Sep 28, 2018 | Volume 8 - Issue 3
Anthony Hartman, Hope Schuermann, Jovanna Kenney
Despite efforts to boost mental health treatment-seeking behaviors by combat veterans, rates have improved relatively little since 2004. Previous work suggests that trust and confidence in the mental health community may be a significant factor. This study explored how professional titles may impact trust and confidence among active-duty U.S. Army soldiers (n = 32). Consistent with previous research, eight vignettes were used to solicit ordinal (ranked) trust and confidence scores for mental health professionals. Highest confidence and trust were seen in clinical psychologists and licensed professional counselors, followed by psychiatrists, licensed clinical social workers, and marriage and family therapists; however, deviations were seen for each individual vignette and the manifested symptoms depicted. Scores for trust and confidence were strongly correlated and both appear to impact soldiers’ treatment-seeking decisions.
Keywords: soldiers, mental health professionals, licensed professional counselors, trust, confidence
The U.S. Army Medical Command’s Department of Behavioral Health provides the following vision: “Our efforts in education, prevention, and early treatment are unprecedented. Our goal is to ensure that every deployed and returning soldier receives the health care they need” (U.S. Army Medical Department, 2016). In 2004, a landmark study by Hoge and colleagues found that only 13–27% of soldiers meeting screening criteria for mental health disorders sought treatment from a mental health professional in the previous year. The researchers concluded that the primary reason for such underutilization was perhaps “concern about how a soldier will be perceived by peers and by the leadership” (Hoge et al., 2004, p. 20). Subsequently, the Army has taken significant actions to reduce negative perceptions toward mental health care and increase confidentiality for those seeking treatment.
Despite substantial efforts to reduce negative stigmas, the number of soldiers seeking mental health care seems to remain significantly low. In a population of soldiers with probable post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or major depression, Schell and Marshall (2008) found that “only 30 percent had received any type of minimally adequate treatment” (p. 101). Specifically, only 18% received minimally adequate talk therapy treatment. Of a sample population of National Guard and Reserve service members reporting psychological problems, Britt et al. (2011) found that only 42% had sought treatment. Most recently, Britt, Jennings, Cheung, Pury, and Zinzow (2015) found that only 40% of soldiers who acknowledged having a mental health issue sought treatment in the last year. Although the percentages of soldiers seeking treatment seem to be improving, the current literature continues to show less than half of those in need seek even a first visit with a mental health care provider. Thus, other significant deterrents to seeking treatment remain beyond the perceptions of leadership and peers.
Research studies indicate that one possible reason for this underutilization of mental health care services could be soldiers’ lack of trust or confidence in the quality of their providers or treatments. When surveyed, one in four soldiers recently returning from deployment indicated a lack of trust in mental health care practitioners (Kim, Britt, Klocko, Riviere, & Adler, 2011). Similarly, in a different sample of soldiers and Marines screening positively for mental health disorders, 38% indicated a lack of trust in mental health providers, while one in four of the same sample indicated a belief that mental health treatments were not effective (Hoge et al., 2004). Further hinting at a lack of trust for mental health care professionals and confidence in treatment, many soldiers would prefer to address their mental health issues with family, friends, or clergy (Schell & Marshall, 2008). Recently, the statement “Marines don’t trust mental health professionals” was rated as one of the top perceptions that mark barriers to care by a sample of enlisted Marine Corps leaders (VanSickle et al., 2016, p. 1022). Ultimately, there seems to be a trend of distrust and a lack of confidence in mental health care treatments and professionals among military populations.
Mental Health Practitioners and Military Treatment
Considering that there are numerous types of mental health professionals (e.g., psychiatrists, mental health counselors), it is possible that soldiers’ perceptions and knowledge of mental health professionals may vary depending on the specific type of provider. This study aims to distinguish soldiers’ perceptions between distinct mental health professionals: psychiatrists, clinical psychologists, licensed clinical social workers (LCSWs), licensed marriage and family therapists (LMFTs), and licensed professional counselors (LPCs). Psychiatrists are distinct in that they must have earned a doctorate in medicine (i.e., MD or DO) and have the nearly exclusive privilege of prescribing pharmaceutical medications for the treatment of mental disorders. Clinical psychologists also must be educated at the doctoral level (i.e., PhD or PsyD) and maintain a licensure in order to practice, but they cannot prescribe medications in most states. LCSWs, LMFTs, and LPCs are educated at least at the master’s level by an institution accredited for their respective field, and must complete respective licensing requirements that include supervised clinical experience following degree completion.
While the educational experience and licensing protocol can easily be distinguished, the mental health professions also have evolved somewhat distinct professional identities in terms of their approaches to mental health treatment. While psychiatrists are trained in various psychotherapeutic modalities, trends indicate the majority of current and future psychiatrists plan to rely more heavily on pharmacological treatments than on talk therapies (Clemens, Plakun, Lazar, & Mellman, 2014; Zisook et al., 2011). As for clinical psychologists, a review of 50 years of literature surrounding this occupation revealed trends around specializing in one particular aspect of the field (i.e., psychotherapy, assessment, research) and one or two treatment modalities (e.g., psychodynamic therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy), and a prevalence of cognitive therapies (Norcross & Karpiak, 2012). Generally speaking, LCSWs are likely to conduct therapy from a holistic approach that heavily considers the social impacts on a person while pursing social justice and equality agendas, such as helping underprivileged groups (Bradley, Maschi, O’Brien, Morgen, & Ward, 2012). While LMFTs are often exposed to or trained in a wide variety of therapeutic paradigms and techniques, they are likely to emphasize a collective rather than individual treatment approach, often marked by working with families and couples to identify and improve systemic or transactional issues between the members (Imber-Black, 2014). As LPCs’ professional identity continues to develop and stabilize (Mellin, Hunt, & Nichols, 2011; Reiner, Dobmeier, & Hernández, 2013), professional counselors train in a variety of treatment modalities and provide a variety of services in the mental health field, including “the diagnosis and treatment of mental and emotional disorders, including addictive disorders; psychoeducational techniques aimed at the prevention of such disorders; consultation to individuals, couples, families, groups, and organizations; and research into more effective therapeutic treatment modalities” (American Counseling Association, 2011, para. 4).
Although the average client may not know or fully understand the distinctions between mental health professionals, the literature suggests clients do exhibit some bias when selecting mental health professionals. Over the past 30 years, researchers have shown a consistent trend of professional titles or education levels impacting perceptions of mental health professionals. Warner and Bradley (1991) and Wollersheim and Walsh (1993) established that both perceptions of and confidence in mental health therapies were impacted by the title and education level of the mental health professional; generally, participants in these studies indicated a lack of confidence and knowledge about clinical psychologists and a preference for treatment from counselors. In a study examining public confidence in mental health professionals, Fall, Levitov, Jennings, and Eberts (2000) found significant differences in confidence based upon their title as well as their education level (i.e., master’s vs. doctoral level); participants mostly favored doctoral-level education and preferred counselors, except when presented with “serious psychiatric disorders” (p. 122). This study was repeated in 2005 with an African American sample that provided similar findings (Fall, Levitov, Anderson, & Clay, 2005). While specific attitudes and perceptions may have changed or evolved over the past three decades, these studies show that distinct perceptions or even biases toward professional titles do exist among civilian populations. This led the researchers to question if similar trends exist in military populations, which may be influencing the treatment-seeking decisions of service members.
To summarize, soldiers’ confidence in treatment for and trust in mental health professionals might be significantly impacting treatment-seeking decisions. In multiple studies, service members have repeatedly indicated relatively low levels of trust and confidence in mental health providers and treatments. Also, researchers have consistently shown that a professional title can impact patient or public perceptions with respect to general confidence in the professional’s abilities. To date, no known research is published on military members’ perceptions and levels of confidence or trust with differing mental health professionals. Thus, the purpose of this study was to explore soldiers’ relative levels of trust for and confidence in mental health professionals based solely upon their title and a presenting issue, in an effort to better understand what may be influencing treatment-seeking decisions among U.S. Army soldiers.
Method
The researchers for this study received approval from the Institutional Review Board of their university, and the survey was approved for distribution to active-duty soldiers by Army public affairs representatives. Sample size was determined by following similar confidence in mental health professional studies that used Friedman non-parametric tests (e.g., Fall et al., 2000; Fall et al., 2005). Participants were surveyed via the online metrics program Qualtrics, ensuring anonymity.
Participants
Active-duty soldiers serving in the U.S. Army were recruited using snowball sampling initiated by public affairs representatives at various Army installations. Each potential participant received a generalized email invitation that included an information sheet about the research and a link to complete an online survey. Participants were encouraged to forward the invitation to others who also met the inclusion criteria, which limited participation to those currently serving on active duty in the U.S. Army with more than 2 years of active-duty service or the National Guard/Army Reserve equivalent. Upon completion of the survey, participants were offered the opportunity to enroll in a raffle drawing to win one of two prizes: a $100 or a $50 gift card.
