Nov 9, 2022 | Volume 12 - Issue 3
Krystle Himmelberger, James Ikonomopoulos, Javier Cavazos Vela
We implemented a single-case research design (SCRD) with a small sample (N = 2) to assess the effectiveness of solution-focused brief therapy (SFBT) for Latine clients experiencing mental health concerns. Analysis of participants’ scores on the Dispositional Hope Scale (DHS) and Outcome Questionnaire (OQ-45.2) using split-middle line of progress visual trend analysis, statistical process control charting, percentage of non-overlapping data points procedure, percent improvement, and Tau-U yielded treatment effects indicating that SFBT may be effective for improving hope and mental health symptoms for Latine clients. Based on these findings, we discuss implications for counselor educators, counselors-in-training, and practitioners, which include integrating SFBT principles into the counselor education curriculum, teaching counselors-in-training how to use SCRDs to evaluate counseling effectiveness, and using the DHS and OQ-45.2 to measure hope and clinical symptoms.
Keywords: solution-focused brief therapy, single-case research design, hope, counselor education, clinical symptoms
Solution-focused brief therapy (SFBT) is a strength-based and evidence-based intervention that helps clients focus on personal strengths, identify exceptions to problems, and highlight small successes (Berg, 1994; Gonzalez Suitt et al., 2016; Schmit et al., 2016). Schmit et al. (2016) conducted a meta-analysis of SFBT for treating symptoms of internalizing disorders and identified that SFBT might be effective in creating short-term changes in clients’ functioning. Other researchers (e.g., Gonzalez Suitt et al., 2016; Novella et al., 2020) also found that SFBT can be helpful with clients from various cultural backgrounds and with different presenting symptoms such as anxiety. Yet, there is scant research evaluating the efficacy of SFBT on subjective well-being with Latine (a gender-neutral term that is more consistent with Spanish language and grammar than Latinx) populations. Additionally, there is not a lot of research that investigates the effectiveness of counseling practices among counselors-in-training (CITs) at community counseling clinics with culturally diverse clients. Although the costs are relatively low, the type of supervision, training, and feedback given to CITs provides community clients with the potential for effective counseling services. However, only a few researchers (e.g., Schuermann et al., 2018) have explored the efficacy of counseling services within a community counseling training clinic. Therefore, empirical research is needed regarding the efficacy of SFBT with Latine populations in a counseling training clinic at a Hispanic Serving Institution.
The Latine population is a fast-growing group in the United States and makes up approximately 19% of the U.S. population (U.S. Census Bureau, 2020). Despite this growth, members of this culturally diverse population continue to face individual, interpersonal, and institutional challenges (Ponciano et al., 2020; Vela, Lu, et al., 2014). Because Latine individuals experience discrimination and negative environments (Cheng & Mallinckrodt, 2015; Ponciano et al., 2020; Ramos et al., 2021), perceive lack of support from counselors and teachers in K–12 school environments (A. G. Cavazos, 2009; Vela-Gude et al., 2009), and experience microaggressions (Sanchez, 2019), they are likely to experience greater mental health challenges. Researchers have identified numerous internalizing and externalizing symptoms that represent Latine individuals’ mental health experiences, likely putting them at greater risk for mental health impairment and poor psychological functioning (Cheng et al., 2016). Researchers also detected that Latine youth had similar or higher prevalence rates of internalizing disorders (e.g., anxiety and depression) when compared with their White counterparts (Merikangas et al., 2010; Ramos et al., 2021). Given that Latine individuals might be at greater risk for psychopathology and their mental health needs are often unaddressed because they do not seek mental health services (Mendoza et al., 2015; Sáenz et al., 2013), further evaluation of the effectiveness of counseling practices for this population is necessary.
Fundamental Principles of Solution-Focused Brief Therapy
Developed from the clinical practice of Steven de Shazer and Insoo Kim Berg, SFBT is a future-focused and goal-directed approach that focuses on searching for solutions and is created on the belief that clients have knowledge and resources to resolve their problems (Kim, 2008). Counselors’ therapeutic task is to help clients imagine how they would like things to be different and what it will take to facilitate small changes. Counselors take active roles by asking questions to help clients look at the situation from different perspectives and use techniques to identify where the solution occurs (de Shazer, 1991; Proudlock & Wellman, 2011).
In SFBT, counselors amplify positive constructs and solutions by using specific strategies and techniques to build on positive factors (Tambling, 2012). Common techniques include the miracle question, scaling questions, exceptions, experiments, and compliments, which are designed to help clients identify personal strengths and cultivate what works (de Shazer, 1991; Proudlock & Wellman, 2011). We agree with Vela, Lerma, et al. (2014) that counselors can use postmodern and strength-based theories (e.g., SFBT) to develop positive psychology constructs such as hope, positive emotions, and subjective well-being. SFBT might be useful to help Latine clients identify strengths, build on what works, and reconstruct a positive future outcome.
Several researchers have indicated the efficacy of SFBT for treating various issues with different populations (Bavelas et al., 2013; Kim, 2008). Schmit et al. (2016) conducted a meta-analysis with 26 studies examining the effectiveness of SFBT for treating symptoms of depression and anxiety. They found that SFBT resulted in moderately successful treatment; however, adults’ treatment effects were 5 times larger when compared to those of youth and adolescents. One possible explanation was that SFBT may require clients’ maturity to integrate and understand SFBT concepts and techniques. Researchers also concluded that the impact of SFBT may be effective in producing short-term changes that will lead to further gains in symptom relief as well as psychological functioning (Schmit et al., 2016).
Brogan et al. (2020) commented that “there are limited studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of this method with the Latine . . . population” (p. 3). However, we postulate that SFBT principles are compatible with Latine cultural and family characteristics (Lerma et al., 2015; Oliver et al., 2011). There are several reasons that make SFBT an appropriate fit for working with the Latine population. For instance, researchers suggest that understanding family dynamics or familismo when evaluating mental health and overall well-being with the Latine population is important (Ayón et al., 2010). Familismo is strong family ties to immediate and extended families in the Latine culture.
In a study investigating Latine families, Priest and Denton (2012) found that family cohesion and family discord were associated with anxiety. Calzada et al. (2013) also highlighted that although family support can positively impact mental health, family can also become a source of conflict and stress, which might result in poor mental health. By using SFBT principles, counselors can help Latine clients identify how familismo is a source of strength through sense of loyalty and cooperation among family members (Oliver et al., 2011).
Another emphasis with SFBT that aligns with the Latine culture is the focus on personal and family resiliency. Because Latine individuals must navigate individual, interpersonal, and institutional challenges (Vela et al., 2015), they have natural resilience and coping skills that align with an SFBT approach. Counselors can use exceptions, scaling questions, and compliments to help Latine individuals discover their inherent resilience and continue to persevere through personal adversity.
Constructs: Hope and Clinical Symptoms
Consistent with a dual-factor model of mental health (Suldo & Shaffer, 2008), we focused on two outcomes: hope and clinical symptoms. First, hope, which has been associated with subjective well-being among Latine populations (Vela, Lu, et al., 2014), refers to a pattern of thinking regarding goals (Snyder et al., 2002). Snyder et al. (1991) proposed Hope Theory with pathways thinking and agency thinking. Pathways thinking refers to individuals’ plans to pursue desired objectives (Feldman & Dreher, 2012), while agency thinking refers to perceptions of ability to make progress toward goals (Snyder et al., 1999). Researchers found that hope was positively related to meaning in life, grit, and subjective happiness among Latine populations (e.g., Vela, Lerma, et al., 2014; Vela et al., 2015). Other researchers (e.g., Vela, Ikonomopoulos, et al., 2016) have explored the impact of counseling interventions on hope among Latine adolescents and survivors of intimate partner violence. Given the association between hope and other positive developmental outcomes among Latine populations, examining this construct as an outcome in clinical mental health counseling services is important.
In addition to hope as an indicator of subjective well-being, we used the Outcome Questionnaire (OQ-45.2; Lambert et al., 1996) to measure clinical symptoms in the current study for several reasons, including its strong psychometric properties, its use in the counseling training clinic where this study took place, and its use in other studies that evaluate the efficacy of counseling or psychotherapy and show evidence based on relation to other variables such as depression and clinical symptoms (Ekroll & Rønnestad, 2017; Ikonomopoulos et al., 2017; Soares et al., 2018). The OQ-45.2 measures three areas that are central to individual psychological functioning: Symptom Distress, Interpersonal Relations, and Social Role Performance.
Purpose of Study and Rationale
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of SFBT for increasing hope and decreasing clinical symptoms among Latine clients. We implemented an SCRD (Lenz et al., 2012) to identify and explore changes in hope and clinical symptoms as a result of participation in SFBT. We evaluated the following research question: To what extent is SFBT effective for increasing hope and decreasing clinical symptoms among Latine clients who receive services at a community counseling clinic?
Methodology
We implemented a small-series (N = 2) AB SCRD with Latine clients admitted into treatment at an outpatient community counseling clinic to evaluate the treatment effect associated with SFBT for increasing hope and reducing clinical symptoms. The rationale for using an SCRD was to explore the impact of an intervention that might help Latine clients at a community counseling training clinic. We used criterion sampling to recruit participants who (a) sought counseling services at a community counseling clinic, (b) had internalizing symptoms related to anxiety and depression, and (c) worked with a CIT who was supervised by faculty in a clinical mental health counseling program.
Participants
Participants in this study were two adults admitted into treatment at an outpatient community counseling clinic in the Southern region of the United States. Both participants identified as Hispanic; one identified as a female and the other identified as a male. During informed consent, we explained to participants that they would be assigned pseudonyms to protect their identity. The participants consented to both treatment and inclusion in the research study.
The two participants for this study were selected to participate in this study because of their presenting internalizing symptoms (e.g., depression, anxiety) and fit for SFBT principles. Because we wanted to increase hope among these Latine clients, we felt that SFBT was an appropriate approach. The fundamental principles of SFBT align with attempting to facilitate hope among clients with various symptoms because it helps clients view mental health challenges as opportunities to cultivate strengths, explore solutions, and identify new skills (Bannik, 2008; Joubert & Guse, 2021). SFBT practitioners also posit that clients can recreate their future, cultivate resilience, and construct solutions, which aligns well with tenets of the Latine culture (J. Cavazos et al., 2010). In the first session prior to treatment, both clients indicated that they believed they were in control of their future mental health and that they could construct solutions. We also informed them that SFBT focuses on future solutions as opposed to focusing on problems and the past. Because these clients indicated a willingness to explore their future through co-constructing solutions, they were a good fit for SFBT principles in counseling.
Participant 1
“Mary” was a 31-year-old Latine female with a history of receiving student mental health services at a university counseling clinic. Mary sought individual counseling services because of a recent separation with the father of her three children who was emotionally abusive. Anxiety associated with this separation was compounded by traumatic experiences from 5 years prior. Mary stated that her Latine culture generated greater symptoms of anxiety while recognizing her new role as a single mother. Mary’s therapeutic goals and focus of treatment were to reduce clinical symptoms of anxiety as well as improve self-identity and self-esteem.
Participant 2
“Joel” was a 20-year-old Latine male with a history of receiving mental health services for symptoms of depression. Joel’s therapeutic goals and focus of treatment were to reduce clinical symptoms of anxiety and associated anger as well as improve self-esteem. Joel reported being a victim of domestic violence and child abuse. Additionally, Joel expressed distress with revealing his sexual identity because of patriarchal roles in the Latine culture that may result in rejection.
Measurements
Outcome Questionnaire (OQ-45.2)
The OQ-45.2 is a 45-item self-report outcome questionnaire (Lambert et al., 1996) for adults 18 years of age and older. Each item is associated with a 5-point Likert scale with responses ranging from never (1) to almost always (5). We used the total score for the OQ-45, which was calculated by summing the three subscale scores with a possible total score ranging from 0–180. Higher scores are reflective of more severe distress and impairment. Sample response items include “I feel worthless” and “I have trouble getting along with friends and close acquaintances.” This assessment was designed to include items relevant to three domains central to mental health: Symptom Distress, Interpersonal Relations, and Social Role Performance (Lambert et al., 1996).
Researchers have examined structural validity and reliability. Coco et al. (2008) used a confirmatory factor analysis to test various models of the factorial structure. They found support for the four-factor, bi-level model, which means that each survey item relates to a subscale as well as an overall maladjustment score. Amble et al. (2014) also examined psychometric properties using confirmatory factor analysis, concluding that “the total score of the OQ-45 is a reliable and valid measure for assessing therapy progress” (p. 511). Their findings are like Boswell et al.’s (2013) findings that found support for the validity of the total OQ-45 score. There is also evidence based on relation to other clinical outcomes measured by the General Severity Index from the Symptom Checklist 90-Revised, the Beck Depression Inventory, and Social Adjustment Scale (Lambert et al., 1996). Additionally, previous psychometric evaluations have revealed evidence of reliability through reliability indices such as Cronbach’s alpha (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2017; Kadera et al., 1996; Umphress et al., 1997). Internal consistency estimates through Cronbach’s alpha range from .71 to .92 (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2017; Lambert et al., 1996).
Hope
The Dispositional Hope Scale (DHS; Snyder et al., 1991) is a self-report inventory to measure participants’ attitudes toward goals and objectives. Participants responded to eight statements evaluated on an 8-point Likert scale ranging from definitely false (1) to definitely true (8). We used the total Hope score, which was obtained by summing scores for both Agency and Pathways subscales. Total scores range from 8–64, with higher scores indicating greater levels of hope. Sample response items include “I can think of many ways to get the things in life that are important to me” and “I can think of many ways to get out of a jam.”
Researchers have examined structural validity and reliability. Galiana et al. (2015) used confirmatory factor analysis to identify that a one-factor structure was the best fit. There is also evidence of validity with other theoretically relevant constructs such as meaning in life (Vela et al., 2017) as well as evidence of concurrent and discriminant validity with other measures related to self-esteem, state hope, and state positive and negative affect (Snyder et al., 1996). There is also evidence of factorial invariance (Nel & Boshoff, 2014), suggesting that factor structure is similar across gender and racial ethnic groups. Additionally, there is evidence of reliability (e.g., internal consistency) as indicated through Cronbach’s alpha coefficients ranging from .85 to .86 (Snyder et al., 2002; Vela et al., 2015).
Study Setting
During the present study, each participant was involved in individual counseling at a community counseling clinic. The facility, located in the Southern region of the United States, provides free counseling services to community members. Individual and group sessions are free and last approximately 45 to 50 minutes. The community counseling clinic offers preventive and early treatment for developmental, emotional, and interpersonal difficulties for community members. CITs at the community counseling clinic are graduate counseling students enrolled in practicum or internship.
Interventionists
Krystle Himmelberger, who was the CIT in the current study, adapted strength-based interventions designed to facilitate positive feelings by helping clients set goals, focus on the future, and find solutions rather than problems. She was a CIT in a clinical mental health counseling program. Prior to the study, she selected and designed interventions and activities according to specific guidelines from SFBT manuals and sources (Buchholz Holland, 2013; de Shazer et al., 2007; Trepper et al., 2010).
James Ikonomopoulos and Javier Cavazos Vela were faculty counseling supervisors who monitored sessions and provided weekly supervision to maintain fidelity of SFBT interventions. Bavelas et al. (2013) suggested that live supervision may provide a second set of clinical eyes to help CITs. Himmelberger received weekly supervision to ensure procedural and treatment adherence (Liu et al., 2020). Furthermore, videotaped supervision and transcriptions provided her with the ability to communicate between sessions. These measures were used to enhance treatment fidelity by focusing on quality and competency.
SFBT Principles and Intervention
Participants received six to nine sessions of individual SFBT using the description of techniques and activities in the following resources: More Than Miracles: The State of the Art of Solution-Focused Brief Therapy (de Shazer et al., 2007), Solution-Focused Therapy Treatment Manual for Working With Individuals (Trepper et al., 2010), and “The Lifeline Activity With a ‘Solution-Focused Twist’” (Buchholz Holland, 2013). We used the following SFBT principles to guide the intervention: focus on specific topics, a positive and co-constructed therapeutic relationship, and questioning techniques (Trepper et al., 2010). First, Himmelberger focused on specific topics such as preferred future, strengths, confidence in finding solutions, and exceptions. She used future-specific and solution-focused language in each session to help clients focus on their preferred futures. Second, she developed a positive therapeutic relationship with clients through shared trust and co-construction of counseling experiences. She was positive and helpful, and she helped instill optimism and hope in her clients. A positive therapeutic relationship was evidenced based on her report as well as live supervision and reviews of session recordings. Finally, Himmelberger used questioning techniques that focused on clients’ strengths, exceptions, and coping skills. She used questioning techniques that helped clients focus on progress toward their preferred future and future-oriented solutions.
The techniques she used included looking for previous solutions, exceptions, the miracle question, scaling questions, compliments, future-oriented questions, and “so what is better” questions. Himmelberger used looking for previous solutions to help clients identify their previous coping strategies to cope with the problem. Based on Himmelberger’s report in supervision sessions, both clients commented that they were surprised that they had been successful in the past when the problem did not exist. She also used exceptions to help clients identify what was different when the problem did not exist. Additionally, she used present- and future-oriented questions to help clients focus on future solutions. This was an important technique as clients were not used to ignoring the problem. When clients provided updates on their progress toward their goals, Himmelberger used compliments to validate what clients were doing well. Using compliments helped cultivate a positive therapeutic relationship with these clients.
Finally, with the miracle question, she asked clients to provide details about their preferred future and what that would look like. She followed up with a question about constructing solutions regarding what work it would take to make that preferred future happen. Then in each session, she conducted progress checks toward that preferred future by asking scaling questions (On a scale from 1–10, where are you now with progress toward your preferred future?) and questions about “what is better” (What is better now when compared to last week?). She complimented clients’ progress toward that preferred future.
Procedures
We used AB SCRD to determine the effectiveness of an SFBT treatment program (Lundervold & Belwood, 2000; Sharpley, 2007) using scores on the DHS and OQ-45.2 total scale as outcome measures (Lambert et al., 1996). The two participants who were assigned to Himmelberger did not begin counseling until they consented to treatment and the research study. In other words, they did not receive counseling services prior to participation in this study. After 4 weeks of data collection, the baseline phase of data collection was completed. Participants did not receive counseling services during the baseline period.
The treatment phase began after the fourth baseline measure. At the conclusion of each individual session, participants completed the DHS and OQ-45.2. Himmelberger collected and stored the measures in each participant’s folder in a locked cabinet in the clinic. After the 12th week of data collection, the treatment phase of data collection was completed, at which point the SFBT intervention was withdrawn.
A percentage of non-overlapping data (PND) procedure was used to analyze quantitative data (Scruggs et al., 1987). A visual representation of change over time is graphically represented with a split-middle line of progress visual trend analysis showing data points from each phase (Lenz, 2015). Statistical process control charting was used to determine whether the characteristics of treatment phase data were beyond the realm of random occurrence with 99% confidence (Lenz, 2015). An interpretation of effect size was estimated using Tau-U to complement PND analysis (Lenz, 2015; Sharpley, 2007).
Data Collection and Analysis
We implemented the PND (Scruggs et al., 1987) to analyze scores on the Hope and OQ-45.2 scales across phases of treatment. The PND procedure yields a proportion of data in the treatment phase that overlaps with the most conservative data point in the baseline phase. PND calculations are expressed in a decimal format that ranges between 0 and 1, with higher scores representing greater treatment effects (Lenz, 2013).
Upon considering the percentage of data exceeding the median procedure (Ma, 2006), we selected the PND because it is considered a robust method of calculating treatment effectiveness (Lenz, 2013). This metric is conceptualized as the percentage of treatment phase data that exceeds a single noteworthy point within the baseline phase. Because we aimed for an increase in DHS scores, the highest data point in the baseline phase was used. Finally, given that we aimed for a decrease in OQ-45.2 total scale scores, the lowest data point in the baseline was used (Lenz, 2013). To calculate the PND statistic, data points in the treatment phase on the therapeutic side of the baseline are counted and then divided by the total number of points in the treatment phase (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2016).
Estimates of Effect Size and Clinical Significance
PND values are typically interpreted using the estimation of treatment effect provided by Scruggs and Mastropieri (1998) wherein values of .90 and greater are indicative of very effective treatments, those ranging from .70 to .89 represent moderate effectiveness, those between .50 to .69 are debatably effective, and scores less than .50 are regarded as not effective (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2015, 2016). Tau-U values are typically interpreted using the estimation of treatment effect provided by Vannest and Ninci (2015) wherein Tau-U magnitudes can be interpreted as small (≤ .20), moderate (.20–.60), large (.60–.80), and very large (≥ .80). These procedures were completed for each participant’s scores on the Hope and OQ-45.2 scales.
Clinical significance was determined in accordance with Lenz’s (2020a, 2020b) calculations of percent improvement (PI) values. Percent improvement values greater than 50% were interpreted as representing clinically significant improvement with large effect sizes, 25% to 49% were interpreted as slightly improved without clinical significance, and less than 25% represented no clinical significance. Lenz (2021) also recommended for researchers to provide sufficient context and visual representation when interpreting and reporting clinical significance. As one example, without context and visual representation, researchers could interpret a PI value of 49% as not having clinical significance.
Results
A detailed description of participants’ experiences is provided below. Figure 1 depicts estimates of treatment effect on the DHS; Figure 2 depicts estimates of treatment effect on the OQ-45.2 total scale.
Figure 1
Ratings for Hope by Participants With Split-Middle Line of Progress
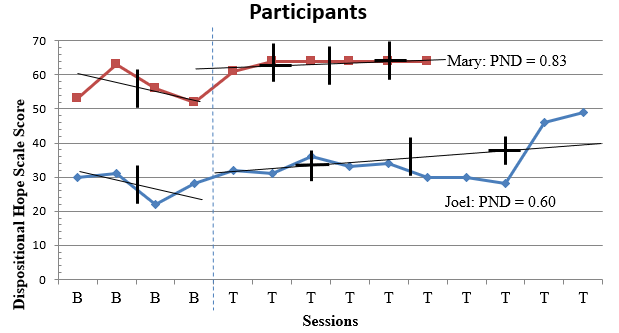
Note. PND = Percentage of Non-overlapping Data.
Figure 2
Ratings for Mental Health Symptoms on OQ-45.2 by Participants with Statistical Process Control Charting
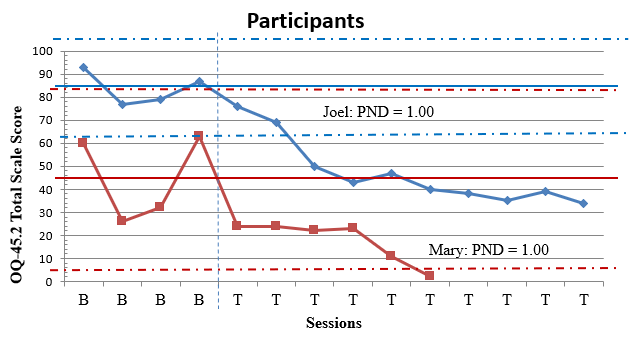
Note. PND = Percentage of Non-overlapping Data.
Participant 1
Data for Mary is represented in Figures 1 and 2 as well as Tables 1 and 2. A comparison of level of Hope across baseline (M = 56.00) and intervention phases (M = 63.50) indicated notable changes in participant scores evidenced by an increase in mean DHS scores over time. Variation between scores in baseline (SD = 3.50) and intervention (SD = 0.83) indicated differential range in scores before and after the intervention. Data in the baseline phase trended downward toward a contra-therapeutic effect over time. Dissimilarly, data in the intervention phase trended upward toward a therapeutic effect over time. Comparison of baseline level and trend data with the first three observations in the intervention phase did suggest immediacy of treatment response for the participant. Data in the intervention phase moved into the desired range of effect for scores representing Hope. Overall, visual inspection of Mary’s ratings on the DHS (see Figure 1) indicates that most of her scores in the treatment phase were higher than her scores in the baseline phase.
Mary’s ratings on the DHS illustrate that the treatment effect of SFBT was moderately effective for improving her DHS score. Evaluation of the PND statistic for the DHS score measure (0.83) indicated that five out of six scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (DHS score of 63). Mary successfully improved Hope during treatment as evidenced by improved scores on items such as “I can think of many ways to get out of a jam,” “I can think of ways to get the things in life that are important to me,” and “I meet the goals that I set for myself.” Scores above the PND line were within a 1-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. This finding is corroborated by the associated Tau-U value (τU = 0.92), which suggested a very large degree of change in which the null hypothesis about intervention efficacy for Mary could be rejected (p = .02). Also, interpretation of the clinical significance estimate of PI is that 13.39% improvement is not clinically significant (Lenz, 2020a, 2020b). See Table 1 for information regarding PND, Tau-U, and PI. Although the PI value is considered not clinically significant, it is important to contextualize this finding within visual inspection of Mary’s Hope scores in Figure 1. Because Mary had moderately high levels of Hope in the baseline phase, her room for improvement based on the ceiling effect as related to Hope was not high. In other words, in the context of Mary’s treatment and visual inspection of her scores, the SFBT intervention helped Mary move from good to better. In the context of Mary’s treatment and a visual representation of her scores on the DHS (see Figure 1), the SFBT intervention had some level of convincingness, which means that some amount of change in Hope occurred for Mary (Kendall et al., 1999; Lenz, 2021).
Table 1
Ratings for Hope by Participants
|
Age |
Ethnicity |
Gender |
Baseline Data |
Intervention Data |
PND |
τU (p) |
PI |
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
| Mary |
31 |
Latina |
Female |
56.00 |
3.50 |
63.50 |
0.83 |
83% |
0.92 (.02) |
13.39% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Joel |
20 |
Latino |
Male |
27.75 |
2.87 |
34.90 |
5.26 |
60% |
0.70 (.05) |
25.75% |
Note. PND = Percentage of Non-overlapping Data.
Table 2
Ratings for OQ-45.2 Total Scale Score by Participants
|
Age |
Ethnicity |
Gender |
Baseline Data |
Intervention Data |
PND |
τU (p) |
PI |
|
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
|
| Mary |
31 |
Latina |
Female |
45.25 |
16.25 |
17.67 |
7.44 |
100% |
−1.00 (.01) |
60.95% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Joel |
20 |
Latino |
Male |
84.00 |
6.00 |
47.10 |
10.74 |
100% |
−1.00 (.004) |
43.93% |
|
Note. PND = Percentage of Non-overlapping Data.
