2013.00106.x
Moss, J. M., Gibson, D. M., & Dollarhide, C. T. (2014). Professional identity development: A grounded theory of transformational tasks of counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 92, 3–12. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2014.00124.x
Nemeroff, C. B., Weinberger, D., Rutter, M., MacMillan, H. L., Bryant, R. A., Wessely, S., . . . Lysaker, P. (2013). DSM-5: A collection of psychiatrist views on the changes, controversies, and future directions. BMC Medicine, 11, 1–19. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-202
O’Hanlon, B., & Bertolino, B. (2012). The therapist’s notebook on positive psychology: Activities, exercises, and handouts. New York, NY: Routledge.
Pedersen, P. (1987). Ten frequent assumptions of cultural bias in counseling. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 15, 16–24.
Pedersen, P. B. (1991). Multiculturalism as a generic approach to counseling. Journal of Counseling & Development, 70, 6–12. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1991.tb01555.x
Pedersen, P. B. (2003). Culturally biased assumptions in counseling psychology. The Counseling Psychologist, 31, 396–403. doi:10.1177/0011000003031004002
Peterson, C. (2013). The strengths revolution: A positive psychology perspective. Reclaiming Children and Youth, 21, 7–14.
Peterson, C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Character strengths and virtues: A handbook and classification. New York, NY: Oxford University Press and Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Pomeroy, E. C., & Anderson, K. (2013). The DSM-5 has arrived. Social Work, 58, 197–200. doi:10.1093/sw/swt028
Rashid, T., & Anjum, A. (2008). Positive psychotherapy for young adults and children. In J. R. Z. Abela & B. L. Hankin (Eds.), Handbook of depression in children and adolescents (pp. 250–287). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Remley, T. P., Jr., & Herlihy, B. P. (2014). Ethical, legal, and professional issues in counseling (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Seligman, M. E. P, Rashid, T., & Parks, A. C. (2006). Positive psychotherapy. American Psychologist, 61, 774–788. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.61.8.774
Snyder, C. R., Lopez, S. J., Edwards, L. M., Pedrotti, J. T., Prosser, E. C., Walton, S. L., . . . Ulven, J. C. (2003). Measuring and labeling the positive and the negative. In S. J. Lopez & C. R. Snyder (Eds.), Positive psychological assessment: A handbook of models and measures (pp. 21–39). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Society of Counseling Psychology, American Psychological Association, Division 17. (2014). What is Counseling Psychology. Retrieved from http://www.div17.org/about/what-is-counseling-psychology/
Sue, D. W., Arredondo, P., & McDavis, R. J. (l992). Multicultural competencies and standards: A call to the profession. Journal of Counseling & Development, 70, 477–486. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1992.tb01642.x
Sue, D. W., Bernier, J. E., Durran, A., Feinberg, L., Pedersen, P., Smith E. J., & Vasquez-Nuttall, E. (1982). Position paper: Cross-cultural counseling competencies. The Counseling Psychologist, 10, 45–52. doi:10.1177/0011000082102008
Sue, D. W., & Sue, D. (2013). Counseling the culturally diverse: Theory and practice (6th ed.). New York, NY: Wiley & Sons.
Sue, D., Sue, D. W., Sue, D., & Sue, S. (2014). Essentials of understanding abnormal behavior (2nd ed.). Belmont, CA: Cengage Learning.
Swartz-Kulstad, J. L., & Martin, W. E. (1999). Impact of culture and context on psychosocial adaptation: The cultural and contextual guide process. Journal of Counseling & Development, 77, 281–293. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.1999.tb02451.x
Washburn, M. (2013). Five things social workers should know about the DSM-5. Social Work, 58, 373–376. doi:10.1093/sw/swt030
Whiteley, J. M. (1984). A historical perspective on the development of counseling psychology as a profession. In S. D. Brown & R. W. Lent (Eds.), Handbook of counseling psychology (pp. 3–55). New York, NY: Wiley and Sons.
Wood, A. M., Linley, P. A., Maltby, J., Kashdan, T. B., & Hurling, R. (2011). Using personal and psychological strengths leads to increases in well-being over time: A longitudinal study and the development of the strengths use questionnaire. Personality and Individual Differences, 50, 15–19. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2010.08.004
World Health Organization. (1979). International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, clinical modification (9th rev.). Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
World Health Organization. (1992). International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems (10th rev.). Geneva, Switzerland: Author.
Wright, B. A., & Lopez, S. J. (2002). Widening the diagnostic focus: A case for including human strengths and environmental resources. In C. R. Snyder & S. J. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of Positive Psychology (pp. 26–44). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Saundra M. Tomlinson-Clarke is an Associate Professor at Rutgers University. Colleen M. Georges is an Adjunct Professor at Rutgers University. Correspondence can be addressed to Saundra Tomlinson-Clarke, 10 Seminary Place, New Brunswick, NJ 08901-1183, saundra.tomlinson-clarke@gse.rutgers.edu.