The sample included 32 active-duty soldiers, 26 males and six females, between the ages of 25 and 50 years (M = 33.3, SD = 7.0). Ethnic identities included 25 non-Hispanic Whites, two Hispanic or Latinos, one African American, one Filipino, one Native American, one White/Korean, and one White/Hispanic. Most of the participants (26) were married, while three were divorced and three had never married. Nearly two-thirds of the sample indicated current responsibility for children in their homes; there was an average of 1.85 children (SD = 1.5) reported by these 20 participants. Thirteen of the soldiers had seen at least one mental health professional (MHP) prior to completing the survey; respondents had seen all five MHPs included in this study. Participants were allowed to list multiple MHPs if applicable, and the MHPs were identified as follows: clinical psychologist, seven times; psychiatrist, five times; LPC, four times; LCSW, three times; LMFT, three times; and “other” or “unsure,”five times.
Regarding military experience, the sample included 18 officers, 11 non-commissioned officers, and three junior-enlisted (i.e., rank of E1–E4) soldiers. Twenty participants had a military occupational specialty (MOS) considered as Combat Arms in the U.S. Army. In the military, not all service members are equally likely to fight in combat; certain MOSs are combat-related while others are supportive in nature (e.g., administrative personnel, mechanics, logisticians). Of our 32 qualifying participants, we had a good mix of combat and non-combat MOSs. To the reader, this may seem to be either irrelevant or not particularly noteworthy information; however, this data can be quite important when forming conclusions about the study. On average, military service was 11.4 years (SD = 7.2), with 17 months (SD = 11.5) deployed to either Iraq or Afghanistan; only two participants had not been deployed to these countries. Seventy-five percent of the sample reported direct exposure to combat, and 59% reported having never seen an MHP for even one visit throughout their life.
Materials
Demographic questionnaire. In order to provide some description of the sample population, a demographics survey of 15 questions regarding age, sex, ethnicity, marital background, parental status, military rank, deployment and combat experience, and previous experience with mental health care providers was collected from participants. Most questions were multiple-choice but offered the options to not respond or provide a unique response if desired. The remaining questions were free-response.
Vignettes. Brief vignettes were used to depict the selected mental health diagnoses or mental health issues of eight fictional soldiers recently returning from a combat deployment. The vignettes were limited in length to approximately half of a standard printed page and were written with the goal of depicting diagnostic criteria in a manner that one might see them manifested by the soldier in the vignette. Authors specifically avoided using the exact clinical terms that an MHP may use while ensuring that enough diagnostic criteria were included to suggest the intended diagnoses may be warranted.
Each vignette was followed immediately by two questions. These questions asked the participant to rank the five MHPs in order according to the participant’s preference for (1) confidence in the MHPs in providing treatment for the soldier in the vignette, and (2) their own personal trust for the professionals if they were experiencing the symptoms described in the vignette. Because both questions were worded similarly, keywords such as trust and confident were bolded or underlined in order to highlight the intent of the question.
Development and validation of the vignettes.
The vignettes and questions were originally drafted by the lead researcher to explore how soldiers may rank MHPs under the two stated conditions (i.e., confidence and trust questions). The four mental health diagnoses selected were PTSD, anxiety disorders, depression, and substance use disorders, as these were identified by Seal, Bertenthal, Miner, Sen, and Marmar (2007) to be the most prevalent for soldiers returning from Iraq. The four common issues were suicide, marital problems, parenting difficulties, and sleep problems; these were selected from the Military Health System’s “After Deployment” (2015) website because they were depicted as common problems faced by soldiers and contributed to the breadth of issues explored in the study. Vignettes were modeled after previous studies using similar metrics to measure populations’ trust of MHPs (e.g., Fall et al., 2000; Fall et al., 2005).
After review and editing within the research team, faculty with extensive clinical and teaching expertise in the area of diagnosis reviewed the vignettes. Based on their recommendations, specific diagnostic labels, such as PTSD and depression, were removed in order to reduce the impact of these labels on participants’ responses, and the keywords trust and confidence were included and bolded in the survey questions. Their input also resulted in the refining of the vignettes to more accurately depict the intended issues based upon their clinical experience and expertise.
Procedures
From January to June of 2017, surveys were administered via Qualtrics software on an electronic device of the participant’s choosing. Respondents were requested to complete the surveys at a location and time presenting minimal distractions. After being provided information about the study and consenting to continue, participants were presented with the demographics survey followed by the vignettes. The survey would not advance to the next page unless a response was recorded to all questions on the previous page. Upon completion of the demographics portion, participants advanced to the vignettes depicting soldiers facing issues upon returning from a combat deployment.
During the vignette portion of the survey, respondents ranked the list of mental health practitioners for both the confidence and trust conditions; see the Appendix for the vignettes presented to participants. The survey would not allow duplicate ranks (i.e., MHPs could not “tie”) for either condition. The vignettes were randomized, with both the trust and confidence questions presented together on the same screen, and the listed order of the MHPs was randomized for each vignette as well.
Analysis
Data analysis focused on three main themes: the mean ranks for trust of the MHPs across the vignettes, the mean ranks for confidence in the MHPs across the vignettes, and potential correlation between trust and confidence. Consistent with the Fall et al. (2005) analysis, Friedman non-parametric tests and Wilcoxon matched-pairs tests were used to determine significant findings in the mean ranks for MHPs in each vignette with respect to both the confidence and trust conditions separately. These tests were completed 16 times—once for each of the eight vignettes for both the trust and confidence questions. Afterward, the data was aggregated separately for both the trust and confidence questions to allow an overall assessment of the mean ranks for each MHP without concern for the particular vignette presented. Both the Friedman and Wilcoxon tests were completed again on the aggregated data. Finally, a Goodman and Kruskall’s gamma test was used to determine the correlation between trust and confidence ranking for each MHP.
Results
For all eight vignettes, significant differences (n = 32, df = 4, p <= .002) were found for mean rankings in both confidence and trust conditions. Subsequently, Wilcoxon matched-pairs tests identified statistically significant differences within groups for each of the 16 conditions; see Table 1 for specific results. Figures 1 and 2 display inverted mean rankings for each MHP by vignette for the confidence and trust questions respectively; higher scores indicate a more favorable ranking.
In both the confidence and trust conditions, the data from each vignette allowed for the separation of the five MHPs into either two or three distinct groups in terms of their rankings. In some instances, some MHPs could be grouped with both the higher- and lower-ranking adjacent MHP; in this case, the MHP was placed in both groups. For example, in Table 1 under the Aggregate Rank column for the confidence condition, there was no significant difference between LPCs and psychiatrists (N = 256, p = .202), or LPCs and psychologists (N = 256, p = .336), but there was a significant difference between psychologists and psychiatrists (N = 256, p = .011).
Lastly, scores from all eight vignettes were aggregated for each MHP to allow an overall measure of the MHP’s ranking for both confidence and trust. Table 1 includes the associated statistically significant grouping, and Figure 3 depicts the aggregated inverted mean ranking for both conditions for each MHP. Using a Goodman and Kruskall’s gamma test on the aggregated data, a strong positive correlation was found between confidence and trust ratings for all five MHPs with G values ranging from 0.72 to 0.88 (N = 256, p < .0005).
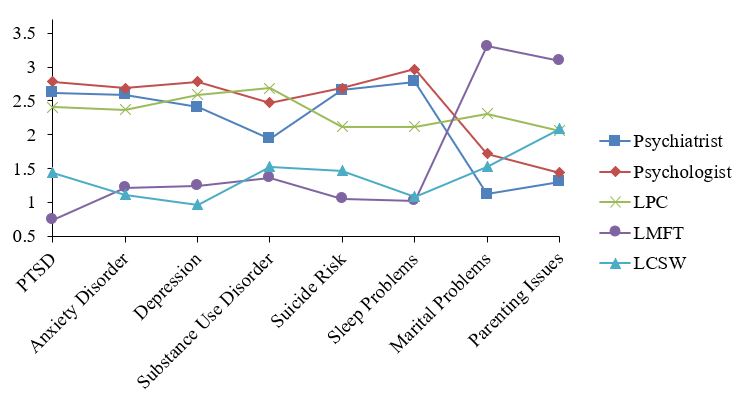
Figure 1. Inverted Mean Ranks for Confidence Question Plotted by Type of Mental Health Professional and Vignette. Higher mean rank equates to higher confidence.