Before treatment began, one of Mary’s baseline measurements was above the cut-score guideline on the OQ-45.2 of a total scale score of 63, which indicates symptoms of clinical significance. Comparison of level of clinical symptoms across baseline (M = 45.25) and intervention phases (M = 17.67) indicated notable changes in participant scores evidenced by a decrease in mental health symptom scale scores over time. Variation between scores in baseline (SD = 16.25) and intervention (SD = 7.44) indicated differential range in scores before and after the intervention. Data in the baseline phase trended upward toward a contra-therapeutic effect over time. Dissimilarly, data in the intervention phase trended downward toward a therapeutic effect over time. Comparison of baseline level and trend data with the first three observations in the intervention phase did suggest immediacy of treatment response for the participant. Data in the intervention phase moved into the desired range of effect for scores representing mental health symptoms.
Mary’s ratings on the OQ-45.2 illustrate that the treatment effect of SFBT was very effective for decreasing her total scale score measuring mental health symptoms. Evaluation of the PND statistic for the OQ-45.2 total scale score measure (1.00) indicated that all six scores were on the therapeutic side below the baseline (total scale score of 26). Mary successfully reduced clinical symptoms during treatment as evidenced by improved scores on items such as “I am a happy person,” “I feel loved and wanted,” and “I find my work/school satisfying.” This contention became most apparent after the first treatment session when Mary continuously scored lower on a majority of symptom dimensions such as Symptom Distress, Interpersonal Relations, and Social Role Performance. Scores below the PND line were within a 24-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. This finding is corroborated by the associated Tau-U value (τU = −1.0), which suggested a very large degree of change in which the null hypothesis about intervention efficacy for Mary could be rejected (p = .01). An analysis of statistical process control charting revealed that one data point in the treatment phase was beyond the realm of random occurrence with 99% confidence. This finding also corresponds with interpretation of the clinical significance estimate of PI that 60.95% improvement is clinically significant (Lenz, 2020a, 2020b). See Table 2 for information regarding PND, Tau-U, and PI. In the context of Mary’s treatment and a visual representation of Mary’s scores on the OQ-45.2 (see Figure 2), the SFBT intervention had a high level of convincingness, which means that a considerable amount of change in clinical symptoms occurred for Mary (Kendall et al., 1999; Lenz, 2021).
Participant 2
Data for Joel is represented in Figures 1 and 2 as well as Tables 1 and 2. Comparison of level of Hope across baseline (M = 27.75) and intervention phases (M = 34.90) indicated notable changes in participant scores evidenced by an increase in mean DHS scores over time. Variation between scores in baseline (SD = 2.87) and intervention (SD = 5.26) indicated differential range in scores before and after the intervention. Data in the baseline phase trended downward toward a contra-therapeutic effect over time. Dissimilarly, data in the intervention phase trended upward toward a therapeutic effect over time. Comparison of baseline level and trend data with the first three observations in the intervention phase did suggest immediacy of treatment response for the participant. Data in the intervention phase moved into the desired range of effect for scores representing Hope.
Joel’s ratings on the DHS illustrate that the treatment effect of SFBT was debatably effective for improving his DHS score. Evaluation of the PND statistic for the DHS score measure (0.60) revealed that six out of ten scores were on the therapeutic side above the baseline (DHS score of 31). Joel successfully improved his Hope during treatment as evidenced by improved scores on items such as “I can think of many ways to get out of a jam,” “I can think of ways to get the things in life that are important to me,” and “I meet the goals that I set for myself.” Scores above the PND line were within an 18-point range. Trend analysis depicted a steady level of scores following the first treatment measure, with scores vacillating around the baseline score until the eighth treatment measure. This finding is corroborated by the associated Tau-U value (τU = 0.70), which suggested a large degree of change in which the null hypothesis about intervention efficacy for Joel could be rejected (p = .047). This finding also corresponds with interpretation of the clinical significance estimate of PI that 25.75% is slightly improved but not clinically significant (Lenz, 2020a, 2020b). One explanation for the lack of clinical significance and moderate effect size is the limited nature of the intervention. Based on results from visual depiction of Joel’s levels of Hope across treatment (see Figure 1), we suspect that this trend would have continued if he had received additional sessions of an SFBT intervention. His treatment was trending in a positive trajectory. In the context of Joel’s treatment and a visual representation of his scores on the DHS (see Figure 1), the SFBT intervention had a moderate level of convincingness, which means that a considerable amount of change in Hope occurred for Joel (Kendall et al., 1999; Lenz, 2021).
Before treatment began, all four of Joel’s baseline measurements were above the cut-score guideline on the OQ-45.2 of a total scale score of 63, which indicates symptoms of clinical significance. Comparison of level of clinical symptoms across baseline (M = 84.00) and intervention phases (M = 47.10) indicated notable changes in participant scores evidenced by a decrease in mental health symptom scale scores over time. Variation between scores in baseline (SD = 6.00) and intervention (SD = 10.74) indicated differential range in scores before and after intervention. Data in the baseline phase trended upward toward a contra-therapeutic effect over time. Dissimilarly, data in the intervention phase trended downward toward a therapeutic effect over time. Comparison of baseline level and trend data with the first three observations in the intervention phase did suggest immediacy of treatment response for the participant. Data in the intervention phase moved into the desired range of effect for scores representing mental health symptoms.
Joel’s ratings on the OQ-45.2 illustrate that the treatment effect of SFBT was very effective for decreasing his total scale score measuring clinical symptoms. Evaluation of the PND statistic for the total scale score measure (1.00) indicated that all 10 scores were on the therapeutic side below the baseline (total scale score of 77). Joel successfully reduced clinical symptoms during treatment as evidenced by improved scores on items such as “I am a happy person,” “I feel loved and wanted,” and “I find my work/school satisfying.” This contention became most apparent after the first treatment session when Joel continuously scored lower on a majority of symptom dimensions such as Symptom Distress, Interpersonal Relations, and Social Role Performance. Scores below the PND line were within a 41-point range. Trend analysis depicted a consistent level of improvement following the first treatment measure. This finding is corroborated by the associated Tau-U value (τU = −1.0), which suggested a very large degree of change in which the null hypothesis about intervention efficacy for Joel can be rejected (p = .004). An analysis of statistical process control charting revealed that eight data points in the treatment phase were beyond the realm of random occurrence with 99% confidence. This finding also corresponds with interpretation of the clinical significance estimate that 43.93% of improvement is slightly improved but not clinically significant (Lenz, 2020a, 2020b). Considering contextual evidence from the intervention as well as data visualization of Figure 2, it was clear that Joel experienced a downward trajectory in clinical symptoms. If he had received additional SFBT sessions, we suspect that he would have continued to experience a reduction in clinical symptoms. In the context of Joel’s treatment and a visual representation of his scores on the OQ-45.2 (see Figure 2), the SFBT intervention had a high level of convincingness, which means that a considerable amount of change in Hope occurred for Joel (Kendall et al., 1999; Lenz, 2021).
Discussion
The purpose of this exploratory study was to examine the impact of SFBT on clinical symptoms and hope among Latine clients. The results yield promising findings and preliminary evidence about the efficacy of SFBT as an intervention for promoting positive change across two Latine clients’ clinical symptoms and hope. The scores varied for each outcome variable, and this is likely related to the length and duration of the intervention as well as each participant’s personal characteristics (Callender et al., 2021) and relationship to their counselor (Liu et al., 2020). Findings from the current study also lend further support regarding the efficacy among CITs who aim to impact clients’ psychological functioning at a community counseling training clinic.
The findings for clinical symptoms showed a trend toward reduction in clinical symptoms across 8 weeks of SFBT. Both participants reported statistically significant improvements (p < .05) in reductions of clinical symptoms on the OQ-45.2. In both cases, the SFBT intervention was within the range of very large treatment effectiveness and clinical significance for improving symptoms of psychopathology. Results from the PND and PI confirmed that these participants experienced reduced clinical symptoms. It appears that there was a steady progression of improvement for these participants after their second treatment session. During this phase of treatment, Himmelberger used techniques such as exceptions to the problem and scaling questions to help participants recognize inner resources and personal strengths, analyze current levels of functioning, and visualize their preferred future (de Shazer, 1991).
In review of counseling session recordings and in supervision, Himmelberger commented that both Joel and Mary provided feedback throughout SFBT that they appreciated the opportunity to focus on small successes, personal strengths, and exceptions to their problems, and the use of scaling questions to assess and track their progress. They also commented that they appreciated how they were able to conceptualize family as a source of strength and element of resiliency (J. Cavazos et al., 2010; Oliver et al., 2011). Researchers have found that using SFBT techniques such as miracle and exceptions questions can help clients reduce negative affect (Brogan et al., 2020; Neipp et al., 2021). Our findings also are like those of Schmit et al. (2016), who found that SFBT may be effective for treating symptoms of internalizing disorders, and Oliver et al. (2011), who commented that SFBT can help Mexican Americans cultivate familismo.
The findings for Hope showed a visual trend toward increased levels of Hope across 8 weeks of SFBT. Both participants reported statistically significant improvements (p < .05) in Hope on the DHS. In both cases, the SFBT intervention was within the range of debatable effectiveness and slight improvement without clinical significance for improving symptoms of Hope. Mary’s rating on the DHS indicates the treatment was moderately effective and PI was not clinically significant. When visualizing Mary’s rating on the DHS, we see that Mary had high levels of Hope in the baseline phase, which means that she did not have much room to improve in the treatment phase. Contextualizing Mary’s treatment and using a visual representation of her scores on the DHS (see Figure 1), we infer that the SFBT intervention had some level of convincingness, which means that some amount of change in Hope occurred for Mary (Kendall, 1999; Lenz, 2021). Additionally, Joel’s rating on the DHS indicate that the treatment effect was debatably effective with a PI that is slightly improved but not clinically significant. When looking closely at Joel’s scores, we see that Joel experienced trends in a positive trajectory. In the context of his treatment and a visual representation of his scores on the DHS (see Figure 1), the SFBT intervention had a moderate level of convincingness, which means that a considerable amount of change in Hope occurred (Kendall, 1999; Lenz, 2021).
Suldo and Shaffer (2008) argued that using a dual-factor model of mental health with indicators of subjective well-being (e.g., hope) and illness (e.g., clinical symptoms) allows researchers and practitioners to measure and understand complete mental health. Although a client’s psychopathology might decrease, subjective well-being might not improve with the same effect. Findings from SFBT treatment with Joel and Mary support a dual-factor model that suggests indicators of personal wellness and psychopathology are different parts of mental health and are important to consider in treatment (Vela, Lu, et al., 2016). For Joel and Mary, SFBT appeared to be efficacious for slightly increasing and maintaining scores on the DHS. Our findings support Joubert and Guse (2021), who recommended SFBT to facilitate hope and subjective well-being among clients. When clients can think about solutions, identify exceptions to their problems, and think about their preferred future, they might be more likely to develop hope for their future as well as improve subjective well-being (Joubert & Guse, 2021).
The findings from this study lend further support regarding the effectiveness of counseling services at a community counseling training clinic. Our findings are like Schuermann et al.’s (2018) findings that lend support for the efficacy of counseling services in a Hispanic-serving counselor training clinic and Dorais et al.’s (2020) findings of counseling students’ motivational interviewing techniques at a university addiction training clinic. Faculty supervision, group supervision, and live supervision have all been associated with increases in counseling interns’ self-efficacy to provide quality counseling services. Himmelberger received weekly supervision and consultation on SFBT principles as well as SCRD principles. It is possible that these forms of supervision helped her provide effective counseling services. Our findings also support the need to continue to design research studies to evaluate the impact of counseling services at community counseling training clinics with clients of different cultural backgrounds and different presenting symptoms.
Implications for Counselor Educators and Counselors-in-Training
Based on our findings, we propose a few recommendations for counselor educators, CITs, and practitioners. First, our study provides evidence that CITs at community counseling centers can provide effective treatments with culturally diverse clients with moderate internalized symptoms such as depression and anxiety. As a result, SFBT can be taught and infused into counselor education curricula and can be delivered by future licensed professional counselors, school counselors, or counseling interns.
Community agencies working with this client population should also consider providing counselors with professional development and training related to SFBT. It is important to mention that when two of us were in graduate programs, we did not receive formal SFBT instruction. This might be due to greater emphasis on humanistic and cognitive behavioral therapies in counseling curricula or among some counselor education faculty. As a result, counselor educators must make a cogent effort to promote and discuss postmodern theories such as SFBT. This is important because SFBT can be effective at improving internalizing disorders among clients (Schmit et al., 2016) and Latine populations (Gonzalez & Franklin, 2016).
Another implication for counselor educators is to consider teaching CITs how to use SCRDs to monitor and assess treatment effectiveness. All counseling interns who work in a community counseling clinic need to demonstrate the effectiveness of their services with clients. Therefore, CITs can learn how to use SCRDs or a single-group pretest/posttest with clinical significance (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2021; Lenz, 2020b) to determine the impact of counseling on client outcomes. Finally, community counseling clinics can consider using the DHS and OQ-45.2 to measure indicators of subjective well-being and clinical symptoms. CITs can use these instruments, which have evidence of reliability and validity with culturally diverse populations, to document the impact of their counseling services on clients’ hope and clinical symptoms.
Implications for Practitioners
There also are implications for practitioners. First, counselors can use SFBT principles and techniques to work with Latine clients. By using a positive and future-oriented framework, counselors can build a positive therapeutic relationship and help Latine clients construct a positive future. Counselors can use SFBT to help Latine clients identify how familismo is a source of strength (Oliver et al., 2011) and draw on their inner resiliency (Vela et al., 2015) to create their preferred future outcome. Practitioners can use SFBT techniques, including looking for previous solutions, exceptions, the miracle question, scaling questions, compliments, and future-oriented questions. SFBT principles and techniques can be used to facilitate hope by helping Latine clients view mental health challenges as opportunities to cultivate strengths and explore solutions (Bannik, 2008; Joubert & Guse, 2021).
Practitioners also can use SCRDs to evaluate the impact of their work with clients. Although most practitioners collect pre- and post-counseling intervention data, they typically use a single data point at pre-counseling and a single data point at post-counseling. Using an SCRD in which a baseline phase and weekly treatment points are collected can help analyze trends over time and identify clinical significance. Lenz (2015) described how practitioners can use SCRDs to make inferences—self as control, flexibility and responsiveness, small sample size, ease of data analysis, and type of data yielded from analyses. In other words, counseling practitioners can analyze data over time with a client and use the data collection and analysis methods in this study to evaluate the impact of their counseling services on client outcomes.
Implications and Limitations
There are several implications for future research. First, researchers can evaluate the impact of SFBT on other indicators related to subjective well-being and clinical symptoms among culturally diverse populations, including subjective happiness, resilience, grit, meaning in life, anxiety, and depression (Karaman et al., 2019). More research needs to explore how SFBT might enhance indicators of subjective well-being and decrease clinical symptoms as well as the intersection between recovery and psychopathology. Although researchers have explored the impact of SFBT on internalizing symptoms (Schmit et al., 2016), more research needs to examine the impact on subjective well-being, particularly among Latine populations and Latine adolescents at a community counseling clinic.
Researchers also should consider using qualitative methods to discover which SFBT techniques are most effective. In-depth interviews and focus groups with SFBT participants would provide insight and perspectives with the miracle question, scaling questions, and other SFBT techniques. Counselors could also collect clients’ journal entries to capture the impact of specific techniques on psychopathology or subjective well-being.
Additionally, using between-group designs to compare SFBT interventions with other evidence-based approaches such as cognitive behavior therapy could provide fruitful investigations. It is also possible to explore the impact of SFBT coupled with another approach such as positive psychology or cognitive behavior therapy with Latine populations. Finally, researchers can continue to explore the impact of CITs who work with clients in a community counseling clinic. Counseling interns can use SCRDs or single-group pretest/posttest designs to measure the impact of their counseling services.
The current study was exploratory in nature. Although both participants demonstrated improvement in measures related to subjective well-being and psychopathology, generalization to a larger Latine population is not appropriate. Because of the exploratory nature of this study, we cannot generate causal inferences regarding the relationship between SFBT and Hope as well as clinical symptoms. Second, we did not include withdrawal measures following completion of the treatment phase (Ikonomopoulos et al., 2016, 2017). Although some researchers use AB and ABA SCRDs to measure counseling effectiveness (Callender et al., 2021), we did not use an ABA design that would have provided stronger internal validity to evaluate changes of SFBT (Lenz et al., 2012). Because Himmelberger completed the academic semester and graduated from the clinical mental health counseling program, collecting withdrawal measures was not possible. Therefore, an AB SCRD was a more feasible approach.
Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first exploratory studies to examine the impact of the effectiveness of SFBT with Latine clients at a community counseling training clinic. This exploratory SCRD serves as a foundation for future data collection and evaluation of CITs who work with culturally diverse clients at community counseling training clinics. Results support the potential of SFBT as an intervention for promoting positive change for Latine clients’ hope and clinical symptoms.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Amble, I., Gude, T., Stubdal, S., Oktedalen, T., Skjorten, A. M., Andersen, B. J., Solbakken, O. A., Brorson, H. H., Arnevik, E., Lambert, M. J., & Wampold, B. E. (2014). Psychometric properties of the Outcome Questionnaire-45.2: The Norwegian version in an international context. Psychotherapy Research, 24(4), 504–513. https://doi.10.1080/10503307.2013.849016
Ayón, C., Marsiglia, F. F., & Bermudez-Parsai, M. (2010). Latino family mental health: Exploring the role of discrimination and familismo. Journal of Community Psychology, 38(6), 742–756.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.20392
Bannik, F. P. (2008). Posttraumatic success: Solution-focused brief therapy. Brief Treatment and Crisis Intervention, 8(3), 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/brief-treatment/mhn013
Bavelas, J., De Jong, P., Franklin, C., Froerer, A., Gingerich, W., Kim, J., Korman, H., Langer, S., Lee, M. Y., McCollum, E. E., Jordan, S. S., & Trepper, T. S. (2013). Solution focused therapy treatment manual for working with individuals. Solution Focused Brief Therapy Association, 1–42. https://bit.ly/solutionfocusedtherapy
Berg, I. K. (1994). Family-based services: A solution-focused approach. W. W. Norton.
Boswell, D. L., White, J. K., Sims, W. D., Harrist, R. S., & Romans, J. S. C. (2013). Reliability and validity of the Outcome Questionnaire–45.2. Psychological Reports, 112(3), 689–693.
https://doi.org/10.2466/02.08.PR0.112.3.689-693
Brogan, J., Contreras Bloomdahl, S., Rowlett, W. H., & Dunham, M. (2020). Using SFBC group techniques to increase Latino academic self-esteem. Journal of School Counseling, 18. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1251785.pdf
Buchholz Holland, C. E. (2013). The lifeline activity with a “solution-focused twist.” Journal of Family Psychotherapy, 24(4), 306–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/08975353.2013.849552
Callender, K. A., Trustey, C. E., Alton, L., & Hao, Y. (2021). Single case evaluation of a mindfulness-based mobile application with a substance abuse counselor. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 12(1), 16–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2019.1686353
Calzada, E. J., Tamis-LeMonda, C. S., & Yoshikawa, H. (2013). Familismo in Mexican and Dominican families from low-income, urban communities. Journal of Family Issues, 34(12), 1696–1724.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513×12460218
Cavazos, A. G. (2009). Reflections of a Latina student-teacher: Refusing low expectations for Latina/o students. American Secondary Education, 37(3), 70–79.
Cavazos, J., Jr., Johnson, M. B., Fielding, C., Cavazos, A. G., Castro, V., & Vela, L. (2010). A qualitative study of resilient Latina/o college students. Journal of Latinos and Education, 9(3), 172–188.
https://doi.org/10.1080/153484431003761166
Cheng, H.-L., Hitter, T. L., Adams, E. M., & Williams, C. (2016). Minority stress and depressive symptoms: Familism, ethnic identity, and gender as moderators. The Counseling Psychologist, 44(6), 841–870.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0011000016660377
Cheng, H.-L., & Mallinckrodt, B. (2015). Racial/ethnic discrimination, posttraumatic stress symptoms, and alcohol problems in a longitudinal study of Hispanic/Latino college students. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 62(1), 38–49. https://doi.org/10.1037/cou0000052
Coco, G. L., Chiappelli, M., Bensi, L., Gullo, S., Prestano, C., & Lambert, M. J. (2008). The factorial structure of the Outcome Questionnaire-45: A study with an Italian sample. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, 15(6), 418–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.601
de Shazer, S. (1991). Putting differences to work. W. W. Norton.
de Shazer, S., Dolan, Y., Korman, H., Trepper, T., McCollum, E., & Berg, I. K. (2007). More than miracles: The state of the art of solution-focused brief therapy. Hawthorne Press.
Dorais, S., Gutierrez, D., & Gressard, C. R. (2020). An evaluation of motivational interviewing based treatment in a university addiction counseling training clinic. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 11(1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2019.1704175
Ekroll, V. B., & Rønnestad, M. H. (2017). Pathways towards different long-term outcomes after naturalistic psychotherapy. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 25(2), 292–301. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.2162
Feldman, D. B., & Dreher, D. E. (2012). Can hope be changed in 90 minutes? Testing the efficacy of a single-session goal-pursuit intervention for college students. Journal of Happiness Studies, 13, 745–759.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-011-9292-4
Galiana, L., Oliver, A., Sancho, P., & Tomás, J. M. (2015). Dimensionality and validation of the Dispositional Hope Scale in a Spanish sample. Social Indicators Research, 120, 297–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0582-1
Gonzalez Suitt, K., Franklin, C., & Kim, J. (2016). Solution-focused brief therapy with Latinos: A systematic review. Journal of Ethnic and Cultural Diversity in Social Work, 25, 50–67.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15313204.2015.1131651
Ikonomopoulos, J., Garza, K., Weiss, R., & Morales, A. (2021). Examination of treatment progress among college students in a university counseling program. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 12(1), 30–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2020.1850175
Ikonomopoulos, J., Lenz, A. S., Guardiola, R., & Aguilar, A. (2017). Evaluation of the Outcome Questionnaire-45.2 with a Mexican-American population. Journal of Professional Counseling: Practice, Theory, & Research, 44(1), 17–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/15566382.2017.12033956
Ikonomopoulos, J., Smith, R. L., & Schmidt, C. (2015). Integrating narrative therapy within rehabilitative programming for incarcerated adolescents. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93(4), 460–470.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12044
Ikonomopoulos, J., Vela, J. C., Smith, W. D., & Dell’Aquila, J. (2016). Examining the practicum experience to increase counseling students’ self-efficacy. The Professional Counselor, 6(2), 161–173. https://doi.org/10.15241/ji.6.2.161
Joubert, J., & Guse, T. (2021). A solution-focused brief therapy (SFBT) intervention model to facilitate hope and subjective well-being among trauma survivors. Journal of Contemporary Psychotherapy, 51, 303–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10879-021-09511-w
Kadera, S. W., Lambert, M. J., & Andrews, A. A. (1996). How much therapy is really enough?: A session-by-session analysis of the psychotherapy dose-effect relationship. Journal of Psychotherapy Practice and Research, 5(2), 132–151.
Karaman, M. A., Vela, J. C., Aguilar, A. A., Saldana, K., & Montenegro, M. C. (2019). Psychometric properties of U.S.-Spanish versions of the grit and resilience scales with a Latinx population. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling, 41, 125–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-018-9350-2
Kendall, P. C., Marrs-Garcia, A., Nath, S. R., & Sheldrick, R. C. (1999). Normative comparisons for the evaluation of clinical significance. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67(3), 285–299.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006x.67.3.285
Kim, J. S. (2008). Examining the effectiveness of solution-focused brief therapy: A meta-analysis. Research on Social Work Practice, 18(2), 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731507307807
Lambert, M. J., Burlingame, G. M., Umphress, V., Hansen, N. B., Vermeersch, D. A., Clouse, G. C., & Yanchar, S. C. (1996). The reliability and validity of the Outcome Questionnaire. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 3(4), 249–258. https://doi.org/10/bmwzbf
Lenz, A. S. (2013). Calculating effect size in single-case research: A comparison of nonoverlap methods. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 46(1), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748175612456401
Lenz, A. S. (2015). Using single-case research designs to demonstrate evidence for counseling practices. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93(4), 387–393. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12036
Lenz, A. S. (2020a). The future of Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 11(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2020.1712977
Lenz, A. S. (2020b). Estimating and reporting clinical significance in counseling research: Inferences based on percent improvement. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 53(4), 289–296.
https://doi.org/10.1080/07481756.2020.1784758
Lenz, A. S. (2021). Clinical significance in counseling outcome research and program evaluation. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 12(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2021.1877097
Lenz, A. S., Speciale, M., & Aguilar, J. V. (2012). Relational-cultural therapy intervention with incarcerated adolescents: A single-case effectiveness design. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 3(1), 17–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/2150137811435233
Lerma, E., Zamarripa, M. X., Oliver, M., & Vela, J. C. (2015). Making our way through: Voices of Hispanic counselor educators. Counselor Education and Supervision, 54(3), 162–175. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12011
Liu, V. Y., La Guardia, A., & Sullivan, J. M. (2020). A single-case research evaluation of collaborative therapy treatment among adults. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 11(1), 45–58.
https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2018.15311238
Lundervold, D. A., & Belwood, M. F. (2000). The best kept secret in counseling: Single-case (N = 1) experimental designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 78(1), 92–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6676.2000.tb02565.x
Ma, H.-H. (2006). An alternative method for quantitative synthesis of single-subject researches: Percentage of data points exceeding the median. Behavior Modification, 30(5), 598–617. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445504272974
Mendoza, H., Masuda, A., & Swartout, K. M. (2015). Mental health stigma and self-concealment as predictors of help-seeking attitudes among Latina/o college students in the United States. International Journal for Advancement of Counselling, 37(3), 207–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-015-9237-4
Merikangas, K. R., He, J.-P., Burstein, M., Swanson, S. A., Avenevoli, S., Cui, L., Benjet, C., Georgiades, K., & Swendsen, J. (2010). Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in U.S. adolescents: Results from the National Comorbidity Study Replication—Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). Journal of Academy Child Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(10), 980–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.05.017
Neipp, M.-C., Beyebach, M., Sanchez-Prada, A., & Álvarez, M. D. C. D. (2021). Solution-focused versus problem-focused questions: Differential effects of miracles, exceptions and scales. Journal of Family Therapy, 43(4), 728–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6427.12345
Nel, P., & Boshoff, A. (2014). Factorial invariance of the Adult State Hope Scale. SA Journal of Industrial Psychology, 40(1), 1–8.