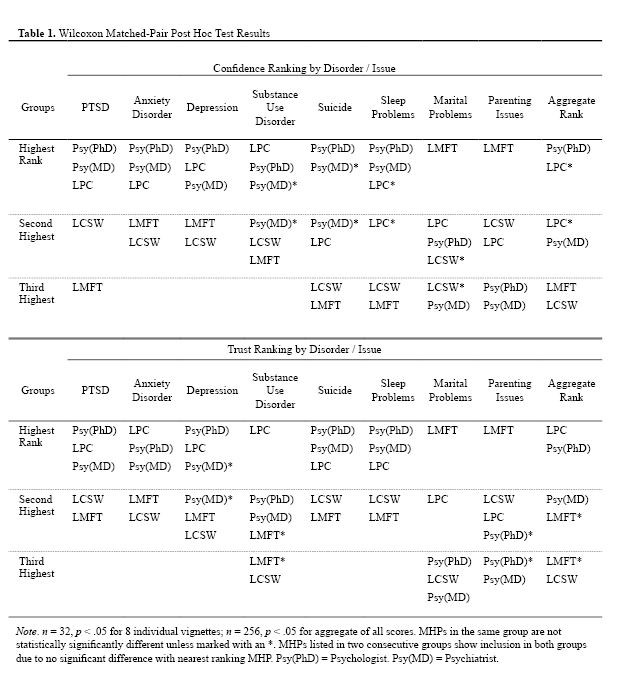
Figure 2. Inverted Mean Ranks for Trust Question Plotted by Type of Mental Health Professional and Vignette. Higher mean rank equates to higher trust.
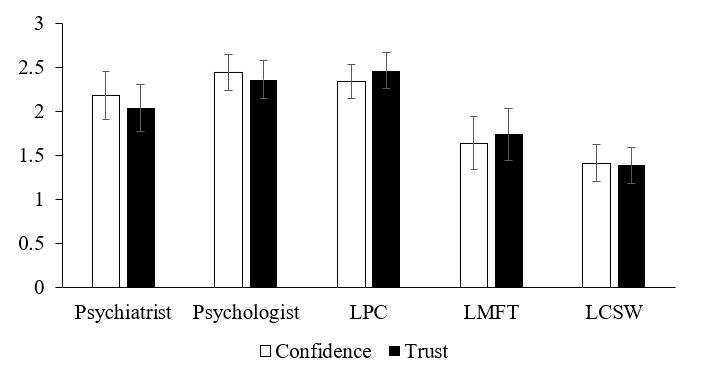
Figure 3. Aggregated Inverted Mean Ranks for Mental Health Professionals for Confidence and Trust Questions. Higher mean rank equates to higher confidence or trust. Error bars indicate standard error based on standard deviation from the mean; they do not indicate statistical significance.
Discussion
This study was designed to explore active-duty Army soldiers’ perceptions toward various mental health care providers with respect to trust and confidence in the MHP. Overall, the sample population of soldiers appears to have the highest confidence and trust in clinical psychologists and LPCs, while LCSWs and LMFTs are significantly less preferred (as seen in Table 1). Psychiatrists seem to be somewhere between each of these two groups, as they appear in both the highest and second-highest preferred groups depending on the condition (i.e., confidence or trust). The statistically significant stratification into these groups suggests that the title of available MHPs may influence a soldier’s decision to seek services. Undoubtedly, other factors are involved, but the title, and perhaps the certifications of the available professional, is likely impacting treatment-seeking behaviors in military communities.
At the heart of this study is the notion that each of the MHPs included could treat any of the soldiers in the vignettes; however, the results suggest that soldiers would seek out different professionals based on the context of the presenting symptoms rather than the type or potential efficacy of the treatment to be received. For example, the marital problems vignette (see Appendix) could arguably have been treated more effectively by a psychiatrist than an LMFT; perhaps the declining relationship was itself a symptom of biochemical issues such as vitamin or neurotransmitter deficiencies, which may be more aptly treated with medicine. Or, it also is possible that an experienced LPC or LCSW could have effectively brought to the surface some other underlying issue in the course of individual therapy rather than the marriage, couple, and family-oriented approach taken by an LMFT. Similar arguments could be made for each of the other vignettes, but the results suggest that soldiers are likely making treatment decisions based upon professional title and presumably the associated reputation. If the Army’s goal is to boost rates of treatment-seeking behaviors, professional titles and perceptions of trust and confidence should not be ignored.
Results also show a strong correlation between trust and confidence across all of the vignettes. This can best be seen by comparing the LMFTs’ rankings for the marital problems and parenting issues vignettes with their consistently lower scores on the other vignettes. The jump in scores was consistent across both conditions, demonstrating that trust and confidence for MHPs are strongly linked. Although less likely, it also is possible that the respondents might have been biased or influenced to provide similar ranks for each professional across both conditions because the survey design allowed them to see their scores for the confidence question while completing the trust question. Regardless of whether trust influences confidence or vice versa, the two should be considered in the quest to boost treatment-seeking rates among soldiers.
Implications for Service Provision
With further validating and corroborating research, the Army may be able to improve treatment-seeking rates among those in need of mental health care by adjusting services based on the perceptions of soldiers. Although LPCs were consistently favored more than LCSWs, the Army currently allows LCSWs to serve as commissioned officers in behavioral health clinics providing individual therapy to soldiers, while the LPC license does not qualify an MHP to commission and serve as an officer (U.S. Department of the Army, 2007). This means soldiers have fewer chances of seeing an LPC without some type of insurance referral because the uniformed personnel initially available will not be LPCs. This study provides evidence that LPCs may be more appropriate and effective in this role by boosting treatment-seeking rates, so it could be beneficial to make treatment with LPCs more accessible to soldiers. Likewise, incorporating the services of LMFTs following deployments could help military families, as they had the highest average trust and confidence ratings of any professional in any vignette in the study when they were the preferred MHP. Perhaps they could advocate for temporary positions following deployments or increased advertisement of their services in military communities with units returning from overseas.
Limitations and Future Research
Future research is certainly needed to further confirm the results of this study. Investigators could explore what drives trust and confidence perceptions in military communities and how prior personal experiences influence the soldiers’ views of MHPs. Studies like this one could be conducted with other branches of the military and include National Guard and Reserve forces. Exploratory qualitative research could seek to identify specific factors that build trust and confidence in the mental health community as a whole. Future studies also should continue to update the disorders or issues selected to accurately represent the issues faced by targeted populations at the time.
Limitations to this study include the sample size, delivery of the survey, and lack of consideration for gender biases. While 32 respondents can provide initial insights, a much larger sample should be surveyed before any significant policy decisions are considered. The research team also recommends administering the surveys in person rather than online with the belief that many soldiers—and people in general—may not complete the digital surveys as earnestly as a paper version following a personal interaction with the research team or a recruiter. With regards to gender, it was not considered how the names of the soldiers in the vignettes may influence the respondents’ rankings; it is possible that the scores could have varied if the soldier in the vignette was of a specific gender.
Future researchers should be cautious to ensure that voluntary participation is not influenced by environmental pressures. In military communities, the researchers recommend seeking a sample population that includes personnel from multiple units, locations, and MOSs, as culture and attitudes can be vastly different among these variables.
Although this study has limitations, the researchers believe it highlights one of the key reasons that soldiers may not seek mental health services when in need: lack of trust and confidence in the resources available. Although the military has significantly addressed other identified issues, such as the associated stigma or impact to a service member’s career, treatment-seeking rates for those in need have changed very little, which indicates other issues are contributing to the decision not to visit with an MHP. The researchers hope the results of this study are built upon and examined for alternative approaches to boost treatment-seeking rates among the military.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
After Deployment. (2015). After deployment: Wellness resources for the military community. Retrieved from
http://afterdeployment.dcoe.mil
American Counseling Association. (2011). Who are licensed professional counselors. Retrieved from
https://www.counseling.org/PublicPolicy/WhoAreLPCs.pdf
Bradley, C., Maschi, T., O’Brien, H., Morgen, K., & Ward, K. (2012). Faithful but different: Clinical social workers speak out about career motivation and professional values. Journal of Social Work Education, 48, 459–477. doi:10.5175/JSWE.2012.201000043
Britt, T. W., Bennett, E. A., Crabtree, M., Haugh, C., Oliver, K., McFadden, A., & Pury, C. L. S. (2011). The theory of planned behavior and reserve component veteran treatment seeking. Military Psychology, 23, 82–96. doi:10.1080/08995605.2011.534417
Britt, T. W., Jennings, K. S., Cheung, J. H., Pury, C. L. S., & Zinzow, H. M. (2015). The role of different stigma perceptions in treatment seeking and dropout among active duty military personnel. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 38, 142–149. doi:10.1037/prj0000120
Clemens, N. A., Plakun, E. M., Lazar, S. G., & Mellman, L. (2014). Obstacles to early career psychiatrists practicing psychotherapy. Psychodynamic Psychiatry, 42, 479–495. doi:10.1521/pdps.2014.42.3.479
Fall, K. A., Levitov, J. E., Anderson, L., & Clay, H. (2005). African Americans’ perception of mental health professions. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling, 27, 47–56.
doi:10.1007/s10447-005-2246-y
Fall, K. A., Levitov, J. E., Jennings, M., & Eberts, S. (2000). The public perception of mental health professions: An empirical examination. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 22, 122–134.