Novella, J. K., Ng, K.-M., & Samuolis, J. (2020). A comparison of online and in-person counseling outcomes using solution-focused brief therapy for college students with anxiety. Journal of American College Health, 70(4), 1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2020.1786101
Oliver, M., Flamez, B., & McNichols, C. (2011). Postmodern applications with Latino/a cultures. Journal of Professional Counseling: Practice, Theory & Research, 38(3), 33–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/15566382.2011.12033875
Ponciano, C., Semma, B., Ali, S. F., Console, K., & Castillo, L. G. (2020). Institutional context of perceived discrimination, acculturative stress, and depressive symptoms among Latina college students. Journal of Latinos and Education, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/15348431.2020.1809418
Priest, J. B., & Denton, W. (2012). Anxiety disorders and Latinos: The role of family cohesion and family discord. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 34(4), 557–575. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739986312459258
Proudlock, S., & Wellman, N. (2011). Solution focused groups: The results look promising. Counselling Psychology Review, 26(3), 45–54.
Ramos, G., Delgadillo, D., Fossum, J., Montoya, A. K., Thamrin, H., Rapp, A., Escovar, E., & Chavira, D. A. (2021). Discrimination and internalizing symptoms in rural Latinx adolescents: An ecological model of etiology. Children and Youth Services Review, 130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2021.106250
Sáenz, V. B., Lu, C., Bukoski, B. E., & Rodriguez, S. (2013). Latino males in Texas community colleges: A phenomenological study of masculinity constructs and their effect on college experiences. Journal of African American Males in Education, 4(2), 82–102.
Sanchez, M. E. (2019). Perceptions of campus climate and experiences of racial microaggressions for Latinos at Hispanic-Serving Institutions. Journal of Hispanic Higher Education, 18(3), 240–253.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1538192717739
Schmit, E. L., Schmit, M. K., & Lenz, A. S. (2016). Meta-analysis of solution-focused brief therapy for treating symptoms of internalizing disorders. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 7(1), 21–39.
https://doi.org/10.1177/2150137815623836
Schuermann, H., Borsuk, C., Wong, C., & Somody, C. (2018). Evaluating effectiveness in a Hispanic-serving counselor training clinic. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 9(2), 67–79.
https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2018.1442680
Scruggs, T. E., & Mastropieri, M. A. (1998). Summarizing single-subject research: Issues and applications. Behavior Modification, 22(3), 221–242. https://doi.org/10.1177/01454455980223001
Scruggs, T. E., Mastropieri, M. A, & Casto, G. (1987). The quantitative synthesis of single-subject research: Methodology and validation. Remedial and Special Education, 8(2), 24–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/074193258700800206
Sharpley, C. F. (2007). So why aren’t counselors reporting n = 1 research designs? Journal of Counseling & Development, 85(3), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2007.tb00483.x
Snyder, C. R., Harris, C., Anderson, J. R., Holleran, S. A., Irving, L. M., Sigmon, S. T., Yoshinobu, J., Gibb, J., Langelle, C., & Harney, P. (1991). The will and the ways: Development and validation of an individual-differences measure of hope. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 60(4), 570–585.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.60.4.570
Snyder, C. R., Michael, S. T., & Cheavens, J. S. (1999). Hope as a psychotherapeutic foundation of common factors, placebos, and expectancies. In M. A. Hubble, B. L. Duncan, & S. D. Miller (Eds.), The heart and soul of change: What works in therapy (pp. 179–200). American Psychological Association.
Snyder, C. R., Shorey, H. S., Cheavens, J., Pulvers, K. M., Adams, V. H., III, & Wiklund, C. (2002). Hope and academic success in college. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94(4), 820–826.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.94.4.820
Snyder, C. R., Sympson, S. C., Ybasco, F. C., Borders, T. F., Babyak, M. A., & Higgins, R. L. (1996). Development and validation of the State Hope Scale. Journal of Personal Social Psychology, 70(2), 321–325.
https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.70.2.321
Soares, M. C., Mondon, T. C., da Silva, G. D. G., Barbosa, L. P., Molina, M. L., Jansen, K., Souza, L. D. M., & Silva, R. A. (2018). Comparison of clinical significance of cognitive-behavioral therapy and psychodynamic therapy for major depressive disorder: A randomized clinical trial. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 206(9), 686–693. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMD.0000000000000872
Suldo, S. M., & Shaffer, E. J. (2008). Looking beyond psychopathology: The dual-factor model of mental health in youth. School Psychology Review, 37(1), 52–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.2008.12087908
Tambling, R. B. (2012). Solution-oriented therapy for survivors of sexual assault and their partners. Contemporary Family Therapy, 34, 391–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10591-012-9200-z
Trepper, T. S., McCollum, E. E., De Jong, P., Korman, H., Gingerich, W., & Franklin, C. (2010). Solution focused therapy treatment manual for working with individuals. Research Committee of the Solution Focused Brief Therapy Association. https://www.andrews.edu/sed/gpc/faculty-research/coffen-research/trepper_2010_solution.pdf
Umphress, V. J., Lambert, M. J., Smart, D. W., Barlow, S. H., & Glenn, C. (1997). Concurrent and construct validity of the Outcome Questionnaire. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 15(1), 40–55.
https://doi.org/10.1177/073428299701500104
U.S. Census Bureau. (2020). Quick facts: United States. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/RH1725221
Vannest, K. J., & Ninci, J. (2015). Evaluating intervention effects in single-case research designs. Journal of Counseling & Development, 93(4), 403–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12038
Vela, J. C., Ikonomopoulos, J., Dell’Aquila, J., & Vela, P. (2016). Evaluating the impact of creative journal arts therapy for survivors of intimate partner violence. Counseling Outcome Research and Evaluation, 7(2), 86–98. https://doi.org/10.1177/2150137816664781
Vela, J. C., Ikonomopoulos, J., Hinojosa, K., Gonzalez, S. L., Duque, O., & Calvillo, M. (2016). The impact of individual, interpersonal, and institutional factors on Latina/o college students’ life satisfaction. Journal of Hispanic Higher Education, 15(3), 260–276. https://doi.org/10.1177/1538192715592925
Vela, J. C., Ikonomopoulos, J., Lenz, A. S., Hinojosa, Y., & Saldana, K. (2017). Evaluation of the Meaning in Life Questionnaire and Dispositional Hope Scale with Latina/o students. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 56(3), 166–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/johc.12051
Vela, J. C., Lerma, E., Lenz, A. S., Hinojosa, K., Hernandez-Duque, O., & Gonzalez, S. L. (2014). Positive psychology and familial factors as predictors of Latina/o students’ hope and college performance. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 36(4), 452–469. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739986314550790
Vela, J. C., Lu, M.-T. P., Lenz, A. S., & Hinojosa, K. (2015). Positive psychology and familial factors as predictors of Latina/o students’ psychological grit. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 37(3), 287–303.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0739986315588917
Vela, J. C., Lu, M.-T. P., Lenz, A. S., Savage, M. C., & Guardiola, R. (2016). Positive psychology and Mexican American college students’ subjective well-being and depression. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 38(3), 324–340. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739986316651618
Vela, J. C., Lu, M.-T. P., Veliz, L., Johnson, M. B., & Castro, V. (2014). Future school counselors’ perceptions of challenges that Latina/o students face: An exploratory study. In Ideas and Research You Can Use: VISTAS 2014, Article 39, 1–12. https://www.counseling.org/docs/default-source/vistas/article_39.pdf?sfvrsn=10
Vela-Gude, L., Cavazos, J., Jr., Johnson, M. B., Fielding, C., Cavazos, A. G., Campos, L., & Rodriguez, I. (2009). “My counselors were never there”: Perceptions from Latina college students. Professional School Counseling, 12(4), 272–279. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156759X0901200407
Krystle Himmelberger, MS, LPC, is a doctoral candidate at St. Mary’s University. James Ikonomopoulos, PhD, LPC-S, is an assistant professor at Texas A&M University–Corpus Christi. Javier Cavazos Vela, PhD, LPC, is a professor at the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley. Correspondence may be addressed to James Ikonomopoulos, 6300 Ocean Drive, Unit 5834, Corpus Christi, TX 78412,
james.ikonomopoulos1@tamucc.edu.
Aug 10, 2022 | Volume 12 - Issue 2
Phillip L. Waalkes, Daniel A. DeCino, Maribeth F. Jorgensen, Tiffany Somerville
Supportive relationships with counselor educators as dissertation chairs are valuable to doctoral students overcoming barriers to successful completion of their dissertations. Yet, few have examined the complex and mutually influenced dissertation-chairing relationships from the perspective of dissertation chairs. Using hermeneutic phenomenology, we interviewed counselor educators (N = 15) to identify how they experienced dissertation-chairing relationship dynamics with doctoral students. Counselor educators experienced relationships characterized by expansive connections, growth in student autonomy, authenticity, safety and trust, and adaptation to student needs. They viewed chairing relationships as fluid and non-compartmentalized, which cultivated mutual learning and existential fulfillment. Our findings provide counselor educators with examples of how empathy and encouragement may help doctoral students overcome insecurities and how authentic and honest conversations may help doctoral students overcome roadblocks. Counselor education programs can apply these findings by building structures to help facilitate safe and trusting relationships between doctoral students and counselor educators.
Keywords: dissertation-chairing relationships, hermeneutic phenomenology, counselor education, doctoral students, relationship dynamics
According to the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP; 2015), doctoral students must develop research skills and complete counseling-focused dissertation research. Research mentorship is often important to counselor education doctoral students’ development as researchers (Flynn et al., 2012; Lamar & Helm, 2017; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015). One of the central research mentoring relationships in doctoral programs is the dissertation-chairing relationship. Supportive research mentoring relationships in counselor education are invaluable to students (Lamar & Helm, 2017), are necessary to successful dissertation chairing (Ghoston et al., 2020; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020), and are a central factor in high-quality doctoral programs (Preston et al., 2020). In fact, a meaningful connection between students and their dissertation chairperson predicts students’ successful completion of their dissertations (Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015; Rigler et al., 2017) and positive dissertation experiences (Burkard et al., 2014). Therefore, to help promote intentional and supportive dissertation-chairing relationships, we examined counselor educators’ experiences of relationship dynamics with doctoral students.
Challenges in Dissertation Completion
Across disciplines, doctoral students can struggle with isolation, motivation, time management, self-regulation, and self-efficacy (Pyhältö et al., 2012). In their development as researchers, doctoral students in counselor education can experience intense emotions, including excitement, exhaustion, frustration, distrust, confusion, disconnection, and pride (Lamar & Helm, 2017). Negative relationships with dissertation chairs can exacerbate challenges to dissertation completion. In one meta-analysis study examining doctoral student attrition across disciplines, doctoral students identified a problematic relationship with their dissertation chairperson as the most significant barrier to their completion of their degrees (Rigler et al., 2017). Doctoral students in counselor education have reported negative experiences when their dissertation chairs were unenthusiastic, unsupportive, and unavailable, and when their guidance was not concrete (Flynn et al., 2012; Lamar & Helm, 2017). In addition, counselor education doctoral students involved in negative dissertation-chairing relationships can feel like they are on their own in their dissertation journeys (Protivnak & Foss, 2009). This feeling of isolation can intensify existing barriers in completing dissertations, including struggles with motivation, self-regulation, self-criticism, and self-efficacy (Burkard et al., 2014; Pyhältö et al., 2012).
Power differentials between doctoral students and dissertation chairs also can serve as a barrier to supportive dissertation-chairing relationships and dissertation completion (Burkard et al., 2014). For example, doctoral students are likely to remain silent in difficult relationships with dissertation chairs unless students perceive there to be a strong relationship built on respect and open communication (Schlosser et al., 2003). Cultural differences and systemic oppression may also impact dissertation-chairing relationships. According to Brown and Grothaus (2019), Black counselor education students can experience overt racism, tokenism, isolation, and internalized racism, which can foster mistrust in cross-racial mentoring relationships. Numerous researchers in counselor education (Borders et al., 2012; Ghoston et al., 2020; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015; Purgason et al., 2018) have recommended mentors use transparent and honest dialogue with explicit attention to expectations, power dynamics, cultural differences, and potential conflicts.
Supportive Dissertation-Chairing Relationships
Dissertation-chairing relationships with individualized supports can help students overcome barriers to completing their dissertations (Ghoston et al., 2020; Purgason et al., 2018). According to Flynn and colleagues (2012), increased dissertation chairperson involvement can counteract counselor education students’ isolation, burnout, and perceptions of lacking support. Dissertation chairs can help doctoral students identify their low research self-efficacy and offer support, encouragement, and instruction to help address it (Burkard et al., 2014). According to Ghoston and colleagues (2020), a supportive relationship during the dissertation process can help doctoral students be more honest about when they are stuck, which, in turn, allows chairs to give more targeted direction and feedback.
Beginning counselor educators have reported faculty mentoring, care, and support were the most valuable components of their doctoral training (Perera-Diltz & Sauerheber, 2017). Specifically, doctoral students in counselor education value when faculty take time with them, express genuine caring, offer guidance, validate and believe in them, and celebrate their efforts and achievements (Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015; Protivnak & Foss, 2009; Purgason et al., 2018). Counselor education doctoral students also appreciate dissertation chairs who offer regular contact, timely support, and clear and authentic communication (Borders et al., 2012; Ghoston et al., 2020; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020).
Despite the importance of supportive dissertation-chairing relationships in counselor education (Flynn et al., 2012; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015), little research exists on how counselor educators experience dissertation-chairing relationships with doctoral students. Although researchers have studied dissertation-chairing relationships from the perspectives of counselor education doctoral students (e.g., Flynn et al., 2012; Lamar & Helm, 2017; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015) and examined relational strategies counselor educators use (e.g., Ghoston et al., 2020; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020), few have examined counselor educators’ perceptions of the relationship as dynamic and mutually constructed. Given their role as faculty and their experiences in multiple dissertation-chairing relationships, dissertation chairs may have more awareness of and broader perspectives on the mutually influenced dissertation relationship and process. Understanding the complexities and nuances of dynamics in chairing relationships may help counselor educators develop more intentional dissertation-chairing practices, subsequently resulting in more successfully completed dissertations. Therefore, we asked the following research question in this hermeneutic phenomenological investigation: What are counselor educators’ lived experiences of dissertation-chairing relationship dynamics with doctoral students?
Method
We utilized a hermeneutic perspective rooted in an interpretive paradigm to guide this study. This perspective aligns with the focus on relationships in our study and emphasizes how individuals make meaning in interaction with others (Heidegger, 1962). Anchored by the viewpoint that all knowledge is relative and based on cultural context, Heidegger’s (1962) hermeneutic phenomenology helped us to construct an evocative description of the essence of participants’ experiences of chairing dissertations in a multi-dimensional and multi-layered way (van Manen, 1990). Hermeneutic phenomenology focuses on uncovering the participants’ experiences of the lifeworld, or their experience of everyday situations and relations (van Manen, 1990). The concept of lifeworld in hermeneutic phenomenology allowed us to examine participants’ lived experiences of human relation, or how they maintain relationships in shared interpersonal space. Therefore, we utilized hermeneutic phenomenology (van Manen, 1990) to investigate counselor educators’ experiences of dissertation-chairing relationships.
Participants and Sampling Procedure
Of 15 participants in our study, eight self-identified as female and seven self-identified as male. Ten participants self-identified as White. Three self-identified with multiple racial and ethnic groups, and two self-identified as African American or Black. Seven participants worked as an associate professor, seven participants worked as a full professor, and one participant worked as an assistant professor. Participants’ ages ranged from 33 to 68 (M = 47.93, SD = 10.18). Years of experience working as a counselor educator ranged from 4 to 29 (M = 16.40, SD = 7.92). Participants reported a wide range of successful chairing experiences, with one to 40 (M = 10.47, SD = 10.39) of their doctoral student advisees defending their dissertations. Nine participants worked at institutions in the Southern Association for Counselor Education and Supervision (ACES) region, three participants worked at institutions in the Western ACES region, two participants worked at institutions in the North Central ACES region, and one participant worked at an institution in the Northeastern ACES region. Five participants worked at institutions with an R2 Carnegie classification (doctoral universities with high research activity). Five participants worked at institutions with an R1 Carnegie classification (doctoral universities with very high research activity). Three participants worked at institutions with an M1 Carnegie classification (master’s colleges and universities with larger programs). Two participants worked at an institution with a D/PU classification (doctoral/professional universities).
Participants qualified for inclusion in this study if they self-identified as a counselor educator working in a CACREP-accredited program and had chaired at least one counseling doctoral student through a successful dissertation defense. After compiling a list of all CACREP-accredited counselor education doctoral programs (N = 33) from information available through the CACREP website, we created a list of names and email addresses of all counselor education faculty (N = 330) working at each of these institutions based on information available on programs’ websites. After receiving IRB approval, we randomly selected 249 faculty members from this list and sent each person a recruitment email and one follow-up email about a week later. Fifteen counselor educators expressed interest, yielding a response rate of 6.05%.
Data Collection
After counselor educators expressed interest in the study, we emailed them a brief demographic data survey, the informed consent document, and the interview questions. We scheduled a time for a semi-structured interview with them and asked them to return their demographic data survey before their interviews. All interviews were conducted through Zoom and audio recorded. The interview protocol consisted of six main open-ended questions and two to four scripted probes for each main question (Patton, 2014). We developed interview questions based on themes within the literature on dissertations and research mentorship (e.g., Flynn et al., 2012; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015) as well as our own experiences chairing dissertations. Sample interview questions included “How would you describe the characteristics of relationships you want to foster with students?” and “What relational factors help students successfully complete their dissertations with you as a dissertation chair?” Interviews lasted between 38 and 64 minutes. After transcribing the interviews using Rev.com, we deleted the audio files. We determined that we reached saturation at our sample size of 15 participants as we observed the same themes repeatedly emerging in our coding process (Patton, 2014).
Research Team
Our research team consisted of four members. Phillip Waalkes and Daniel DeCino served as the coding team. They both identify as White cisgender male counselor educators with experience chairing dissertations. Maribeth Jorgensen and Tiffany Somerville served as auditors. Jorgensen identifies as a White cisgender female counselor educator with experience chairing dissertations, while Somerville identifies as a White cisgender female counselor education doctoral student. Waalkes, DeCino, and Jorgensen developed the study after a conversation of their experiences chairing dissertations and conducting research in this topic area. We identified how we grew in our identities as dissertation chairs and how we adapted our mentoring styles to meet the needs of students. Considering our experiences as dissertation chairs and doctoral students, we wanted to know how counselor educators developed supportive dissertation-chairing relationships.
To promote reflexivity, the coding team, Waalkes and DeCino, used bridling throughout the data analysis process, utilizing written statements and discussion. Bridling is a process in which researchers actively wait for the phenomenon and its meaning to show itself while also scrutinizing their own involvement with the phenomenon. Bridling requires researchers to acknowledge their pre-understandings and loosen them to allow space for holistic understanding of the phenomenon without seeking to understand too quickly or too carelessly (Dahlberg, 2006). In his reflexivity statement, Waalkes wrote about the importance of timely and individualized feedback and the challenges of building relationships when taking over as dissertation chairperson in the middle of a student’s dissertation process. DeCino discussed his beliefs about the importance of individualized mentoring relationships and the impact of his dissertation experience as a doctoral student on his current dissertation-chairing identity. These reflexive conversations continued between Waalkes and DeCino throughout the data analysis process.
Data Analysis
Based on van Manen’s (1990) inductive data analysis procedure for hermeneutic phenomenology, we coded our data with hermeneutic awareness, reflecting on the data in multidimensional context as opposed to accepting it at face value. Additionally, we designed our procedure to create a hermeneutic circle by shifting between examining parts of the text and reflecting on the interviews as a whole (van Manen, 1990). The development of a thematic structure and a holistic statement (a one-sentence summary of the essence of each participant’s experience) as products of our data analysis reflect our hermeneutic circle.
Our data analysis process consisted of four stages. First, for each interview, Waalkes and DeCino individually created initial holistic statements for each participant. Holistic statements summarized the central significance or fundamental meaning of the participant’s transcript (i.e., text) as a whole. For example, Participant 6’s holistic statement was “Structure, organization, following rules, empathy, scheduled standing meetings to check in personally and professionally, and constructive feedback tailored to students’ needs with an awareness of cultural differences are essential to their dissertation-chairing relationships.” Then, they met to discuss their individual holistic statements and reach consensus on the content of each holistic statement. Second, they individually reviewed each transcript and highlighted essential passages throughout each transcript. Waalkes and DeCino selected passages that were particularly essential or revealing (van Manen, 1990). After selecting a passage, they rewrote it with attention to the context of what was below or above each highlighted section. After rewriting a passage, they reviewed the participants’ holistic statement to ensure that the rewritten passage reflected the interview as a whole. They combined their summary statements of essential passages into a shared spreadsheet. Third, in a series of meetings, Waalkes and DeCino discussed their summary statements and coded each one with a possible theme name. Afterward, they looked for frequently reoccurring codes and combined similar codes to create an initial theme list. Then, they checked that their themes were essential and not incidental by assessing them against the holistic statements and using imaginative variation by asking: “Is this phenomenon still the same if we imaginatively change or delete this theme from the phenomenon?” (van Manen, 1990, p. 107). In conversation, Waalkes and DeCino revised the theme list and structure throughout the imaginative variation process. Finally, Jorgensen and Somerville reviewed the theme list and the holistic statements and offered suggestions that helped refine them.
Trustworthiness
We established trustworthiness in the present study through an iterative data analysis process with hermeneutic awareness and a hermeneutic circle, triangulation of investigators, and bridling through reflexive journaling (Dahlberg, 2006; Hays & Singh, 2012). First, our iterative data analysis process promoted hermeneutic awareness and helped us achieve a hermeneutic circle in checking our thematic structure and our holistic statements compared to each other (van Manen, 1990). Reflecting on the data in context involved approaching the data with an awareness that meaning is never simple or one-dimensional but rather multidimensional and multilayered (van Manen, 1990). To do this, we used individual and consensus coding, evaluation of the data in holistic context using holistic statements, and imaginative variation to summarize only essential parts of participants’ experiences (van Manen, 1990). Second, to achieve triangulation of investigators, Waalkes and DeCino reached consensus throughout the data analysis process (Hays & Singh, 2012). We also utilized two external auditors who read the interview transcripts and provided feedback on our thematic structure and holistic statements. Third, we engaged in reflexive journaling and bridling as described in the research team section above.
Findings
We arranged our findings into five themes: (a) expansive connections, (b) growth in student autonomy, (c) authenticity, (d) safety and trust, and (e) adaptation to student needs. We arrived at these five themes by using imaginative variation to determine which of our themes were essential to participants’ experiences. Each theme is described in the sections below.
Expansive Connections
In the expansive connections theme, participants (n = 11) described how chairing relationships defy compartmentalized definitions and can have wide-ranging and mutually beneficial impacts that extend beyond the dissertation project. For example, Participant 15 offered herself “as a person” to students:
When you sign on to . . . work with me on a dissertation, you don’t just get my technical expertise, you get me as a person . . . and that’s what you get first, actually. So again, it’s not a relationship that’s contained in a box. Hopefully, this is something that grows and actually is something we both are learning from and continues to sustain.
Similarly, Participant 9’s relationships with students extended beyond discussions of dissertations:
I try to talk to [the students I chair] about personal stuff as well as just the dissertation stuff. Because it’s not little neat cubby holes that they put their lives in. What’s going on in their personal life is what’s impacting their progress towards completion. Sometimes it’s just a sigh [of] relief when I ask them “How’s your wife doing? Is the baby walking?” And it gives them a chance to just decompress for a moment and regroup.
Participant 5 described a mutuality in learning through an intense working relationship:
It’s not really a top-down thing, but it’s about learning a craft, and intensely working together to learn that craft . . . it’s a formative process. We’re learning about ourselves as we’re going through it. And I learn from my students as well, while I’m chairing their projects . . . this is a career-building, life-extending experience.
Growth in Student Autonomy
Participants (n = 8) described the importance of using the dissertation relationship to help students take initiative and learn to conduct research on their own. Often participants set clear expectations and boundaries in their relationships to help students do this. For example, Participant 9 encouraged students to take accountability over maintaining momentum in the working alliance:
The student has to recognize this as a partnership, and I can’t react until the student acts. So to me, if I don’t see any action taking place, it’s much more difficult to give you feedback, to give you some kind of response. So that working alliance, I keep pushing that to a student. “What’s your responsibility. What’s my responsibility?”
Participant 2 talked about how he wanted students to be autonomous in planning their dissertations while offering resources:
I’m not the timekeeper. I’m not the helicopter parent. . . . “This is your dissertation, right? This is . . . your life. I will help get you resources, figure out what you need to do to get it done, you know? Beg, buy, borrow, and steal resources to get it done, but you gotta come to me with that.” I’m not gonna say, “Okay, you’re done with stuff a. Stuff b is this. Here’s what you need to do.”
Participant 8 did not want to micromanage students even if students expected that of her:
I don’t want to be your mother. . . he’s like this helpless person. So, I was a little worried that he was continuing to perpetuate these types of dynamics in his life where he was looking for maybe strong women to just come in and take care of things for him . . . I’ve had to be really, really clear about that.
Authenticity
In the authenticity theme, nearly all participants (n = 13) described valuing genuine conversations with students, in which there was a mutuality in sharing vulnerable parts of themselves. These conversations involved discussing both parties’ roles and responsibilities in the relationship. Participants co-constructed the dissertation process by inviting students into honest discussions of the abilities of both parties. For example, Participant 3 described facilitating authentic conversations:
It’s not a one-size-fits-all model . . . every student is different and . . . the process of having the conversation about what they need is a really good relationship-building conversation. And I’m quick to say, “There may be things you want that I can’t provide,” just because I don’t have this skill set or the capacity or the bandwidth in a given day . . . just having those conversations that start that co-constructed collaborative process and empowering them to do their work.
Additionally, participants transparently revealed vulnerable parts about themselves to help students overcome anxiety or other challenges. For example, Participant 12 described the importance of mutual authenticity to facilitate using immediacy to address issues that were causing students to get stuck:
I really need to be able to call out what I see if [the student] may be stuck . . . there needs to be that mutual authentic exchange too . . . authentic relating is my really being able [to feel] like there’s someone for me to call out when I noticed there might be something obstructing [the student’s] capacity to keep moving forward.