Hoge, C. W., Castro, C. A., Messer, S. C., McGurk, D., Cotting, D. I., & Koffman, R. L. (2004). Combat duty in Iraq and Afghanistan, mental health problems, and barriers to care. New England Journal of Medicine, 351, 13–22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040603
Imber-Black, E. (2014). Eschewing certainties: The creation of family therapists in the 21st century. Family Process, 53, 371–379. doi:10.1111/famp.12091
Kim, P. Y., Britt, T. W., Klocko, R. P., Riviere, L. A., & Adler, A. B. (2011). Stigma, negative attitudes about treatment, and utilization of mental health care among soldiers. Military Psychology, 23, 65–81.
doi:10.1080/08995605.2011.534415
Mellin, E. A., Hunt, B., & Nichols, L. M. (2011). Counselor professional identity: Findings and implications for counseling and interprofessional collaboration. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 140–147. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2011.tb00071.x
Norcross, J. C., & Karpiak, C. P. (2012). Clinical psychologists in the 2010s: 50 Years of the APA Division of Clinical Psychology. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 19, 1–12.
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2850.2012.01269.x
Reiner, S. M., Dobmeier, R. A., & Hernández, T. J. (2013). Perceived impact of professional counselor identity: An exploratory study. Journal of Counseling & Development, 91, 174–183.
doi:10.1002/j.1556-6676.2013.00084.x
Schell, T. L., & Marshall, G. N. (2008). Survey of individuals previously deployed for OEF/OIF. In T. Tanielian & L. H. Jaycox (Eds.), Invisible wounds of war: Psychological and cognitive injuries, their consequences, and services to assist recovery (pp. 87–115). Santa Monica, CA: RAND Health Center for Military Health Policy Research.
Seal, K. H., Bertenthal, D., Miner, C. R., Sen, S., & Marmar, C. (2007). Bringing the war back home: Mental health disorders among 103,788 US veterans returning from Iraq and Afghanistan seen at Department of Veterans Affairs facilities. Archives of Internal Medicine, 167, 476–482.
U.S. Army Medical Department. (2016). Behavioral health. Retrieved from https://armymedicine.health.mil/Behavioral-Health
U.S. Department of the Army. (2007). Army Medical Department Officer Development and Career Management: Department of the Army Pamphlet 600-4. Retrieved from http://www.apd.army.mil/epubs/DR_pubs/DR_a/pdf/web/p600_4.pdf
VanSickle, M., Werbel, A., Perera, K., Pak, K., DeYoung, K., & Ghahramanlou-Holloway, M. (2016). Perceived barriers to seeking mental health care among United States Marine Corps noncommissioned officers serving as gatekeepers for suicide prevention. Psychological Assessment, 28, 1020–1025.
doi:10.1037/pas0000212
Warner, D. L., & Bradley, J. R. (1991). Undergraduate psychology students’ views of counselors, psychiatrists, and psychologists: A challenge to academic psychologists. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 22, 138–140.
Wollersheim, D. M., & Walsh, J. A. (1993). Clinical psychologists: Professionals without a role? Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 24, 171–175.
Zisook, S., McQuaid, J. R., Sciolla, A., Lanouette, N., Calabrese, C., & Dunn, L. B. (2011). Psychiatric residents’ interest in psychotherapy and training stage: A multi-site survey. American Journal of Psychotherapy, 65, 47–59.
Appendix
Vignettes Used to Depict Mental Health Diagnoses and Issues
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Vignette
Joe returned from deployment to Afghanistan 4 months ago. He was personally involved in combat with enemy insurgents on multiple occasions and was exposed to disfigured, dead bodies of both enemy combatants and fellow soldiers as well. He has often mentioned bad dreams about one of these times in particular and seems obviously distressed (e.g., fidgeting, faster breathing, and sometimes even sweating) whenever he speaks about it. However, when his fellow soldiers from the deployment bring up the event, he seems unwilling to participate in the conversation and has on a few occasions become angry about it. Based on these behaviors, you believe he may be struggling with traumatic experiences.
Anxiety Disorder Vignette
John returned from a combat deployment 9 months ago. Since returning, his family and coworkers have noticed changes in his behavior. He is often restless (or “on edge”), irritable, or physically tense in common, everyday situations. Plus, he has claimed poor or unsatisfying sleep for several months. These symptoms seem to be impairing his work performance and damaging personal relationships with loved ones. When asked, he hasn’t mentioned any particular traumatic events or worries that are bothering him. He simply seems much more anxious and it is affecting his well-being.
Depression Vignette
Jane returned from a combat deployment 3 months ago and has generally seemed a little bit down since coming home. Nearly every day over the past 2 weeks she has seemed to be sad or gloomy throughout the day and has shown very little interest in doing things she used to enjoy. She is clearly tired throughout the day and has mentioned feeling worthless to those around her. It seems like she is suffering greatly based on her unhappy and sad moods.
Substance Abuse Disorder Vignette
Jim returned from a combat deployment 12 months ago. Upon returning, he seemed to seamlessly reintegrate with his family, friends, and former social life. However, he soon began drinking alcohol more heavily than ever before, often binge drinking until passing out on weekdays and weekends. Although never caught in the act, he has even gone to work intoxicated and driven while drunk on multiple occasions. On two distinct occasions, he attempted to reduce his alcohol consumption but failed after only a week or two. Alcohol abuse is beginning to disrupt his work performance, family life, and physical well-being.
Sleep Problems Vignette
Joan returned from a combat deployment 4 months ago. She seems to have reintegrated very successfully into her family, social, and work environments. However, her sleep patterns have become very irregular and unsatisfactory. She rarely gets more than 4 hours of sleep consecutively and often uses her weekends to recover from a week of sleepless nights. Although her family and coworkers haven’t noticed anything wrong, Joan fears her sleep problems will soon begin disrupting her life.
Suicide Risk Vignette
James returned from a combat deployment 6 months ago. Since returning, he has outwardly seemed to have successfully reintegrated into his family, work, and social life. Although he appears to have been changed by his combat experiences, he does not seem to be generally troubled in any way (e.g., depressed, anxious, abusing drugs). However, he has jokingly mentioned “blowing his brains out” to colleagues at work and mentioned a specific plan to take his own life with his pistol. During a conversation with two friends, he has mentioned “ending it all” because he is feeling hopeless. You think James may be at risk for suicide.
Marital Problems Vignette
Jon returned from a combat deployment 5 months ago. He has rejoined his wife of 6 years, but their relationship has changed. While they used to feel very close and connected, they now both feel very distant. They do not enjoy activities together which they used to, such as hiking and dancing. They rarely hold good conversations with each other and are also less physically intimate. Jon and his wife both want their marriage to work but fear that they are nearing divorce. They are facing the most significant period of marital problems they have ever experienced.
Parenting Issues Vignette
Jerry returned from a combat deployment 10 months ago. He rejoined his wife of 16 years, their 13-year-old daughter, and their 5-year-old son. Since returning, Jerry has experienced some difficulty reassuming his role as a parent. His daughter seems to want very little to do with him. Although he thinks this is typical of a 13-year-old, it still causes him distress and he complains that he doesn’t feel like he has any influence in her life. With their son, Jerry often disagrees with his wife on discipline issues, and he can’t seem to find ways to connect with the 5-year-old. His son seems to have little interest in playing anything besides video games and always runs to his mother when Jerry attempts to discipline him. These parenting issues are significantly affecting Jerry’s mental and emotional well-being.
Anthony Hartman is a medical student at UT-Health San Antonio. Hope Schuermann is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Florida. Jovanna Kenney is a therapist at Genesis Psychiatric Center in San Antonio, TX. Correspondence can be addressed to Anthony Hartman, 7703 Floyd Curl Drive, San Antonio, TX 78229, hartmanaj@livemail.uthscsa.edu.
Mar 23, 2016 | Article, Volume 6 - Issue 1
Robert C. Schmidt
Youth suicide is a significant public health concern and efforts to reduce youth suicide remain a national priority (Kung, Hoyert, Xu, & Murphy, 2008; National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention: Research Prioritization Task Force, 2014). In the United States, there were 40,600 suicides in 2012, averaging 111 suicides per day (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2014a). Of the total number of suicides, 5,183 were youth suicides, averaging 14 youth suicides daily, or one youth suicide every 1 hour and 42 minutes (Drapeau & McIntosh, 2014). Youth suicide is the third leading cause of death between the ages of 10 and 14 and has become the second leading cause of death between the ages of 15 and 24 (CDC, 2014a). The results from the 2013 Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance (YRBS) reported 29.9% of high school students felt sad or hopeless almost every day for 2 weeks or more; 17% of high school students seriously considered attempting suicide; 13.6% of high school students made a suicide plan about how they would attempt suicide; and 8% of students attempted suicide one or more times (CDC, 2014b).