Participant 7 viewed being humble and inviting students to share their knowledge as part of being genuine:
I mentioned having that mutual learning attitude and when you do that, that’s being open and honest and genuine with them. Not acting like you know everything. I may be perceived as an expert in some areas, but I don’t want to come off that way actually sometimes. I’ve done a lot of this stuff, but I’m not an expert on this particular area. Tell me what you know. Tell me what you think you know. Tell me what you don’t know that you want to do and I will help you try to get there.
Safety and Trust
In the safety and trust theme, participants (n = 10) discussed how trust and safety served as the foundation for their chairing relationships. Participants acknowledged how mutual trust deepened their connections and helped students feel like their chairperson would help them grow without leaving them floundering. Participants believed safety and trust helped assure students they were going to complete their dissertation and they were not going to be abandoned. For example, Participant 7 discussed the importance of students’ trusting her to offer consistent support:
[Students should] trust me that we can work collaboratively together to make it a good study, that I have the background or I know where to get [help], if you don’t as a student, to help figure out methodology, how to write that prospectus, how to write period. . . . You have to trust me to know how to do that or at least have the resources to help you figure it out, and to trust me that we’re going to be in this together. I’m not going to leave you hanging.
Numerous participants conceptualized students’ needs for safety in terms of expressing and processing strong and often hidden emotions. For example, Participant 5 discussed how students coped with their vulnerability and shame of not feeling good enough:
They need to feel safe . . . I think there’s a lot of shame that goes into developing as a student and maybe even overt or covert. It’s just really tough. It’s such a vulnerable time in your life. I think that doc students, when you get them into groups, they just are very sure and confident. . . . I think that’s such a defensive mechanism to kind of bolster themselves and to kind of propel themselves forward because they’re really trying to, at times, step into these very big roles.
Similarly, Participant 3 conceptualized safety in terms of helping students of color feel like they could make mistakes with him as they navigate biased academic systems:
I really try to bring my years of experience, but I also try to diminish the hierarchy as much as I can. So we have conversations about why we might go this way or why we might go that way rather than it being an edict from me. And I think students appreciate that. I think they feel respected. I think they feel valued. One of the things that I feel very grateful for is that I’ve had the opportunity to have a lot of students of color select me as their dissertation chair. . . . And I think part of that, as they navigate a system that’s still kind of incredibly White and largely biased . . . they feel safe . . . it’s safe to make mistakes . . . They’re going to hand in some versions of drafts that are just not very good. And that’s part of the learning process.
Adaptation to Student Needs
In the adaptation to student needs theme, participants (n = 12) discussed assessing their students’ personalities and tailoring their approaches to meet unique student needs with a mix of support and challenge. For example, Participant 3 described making adjustments based on students’ levels of self-efficacy:
There are some students that I think have a lot of self-efficacy and don’t want me to sugar-coat anything. I can just be very direct and they want me to be direct. They tell me they want me to be direct, but I also recognize for some students, what they’re going to respond better to is more a carrot, less stick. And so, even how I language a comment or something, I’m paying attention to that based on my sense of the student and what they can navigate. If I have a draft of something that it feels like I’ve kind of bled all over and I’ve done a real hatchet job on . . . I’m going to make sure that in the body of the email . . . I’m encouraging.
Similarly, Participant 4 discussed how she personalized encouragement based on students’ needs:
I think of a student I had who needed a lot of validation in the moment, of, “Hey, you’re doing really well. You have all these strengths. These are all the things you’re doing well and I know you can do this. I believe in you.” And then, for others, I know that they needed to sit in the stress or the disappointment a little bit. So to say like, “I hear you. You are struggling right now and I’m going to give you the space for that. And when you’re ready, I’ve got a lot of positive things to say about you. So you let me know when you’re ready for that feedback. It doesn’t sound like you’re ready for it right now.”
Discussion
Because developing as researchers is important for doctoral students (CACREP, 2015) and research mentorship is critical for this purpose (Flynn et al., 2012; Lamar & Helm, 2017; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015), we investigated counselor educators’ experiences of relationship dynamics with doctoral students when chairing dissertations. Participants reported the complex and mutually influenced dynamics of expansive connections, growth in student autonomy, authenticity, safety and trust, and adaptation to student needs. Our finding of dissertation-chairing relationship dynamics as wide-reaching broadens the focus of previous researchers who have explored these relationships in terms of a series of strategies used by the chairperson (Ghoston et al., 2020) or a list of components contributing to successful dissertation completion (Jorgensen & Wester, 2020). Participants viewed chairing relationships as fluid, mutually influenced, and non-compartmentalized (Purgason et al., 2016), involving a blending of personal and collegial connection that could offer shared learning and fulfillment. Numerous researchers (e.g., Burkard et al., 2014; Flynn et al., 2012) have found that supportive dissertation-chairing relationships can have positive impacts on doctoral students. Yet, a unique finding of this study is that chairing relationships can also positively affect dissertation chairs. Participants discussed growing and experiencing feelings including pride, frustration, and fulfillment from their chairing relationships.
In the growth in student autonomy theme, numerous participants discussed helping students develop more independence and step into a more collegial role in their dissertation-chairing relationships. To a degree, this theme aligns with how Jorgensen and Wester (2020) and Ghoston and colleagues (2020) highlighted the need for accountability and developing doctoral students’ researcher identities in chairing relationships. However, our participants framed helping students become more autonomous as a mutually influenced working alliance that required doctoral student initiative and effort for their chairs to reciprocate. In other words, it seems that dissertation chairs believed doctoral students’ steady effort played a role in creating positive relational momentum throughout a consistent pattern of feedback and support. Additionally, for some participants, fostering student autonomy involved discussing boundaries and the navigation of transference and countertransference within the relationship dynamic. Completing a dissertation can be a challenging process in which students face numerous emotional roadblocks (Lamar & Helm, 2017; Pyhältö et al., 2012) and, for some participants, promoting student autonomy involved exploring and discussing how dependence may function as a defense mechanism for students to cover up their embarrassment, fear, or low self-efficacy.
Our findings also deepen the previous research on the importance of authenticity in dissertation-chairing relationships (Ghoston et al., 2020; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020; Purgason et al., 2016). Many participants directed the relationship toward mutually vulnerable places relevant to students’ dissertations. For example, some participants initiated authentic conversations when students felt stuck. When conflict in a relationship is unacknowledged, the person with less power in the relationship often responds in inauthentic ways; therefore, chairs should take the lead in venturing into vulnerable areas to help move the dissertation forward (Jordan, 2000). For participants, vulnerability included helping students overcome roadblocks and honest discussions and broaching of relationship dynamics, emotions, life experiences, and culture (Jordan, 2010; Purgason et al., 2016).
Our theme of adaptation to student needs highlights the way feedback plays out in mutually impacted relationship dynamics (Ghoston et al., 2020; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020). For example, numerous participants described how they adjusted their feedback styles to meet students’ sensitivity levels. In these cases, participants seemed to be using anticipatory empathy, or the ability to recognize and respond to covert and contextual life circumstances that influence a person (Jordan, 2010). These individualized and emotionally aware strategies can help students overcome barriers in their dissertation processes (Purgason et al., 2018). Additionally, consistent with relational pedagogy (Noddings, 2003), participants viewed dissertation-chairing relationships characterized by trust and safety as critical for helping reduce students’ feelings of shame or inadequacy and helping them feel safe in making mistakes. For many participants, developing trust seemed intertwined with their consistent availability and responding to students with empathy instead of judgment (Purgason et al., 2016).
Interestingly, no participants discussed specific methods they used to evaluate their dissertation-chairing relationships despite previous researchers’ calls to strengthen evaluation of research mentoring relationships (Protivnak & Foss, 2009; Purgason et al., 2018). Utilizing evaluative instruments or conversations in combination with reflection of prior or current experiences with dissertation chairing may help chairs intentionally adjust their feedback and relational styles (Ghoston et al., 2020). The list of items contributing to dissertation chair success developed by Jorgensen and Wester (2020) in their Delphi study of expert dissertation chairpersons may serve as a starting point to develop of such an instrument or help facilitate authentic conversations of needs and expectations between chairs and students.
Implications
Doctoral Students
Because chairing relationships can have broad impacts and can evolve into other professional relationships after dissertation completion, doctoral students might recognize the importance of choosing a chairperson—if they have that luxury—with whom they see potential for deeper connection. Identifying their needs in a chairing relationship might help them choose a chair. To do this, doctoral students might reflect on questions such as: “Which characteristics of a dissertation chairperson are most important to me?” or “What do I need to feel safety and trust in a dissertation-chairing relationship?” Additionally, doctoral students may want to learn more about their program faculty before selecting a chairperson. Doctoral students might interview potential chairs and ask them questions about their relationship styles. Such questions might include: “What did being authentic look like for you in previous chairing relationships?” and “How do you adapt your dissertation chairing to meet student needs?” Doctoral students might also consider their feelings and intuitions about relationships with faculty by assessing the levels of safety, trust, and authenticity they experience with various faculty members.
Ideally, dissertation chairs should facilitate authentic conversations about roadblocks for doctoral students throughout the dissertation process. However, sometimes chairs might be unaware of these roadblocks and doctoral students might consider taking risks to share their insecurities and relational needs with their chairs. Depending on the relational dynamics and power differential, doctoral students might consider the potential benefits and downsides of sharing such information and gauge the level of trust and safety they feel in the relationship. If a dissertation-chairing relationship does not feel safe, a student may consider broaching the topic with their chairperson or, depending upon the culture and policies of their program, switching to another chairperson who feels safer. Alternatively, doctoral students could work on their insecurities and roadblocks with others in their lives, including possibly in their own personal counseling. Personal counseling may be a more appropriate venue to discuss some issues as opposed to the dissertation-chairing relationship. Finally, given the prevalence of intense feelings doctoral students can experience during the dissertation process (Lamar & Helm, 2017; Pyhältö et al., 2012), they might reflect on their insecurities related to their dissertations and the ways their insecurities might affect their dissertation-chairing relationships. As participants discussed in the growth in student autonomy theme, discussing these thoughts and feelings through open and honest dialogue within trusting and safe relationships with their dissertation chairs might help deepen relationships and allow for opportunities to receive more personalized support.
Counselor Educators
To help doctoral students overcome roadblocks and insecurities, dissertation chairs can help students feel more connected through intentional creation of mutually empathic, safe, trusting, and authentic relationships. As the individuals with more power in the relationship, chairs should be ready to initiate conversations that are authentic and help set expectations, including conversations where they broach culture (Jordan, 2010; Purgason et al., 2016). For example, dissertation chairs may consider sharing vulnerable stories from their dissertation journeys or their lives to validate and normalize students’ experiences. Similarly, they might demonstrate humility by admitting the limits of their knowledge and skills and apologizing to students for relational ruptures when appropriate. For instance, a chairperson might admit their lack of knowledge about the methodology a student is using in their dissertation while helping them develop autonomy to seek out resources (e.g., other faculty, books, videos) to get the support they need. Additionally, consistently responding to students with empathy and encouragement if they make mistakes or do not meet deadlines may help build trust and self-confidence for students, creating an environment where they feel safer taking risks interpersonally and with their research. A safe and supportive relational foundation is essential for the trust-building required for learning to take place (Noddings, 2003).
Finally, authentic conversations might also include using immediacy to talk about relationship and cultural dynamics. Utilizing relational-cultural theory (Jordan, 2010; Purgason et al., 2016) may help chairs develop skills for initiating authentic and culturally infused conversations with their students. These conversations might happen throughout the dissertation-chairing relationship. Toward the beginning of the relationship, chairs might ask: “What do you need to build trust and safety in a relationship?” or “How do our cultural differences impact our work together?” At this phase in the relationship, chairs may also openly share their cultural backgrounds and their dissertation styles, including strengths and areas for growth as a dissertation chairperson. Closer to the completion of the dissertation, counselor educators can facilitate discussions with students on the wide-reaching impact of their relationships given the non-compartmentalized nature of dissertation relationships. Chairs might ask students questions such as “How are you different because of our relationship?” or “In what ways has our relationship helped you overcome barriers in your dissertation process?” and be willing to share how the relationship has affected them as well. Acknowledging and reflecting on that shared growth in conversation together may help both parties learn and feel more connected (Purgason et al., 2016).
Counselor educators can use ongoing reflective practice to develop and hone intentional approaches to building dissertation-chairing relationships. Counselor educators might ask themselves, “What relational qualities do I have to offer that contribute to helpful dissertation-chairing relationships?”, “How do I believe that mentoring relationships impact mentees’ development as researchers?”, or “What theories drive my research mentorship philosophy?” As a tangible output for addressing these questions, counselor educators can write philosophy of research mentorship statements, similar to philosophy of teaching or supervision statements. These statements can help counselor educators comprehensively define their approaches to research mentoring relationships. Counselor educators might revisit these statements throughout their careers as research on mentoring and their beliefs about dissertation chairing evolve. Additionally, counselor educators might create and share advisor disclosure statements with doctoral students to help clarify roles and expectations (Sangganjanavanich & Magnuson, 2009). Advisor statements may help alleviate role confusion and emphasize to students early in the relationship that doctoral students should grow as autonomous researchers and contribute to building a working alliance.
Counseling Programs
Numerous researchers have called for doctoral counseling programs to integrate more purposeful research mentorship in structured and systematic ways that could help offer more supportive relationships for doctoral students (Lamar & Helm, 2017; Perera-Diltz & Sauerheber, 2017). Counseling programs could establish structures that allow counselor educators and doctoral students to build trust early on in students’ programs. Connections developed between dissertation chairs and students in research apprenticeships; research teams; and co-teaching, advising, and informal program gatherings may provide relationships space to grow before students start their dissertations. Counseling programs might also establish methods for helping counselor educators evaluate dissertation-chairing relationships (Protivnak & Foss, 2009). Gaining an understanding of how students internalize feedback may help dissertation chairs better adapt to student needs and intentionally build expansive relationships (Ghoston et al., 2020). In line with CACREP’s requirement that counseling programs comprehensively evaluate their effectiveness, programs could regularly send out surveys to doctoral students who have recently completed their dissertations or withdrew during the dissertation stage to seek feedback on former students’ experiences of dissertation-chairing relationships (CACREP, 2015, Section 4). Such surveys might ask former students about their experiences of receiving feedback, the impact of their dissertation-chairing relationship, time and resources their chairperson dedicated to them, and challenges and successes they faced during the dissertation process. Program faculty could then use this feedback to improve their research mentoring programs by developing strategic plans including both individual and programmatic concrete goals (Purgason et al., 2018). Alternatively, dissertation chairs could conduct exit interviews with students.
Limitations
We identified several limitations in our study. First, all research team members identified as White, which may have limited our data analysis process based on our shared, privileged racial/ethnic identity. A coding team with different races and ethnicities may have arrived at a different thematic structure and may have more heavily emphasized cultural considerations in dissertation-chairing relationship dynamics. Second, in our interview protocol and demographic data survey, we did not ask many questions eliciting depth on the culture of participants’ institutions. Knowing more about the structures of participants’ programmatic and institutional supports and stressors for faculty members (e.g., teaching loads, policies that may contradict supporting student success) may have helped us analyze our data with a richer appreciation of contexts (van Manen, 1990; Hays & Singh, 2012). Third, our worldviews possibly influenced the questions we did not ask participants regarding how they navigated cultural differences with their students. Even though a few participants talked about navigating cultural differences, we do not have a clear sense of how cultural differences influenced participants’ chairing relationships. Cross-cultural mentorship relationships in counselor education are influenced by a myriad of complex relational and contextual factors related to racial/ethnic identity and White racism inherent in the field of counseling (Brown & Grothaus, 2019). These cross-cultural relationships warrant more focused investigation. Fourth, counselor educators who emphasized relationship-building in their dissertation chairing may have been more likely to participate in our study because they believed in the importance of our topic. Therefore, our findings may not reflect the relationships of those who do not emphasize relational approaches to dissertation chairing. Fifth, we did not explore dissertation relationships that took place in virtual programs. Chairs may experience relationship dynamics differently when interactions only occur virtually as opposed to mostly in person.
Directions for Future Research
First, future researchers might explore how counselor educators and doctoral students navigate power dynamics and cultural context in dissertation-chairing relationships (Borders et al., 2012; Jorgensen & Wester, 2020; Neale-McFall & Ward, 2015; Purgason et al., 2018). Fostering mutually fulfilling connections in dissertation-chairing relationships may help counselor educators attend to the unique needs of underrepresented students (Purgason et al., 2016) and help make research more accessible to doctoral students from more collectivist cultural backgrounds. Given the importance of authentic conversations and egalitarian relationships expressed by participants, further exploration of how counselor educators approach cultural, country of origin, worldview, gender, and other differences in dissertation-chairing relationships between themselves and students seems warranted. Second, participants in this study mostly talked about positive outcomes of dissertation-chairing relationships and helpful strategies they used to build relationships. Given the prevalence of negative dissertation relationships reported by doctoral students and their harmful impact on completion rates and mental health (Flynn et al., 2012; Lamar & Helm, 2017; Protivnak & Foss, 2009; Rigler et al., 2017), future researchers might examine ways that dissertation chairs can identify, navigate, and heal relational ruptures. Third, outcome research could illuminate the positive and negative impacts that dissertation-chairing relationships can have on students’ researcher self-efficacy, researcher identity development, and future research productivity. Because participants described tailoring their feedback styles to meet students’ unique needs but did not clearly describe evaluating the impact of their feedback, future researchers might examine the impact that different forms and styles of feedback have on students. Fourth, future researchers should explore institutional and programmatic factors that complicate chairs’ abilities to provide research mentorship to students. Finally, there are numerous theories of counseling supervision and adult learning that may apply to dissertation-chairing relationships but few theories specific to research mentorship or dissertation-chairing relationships in counselor education (Purgason et al., 2016). Future researchers might develop theories in this area by asking counselor educators about values, beliefs, and attitudes that drive their research mentorship philosophy and practice or by writing conceptual articles applying existing counseling theories to dissertation chairing.
Conclusion
Our research offers insights from counselor educators on how to foster supportive dissertation-chairing relationships. Counselor educators may utilize our findings to facilitate reflection regarding their relationship-building skills in dissertation-chairing relationships. Counselor educators intentionally build dissertation-chairing relationships to help their students overcome barriers to completing their dissertations and preparing them as future scholars.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Borders, L. D., Wester, K. L., Granello, D. H., Chang, C. Y., Hays, D. G., Pepperell, J., & Spurgeon, S. L. (2012). Association for Counselor Education and Supervision guidelines for research mentorship: Development and implementation. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51(3), 162–175.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00012.x
Brown, E. M., & Grothaus, T. (2019). Experiences of cross-racial trust in mentoring relationships between Black doctoral counseling students and White counselor educators and supervisors. The Professional Counselor, 9(3), 211–225. https://doi.org/10.15241/emb.9.3.211
Burkard, A. W., Knox, S. K., DeWalt, T., Fuller, S., Hill, C., & Schlosser, L. Z. (2014). Dissertation experiences of doctoral graduates from professional psychology programs. Counselling Psychology Quarterly, 27(1), 19–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/09515070.2013.821596
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2015). 2016 CACREP standards. https://www.cacrep.org/for-programs/2016-cacrep-standards
Dahlberg, K. (2006). The essence of essences: The search for meaning structures in phenomenological analysis of lifeworld phenomena. International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-Being, 1(1), 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/17482620500478405
Flynn, S. V., Chasek, C. L., Harper, I. F., Murphy, K. M., & Jorgensen, M. F. (2012). A qualitative inquiry of the counseling dissertation process. Counselor Education and Supervision, 51(4), 242–255.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2012.00018.x
Ghoston, M., Grimes, T., Graham, J., Grimes, J., & Field, T. A. (2020). Faculty perspectives on strategies for successful navigation of the dissertation process in counselor education. The Professional Counselor, 10(4), 615–631. https://doi.org/10.15241/mg.10.4.615
Hays, D. G., & Singh, A. A. (2012). Qualitative inquiry in clinical and educational settings. Guilford.
Heidegger, M. (1962). Being and time (J. Macquarrie & E. Robinson, Trans.). Harper and Row.
Jordan, J. V. (2000). The role of mutual empathy in relational/cultural theory. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 56(8), 1005–1016. https://doi.org/cfp6pr
Jordan, J. V. (2010). Relational–cultural therapy. American Psychological Association.
Jorgensen, M. F., & Wester, K. L. (2020). Aspects contributing to dissertation chair success: Consensus among counselor educators. Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 13(3), 117–144.
http://doi.org/10.7729/42.1404
Lamar, M. R., & Helm, H. M. (2017). Understanding the researcher identity development of counselor education and supervision doctoral students. Counselor Education and Supervision, 56(1), 2–18.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12056
Neale-McFall, C., & Ward, C. A. (2015). Factors contributing to counselor education doctoral students’ satisfaction with their dissertation chairperson. The Professional Counselor, 5(1), 185–194.
https://doi.org/10.15241/cnm.5.1.185
Noddings, N. (2003). Caring: A feminine approach to ethics and moral education (2nd ed.). University of California Press.
Patton, M. Q. (2014). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice (4th ed.). SAGE.
Perera-Diltz, D., & Sauerheber, J. D. (2017). Mentoring and other valued components of counselor educator doctoral training: A Delphi study. International Journal of Mentoring and Coaching in Education, 6(2), 116–127. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMCE-09-2016-0064
Preston, J., Trepal, H., Morgan, A., Jacques, J., Smith, J. D., & Field, T. A. (2020). Components of a high-quality doctoral program in counselor education and supervision. The Professional Counselor, 10(4), 453–471. https://doi.org/10.15241/jp.10.4.453
Protivnak, J. J., & Foss, L. L. (2009). An exploration of themes that influence the counselor education doctoral student experience. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48(4), 239–256.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2009.tb00078.x
Purgason, L. L., Avent, J. R., Cashwell, C. S., Jordan, M. E., & Reese, R. F. (2016). Culturally relevant advising: Applying relational-cultural theory in counselor education. Journal of Counseling & Development, 94(4), 429–436. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12101
Purgason, L. L., Lloyd-Hazlett, J., & Avent Harris, J. R. (2018). Mentoring counselor education students: A Delphi study with leaders in the field. Journal of Counselor Leadership and Advocacy, 5(2), 122–136.
https://doi.org/10.1080/2326716X.2018.1452080
Pyhältö, K., Toom, A., Stubb, J., & Lonka, K. (2012). Challenges of becoming a scholar: A study of doctoral students’ problems and well-being. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012.
https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/934941
Rigler, K. L., Bowlin, L. K., Sweat, K., Watts, S., & Thorne, R. (2017). Agency, socialization, and support: A critical review of doctoral student attrition. Paper presented at the 3rd International Conference on Doctoral Education, University of Central Florida.
Sangganjanavanich, V. F., & Magnuson, S. (2009). Averting role confusion between doctoral students and major advisers: Adviser disclosure statements. Counselor Education and Supervision, 48(3), 194–203.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2009.tb00074.x
Schlosser, L. Z., Knox, S., Moskovitz, A. R., & Hill, C. E. (2003). A qualitative examination of graduate advising relationships: The advisee perspective. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 50(2), 178–188.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.50.2.178
van Manen, M. (1990). Researching lived experience: Human science for an action sensitive pedagogy (1st ed.). Althouse Press.
Phillip L. Waalkes, PhD, NCC, ACS, is an assistant professor at the University of Missouri – St. Louis. Daniel A. DeCino, PhD, NCC, LPC, is an assistant professor at the University of South Dakota. Maribeth F. Jorgensen, PhD, NCC, LPC, LMHC, LIMHP, is an assistant professor at Central Washington University. Tiffany Somerville, MS, is a doctoral student at the University of Missouri – Saint Louis. Correspondence may be addressed to Phillip L. Waalkes, 415 Marillac Hall, 1 University Blvd., St. Louis, MO 63121, waalkesp@umsl.edu.
Feb 7, 2022 | Volume 12 - Issue 1
Clark D. Ausloos, Madeline Clark, Hansori Jang, Tahani Dari, Stacey Diane Arañez Litam
Trans youth experience discrimination and marginalization in their homes, communities, and schools. Professional school counselors (PSCs) are positioned to support and advocate for trans youth as dictated by professional standards. However, an extensive review of literature revealed a lack of confidence and competence in counselors working with trans youth and their families. Further, there is a dearth of literature that addresses factors leading to increased school counselor competence with trans students. The current study uses a cross-sectional survey design to contribute to the extant literature and explore how PSCs in the United States work with students in the K–12 public school system. Results from multiple regression analyses indicate that PSCs who have had postgraduate training and report personal and professional experiences with trans students are more competent in working with trans students. Implications for PSCs and school counselor education programs are discussed.
Keywords: trans youth, school counselors, competence, counselor education, multiple regression analysis
Trans people experience an incongruence between their sex assigned at birth and their gender identity (GI; Ginicola et al., 2017; McBee, 2013). The term trans encompasses a wide range of gender-expansive identities, including trans (transgender), nonbinary (one who identifies outside the gender binary of male or female), genderqueer or gender-fluid (one who identifies with gender in a fluid, dynamic way) and agender (one who does not identify as having a gender). Trans people face pervasive discrimination and marginalization (Whitman & Han, 2017), leading to severe physical and mental health disparities, like depression, anxiety, and suicidality (James et al., 2016). In schools, trans students face 4 times higher rates of discrimination when compared with cisgender peers (Kosciw et al., 2020; Williams et al., 2021). Trans students are more vulnerable to mental health disorders, a lack of social support, and an increase in self-harm, suicidal ideations, and suicide attempts (Kosciw et al., 2020; Reisner et al., 2014), especially among transmale and nonbinary students (Toomey et al., 2018). These rates are increasing in national trends and are even higher among Black and Latinx trans students (Vance et al., 2021). The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated barriers and inequities for trans students, with increasing health concerns, isolation, economic hardships, issues with housing, and limited access to essential clinical care (Burgess et al., 2021).
Increasingly, trans students face systemic legal barriers to their health and well-being (Wang et al., 2016). States including Arkansas, Idaho, Montana, South Dakota, and Tennessee have introduced bills that ban trans students from participating in sports that are congruent with their GI (Transgender Law Center, 2021). In April of 2021, Arkansas banned medical gender-affirming services to students under 18 years of age (American Civil Liberties Union [ACLU], 2021). New Hampshire’s House Bill 68 proposed adding gender-affirming treatments to the definition of child abuse (ACLU, 2021). Beyond political oppression, trans youth experience overt discrimination, verbal abuse, physical and sexual assault, and marginalization within their homes, schools, and places of employment (Human Rights Campaign [HRC], 2018; James et al., 2016). Trans youth additionally face disaffirming and incompetent teachers and medical professionals (Grant et al., 2011; James et al., 2016; Whitman & Han, 2017) and embedded systemic transmisia (the hatred of trans persons; Simmons University Library, 2019). Despite the pervasive mental health concerns faced by trans students (i.e., depression, anxiety, disordered eating, self-harm, suicide), professional school counselors (PSCs) continue to be ill equipped in supporting and advocating for this marginalized population within schools (Simons, 2021). Based upon an analysis of the extant body of research, we found that counselor education training programs lack rigor in working with trans students (O’Hara et al., 2013; Salpietro et al., 2019), counselor educators may hold biased views about trans students (Frank & Cannon, 2010), and there is an absence of quality professional development opportunities on trans issues (Salpietro et al., 2019; Shi & Doud, 2017). It is therefore of paramount importance for PSCs and counselor education programs to obtain a deeper understanding of how to better prepare for and support trans students in schools.
Professional School Counselors and Trans Students
PSCs focus on academic, career, and social-emotional growth and work as leaders alongside teachers, administration, families, and other stakeholders. PSCs are therefore well positioned to provide safety and support for trans students, promote change, and act as social justice advocates within schools (Bemak & Chung, 2008). The American School Counselor Association (ASCA) mandates that PSCs “promote affirmation, respect, and equal opportunity for all individuals regardless of . . . gender identity, or gender expression . . . and promote awareness of and education on issues related to LGBT students” (2016a, p. 37). PSCs who work with trans students may provide services through the Multitiered Systems of Support lens (MTSS; ASCA, 2019), through collaboration, by supporting school administration and staff (e.g., trainings, meetings, workshops), and through provision of direct student services (e.g., individual and group counseling, working with families). More specifically, PSCs advocate for and with students for name and pronoun changes within schools, trans-inclusive school policies, and increased visibility and normalization of trans people and issues.
ASCA (2016b) adopted a position that PSCs recognize that “the responsibility for determining a student’s gender identity rests with the student rather than outside confirmation from medical practitioners . . . or documentation of legal changes” (p. 64). It is clear that PSCs should possess knowledge and skills in working with and advocating for trans youth through a range of services at various levels and in coordination with other stakeholders in schools, all while respecting students’ autonomy and authenticity (ASCA, 2016a, 2016b, 2019; Bemak & Chung, 2008).
Counselor Education Programs
Although professional standards provide best practices (ALGBTIC LGBQQIA Competencies Taskforce, 2013; ASCA, 2016a), many PSCs never receive the training necessary to effectively serve trans students (Bidell, 2012; O’Hara et al., 2013; Salpietro et al., 2019). Salpietro and colleagues (2019) reported that counselor incompetence was related to a lack of rigorous training that attends to family systems, intersectionality, and medical issues through gender-affirming therapies (i.e., blockers, hormones, or surgeries). These researchers indicated a need for comprehensive, standardized, and thorough formal training (i.e., graduate school) and informal professional development opportunities. These findings are consistent with Shi and Doud (2017), who recommended PSCs specifically take advantage of conferences and workshops to supplement formal educational curricula. The Gay, Lesbian, and Straight Education Network (GLSEN) conducted a survey that reported about 81% of school mental health professionals received “little to no competency training in their graduate programs related to working with [trans] populations,” and about 74% of participants rated their graduate training programs as “fair or poor” in preparing them for work with trans students (GLSEN et al., 2019, p. xviii). GLSEN and other professional organizations additionally reported about two-thirds of school professionals do not feel prepared to work with trans students (GLSEN et al., 2019). Although there are some professional development opportunities, such as those offered through the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH), the HRC, and the Society for Sexual, Affectional, Intersex, and Gender-Expansive Identities (SAIGE), there is still a lack of concrete training within graduate programs and through fieldwork experiences and an overall lack of accessible, professional trainings. There is a clear need for increased attention to trans issues in formal educational programs and professional development offerings.
Purpose of the Study and Research Questions
This study examines factors that contribute to PSC competence in working with trans students in K–12 public schools. We highlight the need for PSCs and counselor education training programs to better focus on and support trans students. More specifically, we examine the following PSC factors: (a) the PSC’s GI, (b) whether the PSC has received postgraduate training on trans issues or populations, (c) whether the PSC has worked with self-identified trans students, and (d) whether the PSC knows someone who identifies as trans outside of the school setting.
PSC Gender Identity
Researchers recommend that special attention is given within a category of interest (i.e., gender identity) to historically marginalized groups, encouraging counselor-researchers to view all samples “in terms of their particularity and to attend to diversity within samples” (Cole, 2009, p. 176). We were intentional in using PSC GI demographic factors in data analysis, attending to diversity among PSC gender identities, as research indicates there may be relationships between counselor GI, privilege and oppression, and multicultural counselor competence (Cole, 2009). Culturally competent counselors engage in self-reflection, examine their own biases and stereotypes, consider how their positions of privilege or oppression impact the therapeutic alliance, and deliver culturally responsive counseling interventions.
Postgraduate Training Addressing Trans Issues
Researchers note that graduate programs in counselor education are not adequately preparing school counseling students to work with trans students (Bidell, 2012; Farmer et al., 2013; Frank & Cannon, 2010; GLSEN et al., 2019; O’Hara et al., 2013) and that much of the awareness, knowledge, and skills gained in working with this population are result of counselors’ self-seeking professional trainings, education, and workshops that are focused on trans issues and students (Salpietro et al., 2019; Shi & Doud, 2017).
Professional Experiences With Trans Students
O’Hara and colleagues (2013) reported no significance on scores of competence in working with trans clients between counseling students who completed practicum or internship and those who did not. In the present study, our variable relates to PSCs who have already graduated, reflecting on their professional tenure as PSCs, and if these experiences provided opportunities to work with trans students.
Personal Relationships With Trans People
O’Hara and colleagues (2013) reported that participants in their study identified informal sources as necessary for gaining trans-affirming knowledge and skills, such as “exposure to or personally knowing someone who [is trans]” (p. 246). Research supports the concept that increasing affirming attitudes and mitigating negative attitudes and beliefs toward trans individuals can be accomplished by exposure and intentional engagement in fostering personal and professional relationships with trans people (Salpietro et al., 2019; Simons, 2021). In forming relationships with trans people, we can listen to and learn from the lived experiences of this community, examine our own biases, and position ourselves as supportive allies, personally and professionally.
Research Questions
With these factors in mind, the following research questions were identified:
- What is the relationship between PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personally knowing someone who is trans) and levels of PSC self-perceived competence in working with trans students in schools?
- What is the relationship between PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personally knowing someone who is trans) and PSC awareness in working with trans students in schools?
- What is the relationship between PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personally knowing someone who is trans) and PSC knowledge in working with trans students in schools?
- What is the relationship between PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personally knowing someone who is trans) and PSC skills in working with trans students in schools?
We hypothesized there would be a statistically significance difference (p > .05) between PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personally knowing someone who is trans) and levels of PSC self-perceived competence in working with trans students in schools. More specifically, we hypothesized that cisfemale PSCs who have had postgraduate training on trans issues, who have worked with trans students, and who personally know someone who is trans, would report higher scores in measures of awareness, knowledge, skills, and overall competence. Cisgender (cis) refers to someone who experiences congruence between their sex assigned at birth and their GI. Research demonstrates that cismales may express more negative attitudes and hold restrictive views toward queer and trans people when compared with cisfemales (Landén & Innala, 2000; Norton & Herek, 2012).
Method
Participants
With an anticipated medium effect size of 0.15, a desired statistical power level of 0.95, and desired probability level of 0.05 (Israel, 2013), we determined an appropriate minimum sample size for the proposed study was 120 PSCs. Initially, 499 responses were recorded. Of those, 110 were incomplete or had missing data, yielding a total of 389 fully completed surveys. Participants in this study (N = 389) were PSCs with a valid school counseling license working in a public school setting, from kindergarten through 12th grade, in the United States. Participant demographic information can be found in Table 1.
Table 1
Demographic Characteristics of Professional School Counselors (PSCs)
Procedures
For ease of use and accuracy of representation, we used probability sampling, more specifically, a simple random sample selection process (Creswell, 2013). Upon approval by the IRB, we posted a series of three recruitment letters (with 2 weeks between each posting) to PSCs through an online professional forum, ASCA Scene. We also posted our recruitment letter on ASCA Aspects, a monthly e-newsletter. Data were collected over a period of 6 weeks. PSCs who elected to participate were directed to the electronic informed consent document and the survey.
Instrumentation
Demographic Questionnaire
Participants completed a questionnaire with write-in options for both age and gender and forced-choice responses to gather racial-ethnic identity, years working as a licensed school counselor, the region in which they practiced, and grade levels in which the participants worked. Our four independent variables were collected through the demographic questionnaire. Participants indicated their experiences, if any, with trans students, experiences with postgraduate training on trans issues, and personal relationships with trans people.
Gender Identity Counselor Competency Scale
The Gender Identity Counselor Competency Scale (GICCS), a revised version of the Sexual Orientation Counselor Competency Scale (Bidell, 2005), was used to assess PSC competence, the dependent variable in the study. This is the instrument best suited for intended measurement of self-perceived competence (Bidell, 2012; O’Hara et al., 2013). Bidell (2005) developed the instrument based on Sue and colleagues’ (1992) research of multicultural counseling competencies, with the domains of attitudinal awareness, knowledge, and skills. Bidell (2005) reported the Cronbach’s alpha of .90, with subscale scores for internal consistency of .88 for the Awareness subscale, .71 for the Knowledge subscale, and .91 for the Skills subscale (Bidell, 2005, 2012). Test-retest reliability for the overall instrument was found to be .84, with .85 for the Awareness subscale, .84 for the Knowledge subscale, and .83 for the Skills subscale (Bidell, 2005). The GICCS is a 29-item self-report assessment on a 7-point Likert scale (where 1 is not at all true and 7 is totally true). Examples of questions include: “I have received adequate clinical training and supervision to counsel transgender clients” and “The lifestyle of a transgender client is unnatural or immoral” (O’Hara et al., 2013, p. 242). Cronbach’s alpha in the present study was .70, adequate for our analysis.
Awareness Subscale. The Awareness subscale consists of 10 items focused on counselors’ attitudinal awareness and prejudice about trans clients, including statements like “It would be best if my clients viewed a [cisgender] lifestyle as ideal” and “I think that my clients should accept some degree of conformity to traditional [gender] values” (Bidell, 2005, p. 273). Cronbach’s alpha for the Awareness subscale has been reported as .88 (Bidell, 2005) and was .89 in the present sample. Self-awareness and reflection are critical skills for counselors in examining deeply held biases and beliefs and in asking culturally responsive questions to strengthen the therapeutic alliance.
Knowledge Subscale. This subscale of the GICCS consists of eight items focused on counselors’ experiences and skills with trans clients, including statements like “I am aware that counselors frequently impose their values concerning [gender] upon [trans] clients” and “I am aware of institutional barriers that may inhibit [trans] clients from using mental health services” (Bidell, 2005, p. 273). Cronbach’s alpha for the Knowledge subscale was reported as .76 (Bidell, 2005), and was .73 in the present sample. Counselors who impose their own values on a client may cause rifts in the therapeutic alliance and could potentially even harm clients.
Skills Subscale. This subscale of the GICCS consists of 11 items focused on counselors’ experiences and skills with trans clients, including statements like “I have experience counseling [trans male] clients” and “I have received adequate clinical training and supervision to counsel [trans] clients” (Bidell, 2005, p. 273). Cronbach’s alpha for the Skills subscale was reported as .91 (Bidell, 2005) but was .75 in the present sample. Counselors working with trans students need to understand the importance of evolving language and terminologies; utilize affirmative, celebratory, and liberating counseling; and have knowledge of and connection to medical providers who support gender-affirming interventions.
Data Analysis Procedures
Data Cleaning
We first screened the data to ensure it was usable, reliable, and valid to proceed with statistical analyses. We continued data cleaning by coding the demographic variable of GI 1 through 4: cisfemale (1); cismale (2); nonbinary, trans, and/or genderqueer (3); and agender (4). Racial-ethnic identities were coded 1 through 10: American Indian or Alaska Native (1); Asian or Asian American (2); Black or African American (3); Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish Origin (4); Middle Eastern or North African (5); Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander (6); White (7); Some Other Race, Ethnicity, or Origin (8); Prefer Not to Answer (9); and Multiracial Identity (10). PSC location was also coded 1 through 6: Midwest (1), Northeast (2), South (3), West (4), Puerto Rico or other U.S. Territories (5), and Other (6). Last of the demographic variables, we coded PSC School Level 1 through 4: Elementary (1), Middle School (2), High School (3), and Other (4). In addition, we cleaned variables highlighting PSC professional and personal training and experiences with trans persons. The first variable was dummy coded to reflect participants who had worked with trans students (1; n = 297, 76.3%) and participants who indicated not working with trans students (0; n = 92, 23.7%). The next variable, PSC postgraduate training, was dummy coded for use in data analyses, reflecting those who indicated they engaged in postgraduate training (1; n = 193, 49.6%) and participants who indicated they did not engage in postgraduate training (0; n = 196, 50.4%). The final variable was dummy coded to reflect participants who know someone who is trans outside of the school setting (1; n = 93, 23.9%) and those participants who do not know someone who is trans outside of the school setting (0; n = 296, 76.1%). Per Bidell (2005), we started by reverse scoring coded GICCS items and created new variables for the GICCS total mean score, attitudinal Awareness, Skills, and Knowledge subscales.
Data Analysis
Post–data cleaning, we entered all the data from the demographic questionnaire and the GICCS into SPSS 26. To best answer the research questions, we used a series of standard multiple regression analyses to determine “the existence of a relationship and the extent to which variables are related, including statistical significance” (Sheperis et al., 2017, p. 131). Although multiple regression analysis can be used in prediction studies, it can also be used to determine how much of the variation in a dependent variable is explained by the independent variables, which is what we intended to measure (Johnson, 2001). Our independent variables were four categorical variables measured by our demographic questionnaire: PSC GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personal relationships with someone who is trans. Our dependent variable was school counselor competence in working with trans students, as measured by the GICCS (Bidell, 2005).
There are many assumptions to consider when conducting a multiple regression analysis, including (a) two or more continuous or categorical independent variables, (b) a continuous dependent variable, (c) independence of residuals (or observations), (d) linearity (both between dependent variable and each of the independent variables, and between the dependent variable and the independent variables as a whole), (e) homoscedasticity, (f) absence of multicollinearity, (g) no significant outliers, and (h) normally distributed residuals (Flatt & Jacobs, 2019). The research variables met assumptions (a) and (b) in conducting multiple regressions. In analyzing data in SPSS, independence of residuals was determined by using the Durbin-Watson statistic, which ranges in value from 0 to 4, with a value near 2 indicating no correlation between residuals. Assumption (c) was met, as the Durbin-Watson value found was 1.46 (Savin & White, 1977). Additionally, we plotted a scatterplot using variables, as well as a partial regression with each of the independent variables and the dependent variable, and observed linear relationships, attending to the assumptions of linearity (d; i.e., a linear relationship between dependent and independent variables) and homoscedasticity (e; i.e., residuals are equal for all values of the predicted dependent variable). Homoscedasticity was also assessed by visual inspection of a plot of studentized residuals versus unstandardized predicted values. To assess the absence of multicollinearity (f), we considered the variance inflation factors (VIF) indicated in the coefficients table (Flatt & Jacobs, 2019). We found VIF values ranging from 1.01 to 1.05, indicating an absence of multicollinearity (f). VIF is a measure of the amount of multicollinearity in a set of multiple regression variables (Flatt & Jacobs, 2019). We checked for unusual points (g): outliers, high leverage points, and highly influential points. We did identify a significant outlier (−3.10) in case number 133 by examining the range of standardized residuals ([−3.10 to 2.34]), which is outside the common cut-off range of three standard deviations (SD). We then inspected the studentized deleted residual values and found a value in case number 133 (−3.15), which falls outside the common cut-off range of 3 SD.
Additionally, we determined two cases of problematic leverage values that were greater than the safe value of 0.2 (0.36 and 0.23). The cases that violated assumptions were filtered out and the standard multiple regression analysis was run again. This time, the data did not violate assumptions (a) through (g). Last, we observed normally distributed standardized residuals (h). To determine if any cases were influential in the data, we examined the Cook’s Distance values, which ranged from .000 to .090. As there were no values above 1, there were no highly influential points. To answer the first research question (the relationship between PSC factors and levels of PSC self-perceived competence in working with trans students in schools as measured by total scores on the GICCS), we used a standard multiple regression analysis (Sheperis et al., 2017). To answer research questions 2 through 4, we conducted standard multiple regression analyses using the Awareness, Knowledge, and Skills subscales as the dependent variables, respectively.
Results
Correlations Between Variables of Interest
Prior to the regression analysis, we examined correlations between the variables: PSC GI (cisfemale, cismale, trans, agender), having worked with trans students, postgraduate training experiences, personally knowing someone who is trans, the GICCS Awareness subscale, the GICCS Skills subscale, the GICCS Knowledge subscale, and the GICCS total score. Correlations of variables of interest are found in Table 2. There were multiple significant correlations as determined by Pearson product moment correlations (r). The GICCS total score was significantly correlated with the Awareness subscale (r = −.65, p < .001), the Skills subscale (r = .83, p < .001), and the Knowledge subscale (r = .66, p < .001). The Awareness subscale was significantly correlated with the Skills subscale (r = −.26, p < .001) and the Knowledge subscale (r = .30, p < .001). The Knowledge subscale was also significantly correlated with the Skills subscale (r = .30, p < .001). In examining demographic factors, cisfemale GI was significantly correlated with cismale GI (r = −.90, p < .001), trans GI (r = −.37, p < .001), and agender GI (r = −.21, p < .001). Additionally, cisfemale GI was significantly correlated with having worked with trans students (r = −.12, p = .036), as well as the GICCS total score (r = −.14, p = .005), the Skills subscale (r = −.14, p = .005), and the Knowledge subscale (r = −.15, p = .003). Cismale GI was significantly correlated with the GICCS total score (r = .11, p = .038), the Skills subscale (r = .12, p = .017), and the Knowledge subscale (r = .11, p = .003). Trans GI was significantly correlated with personally knowing someone who is trans (r = .12, p = .002), as well as with the GICCS total score (r = .12, p = .034). Having worked with trans students was significantly correlated with the GICCS total score (r = .41, p <.001), the Skills subscale (r = .55, p < .001), and the Awareness subscale (r = −.11,
p = .032). Postgraduate training was significantly correlated with many variables, including personally knowing someone who is trans (r = .14, p = .005), and with the GICCS total scores (r = .36, p < .001), the Skills subscale (r = .41, p < .001), the Knowledge subscale (r = .19, p < .001), and the Awareness subscale (r = −.10, p = .040). Last, personally knowing someone who is trans was significantly correlated with the GICCS total score (r = .35, p < .001), the Skills subscale (r = .29, p < .001), the Knowledge subscale
(r = .25, p < .001), and the Awareness subscale (r = −.22, p < .001).
Table 2
Correlation Table for Variables of Interest
Model 1: PSC Competency
R² for the overall model was 35.2%, with an adjusted R² of 34.1%, a small to moderate size according to Cohen (1988). PSC factors significantly predicted levels of PSC self-perceived competence in working with trans students in schools, F(6, 381) = 34.430, p < .001. In examining beta weights (β), having worked with trans students received the strongest weight in the model (β = .35), followed by postgraduate training (β = .29) and personally knowing someone who is trans (β = .27). The variable with the most weight, having worked with trans students, had a structure coefficient (rs) of .67, and rs2 was 45.2%, meaning that of the 35.2% effect (R2), this variable accounts for 45.2% of the explained variance by itself. This shows that PSCs’ competence is increased by experiences with trans students, engaging in postgraduate trainings, and personally knowing someone who is trans. A summary of regression coefficients and standard errors can be found in Table 3.
Table 3
Multiple Linear Regression Analyses Exploring Professional School Counselor Competence
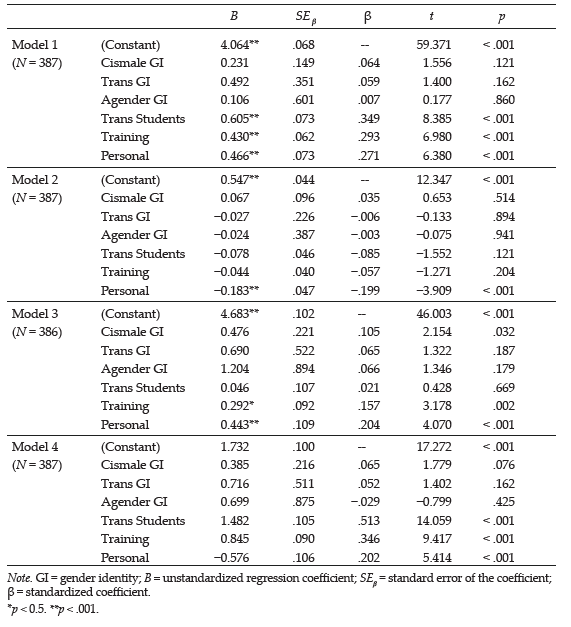
Model 2: PSC Awareness
R² for the overall model was 5.8%, with an adjusted R² of 6.2%, a very small effect size (Cohen, 1988). PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personal relationship with someone who is trans) significantly predicted awareness of PSC self-perceived competence in working with trans students in schools, F(6, 380) = 3.873, p = .001. Personally knowing someone who is trans was the only significant predictor in this model. We examined the regression coefficients and corresponding data (β = −.20, rs = −0.90, rs2 = 80%). Of the 5.8% effect (R²), personally knowing someone who is trans accounted for 80% of the explained variance by itself.
Model 3: PSC Knowledge
R² for the overall model was 10.3%, with an adjusted R² of 8.9%, a small effect size (Cohen, 1988). PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personal relationship with someone who is trans) significantly predicted knowledge of PSC self-perceived competence in working with trans students in schools, F(6, 379) = 7.257, p < .001. Personally knowing someone who is trans, postgraduate training, and cismale GI were all significant in this model. Personally knowing someone who is trans received the strongest weight in the model (β = .20, rs = .76), followed by postgraduate training (β = .16, rs = .58) and cismale GI (β = .12, rs = .35). After examining regression coefficients and corresponding data, we determined that of the 10.3% effect (R2), personally knowing someone who is trans accounted for 58.3% of the explained variance by itself. These findings demonstrate that PSC knowledge is strongly supported through fostering personal relationships with trans people.
Model 4: PSC Skills
R² for the overall model was 50.2%, with an adjusted R² of 49.5%, a medium effect size according to Cohen (1988). PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personal relationship with someone who is trans) significantly predicted self-perceived PSC skills in working with trans students in schools, F(6, 380) = 63.945, p < .001. Having worked with trans students, postgraduate training, and personally knowing someone who is trans were all significant in this model. Having worked with trans students received the strongest weight in the model (β = .51), followed by postgraduate training (β = .35) and personally knowing someone who is trans (β = .20). After examining regression coefficients and corresponding data, we determined that of the 50.2% effect (R2), having worked with trans students accounted for 79% of the explained variance by itself. Counselors can augment their skills by staying updated on appropriate language and terminologies and by fostering relationships with affirming providers and medical professionals in the community.
Discussion
The most salient finding in this model is that PSCs who worked with trans students were strongly positively correlated with GICCS total scores (r = .61, p < .001). This finding may indicate that increased exposure to trans students may subsequently increase competency in working with trans populations. Our research findings supplement existing studies that reported a relationship between affirming attitudes toward trans students and professional exposure to trans people (Salpietro et al., 2019; Simons, 2021). Avoidance of counseling trans students because of discomfort is not only unethical (ASCA, 2016b) but inhibits a PSC’s ability to develop their GI competence (Henry & Grubbs, 2017). Thus, it is imperative that PSCs receive opportunities to work with trans students (through practicum or internship experiences); consult with experienced, gender-affirming PSCs who have worked with trans students; and “expose themselves to published texts . . . films . . . [and] service-learning activities . . . to gain a better understanding of the experiences of [trans] persons” (O’Hara et al., 2013, p. 251). Additionally, PSCs must engage in constant self-reflection, introspection, and processing of biases and worldviews to provide culturally competent care to trans students.
Counseling Competence
Postgraduate training was moderately positively correlated with GICCS total score (r = .43, p < .001), indicating that additional postgraduate training in trans issues increased competence in the present sample (Model 1). This is consistent with extant literature, which demonstrated that PSCs who received postgraduate training were more competent in providing affirming services to trans students compared to PSCs who had not received the training (Salpietro et al., 2019; Shi & Doud, 2017). Finally, the presence of personal relationships with trans people was moderately positively correlated with GICCS total scores (r = .47, p < .001). These results support current literature in that PSCs who currently have or have had personal relationships with trans people were more competent in providing affirming services to trans students (GLSEN et al., 2019; O’Hara et al., 2013; Salpietro et al., 2019; Simons, 2021).
Awareness
We explored the relationship between PSC factors on the Awareness subscale of the GICCS in the second research question (Model 2). In examining coefficients for the model, having personal relationships with trans people is associated with a decrease in GICCS Awareness subscale scores, a weak, negative correlation (r = −.19, p = .001). This finding may indicate that people who did not know someone personally who is trans would score slightly higher on the Awareness subscale. These unexpected findings are contrary to existing research, which reported that engaging in personal relationships with trans people increased affirming attitudes and mitigated negative attitudes (Henry & Grubbs, 2017; Salpietro et al., 2019). Because of the lack of practical significance of PSC factors (i.e., GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personal relationship with someone who is trans) on the Awareness subscale, these results should be considered with caution.
Knowledge
In the third research question, we explored the relationship between PSC factors on the Knowledge subscale of the GICCS (Model 3). In examining coefficients for the model, PSC cisgender male GI was moderately positively correlated with the Knowledge subscale scores (r = .476, p = .032), indicating that cismale PSCs scored moderately higher on the Knowledge subscale when compared with other PSC gender identities in the present sample. One possible explanation is the present study’s sample of cisfemales (N = 368, 94.6%) and cismales (N = 17, 4.4%). Within this sample, the ages of the cismale PSCs could reflect a time in which counselor education programs increased attention to diversity, whereas this was not always a main tenet in training among older PSCs (who may be more represented by cisfemale PSCs in this sample [Bemak & Chung, 2008]). Presently, the Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP; 2015) requires accredited counselor education programs to deliver a counseling curriculum that includes specific attention to social and cultural diversity, an essential foundation of competent counselors. Additionally, PSC postgraduate training was weakly positively correlated with Knowledge subscale scores (r = .292, p = .002), which supports the literature that PSCs who engage in professional training opportunities outside of graduate school increase their knowledge of trans students and trans issues (Salpietro et al., 2019; Shi & Doud, 2017). Having personal experiences with trans people was moderately positively correlated with Knowledge subscale scores (r = .434, p < .001), indicating that those PSCs who personally knew a trans person felt more confident and competent in their knowledge about trans students and issues. This supports current literature (GLSEN et al., 2019; Henry & Grubbs, 2017; O’Hara et al., 2013; Salpietro et al., 2019) showing that PSCs who intentionally engaged in and fostered personal relationships with trans people reported greater competence.