Efforts to address the increasing rate of youth suicide call for the identification of existing training and preparation gaps currently faced by practitioners (National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention: Research Prioritization Task Force, 2014). These gaps pose many challenges for practitioners to effectively provide appropriate interventions. Although previous studies have investigated training gaps among specific professional disciplines (Debski, Spadafore, Jacob, Poole, & Hixson, 2007; Dexter-Mazza, & Freeman, 2003; O’Connor, Warby, Raphael, & Vassallo, 2004), the current study investigated a broader representation of disciplines including social workers, school counselors, professional counselors, school psychologists and psychologists. This study examined practitioner self-perceived levels of preparedness, levels of confidence and methods used in the assessment of youth suicide.
Practitioner readiness in suicide assessment. In approximately eight of ten suicides, youth give advance clues or warning signs of their intentions that can be detected by others (McEvoy & McEvoy, 2000; Poland & Lieberman, 2002). In a study spanning four years of youth in a rural school district (N = 5,949) screened for suicidal thoughts, 670 (11%) reported having suicidal thoughts within the past year or past few days (Schmidt, Iachini, George, Koller, & Weist, 2015). Practitioners working within school or community mental health settings have an opportunity to play a critical role in the identification, assessment and prevention of youth suicide (Singer & Slovak, 2011). Within either setting, practitioners will encounter clients having suicidal thoughts or behaviors (Rudd, 2006). The practitioner’s responsibility in the assessment of suicide is to estimate risk based on identifying warning signs and associated behaviors and to respond appropriately (Bryan & Rudd, 2006).
In a national sampling of social workers, 93% of the respondents reported having worked with a suicidal patient (Feldman & Freedenthal, 2006), and 55% of clinical social workers reported having a patient attempt suicide (Sanders, Jacobson, & Ting, 2008). In a study of psychology doctoral interns (N = 238) completed by Dexter-Mazza and Freeman (2003), 99% reported providing services to suicidal patients and 5% reported experiencing a patient death by suicide. Across professional disciplines, 22% to 30% of social workers, counselors and psychologists reported having a patient die by suicide (Jacobson, Ting, Sanders, & Harrington, 2004).
Irrespective of the level of suicide training, comfort level or experience (i.e., even those with limited training and preparedness), the circumstances for which practitioners meet with a suicidal client are not only stressful, but also have legal and ethical ramifications (Cramer, Johnson, McLaughlin, Rausch, & Conroy 2013; Poland & Lieberman, 2002). Research suggests significant gaps exist related to the practitioner’s training and readiness to perform suicide risk assessments, highlighting training deficits in the level of preparedness, level of confidence and methods used to determine suicide risk level (Smith, Silva, Covington, & Joiner, 2014).
Although youth suicide remains a national concern and priority, gaps appear most prominent in translating research into practice in developing and providing appropriate levels of training and supervision for practitioners (Smith et al., 2014). Research to support this concern offers valuable recommendations (Osteen, Frey, & Ko 2014; Schmitz, Allen, Feldman, et al., 2012); however, despite these recommendations, training and preparation continue to lag (Rudd, Cukrowicz, & Bryan, 2008). Practitioner competency skills in suicide assessment continue to be neglected by colleges, universities, licensing bodies, clinical supervisors and training sites that can have the greatest impact in reducing youth and adult suicide (Schmitz et al., 2012).
Practitioner preparedness. In the past several decades, researchers began identifying gaps in suicide risk knowledge, finding that practitioners were inadequately prepared to assess suicide risk. In master’s and doctoral clinical and counseling psychology training programs, 40–50% were found to offer formalized training in suicide assessment and management of suicide risk (Kleespies, Penk, & Forsyth, 1993). Suicide-specific training was only included in 2% of accredited professional counseling programs and 6% of accredited marriage and family therapist training programs (Wozny, 2005).
Training also has been identified as limited among social work graduate programs,
averaging 4 hours or fewer specific to suicide education (Ruth et al., 2009). In a study by Feldman and Freedenthal (2006) randomly surveying social workers through the National Association of Social Workers (N = 598), almost all of the social work participants (92.3%) reported working with a suicidal client; however, only 21.1% received any formal suicide-related training in their master’s program. Of the 21.1% of social workers receiving formal training, 46% specified their suicide-devoted training was less than 2 hours.
This pattern continued as additional studies found psychology doctoral interns did not receive adequate training in suicide assessment and/or managing suicide risk in clients. Neither did they receive the necessary levels of clinical supervision in suicide assessment (Mackelprang, Karle, Reihl, & Cash, 2014). In a study of psychology graduate school programs, 76% of the program directors indicated a need for more suicide-specific training and education within their programs but discovered barriers to implement this training (Jahn et al., 2012). The chief barrier reported by the directors was the absence of guidance and curriculum requirements to provide training and, secondly, the inability of colleges to create space in the existing curriculum schedule for added classes (Jahn et al., 2012).
In a survey that included members of the National Association of School Psychologists (N = 162), less than half (40%) of the respondents reported receiving graduate-level training in suicide risk assessment (Debski et al., 2007). Most school psychologists in this study reported feeling at least somewhat prepared to work with suicidal students while doctoral trained practitioners reported feeling well prepared.
School counselors share similar gaps in their preparation to provide suicide intervention and assessment to youth. Research conducted by Wachter (2006) indicated that 30% of school counselors had no suicide prevention training. In a study conducted by Wozny (2005), findings indicated that just 52.3% of the school counselors, averaging 5.6 years of experience, were able to identify critical suicide risk factors. This study exposed competency gaps in suicide assessment, training and intervention consistent with practitioner disciplines that were identified within this study. This is consistent with previous study findings (National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention, 2014; Schmitz et al., 2012) that identified insufficient training and preparation of practitioners in the assessment and prevention of youth suicide and suicide in general.
Practitioner confidence. Although most practitioners will encounter youth with suicidal thoughts and behaviors, many lack the self-confidence to effectively work with suicidal youth. The lack of confidence appears related to competency levels and limited training (National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention, 2014; Oordt, Jobes, Fonseca, & Schmidt, 2009).
In contrast, researchers found that as practitioner risk assessment skills increased through suicide-specific training, noticeable increases were measured in practitioner self-confidence (McNiel et al., 2008). Oordt and colleagues (2009) studied mental health practitioner levels of confidence after receiving empirically-based suicide assessment and treatment training. The results indicated that self-reported levels of practitioner confidence increased by 44% and measured a 54% increase specific to self-confidence levels related to the management of suicidal patients. In addition, studies of school counselors identified correlations between self-efficacy, confidence and the ability to improve clinical judgment in providing suicide interventions and assessment (Al-Damarki, 2004).
Adequate training and experience in suicide prevention and assessment has been found to increase practitioner levels of confidence in conducting risk assessments and management planning (Singer & Slovak, 2011). Research suggests that confidence increases the practitioner’s ability to estimate suicide risk level, make effective treatment decisions and base recommendations when conducting a quality assessment. However, when the assessor is not confident, the assessment is more prone to errors or missed information, decreasing the accuracy of their assessment (Douglas & Ogloff, 2003). Paradoxically, overconfidence produces similar results as practitioners lacking confidence. Tetlock (2005) reported that overconfident practitioners are more prone to making errors during a suicide risk assessment unless their clinical judgment is further supported by objective evidence such as using a formal, validated and reliable method of assessment.
Methods Used in Suicide Assessment
There are several categories of suicide assessment instruments developed for youth (Goldston, 2003; National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention, 2014). These include detection instruments like structured and semi-structured interviews; survey screenings that include self-report inventories and behavior checklists; and risk assessment instruments that include screenings, self-report questionnaires and multi-tier screening assessments.
Across settings including schools, emergency departments, primary care offices and community mental health offices, studies indicate that inconsistent methods are used to assess suicide risk (Horowitz, Ballard, & Paoa, 2009). In most instances, the use of published and validated suicide screening tools are not being properly used as intended or designed, which impacts their reliability and validity (Boudreaux & Horowitz, 2014). This may represent and reflect the practitioner’s limited training, confidence and experience in these areas.
In addition, the documentation of the suicide assessment also can reflect the level of the practitioner’s training and knowledge of suicide assessment. O’Connor and colleagues (2004) noted that practitioner skill deficiencies in youth suicide assessment are likely to appear in clinic notes as a brief statement, “patient currently denies suicidal thoughts,” based on the practitioner’s impressionistic and subjective perception after completing a brief unstructured interview. This is commonly the only form of documentation obtained by the practitioner (O’Connor et al., 2004). Research consistently provides evidence across disciplines that some practitioners are not prepared to make clinical judgments (Debski et al., 2007; Jahn et al., 2012; Mackelprang, et al., 2014; Ruth et al., 2009; Smith et al., 2014). This study offered an opportunity to contribute to the understanding of practitioners’ self-perceived competencies in the assessment of youth suicide while identifying existing gaps in training.