Skills
Finally, we explored the relationship between PSC factors (GI, postgraduate training, PSC work with trans students, and PSC personal relationship with someone who is trans) on the Skills subscale of the GICCS in research question 4 (Model 4). In examining coefficients for the model, having worked with trans students was moderately positively correlated with Skills subscale scores (r = .545, p < .001), which may indicate that PSCs who work with trans students will be more likely to employ the necessary supports to ensure growth in “academic, career and social/emotional development” (ASCA, 2016a, para. 1). This is supported by literature in which researchers reported number of students worked with and “interpersonal contact” (personal exposure) as positive predictors of affirmative counselor competence (Bidell, 2012; Farmer et al., 2013). PSCs play an essential role in advocating for and removing barriers for trans students, which improves trans students’ well-being, academic success, and interpersonal growth. PSC postgraduate training was strongly positively correlated with Skills subscale scores (r = .845, p < .001), which may indicate that PSCs who engage in professional development opportunities and trainings gain essential skills for working with trans students. This finding is consistent with extant research that reported the importance of postgraduate training and professional development opportunities on trans topics (Bidell, 2012; Frank & Cannon, 2010; GLSEN et al., 2019; O’Hara et al., 2013). Finally, knowing someone personally who is trans was moderately positively correlated with Skills subscale scores (r = .576, p < .000), which may mean that having familiarity and exposure to trans folks increases PSC’s self-perceived skills.
Implications
Professional School Counselors
Based on the results of our study, PSCs who worked with trans students reported significantly higher scores of overall self-perceived competence compared to PSCs who had not worked with trans students. Specifically, our results indicate a link between PSCs having worked with trans students and higher scores on the Knowledge subscale. The GICCS Knowledge subscale addresses PSC knowledge of trans psychosocial issues (Bidell, 2005). This supports the idea that PSCs who work with self-identified trans students have a deeper understanding of the social and psychological challenges faced by trans people, and these experiences increase their comfort in working with trans students. All PSCs are required to protect and support the well-being of queer and trans youth and must have foundational knowledge and familiarity with trans students and issues (ASCA, 2016b). PSCs must attend professional development offerings on trans issues, and counselor education programs must provide increased time and attention to discussing trans issues, clients, and students.
PSC postgraduate training experiences are significantly linked to an overall increase in scores on the GICCS, indicating that PSC postgraduate experiences contribute to PSCs feeling more confident and competent in working with trans students. We conceptualized postgraduate training experiences as any training or education focused on trans persons or issues that a PSC received after their graduate program education. These results indicate that to increase competence and provide affirming, ethical care to trans students, PSCs should engage in some type of postgraduate training on trans issues and students, especially if they are unfamiliar with trans issues. These results are congruent with other studies, which found no significance in the relationship between groups on the Awareness subscale, but significant relationships on both the Knowledge and Skills subscales, with professional training experiences (Bidell, 2005; Rutter et al., 2008). PSCs are therefore encouraged to join professional organizations that promote best practices in working with trans students, like WPATH, the HRC, and SAIGE, as these organizations often offer professional development opportunities. It is essential that PSCs seek out trainings that are specific to trans students and issues, attend to unique psychosocial barriers, outline best practices, describe social/medical affirming care, and provide an overview of ethical and legal issues.
Of all the variables in the present study, PSCs knowing someone who identifies as trans was significantly linked to an increase in overall confidence and competence, as well as a significant increase in both Knowledge and Skills. Surprisingly, PSCs who indicated they did not know someone who identified as trans scored slightly higher on the Awareness subscale scores when compared with PSCs who did. The Awareness subscale of the GICCS examines a PSC’s self-awareness of anti-trans biases and stigmatization (Bidell, 2005). This result is contrary to existing research, which reported that engaging in personal relationships with trans folks increased affirming attitudes and mitigated negative attitudes (Henry & Grubbs, 2017; Salpietro et al., 2019). The link between a PSC personally knowing someone who is trans and a counselor’s competence in knowledge and skills supports extant literature that speaks to the importance of non–work-related experiences with trans people (e.g., personal, familial, social) and an increase in counselors’ competence in working with trans students (Whitman & Han, 2017). It is important that PSCs continue to monitor and increase their personal engagement with trans communities, as this significantly links to PSCs feeling more comfortable and more competent in working with trans students. Personal experiences may include fostering connections to trans family members, friends, and trans people through community organizations (GLSEN et al., 2019; Henry & Grubbs, 2017; Salpietro et al., 2019). Given the findings of our study, it is important for PSCs to connect to affirming resources in their communities. PSCs may consider exploring the multitude of resources offered by GLAAD (glaad.org), the National Center for Transgender Equality (NCTE; transequality.org), and PFLAG (pflag.org).
Counselor Education Programs
Our results indicate that those PSCs who engage in professional development are more competent than those who do not. Professional counseling organizations (i.e., ASCA) and accrediting bodies (i.e., CACREP) mandate that school counselors-in-training receive formal training in social and cultural diversity (F.2; CACREP, 2015), including multicultural counseling competencies (F.2.c.; CACREP, 2015), and deliver a comprehensive “counseling program that advocates for and affirms all students . . . including . . . gender, gender identity and expression” (ASCA, 2016a, para. 3). Although current standards call for the inclusion of LGBTQIA+ issues within counselor education curricula, the reality is that counselors-in-training receive minimal training in working with trans and gender-expansive students (Frank & Cannon, 2010; O’Hara et al., 2013). It is imperative that CE programs and counselor educators broaden the scope of learning about trans issues, going beyond the minimal requirements (CACREP, 2015) and providing depth and rigor in gender-related coursework in diversity courses. This research supports other emergent literature which recommends that counselor education programs offer additional, specific courses related to affectional and sexual identities (LGBQ+), and gender-expansive identities (trans, nonbinary), as covering specific issues and populations increases counselor competency (Bidell, 2012; Henry & Grubbs, 2017; O’Hara et al., 2013, Salpietro et al., 2019).
Limitations and Directions for Future Research
Limitations of the study include potential social desirability factors and inattentive responding, which may influence the quality of the data, as the study relied on self-report. Particularly, we note that the findings of higher self-awareness for PSCs who did not know someone who identified as trans could be a potential result of social desirability factors. Although the present study confirms that certain professional and personal factors contribute to PSCs increased competence in working with trans students in the present sample, additional research should be conducted. Also, much of our sample consisted of White ciswomen and, therefore, we caution readers about generalizing these findings to school counselors outside of those identities. The revised GICCS has not been used in many studies focusing on trans populations and additional research is needed to assess its validity with PSCs and trans youth (Bidell, 2005, 2012). Future researchers should consider additive studies that more deeply examine the types of professional development opportunities that promote PSC competency, including length, location, modality, themes, and expertise of presenter(s). Knowing these factors is important for crafting and delivering meaningful and competence-fostering professional development opportunities for PSCs. Also, future studies should examine unique nuances within trans groups, such as nonbinary and gender-fluid students (Toomey et al., 2018), and highlight the voices of trans students of color (Vance et al., 2021). Finally, future studies should also include demographic factors like religiosity and spirituality and their correlation to PSC GI competence, building on the work of Farmer and colleagues (2013).
Conclusion
This study highlights the need for increased attention to trans issues in many domains: among PSCs, within school counseling training programs, and in existing professional development offerings. ASCA mandates that PSCs be advocates for trans students, but there is a lack of attention to trans issues in school counseling training programs, leading PSCs to feel unprepared and to seek outside professional development offerings. The study also highlights the importance of building community and connections with trans people in and outside of professional settings, leading to increased PSC competence in professional settings. PSCs should continue to learn about the evolving language, trends, and needs of the trans community, ideally from those who are part of that community. Additionally, PSCs should engage with and use resources from professional trans-affirming organizations, such as WPATH, HRC, SAIGE, GLAAD, NCTE, and PFLAG.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
ALGBTIC LGBQQIA Competencies Taskforce. (2013). Association for Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Issues in counseling competencies for counseling with Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Queer, Questioning, Intersex, and Ally individuals. Journal of LGBT Issues in Counseling, 7(1), 2–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538605.2013.755444
American Civil Liberties Union. (2021). Legislation affecting LGBTQ rights across the country 2021.
https://www.aclu.org/legislation-affecting-lgbt-rights-across-country
American School Counselor Association. (2016a). ASCA ethical standards for school counselors. https://www.schoolcounselor.org/getmedia/f041cbd0-7004-47a5-ba01-3a5d657c6743/Ethical-Standards.pdf
American School Counselor Association. (2016b). The school counselor and transgender/gender-nonconforming youth. https://schoolcounselor.org/Standards-Positions/Position-Statements/ASCA-Position-Statements/The-School-Counselor-and-Transgender-Gender-noncon
American School Counselor Association. (2019). ASCA school counselor professional standards & competencies.
https://www.schoolcounselor.org/getmedia/a8d59c2c-51de-4ec3-a565-a3235f3b93c3/SC-Competencies.pdf
Bemak, F., & Chung, R. C.-Y. (2008). New professional roles and advocacy strategies for school counselors: A multicultural/social justice perspective to move beyond the nice counselor syndrome. Journal of Counseling & Development, 86(3), 372–381. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2008.tb00522.x
Bidell, M. P. (2005). The Sexual Orientation Counselor Competency Scale: Assessing attitudes, skills, and knowledge of counselors working with lesbian, gay, and bisexual clients. Journal of Counselor Education and Supervision, 44(4), 267–279. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2005.tb01755.x
Bidell, M. P. (2012). Examining school counseling students’ multicultural and sexual orientation competencies through a cross-specialization comparison. Journal of Counseling & Development, 90(2), 200–207.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-6676.2012.00025.x
Burgess, C. M., Batchelder, A. W., Sloan, C. A., Ieong, M., & Streed, C. G., Jr. (2021). Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on transgender and gender diverse health care. The Lancet, 9(11), 729–731.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00266-7
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed). Routledge.
Cole, E. R. (2009). Intersectionality and research in psychology. American Psychologist, 64(3), 170–180. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014564
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2015). 2016 CACREP standards. https://www.cacrep.org/for-programs/2016-cacrep-standards
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.). SAGE.
Farmer, L. B., Welfare, L. E., & Burge, P. L. (2013). Counselor competence with lesbian, gay, and bisexual clients: Differences among practice settings. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 41(4), 194–209. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-1912.2013.00036.x
Flatt, C., & Jacobs, R. L. (2019). Principle assumptions of regression analysis: Testing, techniques, and statistical reporting of imperfect data sets. Advances in Developing Human Resources, 21(4), 484–502.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1523422319869915
Frank, D. A., II, & Cannon, E. P. (2010). Queer theory as pedagogy in counselor education: A framework for diversity training. Journal of LGBT Issues in Counseling, 4(1), 18–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538600903552731
Ginicola, M. M., Smith, C., & Filmore, J. M. (2017). Affirmative counseling with LGBTQI+ people. American Counseling Association.
Gay, Lesbian, & Straight Education Network, American School Counselor Association, American Council for School Social Work, & School Social Work Association of America. (2019). Supporting safe and healthy schools for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer students: A national survey of school counselors, social workers, and psychologists. GLSEN. https://www.glsen.org/sites/default/files/2019-11/Supporting_Saf
e_and_Healthy_Schools_%20Mental_Health_Professionals_2019.pdf
Grant, J. M., Mottet, L. A., Tanis, J., Harrison, J., Herman, J. L., & Keisling, M. (2011). Injustice at every turn: A report of the National Transgender Discrimination Survey. National Center for Transgender Equality and National Gay and Lesbian Task Force. https://transequality.org/sites/default/files/docs/resources/NTDS_Report.pdf
Henry, H. L., & Grubbs, L. (2017). Best practices for school counselors working with transgender students. In G. R. Walz & J. C. Bleuer (Eds), Ideas and research you can use: VISTAS 2016. https://bit.ly/HenryTrans2017
Human Rights Campaign. (2018). 2018 LGBTQ Youth Report. https://bit.ly/HRCLGBTQReport
Israel, G. D. (2013). Determining sample size. Agricultural Education and Communication Department, UF/IFAS Extension. https://bit.ly/Israel2013SampleSize
James, S. E., Herman, J. L., Rankin, S., Keisling, M., Mottet, L., & Anafi, M. (2016). The report of the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey. National Center for Transgender Equality. https://transequality.org/sites/default/file
s/docs/usts/USTS-Full-Report-Dec17.pdf
Johnson, B. (2001). Toward a new classification of nonexperimental quantitative research. Educational Researcher, 30(2), 3–13. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X030002003
Kosciw, J. G., Clark, C. M., Truong, N. L., & Zongrone, A. D. (2020). The 2019 National School Climate Survey: The experiences of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer youth in our nation’s schools. GLSEN. https://www.glsen.org/sites/default/files/2020-10/NSCS-2019-Full-Report_0.pdf
Landén, M., & Innala, S. (2000). Attitudes toward transsexualism in a Swedish national survey. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 29(4), 375–388. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001970521182
McBee, C. (2013). Towards a more affirming perspective: Contemporary psychodynamic practice with trans* and gender non-conforming individuals. The University of Chicago School of Social Service Administration (Org.) Advocates’ Forum: The University of Chicago, 37–52. The University of Chicago. https://crownschool.uchicago.edu/contemporary-psychodynamic-trans-and-gender-non-conforming-individuals
Norton, A. T., & Herek, G. M. (2012). Heterosexuals’ attitudes toward transgender people: Findings from a national probability sample of U.S. adults. Sex Roles, 68, 738–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-011-0110-6
O’Hara, C., Dispenza, F., Brack, G., & Blood, R. A. C. (2013). The preparedness of counselors in training to work with transgender clients: A mixed methods investigation. Journal of LGBT Issues in Counseling, 7(3), 236–256. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538605.2013.812929
Reisner, S. L., White, J. M., Dunham, E. E., Heflin, K., Begenyi, J., Cahill, S., & Project VOICE Team. (2014). Discrimination and health in Massachusetts: A statewide survey of transgender and gender nonconforming adults. The Fenway Institute. http://fenwayfocus.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/The-Fenway-Institut
e-MTPC-Project-VOICE-Report-July-2014.pdf
Rutter, P. A., Estrada, D., Ferguson, L. K., & Diggs, G. A. (2008). Sexual orientation and counselor competency: The impact of training on enhancing awareness, knowledge and skills. Journal of LGBT Issues in Counseling, 2(2), 109–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538600802125472
Salpietro, L., Ausloos, C., & Clark, M. (2019). Cisgender professional counselors’ experiences with trans* clients. Journal of LGBT Issues in Counseling, 13(3), 198–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538605.2019.1627975
Savin, N. E., & White, K. J. (1977). The Durbin-Watson Test for serial correlation with extreme sample sizes or many regressors. Econometrica, 45(8), 1989–1996. https://doi.org/10.2307/1914122
Sheperis, C. J., Young, J. S., & Daniels, M. H. (2017). Counseling research: Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods (2nd ed.). Pearson.
Shi, Q., & Doud, S. (2017). An examination of school counselors’ competency working with lesbian, gay and bisexual and transgender (LGBT) Students. Journal of LGBT Issues in Counseling, 11(1), 2–17.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15538605.2017.1273165
Simmons University Library. (2019). Anti-Oppression: Anti-Transmisia. https://simmons.libguides.com/anti-opp
ression/anti-transmisia
Simons, J. D. (2021). School counselor advocacy for gender minority students. PLoS ONE, 16(3), e0248022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248022
Sue, D. W., Arredondo, P., & McDavis, R. J. (1992). Multicultural counseling competencies and standards: A call to the profession. Journal of Counseling & Development, 70(4), 477–486. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6676.1992.tb01642.x
Toomey, R. B., Syvertsen, A. K., & Shramko, M. (2018). Transgender adolescent suicide behavior. Pediatrics, 142(4), e20174218. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-4218
Transgender Law Center. (2021). National equality map. https://transgenderlawcenter.org/equalitymap
Vance, S. R., Jr., Boyer, C. B., Glidden, D. V., & Sevelius, J. (2021). Mental health and psychosocial risk and protective factors among Black and Latinx transgender youth compared with peers. JAMA Network Open, 4(3), e213256. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3256
Wang, T., Solomon, D., Durso, L. E., McBride, S., & Cahill, S. (2016). State anti-transgender bathroom bills threaten transgender people’s health and participation in public life: Policy brief. The Fenway Institute and Center for American Progress. https://fenwayhealth.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/COM-2485-Transgender-Bathroom-Bill-Brief_v8-pages.pdf
Whitman, C. N., & Han, H. (2017). Clinician competencies: Strengths and limitations for work with transgender and gender non-conforming (TGNC) clients. International Journal of Transgenderism, 18(2), 154–171. https://doi.org/10.1080/15532739.2016.1249818
Williams, A. J., Jones, C., Arcelus, J., Townsend, E., Lazaridou, A., & Michail, M. (2021). A systematic review and meta-analysis of victimisation and mental health prevalence among LGBTQ+ young people with experiences of self-harm and suicide. PLoS ONE, 16(1), e0245268.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245268
Clark D. Ausloos, PhD, NCC, LPC, LPSC, is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Denver. Madeline Clark, PhD, NCC, ACS, LPC (VA), LPCC (OH), is an associate professor at the University of Toledo. Hansori Jang, PhD, NCC, is an assistant professor at Hankuk University of Foreign Studies. Tahani Dari, PhD, NCC, LPC (MI), LPSC, is an assistant professor at the University of Toledo. Stacey Diane Arañez Litam, PhD, NCC, CCMHC, LPCC-S, is an assistant professor at Cleveland State University. Correspondence may be addressed to Clark D. Ausloos, 15578 John F. McCarthy Way, Perrysburg, OH 43551, clark.ausloos@du.edu.
Aug 20, 2021 | Volume 11 - Issue 3
Eric G. Suddeath, Eric R. Baltrinic, Heather J. Fye, Ksenia Zhbanova, Suzanne M. Dugger,
Sumedha Therthani
This study examined differences in 149 counselor education doctoral students’ self-efficacy toward teaching related to their number of experiences with fieldwork in teaching (FiT). Results showed counselor education doctoral students began FiT experiences with high levels of self-efficacy, which decreased after one to two FiT experiences, increased slightly after three to four FiT experiences, and increased significantly after five or more FiT experiences. We discuss implications for how counselor education doctoral programs can implement and supervise FiT experiences as part of their teaching preparation practices. Finally, we identify limitations of the study and offer future research suggestions for investigating FiT experiences in counselor education.
Keywords: teaching preparation, self-efficacy, fieldwork in teaching, counselor education, doctoral students
Counselor education doctoral students (CEDS) need to engage in actual teaching experiences as part of their teaching preparation (Baltrinic et al., 2016; Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Barrio Minton, 2020; Swank & Houseknecht, 2019), yet inconsistencies remain in defining what constitutes actual teaching experience. Fortunately, several researchers (e.g., Association for Counselor Education and Supervision [ACES], 2016; Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011; Suddeath et al., 2020) have identified examples of teaching experiences, which we aggregated and defined as fieldwork in teaching (FiT). FiT includes the (a) presence of experiential training components such as co-teaching, formal teaching practicums and/or internships, and teaching assistantships (ACES, 2016); (b) variance in amount of responsibility granted to CEDS (Baltrinic et al., 2016; Barrio Minton & Price, 2015; Orr et al., 2008; Suddeath et al., 2020); and (c) use of regular supervision of teaching (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Suddeath et al., 2020). Findings from several studies suggested that a lack of FiT experience can thwart CEDS’ teaching competency development (Swank & Houseknecht, 2019), contribute to CEDS’ feelings of insufficient preparation for future teaching roles (Davis et al., 2006), create unnecessary feelings of stress and burnout for first-year faculty (Magnuson et al., 2004), and lead to feelings of inadequacy among new counselor educators (Waalkes et al., 2018). Counselor education (CE) researchers reference FiT experiences (Suddeath et al., 2020) among a variety of teaching preparation practices, such as co-teaching (Baltrinic et al., 2016), supervision of teaching (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a), collaborative teaching teams (CTT; Orr et al., 2008), teaching practicums (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Hall & Hulse, 2010), teaching internships (Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011), teaching to peers within teaching instruction courses (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020b; Elliot et al., 2019), and instructor of record (IOR) experiences (Moore, 2019).
Participants across studies emphasized the importance of including FiT experiences within teaching preparation practices. Both CEDS and new faculty members reported that engaging in actual teaching (e.g., FiT) as part of their teaching preparation buffered against lower teaching self-efficacy (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Elliot et al., 2019; Suddeath et al., 2020). These findings are important because high levels of teaching self-efficacy are associated with increased student engagement (Gibson & Dembo, 1984), positive learning outcomes (Goddard et al., 2000), greater job satisfaction, reduced stress and emotional exhaustion, longevity in the profession (Klassen & Chiu, 2010; Skaalvik & Skaalvik, 2014), and flexibility and persistence during perceived setbacks in the classroom (Elliot et al., 2019; Gibson & Dembo, 1984).
FiT Within Counselor Education
Existing CE teaching literature supports the presence and use of FiT within a larger framework of teaching preparation. Despite existing findings, variability exists in how FiT is both conceptualized and implemented among doctoral programs and in how doctoral students specifically engage in FiT during their program training. Current literature supporting FiT suggests several themes, which are outlined below, to support our gap in understanding of (a) whether FiT experiences are required, (b) the number of FiT experiences in which CEDS participate, (c) the level and type of student responsibility, and (d) the supervision and mentoring practices that support student autonomy within FiT experiences (e.g., Baltrinic et al., 2016, 2018; Orr et al., 2008; Suddeath et al., 2020).
Teaching Internships and Fieldwork
Teaching internships are curricular teaching experiences in which CEDS co-teach (most often) a master’s-level course with a program faculty member or with peers while receiving regular supervision (Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011). These experiences are offered concurrently with pedagogy or adult learning courses (Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011) or after taking a course (Waalkes et al., 2018). Teaching internships typically include group supervision (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a), though the frequency and structure of supervision varies greatly (Suddeath et al., 2020). Participants in Baltrinic and Suddeath’s (2020a) study reported that teaching practicum and internship experiences are often included alongside multiple types of internships (e.g., clinical, supervision, and research), which led to less time to process their own teaching experiences. The level of responsibility within FiT experiences also varies. Specifically, CEDS may take on minor roles, including “observing faculty members’ teaching and . . . contributing anecdotes from their counseling experiences to class discussion” (Baltrinic et al., 2016, p. 38), providing the occasional lecture or facilitating a class discussion, or engaging in administrative duties such as grading and making copies of course materials (Hall & Hulse, 2010; Orr et al., 2008). Research also suggests that CEDS may share the responsibility for designing, delivering, and evaluating the course (Baltrinic et al., 2016). Finally, CEDS may take on sole/primary responsibility, including the design and delivery of all aspects of a course (Orr et al., 2008).
Co-Teaching and CTT
It is important to distinguish formal curricular FiT experiences such as teaching practicums and internships from informal co-curricular co-teaching experiences. For example, Baltrinic et al. (2016) identified co-teaching as a process of pairing experienced faculty members with CEDS for the purpose of increasing their knowledge and skill in teaching through supervised teaching experiences. CEDS often receive more individual supervision and mentoring in these informal experiences based on individual agreements between the CEDS and willing faculty members (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a). One example of a formal co-teaching experience (i.e., CTT) comes from Orr et al. (2008). In this model, CEDS initially observe a course or courses while occasionally presenting on course topics. The CEDS then take the lead for designing and delivering the course while under the direct supervision (both live in the classroom and post-instruction) of counseling faculty members.
Instructor of Record
At times, CEDS have the opportunity to teach a course as the sole instructor, what Moore (2019) and Orr et al. (2008) defined as an instructor of record (IOR). In these cases, IORs are fully responsible for the delivery and evaluation components of the course, including determining students’ final grades. CEDS may take on IOR roles after completing a progression of teaching responsibilities over time under supervision (Moore, 2019; Orr et al., 2008). In some instances, CEDS who serve as IORs are hired as adjunct or part-time instructors (Hebbani & Hendrix, 2014). Ultimately, it seems like a respectable outcome of teaching preparation in general, and specifically FiT, to prepare CEDS to transition into IOR roles. CEDS who attain the responsibility of IOR for one class are partially prepared for managing a larger teaching workload as a faculty member (i.e., teaching three classes per semester; 3:3 load).
Impact of Teaching Fieldwork
Overall, researchers identified FiT experiences as essential for strengthening CEDS’ feelings of preparedness to teach (Hall & Hulse, 2010), for fostering their teaching identities (Limberg et al., 2013; Waalkes et al., 2018), and for supporting their perceived confidence and competence to teach (Baltrinic et al., 2016; Orr et al., 2008). CE research suggests several factors that contribute to the relative success of the FiT experience. For example, Hall and Hulse (2010) found fieldwork most helpful when the experiences mimicked the actual roles and responsibilities of a counselor educator rather than guest lecturing or providing the occasional lecture. Participants in Hunt and Weber Gilmore’s (2011) study echoed this sentiment, emphasizing the importance of experiences related to the design, delivery, and evaluation of a course. Important experiences included developing or co-developing course curriculum and materials (e.g., exams, syllabi, grading rubrics), facilitating class discussions, lecturing, and evaluating student learning. Additionally, these experiences helped CEDS to translate adult learning theories and pedagogy into teaching practice, which is an essential process for strengthening CEDS’ teaching identity (Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011; Waalkes et al., 2018). CE literature also points to the importance of providing CEDS with multiple supervised, developmentally structured (Orr et al., 2008) FiT experiences to increase levels of autonomy and responsibility with teaching and related duties (Baltrinic et al., 2016; Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Orr et al., 2008). Hall and Hulse found that teaching a course from start to finish contributed most to CEDS’ perceived preparedness to teach. The CTT approach (Orr et al., 2008) is one example of how CE programs developmentally structure FiT experiences.
Research affirms the integration of supervision across CEDS’ FiT experiences (e.g., Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Elliot et al., 2019; Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011). CEDS receive the essential support, feedback, and oversight during supervision that helps them make sense of teaching experiences and identify gaps in teaching knowledge and skills (Waalkes et al., 2018). Research suggests that structured, weekly supervision is most helpful in strengthening CEDS’ perceived confidence (Suddeath et al., 2020) and competence in teaching (Orr et al., 2008). Baltrinic and Suddeath (2020a) and Elliot et al. (2019) also identified supervision of FiT as an essential experience for buffering against CEDS’ fear and anxiety associated with initial teaching experiences. Both studies found that supervision led to fewer feelings of discouragement and perceived failures related to teaching, as well as increased confidence in their capabilities, even when teaching unfamiliar material. Elliot et al. attributed this to supervisors normalizing CEDS’ teaching experiences as a part of the developmental process, which helped them to push through the initial discomfort and fear in teaching and reframe it as an opportunity for growth.
Self-Efficacy Toward Teaching
Broadly defined, self-efficacy is the future-oriented “belief in one’s capabilities to organize and execute the courses of action required to produce given attainments” (Bandura, 1997, p. 3). Applied to teaching, it is confidence in one’s ability to select and utilize appropriate teaching behaviors effectively to accomplish a specific teaching task (Tschannen-Moran et al., 1998). Research in CE has outlined the importance of teaching self-efficacy on CEDS’ teaching development, including its relationship to a strengthened sense of identity as a counselor educator (Limberg et al., 2013); increased autonomy in the classroom (Baltrinic et al., 2016); greater flexibility in the application of learning theory; increased focus on the teaching experience and students’ learning needs instead of one’s own anxiety; and pushing through feelings of fear, self-doubt, and incompetence associated with initial teaching experiences (Elliot et al., 2019). Previous research affirms FiT as a significant predictor of teaching self-efficacy (Olguin, 2004; Suddeath et al., 2020; Tollerud, 1990). Recently, Suddeath et al. (2020) found that students participating in more FiT experiences also reported higher levels of teaching self-efficacy.
Purpose of the Present Study
In general, research supports the benefits of FiT experiences (e.g., increased self-efficacy, strengthened teaching identity, and a better supported transition to the professoriate) and ways in which FiT experiences (e.g., multiple, developmentally structured, supervised) should be provided as part of CE programs’ teaching preparation practices. Past and current research supports a general trend regarding the relationship between CE teaching preparation, including FiT experiences, and teaching self-efficacy (Suddeath et al., 2020). However, we know very little about how the number of FiT experiences, specifically, differentially impacts CEDS’ teaching self-efficacy. To address this gap, we examined the relationship between the number of CEDS’ FiT experiences and their reported self-efficacy in teaching. Accordingly, we proceeded in the present study guided by the following research question: How does CEDS’ self-efficacy toward teaching differ depending on amount of FiT experience gained (i.e., no experience in teaching, one to two experiences, three to four experiences, five or more experiences)? This research question was prompted by the work of Olguin (2004) and Tollerud (1990), who investigated CEDS’ reported differences in self-efficacy toward teaching across similarly grouped teaching experiences. We wanted to better understand the impact of FiT experiences on CEDS’ teaching self-efficacy given the prevalence of teaching preparation practices used in CE doctoral programs.
Method
Participant Characteristics
A total of 171 individuals responded to the survey. Participants who did not finish the survey or did not satisfy inclusionary criteria (i.e., 18 years or older and currently enrolled in a doctoral-level CACREP-accredited CE program) were excluded from the sample, leaving 149 usable surveys. Of these 149 participants, 117 (79%) were female and 32 (21%) were male. CEDS ranged in age from 23–59 years with a mean age of 34.73. Regarding race, 116 CEDS (73%) identified as White, 25 (17%) as Black, six (4%) as Asian, one (0.7%) as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and one (0.7%) as multiracial. Fifteen participants (10%) indicated a Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Of the 149 participants, 108 provided their geographic region, with 59 (39%) reportedly living in the Southern United States, 32 (21%) in the Midwest, 10 (7%) in the West, and eight (5%) in the Northeast. Participants’ time enrolled in a CE program ranged from zero semesters (i.e., they were in their first semester) to 16 semesters (M = 6.20).
Sampling Procedures
After obtaining IRB approval, we recruited participants using two convenience sampling strategies. First, we sent counselor education and supervision doctoral program liaisons working in CACREP-accredited universities a pre-notification email (Creswell & Guetterman, 2019), which contained an explanation and rationale for this proposed study; a statement about informed consent and approval; a link to the composite survey, which included the demographic questionnaire; a question regarding FiT experiences; the Self-Efficacy Toward Teaching Inventory (SETI; Tollerud, 1990); and a request to forward the recruitment email (which was copied below the pre-notification text) to all eligible doctoral students. Next, we solicited CEDS’ participation through the Counselor Education and Supervision Network Listserv (CESNET-L), which is a professional listserv of counselors, counselor educators, and master’s- and doctoral-level CE students. We sent two follow-up participation requests, one through CESNET-L and the other to doctoral program liaisons (Creswell & Guetterman, 2019) to improve response rates. We further incentivized participation through offering participants a chance to win one of five $20 gift cards through an optional drawing.
Data Collection
We collected all research data through the survey software Qualtrics. CEDS who agreed to participate clicked the survey link at the bottom of the recruitment email, which took them to an informed consent information and agreement page. Participants meeting inclusionary criteria then completed the basic demographic questionnaire, a question regarding their FiT experiences, and the SETI.
Measures
We used a composite survey that included a demographic questionnaire, a question regarding FiT experiences, and a modified version of the SETI. To strengthen the content validity of the composite survey, we selected a panel of three nationally recognized experts known for their research on CEDS teaching preparation to provide feedback on the survey items’ “relevance, representativeness, specificity, and clarity” as well as “suggested additions, deletions, and modifications” of items (Haynes et al., 1995, pp. 244, 247). We incorporated feedback from these experts and then piloted the survey using seven recent graduates (i.e., within 4 years) from CACREP-accredited CE doctoral programs. Feedback from the pilot group influenced final modifications of the survey.
Demographic Questionnaire
The demographic questionnaire included questions regarding CEDS’ sex, age, race/ethnicity, geographic region, and time in program. Example items included: “Age in years?,” “What is your racial background?,” “Are you Hispanic or Latino?,” and “In which state do you live?”
Fieldwork Question
We used CE literature (e.g., ACES, 2016; Baltrinic et al., 2016; Orr et al., 2008) as a guide for defining and constructing the item to inquire about CEDS’ FiT experiences, which served as the independent variable in this study. In the survey, FiT was defined as teaching experiences within the context of formal teaching internships, informal co-teaching opportunities, graduate teaching assistantships, or independent teaching of graduate or undergraduate courses. Using this definition, participants then indicated “the total number of course sections they had taught or cotaught.” Following Tollerud (1990) and Olguin (2004), we also grouped participants’ FiT experiences into four groups (i.e., no experience, one to two experiences, three to four experiences, five or more experiences) to extend their findings.
Self-Efficacy Toward Teaching
To measure self-efficacy toward teaching, the dependent variable in this study, we used a modified version of the SETI. The original SETI is a 35-item self-report measure in which participants indicate their confidence to implement specific teaching skills and behaviors in five teaching domains within CE: course preparation, instructor behavior, materials, evaluation and examination, and clinical skills training. We modified the SETI according to the expert panel’s recommendations, which included creating 12 new items related to using technology in the classroom and teaching adult learners, as well as modifying the wording of several items to match CACREP 2016 teaching standards. This modified version of the SETI contained 47 items. Examples of new and modified items in each of the domains included: “Incorporate models of adult learning” (Course Preparation), “Attend to issues of social and cultural diversity” (Instructor Behavior), “Utilize technological resources to enhance learning” (Materials), “Construct multiple choice exams” (Evaluation and Examination), and “Provide supportive feedback for counseling skills” (Clinical Skills Training). The original SETI produced a Cronbach’s alpha of .94, suggesting strong internal consistency. Other researchers using the SETI reported similar findings regarding the internal consistency including Richardson and Miller (2011), who reported alphas of .96, and Prieto et al. (2007), who reported alphas of .94. The internal consistency for the modified SETI in this study produced a Cronbach’s alpha of .97, also suggesting strong internal consistency of items.
Design
This study used a cross-sectional survey design to investigate group differences in CEDS’ self-efficacy toward teaching by how many FiT experiences students had acquired (Creswell & Guetterman, 2019). Cross-sectional research allows researchers to better understand current beliefs, attitudes, or practices at a single point in time for a target population. This approach allowed us to gather information related to current FiT trends and teaching self-efficacy beliefs across CE doctoral programs.
Data Preparation and Analytic Strategy
After receiving the participant responses, we coded and entered them into SPSS (Version 27) for conducting all descriptive and inferential statistical analyses. Based upon previous research by Tollerud (1990) and Olguin (2004), we then grouped participants according to the number of experiences reported: no fieldwork experience, one to two experiences, three to four experiences, and five or more experiences. We then ran a one-way ANOVA to determine if CEDS’ self-efficacy significantly (p < .05) differed according to the number of teaching experiences accrued, followed by post hoc analyses to determine which groups differed significantly.
Results
We sought to determine whether CEDS with no experience in teaching, one to two experiences, three to four experiences, or five or more experiences differed in terms of their self-efficacy toward teaching scores. Overall, individuals in this study who reported no FiT experience indicated higher mean SETI scores (n = 10, M = 161.00, SD = 16.19) than those with one to two fieldwork experiences (n = 37, M = 145.59, SD = 21.41) and three to four fieldwork experiences (n = 32, M = 148.41, SD = 20.90). Once participants accumulated five or more fieldwork experiences (n = 70, M = 161.06, SD = 19.17), the mean SETI score rose above that of those with no, one to two, and three to four FiT experiences. The results also indicated an overall mean of 5.51 FiT experiences (SD = 4.63, range = 0–21).
As shown in Table 1, a one-way ANOVA revealed a statistically significant difference between the scores of the four FiT groups, F (3, 145) = 6.321, p < .001, and a medium large effect size (h2 = .12; Cohen, 1992). Levene’s test revealed no violation of homogeneity of variance (p = .763). A post hoc Tukey Honest Significant Difference test allowed for a more detailed understanding of which groups significantly differed. Findings revealed a statistically significant difference between the mean SETI scores for those with one to two fieldwork experiences and five or more experiences (mean difference = −15.46, p = .001) and for those with three to four and five or more experiences (mean difference = −12.65, p = .018). There was no significant difference between those with no FiT experience and those with five or more experiences, and in fact, these groups had nearly identical mean scores (i.e., 161.00 and 161.06, respectively). Although the drop is not significant, there is a mean difference of 15.40 from no FiT experience to one to two experiences. These results suggest that perceived confidence in teaching, as measured by the SETI, began high, dropped off after one to two experiences, slightly rose after three to four, and then increased significantly from 148.41 to 161.06 after five or more experiences, returning to pre-FiT levels.
Table 1
Means, Standard Deviations, and One-Way Analysis of Variance for Study Variables
| Measure |
No FiT |
1–2 FiT |
3–4 FiT |
5 or More FiT |
F (3, 145) |
h2 |
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
| SETI |
161.00 |
16.19 |
145.59 |
21.41 |
148.41 |
20.90 |
161.06 |
19.17 |
6.321* |
.12 |
Note. SETI = Self-Efficacy Toward Teaching Inventory; FiT = fieldwork in teaching.
*p < .001.
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether CEDS with no experience in teaching, one to two experiences, three to four experiences, or five or more experiences differed in terms of their self-efficacy toward teaching scores. Overall, one-way ANOVA results revealed a significant difference in SETI scores by FiT experiences. Post hoc analyses revealed an initial substantial drop from no experience to one to two experiences and a significant increase in self-efficacy toward teaching between one to two FiT experiences and five or more experiences as well as between three to four FiT experiences and five or more experiences.
The CE literature supports the general trend observed in this study, that as the number of FiT experiences increases, so does CEDS’ teaching self-efficacy (e.g., Baltrinic & Suddeath 2020a; Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011; Suddeath et al., 2020). Many authors have articulated the importance of multiple fieldwork experiences for preparing CEDS to confidently transition to the professoriate (e.g., Hall & Hulse, 2010; Orr et al., 2008). Participants in a study by Hunt and Weber Gilmore (2011) identified engagement in multiple supervised teaching opportunities that mimicked the actual teaching responsibilities required of a counselor educator as particularly helpful. Tollerud (1990) and Olguin (2004) found that the more teaching experiences individuals acquired during their doctoral programs, the higher their self-efficacy toward teaching. Encouragingly, nearly half of CEDS in this study (47%) indicated that participating in five or more teaching experiences increased their teaching self-efficacy. This increase in teaching self-efficacy may be due to expanded use of teaching preparation practices within CE doctoral programs (ACES, 2016).
Participants in the current study reported an initial drop in self-efficacy after their initial FiT experiences, which warrants explanation. Specifically, the initial drop in CEDS’ self-efficacy could be due to discrepancies between their estimation of teaching ability and their actual capability, further supporting the idea of including actual FiT earlier in teaching preparation practices, albeit titrated in complexity. Though one might assume that as participants acquired additional teaching experience their SETI scores would have increased, the initial pattern from no experience to one to two FiT experiences did not support this. However, self-efficacy is not necessarily a measure of actual capability, but rather one’s confidence to engage in certain behaviors to achieve a certain task (Bandura, 1997). It is plausible that participants may have initially overestimated their own abilities and level of control over the new complex task of teaching, which may explain the initial drop in self-efficacy among participants. For participants lacking FiT experience, social comparison may have led them to “gauge their expected and actual performance by comparison with that of others” (Stone, 1994, p. 453)—in this case, with other CEDS with more FiT experiences.
Social comparisons used to generate appraisals of teaching self-efficacy beliefs may be taken from “previous educational experiences, tradition, [or] the opinion of experienced practitioners” (Groccia & Buskist, 2011, p. 5). Thus, participants in this study who lacked prior teaching experience may have initially overestimated their capability as a result of previous educational experiences. When individuals initially overestimate their abilities to perform a new task, they may not put in the time or effort needed to succeed at a given task. Tollerud (1990) suggested that those without any actual prior teaching experience may not realize the complexity of the task, the effort required, or what skills are needed to teach effectively. In the current study, this realization may be reflected in participants’ initial drop in mean SETI scores from no teaching experiences to one to two teaching experiences.
The CE literature offers clues for how to buffer against this initial drop in self-efficacy. For example, CE teaching preparation research suggests the importance of engaging in multiple teaching experiences (Suddeath et al., 2020) with a gradual increase in responsibility (Baltrinic et al., 2016) and frequent (i.e., weekly) supervision from CE faculty supervisors, as well as feedback and support from peers (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a, 2020b; Elliot et al., 2019). These authors’ findings reportedly support students’ ability to normalize their initial anxiety, fears, and self-doubts; conceptualize their struggle and discomfort as a part of the developmental process; push through perceived failings; and reflect on and grow from initial teaching experiences. Elliot et al. (2019) noted specifically that supervision with peer support increased participants’ (a) ability to access an optimistic mindset amidst self-doubt, (b) self-efficacy in teaching, (c) authenticity in subsequent teaching experiences, and (d) facility with integrating theory into teaching practice. Overall, the current findings add to the CE literature by suggesting CE programs increase the number of FiT experiences (to at least five, preferably) for CEDS.
Our findings also reflect similarities in CEDS’ self-efficacy patterns to those of Tollerud (1990) and Olguin (2004). Similar to Tollerud and Olguin, we grouped participants according to the number of FiT experiences: no fieldwork experience, one to two experiences, three to four experiences, and five or more experiences. This study identified the same pattern in teaching self-efficacy as observed by Tollerud and Olguin, with those who reported no FiT experience indicating higher mean SETI scores than those with one to two FiT experiences and three to four FiT experiences. Although scores slightly increased from one to two FiT experiences to three to four FiT experiences, it was not until CEDS accumulated five or more FiT experiences that the mean SETI score rose above that of those with no FiT experiences. The consistency of this pattern over the span of 30 years seems to confirm the importance of providing CEDS several FiT opportunities (i.e., at least five) to strengthen their self-efficacy in teaching. Though responsibility within FiT experiences was aggregated in this study as it was in Tollerud and Olguin, research (e.g., Baltrinic et al., 2016; Orr et al., 2008) and common sense would suggest that CEDS need multiple supervised teaching opportunities with progressively greater responsibility and autonomy. However, future research is needed to examine how CEDS’ self-efficacy toward teaching changes over time as they move from having no actual teaching experience, to beginning their FiT, to accruing substantial experiences with FiT.
Implications
For many counselor educators, teaching and related responsibilities consume the greatest proportion of their time (Davis et al., 2006). As such, providing CEDS multiple supervised opportunities (Orr et al., 2008; Suddeath et al., 2020) to apply theory, knowledge, and skills in the classroom before they transition to the professoriate seems important for fostering teaching competency (Swank & Houseknecht, 2019) and, ideally, mitigating against feelings of stress and burnout that some first-year counselor educators experience as a result of poor teaching preparation (Magnuson et al., 2006). Given the initial drop in self-efficacy toward teaching as identified in this study and the relationship between higher levels of self-efficacy and increased student engagement (Gibson & Dembo, 1984) and learning outcomes (Goddard et al., 2000), greater job satisfaction, reduced stress and emotional exhaustion (Klassen & Chiu, 2010; Skaalvik & Skaalvik, 2014), and flexibility and persistence during perceived setbacks in the classroom (Elliot et al., 2019), several suggestions are offered.
Although it is an option in many CE doctoral programs, some CEDS may graduate without any significant FiT experiences (Barrio Minton & Price, 2015; Hunt & Weber Gilmore, 2011; Suddeath et al., 2020). Although not all CEDS want to go into the professoriate, for those interested in working in academia, it is our hope that programs will provide students with multiple—and preferably at least five—developmentally structured supervised teaching opportunities. Whether these are formal curricular FiT experiences such as teaching practicums and internships or informal co-curricular co-teaching or IOR experiences (and likely a combination of the two), CE literature suggests that these experiences should include frequent and ongoing supervision (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a) and progress from lesser to greater responsibility and autonomy within the teaching role (Baltrinic et al., 2016; Hall & Hulse, 2010; Orr et al., 2008). These recommendations for the structuring of FiT are important given the incredible variation in this aspect of training (e.g., Orr et al., 2008; Suddeath et al., 2020) and the consistency in the observed pattern of self-efficacy toward teaching and the number of FiT experiences (Olguin, 2004; Tollerud, 1990).
To help buffer against the initial drop in self-efficacy toward teaching scores from zero to one to two teaching experiences in this study and previous research (Olguin, 2004; Tollerud, 1990), research emphasizes the importance of increased oversight and support of CEDS before and during their first teaching experiences (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Elliot et al., 2019; Stone, 1994). CE faculty members who teach coursework in college teaching, are instructors for teaching internships, and/or are providing supervision of teaching for FiT experiences should normalize initial anxiety and self-doubt (Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a; Elliot et al., 2019) and encourage realistic expectations for students’ first teaching experiences (Stone, 1994). Stone (1994) suggested that fostering realistic expectations in those engaging in a new task may actually “increase effort, attention to strategy, and performance by increasing the perceived challenge of tasks” (p. 459). This was evident in Elliot et al.’s (2019) study in which CEDS reframed the initial struggles with teaching experiences as opportunities for growth and development. On the other hand, individuals who overestimate or strongly underestimate self-efficacy may not put in the time or effort needed to succeed at a given task. For example, those who overestimate their capabilities may not increase their effort, as they already believe they are going to perform well (Stone, 1994). Similarly, those who underestimate their ability may not increase effort or give sufficient attention to strategy, as they perceive that doing so would not improve their performance anyway. These findings support the need for CE programs to provide oversight and support and engender realistic expectations before or during students’ first FiT experiences.
Limitations and Future Research
Limitations existed related to the sample and survey. Representativeness of the sample, and thus generalizability of findings, is limited by the voluntary nature of the study (i.e., self-selection), cross-sectional design (i.e., tracking efficacy beliefs over time), and solicitation of participants via CESNET-L (i.e., potential for CEDS to miss the invitation to participate) and doctoral program liaisons (i.e., unclear how many forwarded the invitation). Another limitation relates to the variability in participants’ FiT experiences, such as the assigned role and responsibility within FiT, frequency and quality of supervision, and whether and how experiences were developmentally structured. Additionally, self-report measures were used, which are prone to issues of self-knowledge (e.g., over- or underestimation of capability with self-efficacy, accurate recall of FiT experiences) and social desirability.
Future research could utilize qualitative methods to investigate what components of FiT experiences (e.g., quality, type of responsibility) prove most helpful in strengthening CEDS’ self-efficacy and how it changes with increased experience. Given the limitations of self-efficacy, researchers could also investigate other outcomes (e.g., test scores, student evaluations) instead of or alongside self-efficacy. Although this study identified the importance of acquiring at least five FiT experiences for strengthening SETI scores, little is known about how to developmentally structure FiT experiences so as to best strengthen self-efficacy toward teaching. Researchers could use quantitative approaches to investigate the relationship between various aspects of CEDS’ FiT experiences (e.g., level of responsibility and role, frequency and quality of supervision) and SETI scores. Researchers could also develop a comprehensive model for providing FiT that includes recommendations as supported by CE research (e.g., Baltrinic et al., 2016; Baltrinic & Suddeath, 2020a, 2020b; Elliot et al., 2019; Orr et al., 2008; Suddeath et al., 2020; Swank & Houseknecht, 2019). Finally, instead of investigating FiT experiences of CEDS and their impact on teaching self-efficacy, future research could investigate first-year counselor educators to determine if and how their experience differs.
Conclusion
Investigating teaching preparation practices within CE doctoral programs is essential for understanding and improving training for future counselor educators. Although research already supports the inclusion of multiple supervised teaching experiences within CE doctoral programs (Suddeath et al., 2020), the results of this study provide greater clarity to the differential impact of FiT experiences on CEDS’ teaching self-efficacy. Given the consistently observed pattern of teaching self-efficacy and FiT experiences from this and other studies over the last 30 years, doctoral training programs should thoughtfully consider how to support students through their first FiT experiences, and ideally, offer students multiple opportunities to teach.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Association for Counselor Education and Supervision. (2016). Best practices in teaching in counselor education report. https://acesonline.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/ACES-Teaching-Initiative-Taskforce-Final-Report-2016.pdf
Baltrinic, E. R., Jencius, M., & McGlothlin, J. (2016). Coteaching in counselor education: Preparing doctoral students for future teaching. Counselor Education and Supervision, 55(1), 31–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12031
Baltrinic, E. R., Moate, R. M., Hinkle, M. G., Jencius, M., Taylor, J. Z. (2018). Counselor educators’ teaching mentorship styles: A Q methodology study. The Professional Counselor, 8(1), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.15241/erb.8.1.46
Baltrinic, E. R., & Suddeath, E. (2020a). Counselor education doctoral students’ lived experiences with supervision of teaching. Counselor Education and Supervision, 59(3), 231–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12186
Baltrinic, E. R., & Suddeath, E. G. (2020b). A Q methodology study of a doctoral counselor education teaching instruction course. The Professional Counselor, 10(4), 472–487. https://doi.org/10.15241/erb.10.4.472
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. Freeman.
Barrio Minton, C. A. (2020). Signature pedagogies: Doctoral-level teaching preparation. Teaching and Supervision in Counseling, 2(2), 39–46. https://doi.org/10.7290/tsc020205
Barrio Minton, C. A., & Price, E. (2015, October). Teaching the teacher: An analysis of teaching preparation in counselor education doctoral programs. Presentation session presented at the meeting of the Association for Counselor Education and Supervision Biannual Conference, Philadelphia, PA.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155–159. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155
Creswell, J. W., & Guetterman, T. C. (2019). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (6th ed.). Pearson.
Davis, T. E., Levitt, D. H., McGlothlin, J. M., & Hill, N. R. (2006). Perceived expectations related to promotion and tenure: A national survey of CACREP program liaisons. Counselor Education and Supervision, 46(2), 146–156. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2006.tb00019.x
Elliot, A., Salazar, B. M., Dennis, B. L., Bohecker, L., Nielson, T., LaMantia, K., & Kleist, D. M. (2019). Pedagogical perspectives on counselor education: An autoethnographic experience of doctoral student development. The Qualitative Report, 24(4), 648–666. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2019.3714
Gibson, S., & Dembo, M. H. (1984). Teacher efficacy: A construct validation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 76(4), 569–582. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.76.4.569
Goddard, R. D., Hoy, W. K., & Hoy, A. W. (2000). Collective teacher efficacy: Its meaning, measure, and impact on student achievement. American Educational Research Journal, 37(2), 479–507. https://doi.org/10.2307/1163531
Groccia, J. E., & Buskist, W. (2011). Need for evidence-based teaching. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 2011(128), 5–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.463
Hall, S. F., & Hulse, D. (2010). Perceptions of doctoral level teaching preparation in counselor education. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 1(2), 2–15. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234957931.pdf
Haynes, S. N., Richard, D. C. S., & Kubany, E. S. (1995). Content validity in psychological assessment: A functional approach to concepts and methods. Psychological Assessment, 7(3), 238–247.
https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.7.3.238
Hebbani, A., & Hendrix, K. G. (2014). Capturing the experiences of international teaching assistants in the US American classroom. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 2014(138), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.20097
Hunt, B., & Weber Gilmore, G. (2011). Learning to teach: Teaching internships in counselor education and supervision. The Professional Counselor, 1(2), 143–151. https://doi.org/10.15241/bhh.1.2.143
Klassen, R. M. & Chiu, M. M. (2010). Effects on teachers’ self-efficacy and job satisfaction: Teacher gender, years of experience, and job stress. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102(3), 741–756. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019237
Limberg, D., Bell, H., Super, J. T., Jacobson, L., Fox, J., DePue, M. K., Christmas, C., Young, M. E., & Lambie, G. W. (2013). Professional identity development of counselor education doctoral students: A qualitative investigation. The Professional Counselor, 3(1), 40–53. https://doi.org/10.15241/dll.3.1.40
Magnuson, S., Black, L. L., & Lahman, M. K. E. (2006). The 2000 cohort of new assistant professors of counselor education: Year 3. Counselor Education and Supervision, 45(3), 162–179.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2006.tb00140.x
Magnuson, S., Shaw, H., Tubin, B., & Norem, K. (2004). Assistant professors of counselor education: First and second year experiences. Journal of Professional Counseling: Practice, Theory, and Research, 32(1), 3–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/15566382.2004.12033797
Moore, A. (2019). Counselor education and supervision doctoral students’ experiences as instructors of record teaching a master’s level counseling course: A descriptive phenomenological investigation [Doctoral dissertation, Kent State University]. OhioLINK. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=kent1573225509664446
Olguin, D. L. C. (2004). Determinants of preparation through perceptions of counseling and teaching self-efficacy among prospective counselor educators [Doctoral dissertation, University of New Orleans]. ProQuest.