The Current Study
In previous studies, research has focused on confidence and preparedness levels only in specific disciplines related to the identification and assessment of suicidal youth (Al-Damarki, 2004; Debski et al., 2007; Wozny, 2005). This study encompassed a much broader representative sample of practitioner disciplines including psychologists, social workers, school counselors, professional counselors and school psychologists.
The purpose of this study was to determine relationships among practitioners’ self-perceived levels of preparedness, levels of confidence and methods used to perform suicide risk assessments in youth. These efforts were guided by the following research question: What are the relationships among the self-perceived levels of preparedness, levels of confidence, and methods used in the assessment of suicide risk for practitioners whose responsibilities require suicide risk assessment and management? In order to address this, survey questions were designed to obtain participant responses related to skill development, preparation, confidence and methods used in the process of conducting suicide risk assessments.
Method
Procedures and Instrumentation
Since this study sought to collect data using human subjects, the proposal was reviewed and approved by the Wilmington University Human Subjects Review Committee prior to beginning this study. An exploratory descriptive survey design examined practitioner self-perceived levels of preparedness, levels of confidence and methods used to assess suicide risk in youth. Using a quantitative method to guide this study, the researcher attempted to recruit practitioners positioned and responsible for suicide risk assessment. This included working in cooperation with and posting the survey on the Maryland School Psychologists’ Association Web site and the University of Maryland Center for School Mental Health Web site. The survey was forwarded to school districts in Maryland and Virginia and directed to school counselors, school psychologists, and school-based mental health professionals, including social workers and professional counselors. In addition, the survey was forwarded to multiple outpatient mental health clinics in the mid-Atlantic region of the United States. Practitioners were provided with information about the survey, study purposes and ethical standards, and it was noted that participation was voluntary and confidential. Practitioners submitted their responses online, allowing the researcher to evaluate self-reported levels related to suicide assessment. Participants were provided with an access link to anonymously complete the survey using SurveyGizmo. The completed data were then entered into an Excel spreadsheet database.
The Child and Adolescent Suicide Intervention Preparedness Survey was the instrument developed for this study. This researcher received prior approval from the authors of two previously published surveys (Debski, et al., 2007; Stein-Erichsen, 2010) while adding specific queries for the purposes of this study. The survey by Debski and colleagues (2007) included a 42-item questionnaire with vignettes that measured the training, roles and knowledge of school psychologists. These questions targeted participant confidence and perceived levels of preparedness that also were sought in this current study, but from a broader discipline base.
The survey by Stein-Erichsen (2010) included a 55-item measure designed to identify confidence levels of school psychologists providing suicide intervention and prevention within schools. The survey questionnaires designed by Stein-Erichsen (2010) and Debski and colleagues (2007) offered questions adapted for this study specifically focusing on preparedness levels, confidence, roles, methods used to assess suicide levels, and omitted survey questions not relevant to this study. This resulted in a 23-item survey targeting practitioner levels of training, preparedness, confidence and the identification of additional training needs.
Participants
The study had 339 participants representing school counselors (N = 107/32%); social workers (N = 90/27%); school psychologists (N = 37/11%); professional counselors (N = 35/11%); psychologists (N = 5/1%); other (N = 62/18%); and three participants with unknown professional identification.
The final sampling of participants included 43 males, 292 females and four participants with unknown gender identification. Participants averaged in age ranges 22–29 (N = 33/10%), 30–39 (N = 105/31%), 40–49 (N = 94/28%), 50–59 (N = 61/18%) and ages 60 and above (N = 45/13%). The participants responded to the item querying level of education as having a bachelor’s degree (N = 18/6%), doctoral degree (N = 14/4%), master’s degree (N = 275/81%), and other (N = 28/8%) including associate levels of education, as well as four (1%) participants with unknown educational levels.
The participants represented a broad but targeted sampling from a variety of employers, including school settings (N = 166/49%); outpatient mental health settings (N = 108/32%); mental health agencies (N = 31/9%); and other settings (N = 33/10%); as well as one participant with an unknown employment setting. The participants also identified their employment environment as urban (N = 56/60%), rural (N = 174/52%), and suburban (N = 105/31%).
Participants identified the practitioner responsible to assess suicide risk within their work setting having multiple response options (see Table 1). These included a psychiatrist (N = 85/25%), nurse (N = 57/17%), school counselor (N = 179/53%), social worker (N = 168/50%), teacher (N = 7/2%), school psychologist (N = 154/46%), school mental health professional (N = 125/37%), psychologist (N = 64/19%), professional counselor (N = 101/30%), and other (N = 29/9%) including paraprofessionals, while 19 participants (6%) reported they do not complete suicide risk assessments.

Prior exposure with suicidal students/clients. In the survey, 288 (86%) of the participants reported having a student or client referred to them for being potentially suicidal; 45 (14%) did not receive a similar referral; and six participants did not respond. A majority of participants (N = 287/86%) reported having worked with a student or client initially found to be presenting with active suicidal thoughts and 48 (14%) reported not yet having worked with a suicidal student or client.
Analysis
Using descriptive data, participant responses were further examined to determine frequency and percentages of the total responses. In addition, inferential statistics were used to compute possible relationships among variables using SPSS. Data from the primary survey questions provided guidance toward establishing possible relationships between practitioner preparedness, confidence and the methods used in determining suicide risk level.
Results
Self-perceived preparedness in suicide assessment. The majority of the respondents reported some type of exposure or training in suicide intervention and assessment. The participants had an opportunity to select multiple answers: graduate course work (N = 174/52%), attending professional development workshops (N = 233/69%), in-service trainings at work (N = 213/63%), and having not received any training (N = 21/6%). In addition, participants had multiple answer options that represented self-perceived preparedness levels: not feeling at all prepared (N = 15/4%), feeling somewhat prepared (N = 120/36%), feeling well prepared (N = 202/60%), and requesting that someone more prepared meet or assess a suicidal student/client (N = 32/9%).
Self-reported confidence in suicide assessment. The confidence levels reported by the participants reflect professional skill development to conduct suicide risk assessments. The responses included feeling very confident (N = 49/15%), confident (N = 212/63%), and not very confident (N = 63/19%). A similar survey item asked about confidence levels working with a suicidal student or client. The responses included feeling very confident (N = 42/12%), confident (N = 231/69%), and not very confident (N = 63/19%). An additional survey item sought information regarding participant feelings when assessing for suicidal thoughts. Results indicated feeling not prepared (N = 39/12%), anxious (N = 116/34%), calm (N = 145/43%), and confident (N = 185/55%).
Methods Used to Determine Suicide Risk Level During Assessment. Several survey items queried participant levels of training and methods used to assess a suicidal student or client. A survey item asked participants if they had received formal training to conduct suicide risk assessments. The respondents indicated Yes (N = 201/60%) or No (N = 133/40%). In addition, a survey question asked participants if they felt qualified to complete a suicide risk assessment: Yes (N = 241/73%) or No (N = 91/27%). A follow-up survey item asked participants how they determined if the student or client was at imminent risk, high to moderate risk or low risk. The participant responses indicated they would conduct an informal, non-structured interview (N = 213/64%) or use a formal, valid suicide assessment instrument (N = 90/27%); the remaining respondents indicated other (N = 31/9%).
Participants were asked what would limit their ability to provide a suicide intervention. Using a “check all that apply” format, responses included practitioners not receiving formal training to work with suicidal students or clients (N = 55/17%), the role of suicide interventions and response is the job of others (N = 19/6%), not feeling adequately prepared to provide a suicide intervention or assessment (N = 65/20%), workplace policy does not allow formal suicide assessments (N = 12/4%), and feeling prepared (N = 225/68%). The discipline most frequently reported to encounter and assess a youth presenting with suicidal thoughts or behaviors in this study was the school counselor (53%). This supported previous research by Poland (1989) who identified that “the task of suicide assessment was likely to fall on the school counselor” (p. 74).
To determine whether relationships existed among self-perceived levels of preparedness, levels of confidence, and methods used in youth suicide assessment, the researcher completed a chi-square statistical analysis to measure numerical and categorical differences. In order to compare differences among several groups, variables were collapsed to include confident/not confident and prepared/not prepared. The first group compared practitioners’ responses of reporting confident/not confident to prepared/not prepared in the process of providing an informal versus formal suicide risk assessment in youth. The analysis indicated that there were significant differences in preparedness levels according to the method used. Seventy-three percent of those reporting use of formal assessments versus approximately 50% of those using informal assessments indicated confidence in their preparedness abilities (X2 = 12.79; df = 1. Cramer’s V = .206, p = .000). A further analysis indicated there were similar significant differences in practitioner confidence levels conducting informal, non-structured suicide risk assessments and formal assessments (X2 = 23.54, DF = 1. Cramer’s V=.280, p = .000). The results showed that 95.6% of the practitioners using formal suicide risk assessments reported higher levels of confidence versus 70.1% of the practitioners using informal, non-structured suicide risk assessments.
To identify existing gaps, participants were asked to rank by priority the trainings they needed to increase competency levels. The highest priority was (1) to receive a comprehensive training on warning signs, symptoms and suicidal behaviors, and (2) to attend several suicide assessment workshops.
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to determine if relationships existed among practitioners’ self-perceived levels of preparedness, levels of confidence and methods used when assessing for suicide risk in youth. A survey was designed to query participants representing a broad sampling of disciplines related to their perceptions, experience and involvement in youth suicide risk assessment. The results of the survey were analyzed using chi-square to determine if relationships existed among variables, including participant perceptions of feeling prepared and confident, and if this contributed to the methods used to determine suicide risk in youth.
Results of the survey indicated that a majority of the participants (86%) reported having worked with suicidal youth; however, inconsistencies in participant responses emerged related to the constructs of feeling prepared and confident in the assessment of suicide. The results suggested preparedness and training in suicide assessment is linked to practitioner confidence levels when assessing for suicide risk among youth. This finding is supported by earlier research by Oordt and colleagues (2009), who reported that practitioner confidence in suicide assessment is primarily related to competency and training levels. The interrelationship between preparedness and confidence is often reflected in the practitioner’s ability to accurately estimate risk level. This may potentially increase the likelihood of omitting critical information, which may affect the estimate of suicide risk (Douglas & Ogloff, 2003; Singer & Slovak, 2011). The results represent an important finding and highlight existing gaps in practitioner preparation. These gaps may reflect a struggle for most university and college graduate school degree programs to offer a more diversified curriculum (Allen, Burt, Bryan, Carter, Orsi, & Durkan, 2002) that includes courses specific to identifying, intervening in and assessing for suicide risk in youth (Schmitz et al., 2012).
The inconsistencies in participant responses related to feeling prepared and confident became apparent when participants rated themselves in working with a suicidal youth. Although over half of the respondents reported feeling well prepared and qualified in their ability, a much smaller percentage reported feeling confident in themselves (12%) and their skill preparation (15%) to assess for suicide. This finding may reflect a self-evaluation dilemma in wanting to self-report feeling prepared to work with a suicidal youth, but in actuality not feeling prepared or confident to provide a suicide intervention or complete an assessment.
As this study broadened its review of practitioner responses related to preparedness and confidence, findings indicated additional inconsistencies in participant responses related to self-reported feelings of preparedness and confidence when conducting a suicide intervention or suicide assessment. Despite predominantly higher levels of reported confidence, skill development and preparedness to determine if a student or client was at imminent risk, high to moderate risk, or low risk, few participants (27%/N = 90) reported using a formal suicide assessment instrument. Most respondents (64%/N = 213) reported basing their clinical judgment solely on using an informal, non-structured interview. Although practitioners reported feeling prepared and having a sense of confidence assessing for suicide risk, basing clinical judgment on this method alone raises concerns. O’Connor and colleagues (2004) described that practitioner skill deficiencies in suicide assessment are commonly reflected in clinic notes such as “patient currently denies suicidal thoughts,” based on the practitioner’s impressionistic and subjective perceptions. Consistent with identifying training deficiencies in preparation, 52% (N = 174) of the participants reported receiving limited suicide intervention or assessment training in graduate coursework.
The participants in this study who reported using a formal suicide assessment, however, indicated feeling better prepared to conduct a suicide assessment versus practitioners using an informal, non-structured interview. In addition, practitioners using a formal assessment also had greater confidence levels versus practitioners using an informal, non-structured interview. When participants were asked to rank their own levels of needed training to provide a more thorough suicide intervention, participants identified skill deficiencies and training gaps in identifying warning signs and behaviors and assessing for suicide using a suicide risk assessment. These deficiencies pose great concern and competency challenges for practitioners charged with assessing for suicide risk. The combination of skill attributes, guided interview and diagnostic assessment synthesizes the information and allows practitioners to determine risk level and base clinical judgment on a variety of sources (Rudd, 2006; Sullivan & Bongar, 2009). The skill deficiencies reflected across all disciplines represented significant training gaps. This study suggests the need for increased commitment by colleges and universities to prepare future practitioners to more effectively address the growing national youth suicide crisis.
Implications
Despite suicide being identified as a national public health priority, no significant reduction in suicide has been recorded in the past 50 years (Kung et al., 2008; National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention, 2014). “With the majority of youth suicide deaths being preventable,” (O’Connor, Platt, & Gordon, 2011, p. 581), continued and more urgent calls for increasing practitioner preparedness, confidence and competency skills continue to be neglected.
Each of the disciplines represented in this study is faced with the challenge to address and estimate suicide risk. This study highlighted the critical role of school counselors as being identified by participants (53%) to be the most likely practitioner to respond and provide a suicide assessment. Representing a variety of disciplines and settings, participant responses suggest training deficiencies in the levels of preparedness, confidence and exposure to formal assessment measures. Previous research has made strong recommendations to increase the provisions and training in suicide assessment. Despite heeding previous calls and recommendations to prepare practitioners, more attention is needed to address previous and current identified training deficiencies among practitioners.
Transitioning research into practice includes revisiting several identified recommendations by Schmitz et al. (2012). This includes providing consistent core standards and competencies across disciplines by educational accrediting institutions. This may call for increased suicide-specific educational and training requirements beyond the baccalaureate degree level and include dissecting vignettes, role-playing, exposing practitioners to several suicide assessment instruments and interpreting the results (Fenwick, Vassilas, Carter, & Haque, 2004). This would include increased emphasis on recognizing the signs and symptoms of depression, suicidal thoughts and behaviors and increasing an understanding of potential next steps once a suicide risk level has been determined. In addition, to sustain these skills, state licensing boards can require continuing education specific to suicide identification, assessment and management. Rudd and colleagues (2008) placed emphasis on practitioners receiving increased suicide assessment strategies through supervision. The prevailing need practitioners identified as a chief priority in this study was to become more familiar with the warning signs, symptoms and behaviors associated with suicide and suicide assessment. The findings included within this study offer future research opportunities to monitor suicide training, preparation and continuing educational requirements of colleges, universities and licensing boards that govern and are responsible for the production of competent practitioners.
Although attention has focused on practitioner training deficits in the identification and assessment of youth suicide, future studies also are warranted in the measurement and impact of existing suicide prevention training programs that may provide opportunities for practitioners to increase skill sets in these areas. Another area meriting future study might include a national sampling of school counselor preparation in the identification, assessment and exposure to assessment tools. In this study, school counselors were identified to be the most likely practitioner called upon to provide an initial suicide intervention or assessment given their access to a large number of youth. This serves as a valuable finding, highlighting the call for increased and expanded counselor education, training and preparation in suicide risk identification and assessment in graduate school.
Limitations
Providing a suicide intervention or assessment involves many complex issues, and addressing the many variables paralleling these efforts could not be entirely assessed in this study. This study was intended to explore current levels of practitioner preparedness, confidence and the methods used to assess youth suicide. There are some notable limitations regarding the current study; therefore, caution is warranted regarding the generalizability of the findings.
Although the Internet provided a greater opportunity for the researcher to create survey access to targeted participants and disciplines, this method did not provide a sample size completion rate. In addition, previous Internet survey research (W. Schmidt, 1997) reported that participants have access to multiple submissions, although ethical practice instructions and consent to complete this survey was provided. In order to access participants from multiple disciplines, the survey used in this study was available online as a self-report method of completion. In this process, self-report instruments, including surveys, inherently contain participant response bias. This may be reflected in responding to questions in a socially desirable or expected manner (Heppner, Wampold, & Kivlighan 2007). In addition, online surveys can be submitted containing omitted and blank responses (Sue & Ritter, 2012).
As previously noted, The Child and Adolescent Suicide Intervention Preparedness Survey used in this study was adapted from two previous research surveys (Debski et al., 2007; Stein-Erichsen, 2010). In this study design, survey questions were created and adapted to measure participant constructs in the assessment of youth suicide. The use of a psychometrically sound survey instrument would be an ideal application to implement and duplicate for future research.
Conclusion
The findings from this study identify significant interrelationships between the practitioner’s self-perceived feelings of preparedness, confidence levels and methods used to assess for suicide risk among youth. The self-reported feelings of being prepared and confident seem to contradict the method used to obtain a suicide risk level. This finding suggests many practitioners are well intended, but lack the necessary skills to conduct a thorough suicide risk assessment. The majority of practitioners participating in this study reported conducting a suicide risk intervention using an informal, non-structured interview to formulate a suicide risk level versus using a formalized suicide risk assessment instrument. Prior experience and exposure to suicide risk assessment instruments and increased emphasis in suicide-specific training curriculum in graduate school can offer the opportunity for a practitioner to feel better prepared, feel more confident and utilize a more effective method to determine a youth’s suicide risk level. Practitioner gaps in training are typically augmented by the practitioner seeking personal training and workshops to fill these gaps. Efforts must be made by colleges and universities to increase the competency skills in this area if we are to ever reduce the growing number of youth suicides. The findings from this study supported limited previous research sounding urgent calls to better prepare practitioners, especially school counselors, in the identification of youth presenting with suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Al-Damarki, F. R. (2004). Counselor training, anxiety, and counseling self-efficacy: Implications for training psychology students from the United Arab Emirates University. Social Behavior and Personality, 32, 429–439. doi:10.2224/sbp.2004.32.5.429
Allen, M., Burt, K., Bryan, E., Carter, D., Orsi, R., & Durkan, L. (2002). School counselor’s preparation for and participation in crisis intervention. Professional School Counseling, 6, 96–102.
Boudreaux, E. D., & Horowitz, L. M. (2014). Suicide risk screening and assessment: Designing instruments with dissemination in mind. American Journal of Preventative Medicine, 47(32), 163–169.
doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2014.06.005
Bryan, C. J., & Rudd, D. M. (2006). Advances in the assessment of suicide risk. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62, 185–200.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014a). Fatal injury data. Web-based injury statistics query and reporting system (WISQARS). Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/injury/wisqars/index.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014b). Youth risk behavior surveillance, United States, 2003. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 63(SS-4), 1–168.
Cramer, R. J., Johnson, S. M., McLaughlin, J., Rausch, E. M., & Conroy, M. A. (2013). Suicide risk assessment training for psychology doctoral programs. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 7, 1–11.
Debski, J., Spadafore, C. D., Jacob, S., Poole, D. A., & Hixson, M. D. (2007). Suicide intervention: Training, roles and knowledge of school psychologists. Psychology in the Schools, 44, 157–170. doi:10.1002/pits.20213
Dexter-Mazza, E. T., & Freeman, K. A. (2003). Graduate training and the treatment of suicidal clients: The students’ perspective. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 33, 211–218.
Douglas, K. S., & Ogloff, J. R. P. (2003). The impact of confidence on the accuracy of structured professional and actuarial violence risk judgments in a sample of forensic psychiatric patients. Law and Human Behavior, 27, 573–587.
Drapeau, C. W., & McIntosh, J. L. (2014). U.S.A suicide 2012: Official final data. Washington, DC: American Association of Suicidology.
Feldman, B. N., & Freedenthal, S. (2006). Social work education in suicide intervention and prevention: An unmet need? Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 36, 467–480.
Fenwick, C. D., Vassilas, C. A., Carter, H., & Haque, M. S. (2004). Training health professionals in the recognition, assessment and management of suicide risk. International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice, 8, 117–121. doi:10.1080/13651500410005658
Goldston, D. B. (2003). Measuring suicidal behavior and risk in children and adolescents. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Heppner, P. P., Wampold, B. E., & Kivlighan, Jr. D. M. (2007). Research design in counseling: Research, statistics, and program evaluation (3rd ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Horowitz, L., Ballard, E., & Paoa, M. (2009). Suicide screening in schools, primary care and emergency departments. Current Opinion in Pediatrics, 21, 620–627.
Jacobson, J. M., Ting, L., Sanders, S., & Harrington, D. (2004). Prevalence of and reactions to fatal and nonfatal client suicidal behavior: A national study of mental health social workers. Omega, 49, 237–248.
Jahn, D. R., Wacha-Montes, A., Dra-Peau, C. W., Grant, B., Nadorff, M. R., Pusateri, M. J., Jr., . . . & Cukrowicz, K. C. (2012). Suicide-specific courses and training: Prevalence, beliefs, and barriers. Part I: Graduate psychology programs and professionals schools of psychology. Manuscript in preparation.
Kleespies, P., Penk, W., & Forsyth, J. (1993). The stress of patient suicidal behavior during clinical training: Incidence, impact, and recovery. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 24, 293–303.
Kung, H. S., Hoyert, D. L., Xu, J., & Murphy, S. L. (2008). Deaths: Final data for 2005. National Vital Statistics Reports, 56, 1–66.
Mackelprang, J. L., Karle, J., Reihl, K. M., & Cash, R. E. (2014). Suicide intervention skills: Graduate training and exposure to suicide among psychology trainees. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 8, 136–142.
McEvoy, M. L., & McEvoy, A. W. (2000). Preventing youth suicide: A handbook for educators and human service professionals. Holmes Beach, FL: Learning Publications.
McNiel, D. E., Fordwood, S. R., Weaver, C. M., Chamberlain, J. R., Hall, S. E., & Binder, R. L. (2008). Effects of training on suicide risk assessment. Psychiatric Services, 59, 1462–1465. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.59.12.1462
National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention: Research Prioritization Task Force. (2014). A prioritized research agenda for suicide prevention: An action plan to save lives. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Mental Health.
O’Connor, R. C., Platt, S., & Gordon, J. (2011). International Handbook of Suicide Prevention: Research, Policy and Practice. United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
O’Connor, N., Warby, M., Raphael, B., & Vassallo, T. (2004). Changeability, confidence, common sense and corroboration: Comprehensive suicide risk assessment. Australasian Psychiatry, 12, 352–360.
Oordt, M. S., Jobes, D. A., Fonseca, V. P., & Schmidt, S. M. (2009). Training mental health professionals to assess and manage suicidal behavior: Can provider confidence and practice behaviors be altered? Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 39, 21–32. doi:10.1521/suli.2009.39.1.21
Osteen, P. J., Frey, J. J., & Ko, J. (2014). Advancing training to identify, intervene, and follow up with individuals at risk for suicide through research. American Journal of Preventative Medicine, 47, 216–221. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2014.05.033
Poland, S. (1989). Suicide intervention in the schools. New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Poland, S., & Lieberman, S. (2002). Best practices in suicide intervention. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology IV – Volume II (pp. 1151–1165). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Rudd, M. D. (2006). The assessment and management of suicidality. Sarasota, FL: Professional Resource Press.
Rudd, M. D., Cukrowicz, K. C., & Bryan, C. J. (2008). Core competencies in suicide risk assessment and management: Implications for supervision. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 2, 219–228.
Ruth, B. J., Muroff, J., Gianino, M., Feldman, B. N., McLaughlin, D., Ross, A., & Hill, E. (2009). Suicide prevention education in social work education: What do MSW deans, directors and faculty have to say? Paper session presented at the meeting of the American Public Health Association, Philadelphia, PA.
Sanders, S., Jacobson, J. M., & Ting, L. (2008). Preparing for the inevitable: Training social workers to cope with client suicide. Journal of Teaching in Social Work, 28, 1–18.
Schmidt, W. C. (1997). World-wide web survey research: Benefits, potential problems, and solutions. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 29, 274–279.
Schmidt, R. C., Iachini, A. L., George, M., Koller, J., & Weist, M. (2015). Integrating a suicide prevention program into a school mental health system: A case example from a rural school district. Children & Schools, 37, 18–27.
Schmitz, W. M., Allen, M. H., Feldman, B. N., Gutin, N, J., Jahn, D. R., Kleespies, P. M., . . . & Simpson, J. D. (2012). Preventing suicide through improved training in suicide risk assessment and care: An American Association of Suicidology task force report addressing serious gaps in U.S. mental health training. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 42, 292–304. doi:10.1111/j.1943-278X.2012.00090.x
Singer, J. B., & Slovak, K. (2011). School social workers’ experiences with youth suicidal behavior: An exploratory study. Children & Schools, 33, 215–228.
Smith, A. R., Silva, C., Covington, D. W., & Joiner, T. E. (2014). An assessment of suicide related knowledge and skills among health professionals. Health Psychology, 33, 110–119.
Stein-Erichsen, J. L. (2010). School psychologists’ confidence level with suicide intervention and prevention in the schools. Retrieved from: http://digitalcommons.pcom.edu/psychology_dissertations/132.
Sue, V. M., & Ritter, L. A. (2012). Conducting online surveys (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sullivan, G. R., & Bongar, B. (2009). Assessing suicide risk in the adult patient. In P. M. Kleespies (Ed.), Behavioral emergencies: An evidenced –based resource for evaluating and managing risk of suicide, violence, and victimization (pp. 59–78). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Tetlock, P. E. (2005). Expert political judgment: How good is it? How can we know? Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Wachter, C. A. (2006). Crisis in the schools: Crisis, crisis intervention training and school counselor burnout. ACES Research Grant. Association for Counselor Education and Supervision. Retrieved from http://libres.uncg.edu/ir/uncg/f/umi-uncg-1190.pdf
Wozny, D. A. (2005). Suicide risk assessment: Counselor competency. In J. R. Rodgers (Ed.), Suicide 2006: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the American Suicidology Association (pp. 224–227). Washington, DC: American Association of Suicidology.
Robert C. Schmidt, NCC, is a Behavioral Specialist at Talbot County Public Schools in Easton, MD. Correspondence can be addressed to Robert C. Schmidt, Talbot County Public Schools, 12 Magnolia Street, Easton, MD 21601, rschmidt@tcps.k12.md.us.