Orr, J. J., Hall, S. F., & Hulse-Killacky, D. (2008). A model for collaborative teaching teams in counselor education. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47(3), 146–163. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2008.tb00046.x
Prieto, L. R., Yamokoski, C. A., & Meyers, S. A. (2007). Teaching assistant training and supervision: An examination of optimal delivery modes and skill emphases. Journal of Faculty Development, 21(1), 33–43.
Richardson, R., & Miller, D. (2011). Predicting the use of learner-centered instructional methods by undergraduate social work faculty. Journal of Baccalaureate Social Work, 16(2), 115–130.
https://doi.org/10.18084/basw.16.2.v17824840x8v130l
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2014). Teacher self-efficacy and perceived autonomy: Relations with teacher engagement, job satisfaction, and emotional exhaustion. Psychological Reports, 114(1), 68–77. https://doi.org/10.2466/14.02.pr0.114k14w0
Stone, D. N. (1994). Overconfidence in initial self-efficacy judgments: Effects on decision processes and performance. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 59(3), 452–474.
https://doi.org/10.1006/obhd.1994.1069
Suddeath, E. G., Baltrinic, E., & Dugger, S. (2020). The impact of teaching preparation practices on self-efficacy toward teaching. Counselor Education and Supervision, 59(1), 59–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12166
Swank, J. M., & Houseknecht, A. (2019). Teaching competencies in counselor education: A Delphi study. Counselor Education and Supervision, 58(3), 162–176. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12148
Tollerud, T. R. (1990). The perceived self-efficacy of teaching skills of advanced doctoral students and graduates from counselor education programs [Doctoral dissertation, University of Iowa]. ProQuest.
Tschannen-Moran, M., Hoy, A. W., & Hoy, W. K. (1998). Teacher efficacy: Its meaning and measure. Review of Educational Research, 68(2), 202–248. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543068002202
Waalkes, P. L., Benshoff, J. M., Stickl, J., Swindle, P. J., & Umstead, L. K. (2018). Structure, impact, and deficiencies of beginning counselor educators’ doctoral teaching preparation. Counselor Education and Supervision, 57(1), 66–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12094
Eric G. Suddeath, PhD, LPC-S (MS), is an associate professor at Denver Seminary. Eric R. Baltrinic, PhD, LPCC-S (OH), is an assistant professor at the University of Alabama. Heather J. Fye, PhD, NCC, LPC (OH), is an assistant professor at the University of Alabama. Ksenia Zhbanova, EdD, is an assistant professor at Mississippi State University-Meridian. Suzanne M. Dugger, EdD, NCC, ACS, LPC (MI), SC (MI, FL), is a professor and department chair at Florida Gulf Coast University. Sumedha Therthani, PhD, NCC, is an assistant professor at Mississippi State University. Correspondence may be addressed to Eric G. Suddeath, 6399 South Santa Fe Drive, Littleton, CO 80120, ericsuddeath@gmail.com.
Apr 1, 2021 | Volume 11 - Issue 2
Taylor Irvine, Adriana Labarta, Kelly Emelianchik-Key
Counselor education (CE) programs are expected to provide counselors-in-training (CITs) with a diversity-infused curriculum. Throughout the CE literature, there are many available methods to accomplish this goal, yet trainees have reported a lack of self-efficacy in essential multicultural competencies before entering clinical work. Graduates of CE programs have also noted feeling unprepared when working with culturally diverse clients. The integration of culturally responsive models in CE programs is limited, and methods to decolonize current educational practices remain sparse. To address these gaps, we propose a culturally responsive and decolonizing framework grounded in the extant research that integrates relational-cultural theory (RCT) and Adlerian theory principles. The Relational-Cultural and Adlerian Multicultural Framework (RAMF) is intended to be a new pedagogical approach to enhance multicultural education across CE programs. By integrating RCT and Adlerian theory frameworks, the RAMF may offer a more comprehensive lens to view multicultural and social justice issues.
Keywords: relational-cultural theory, Adlerian theory, multicultural competencies, counselor education, decolonizing
Counselor education (CE) programs are charged with preparing counselors-in-training (CITs) to become culturally competent counselors. The Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) and the American Counseling Association (ACA) require multicultural education training to ensure that CITs develop essential multicultural competencies needed to ethically and effectively serve diverse client populations (ACA, 2014; CACREP, 2015). The 2016 CACREP Standards define multicultural as “denoting the diversity of racial, ethnic, and cultural heritage; socioeconomic status; age; gender; sexual orientation; and religious and spiritual beliefs, as well as physical, emotional, and mental abilities” (CACREP, 2015, p. 42). CE programs must equip trainees with the knowledge and skills crucial to providing culturally responsive treatment (ACA, 2014; CACREP, 2015). We begin by defining multicultural competence as it relates to the counseling profession, followed by a review of key terms that lay the groundwork for the proposed pedagogical framework.
Multicultural Competence
Many definitions of multicultural competence exist in the literature. We operationally define multicultural competence as a counselor’s awareness and knowledge of their own culture and their clients’ cultures, which allows them to tailor counseling approaches to client cultural identities and appreciate and embrace cultural differences (Ratts et al., 2016; Sue et al., 1992). C. C. Lee (2019) also outlined three self-reflective questions to promote multicultural competence: “1) Who am I as a cultural being? . . . 2) What do I know about cultural dynamics and how they may influence my client’s worldview? . . . [and] 3) How do I promote client mental health and well-being in a culturally competent manner?” (p. 10). These reflective questions are crucial to multicultural competence development, particularly given the recent increase in cultural pluralism throughout the United States (C. C. Lee, 2019). In response to the growth in diverse client populations and the call to infuse social justice into CE, the Association for Multicultural Counseling and Development has endorsed the revised Multicultural and Social Justice Counseling Competencies (MSJCC; Ratts et al., 2016) to facilitate clinical competency in this domain.
The Multicultural and Social Justice Counseling Competencies (MSJCC)
The MSJCC serve to impact, influence, and broaden the scope of multicultural training in CE programs (Ratts et al., 2016). Building from Sue et al.’s (1992) seminal tripartite model, four essential competencies comprise the MSJCC and are inherent to producing culturally competent counselors: attitudes and beliefs, knowledge, skills, and action (Ratts et al., 2016). More than ever, our current sociopolitical climate tasks counselors with the ethical responsibility of cultural sensitivity and increased diversity awareness, which is central to being multiculturally competent and fundamental to the counseling relationship itself (ACA, 2014).
The MSJCC highlight the importance of social justice and advocacy by addressing mental health disparities and empowering marginalized groups (Ratts et al., 2016). Throughout the professional literature, there is a lack of consensus on defining this construct, furthering the experience of oppression for marginalized group members (C. C. Lee, 2019). For this article, we operationally define marginalized group members as historically oppressed persons and communities in society that experience discrimination and lack access to systemic benefits that privileged groups receive because of structural power advantages; this power imbalance occurs within sociopolitical, economic, and cultural dimensions (C. C. Lee, 2019; Ratts et al., 2016). Marginalized group members include a host of group identities, including but not limited to Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC); LGBTGEQIAP+ individuals; persons with disabilities; and undocumented immigrants and refugees (C. C. Lee, 2019). Integral to the MSJCC and overall multicultural competence is an awareness of clients’ and counselors’ intersecting identities, which allows for a deeper examination of privilege, power, and oppression dynamics.
Intersecting Identities
Because culture encompasses classifications that extend beyond race and ethnicity, cultural identity can be viewed as one’s self-identification as a member of a specific group based on a connection with the group’s core beliefs and values that fit with one’s sense of self (C. C. Lee, 2019; Ratts et al., 2016; Singh et al., 2020). According to intersectionality theory, individuals who hold multiple marginalized identities may experience a greater risk of mental health concerns because of the compounding effects of various forms of discrimination and oppression (Crenshaw, 1989). Thus, CITs must understand intersecting identities (e.g., Hispanic Christian lesbian) to holistically and effectively conceptualize clients’ presenting issues and examine dynamics of identity and power within the counseling relationship (Ratts et al., 2016). Intersectionality theory also provides a framework for counselors to critically investigate Westernized counseling theories stemming from a White Eurocentric lens and move toward a decolonizing paradigm. When conducting multicultural and social justice research, Hays (2020) noted the cruciality of applying intersectionality and decolonizing practices to enhance client and training outcomes.
Decolonizing Counseling and CE
A definition of decolonization is warranted to further the discussion on dismantling oppressive systems impacting marginalized communities. In the literature, scholars have described coloniality as the dominant culture’s attempts to socialize marginalized communities into adopting Westernized ideals and values (Goodman & Gorski, 2015; Hernández-Wolfe, 2011; Singh et al., 2020). Therefore, decolonization requires critically analyzing and challenging hierarchical structures that perpetuate inequities and injustices in underrepresented groups (Hernández-Wolfe, 2011). Integration of decolonization is also crucial to informing multicultural counseling and education (Goodman & Gorski, 2015; Singh et al., 2020). Within CE programs, Singh et al. (2020) argued that social justice theories should be “taught alongside traditional counseling theories” to provide culturally responsive counseling and challenge colonizing educational practices (p. 262). Despite the persistent calls to incorporate the MSJCC and decolonizing practices into counseling and educational paradigms, scholars have continued to note deficits within multicultural education (Barden & Greene, 2015; Singh et al., 2020).
Deficits in Multicultural Education
The literature reveals gaps between the pedagogical practices, acquired skill development and theory integration, and personal awareness needed to become culturally competent and prepared to work with diverse clients (Barden & Greene, 2015; Priester et al., 2008). CITs have also indicated a lack of self-efficacy in essential multicultural competencies upon entering their practicum sequence (Flasch et al., 2011). In addition, graduates of counseling programs have reported feeling unprepared to work with culturally diverse clients (Barden et al., 2017; Bidell, 2012; Schmidt et al., 2011). This issue reflects the current deficits in multicultural education among CE programs. Many definitions of multicultural education exist in the literature. For this study, we define it as a holistic approach to critically analyzing systems of power and privilege and inequitable policies that serve to disenfranchise marginalized group members; at the same time, multicultural education centralizes matters of social justice and the decolonization of discriminatory educational practices (Gorski, 2016; Singh et al., 2020).
Across CE programs, one notable factor that influences multicultural education is educational delivery method. Swank and Houseknecht (2019) conducted a Delphi study of teaching competencies in CE, which revealed that students were twice as likely to rate a professor as effective based on their content knowledge and delivery method. Thus, educational delivery method may play a significant role in facilitating multicultural competence among CITs. As such, there is a need for more effective diversity training approaches in CE programs, with an emphasis on fostering CITs’ ability to integrate theory and therapeutic techniques to fully meet clients’ needs with diverse and deep intersectional ties (Killian & Floren, 2020).
Although studies conducted on multicultural education have increased (Chang & Rabess, 2020; Uzunboylu & Altay, 2021), there remains a paucity of available research on integrating culturally responsive models in CE programs (Pieterse et al., 2009; Shelton, 2020; Trahan & Keim, 2019). Similarly, researchers in related fields, such as teacher education, have also noted ongoing challenges pertaining to multicultural education, including minimizing or avoiding challenging conversations about race and privilege, misrepresenting the voices of marginalized group members, integrating content over equity-based practices, and underemphasizing the factors that impact the teaching practices of multicultural educators (Chouari, 2016; Gorski, 2016; Kim, 2011; McGee Banks & Banks, 1995). Relational-cultural theory (RCT) and Adlerian theory are detailed and presented as grounding for a proposed pedagogical approach to address these training limitations.
Relational-Cultural Theory (RCT)
RCT is a feminist approach rooted in Jean Baker Miller’s (1976) Toward a New Psychology of Women. In collaboration with colleagues Judith Jordan, Janet Surrey, and Irene Stiver, Miller developed RCT and challenged Westernized psychotherapy theories that portray human development as a journey from dependence to independence (Jordan, 2010). From an RCT lens, healing occurs in the context of mutually empathic, growth-fostering relationships. Rather than focusing on separation and self-sufficiency, RCT is grounded in the assertion that human beings need connection to flourish. J. B. Miller and Stiver (1997) stated that “five good things” occur when individuals engage in growth-fostering relationships: 1) a greater sense of “zest,” or vitality and energy; 2) increased self-worth; 3) a better understanding of self and others in the context of relationships; 4) elevated levels of productivity and creativity; and 5) a desire for more connection.
Conversely, isolation is perceived as a significant source of suffering (Jordan, 2018). Across the life span, relational development is highly interrelated with a person’s racial, cultural, and social identities (Pedersen et al., 2008). RCT addresses the breadth and depth that identity and power structures have within relationships and the intersectionality of culture across various contexts (Comstock et al., 2008; Schwartz, 2019). RCT also emphasizes acknowledgement of how hierarchical systems contribute to cultural oppression and social isolation for traditionally marginalized communities. Further, this theory centers contextual and relational factors that impact clients and encourages counselors to examine dynamics of privilege and oppression that perpetuate suffering and create disconnection (Jordan, 2018). Disconnection can be conceptualized as a routine part of relationships, yet when left unaddressed, the invalidated person may experience shame, withdrawal, and disempowerment. Therefore, RCT highlights the importance of attending to ruptures in relationships when they occur. By centering connection, authenticity, and mutual empowerment, humans can differentiate relational patterns and develop meaningful self and other relationships (Jordan, 2010). RCT also recognizes the ability for multiple truths within a relationship, which allows the individual’s unique experiences and perspectives to be acknowledged within the social and cultural subsystems that they are embedded within (Comstock et al., 2008; Jordan, 2018).
RCT has feminist, postmodern epistemological underpinnings that make it a suitable theoretical framework to implement in the various facets of CE. Several authors have proposed the use of RCT as a framework for pedagogy (Byers et al., 2020; K. G. Hall et al., 2014), mentorship (Lewis & Olshansky, 2016), supervision (Bradley et al., 2019), and advising students of color (Dipre & Luke, 2020). As a pedagogical model, RCT is applied in several courses, including human diversity (Byers et al., 2020), group counseling (B. S. Hall et al., 2018), and counseling theories (Lertora et al., 2020). Thus, RCT appears to be an emerging and robust framework to enhance students’ relational, multicultural, and social justice competencies.
Adlerian Theory
Individual psychology, better known as Adlerian theory, is a phenomenological framework that examines the social and contextual factors which inform a person’s reality (Bitter et al., 2009; Watts, 2013). At its core, Adlerian theorists believe in social embeddedness, or the idea that individuals are comprehensively understood within a social-relational context (R. Miller & Taylor, 2016). Additionally, this framework is rooted in the following core principles: 1) behavior is purposeful (teleological) and used to satisfy the primary need of belongingness; 2) human beings are innately creative and unique; 3) human beings are indivisible and, therefore, must be viewed holistically; 4) human beings prosper through social interest (community feeling); and 5) relational interactions are influenced by one’s lifestyle, or their cognitive worldview (Adler, 1946). Adlerian theory possesses flexible and growth-fostering tenets, making it well-suited for incorporation into a multicultural pedagogical model, such as the MSJCC.
Adlerian theory eschews fundamentally decolonizing tenets such as an either/or perspective and values a dialectical stance to view the individual and social environment as mutually interacting factors (Watts, 2003). The research literature has long documented the integration of Adlerian theoretical principles with supervision (Bornsheuer-Boswell et al., 2013), counseling (Yee et al., 2016), and school frameworks (Pryor & Tollerud, 1999). Adlerian theory has also demonstrated applications as a creative pedagogical framework for enhancing case conceptualization competency among CITs (Davis et al., 2019) and promoting student satisfaction with the learning environment and student–teacher relationships (Soheili et al., 2015).
In a clinical setting, Adlerian counselors conceptualize clients from a social-contextual perspective to gain a deeper understanding of how they perceive events. One of an Adlerian counselor’s roles is to assist the client with examining maladaptive lifestyle convictions while also encouraging engagement in cooperative and social interactions to inhibit disconnection, considered to be the root of suffering (Watts, 2013). Neuroscience findings have supported this focus on social interest as critical to improving relationships and enhancing overall mental health (R. Miller & Taylor, 2016). In addition, its social-relational orientation makes it well-suited for increasing multicultural competence among counselors. Specifically, this framework supports client examination of multicultural issues through a lens of community feeling, in which establishing equality is central to addressing challenges (Bitter et al., 2009). Key tenets and values of Adlerian theory align with pro-feminist and decolonizing values, making it inclusive of marginalized group members (Watts, 2013) through its support of social interest, equality and advocacy, egalitarian relationships, empowerment and individual choice, and a social-cultural view of issues (Bitter et al., 2009; Davis et al., 2019; Soheili et al., 2015).
The Relational-Cultural and Adlerian Multicultural Framework (RAMF)
We aim to bridge research and training gaps in multicultural education by integrating RCT with Adlerian theory. The core tenets of these two frameworks undergird the Relational-Cultural and Adlerian Multicultural Framework (RAMF), a pedagogical approach to enhance multicultural competence among CITs. In order to develop multicultural and social justice competence, trainees must first learn and understand the subtle complexities of theory before they can use and integrate it into their clinical practice. We believe that the RAMF can bolster current multicultural education practices by promoting the development of clinical competence in this domain while also modeling theoretical integration for CITs.
A Cross-Paradigm Framework for Pedagogy
In the realm of counseling, an individual conceptualization has long dominated as the primary means to conceptualize clients’ issues. In this regard, Singh et al. (2020) highlighted the need to critically examine and move beyond Westernized counseling theories:
Although traditional counseling theories certainly may be utilized in culturally competent ways, they are often situated in a paradigm that focuses on the individual when the source of difficulties may be rooted in oppressive structures within the environment that require direct advocacy. (p. 261)
The integrative nature of the RAMF may lend to improved multicultural and social justice competency among CITs and clinicians. This framework can be conceptualized as a cross-paradigm pedagogical approach, rooted in psychological and postmodern/social-constructivist paradigms, which blend techniques and tenets from both theories (Cottone, 2012). Despite RCT and Adlerian theory originating from different theoretical paradigms, these theories are complementary and have overlapping social and relational constructs. Specifically, Adlerian theory originated from the psychological paradigm of counseling and psychotherapy, as it centralizes an individual conceptualization of clients’ issues (Cottone, 2012). However, Watts (2003) noted that this theory’s unique encapsulation of cognitive constructivist and social constructionist elements make it better classified as a relational constructivist paradigm (i.e., emphasizing individual agency within a social-relational context). On the other hand, RCT is rooted in a postmodern philosophy, best categorizing this theory as belonging to the social-constructivist paradigm (Cottone, 2012), given its emphasis on the role that social-contextual factors (i.e., hierarchical systems) play in perpetuating oppression, inequity, and suffering. Moreover, Singh et al. (2020) recently recognized RCT as a social justice theory that can help counselors decolonize counseling and integrate the MSJCC in their work with clients.
The RAMF is intended to be a new decolonizing pedagogical approach to multicultural education that fosters an equitable learning environment and overall inclusive program culture. The RAMF is a unique approach that integrates the counseling profession’s core values, such as social justice, cultural competence, advocacy, and wellness (ACA, 2014). In contrast, many other theories, such as critical pedagogy, stem from educational fields and have different core values central to their professions. Combining RCT and Adlerian theory frameworks may provide a more holistic lens to view multicultural and social justice issues. Within the classroom, the RAMF centralizes growth-fostering relationships between students and professors. This outcome requires that professors be mindful of their positionality, minimize the power differential inherent in the professor–student relationship, and create mutually empowering relationships within the classroom (Walker, 2015). The RAMF also promotes practicing intentionality, incorporating experiential training strategies, and routine processing of CITs’ reactions to further develop multicultural competence. Ultimately, the RAMF seeks to address bias and inequity by promoting self-awareness, authenticity, personal responsibility, mutual empowerment, acceptance of differing worldviews, and a non-judgmental and curious attitude. Because the RAMF aims to cultivate a culture of mutual empowerment and social interest, diverse students may feel more supported and valued. In this next section, we will outline components comprising the RAMF, offer an integrative description to apply the RAMF effectively, and discuss implications for future research.
RAMF Components
The following three components found in Figure 1 are proposed as foundational to the RAMF and stem from RCT’s and Adlerian theory’s tenets: an equitable learning environment, awareness of individual and relational dynamics, and active engagement. These components and supporting research are examined in depth below.
Figure 1
RAMF Components
Equitable Learning Environment
Successful implementation of the RAMF requires an equitable learning environment to effectively assist diverse students while also fostering multicultural and social justice competence (see Figure 2). Gorski and Swalwell (2015) purported that multicultural education is grounded in social justice and equity values. Failure to ensure both equity and equality in the classroom poses detrimental implications to student professional growth and overall well-being. For instance, in a qualitative study conducted by Baker et al. (2015), marginalized doctoral students in a CE program expressed feeling excluded from class information and discussions; they also shared concerns about being misjudged because of their racial identities. These findings are consistent with previous research on the experiences of marginalized master’s-level CITs across CE programs (Henfield et al., 2013; Seward, 2014).
Figure 2
RAMF Integration Application
| RCT |
Adlerian Theory |
RAMF
Component |
Integrative Application Examples |
| Growth-fostering relationships |
Social interest |
Equitable learning environment |
Creating a safe space for all students to contribute in a way that empowers them; open discussions/exposure to diverse worldviews |
| Mutual empathy and empowerment |
Social equality and advocacy |
Active engagement |
Creating a classroom environment that mutually benefits both students and professor; collaborating on
journal article |
| Exploration of power differentials |
Egalitarian relationships |
Equitable learning environment |
Offering an outlet for students to provide anonymous feedback |
| Authenticity in relationships |
Empowerment and individual choice |
Individual and relational dynamics |
Giving yourself permission to be human; cultural humility |
| Consideration of contextual and relational factors |
Being curious about diverse perspectives; social-cultural view of issues |
Individual and relational dynamics |
Awareness of self and other cultural identity membership; role-plays, reflective journaling, classroom dialogue, etc. |
Using the RAMF, an equitable learning environment is cultivated through embracing classroom norms driven by Adlerian and RCT values. Examples include embracing a genuinely curious attitude, accepting differing worldviews, exhibiting compassion for self and others while navigating conflicts, and modeling authenticity during moments of disconnection (i.e., cultural humility). Additionally, fostering this classroom atmosphere is contingent upon incorporating decolonizing educational practices. CE programs can accomplish this task through the intentional examination of course curricula. Specific examples include things like being mindful of the language used in course content and infusing textbooks, assignments, and supplementary materials in the syllabi to address inequitable practices and discrimination against marginalized group members (e.g., current news reports, community service-learning experiences within marginalized communities, guest speakers). Thus, the RAMF encourages counselor educators to practice intentionality by diversifying curriculum and incorporating diverse scholars’ perspectives to dismantle colonized counseling and pedagogical practices.
The RAMF also stresses the importance of acknowledging the significant impact of professor interactions in fostering an equitable learning environment. Research findings have noted several factors that strengthen trainees’ experience of their learning environments, such as an emphasis on teaching and mentorship, peer support, and faculty–student connections (Henfield et al., 2013; Sheperis et al., 2020). In this regard, enhancing relational factors among professors may alleviate the power differential between professors and CITs, thereby facilitating a more equitable learning environment. Additionally, student feedback and perceptions of the teaching environment should constantly be solicited in any learning environment that aspires to be inclusive and equitable. Hopefully, if a safe and collaborative learning environment is achieved, this feedback will be provided authentically and without direct solicitation. Anonymous feedback can also be gathered in various formal and informal approaches, such as the use of specific assessments or scaling and qualitative inquiry.
Gorski (2016) noted the importance of systemic change as crucial to analyzing power and privilege in the classroom; thus, faculty support is necessary to effectively carry out this systemic endeavor. As such, it is recommended that CE programs assess their organizational climate before implementing the RAMF. A discriminatory CE program climate serves to uphold colonizing and inequitable learning practices, thereby interfering with the development of multicultural and social justice competencies. The RAMF seeks to dismantle this issue by valuing diversity and modeling equity in the classroom, directly influencing CITs’ perspectives and overall multicultural competence growth. Sanchez Bengoa et al. (2018) found that students developed multicultural competency skills faster in international teams than national teams; this finding speaks to the critical need to foster a culturally rich classroom environment where students can be exposed to diverse worldviews and engage in a cooperative learning process.
Awareness of Individual and Relational Dynamics
As a cross-paradigm approach, the RAMF acknowledges the importance of individual and relational dynamics that impact the overall learning process and program experience. Within counseling programs, CITs are encouraged to engage in ongoing self-reflection, which is essential in multicultural education. According to the MSJCC framework (Ratts et al., 2016), self-awareness is at the core of multicultural and social justice competence. Counselors must critically examine their personally held attitudes, beliefs, and biases that affect their work with diverse clients. This awareness may then contribute to counselors’ understanding of power, privilege, and oppression dynamics that impact the therapeutic relationship (Ratts et al., 2016). The RAMF takes a unique perspective on trainee self-awareness by drawing on core counseling values, such as examining the individual’s role and identity in the context of relationships. From a RAMF lens, professors can facilitate this process with CITs by modeling authentic interactions (e.g., cultural humility), which may promote personal exploration and shared disclosures in a classroom setting. In Morgan Consoli and Marin’s (2016) qualitative study on graduate students’ experiences in diversity courses, students noted the essentiality of instructor self-disclosure and viewed it as indispensable to a positive diversity course experience. Thus, valuing authenticity and cultural humility may instill the importance of multicultural competence as a lifelong process (Hook et al., 2013).
Although an individual commitment to learning and self-awareness is at the core of multicultural competence, counselors must move beyond self-reflection to foster empowering therapeutic relationships. In a descriptive content analysis of multicultural course syllabi, Pieterse et al. (2009) found that a large percentage of course syllabi focused on developing knowledge, awareness, and skills; yet, knowledge and awareness were emphasized more often, while relational skill development was not. The RAMF emphasizes relational skill development by actively addressing ruptures that may occur between professors and CITs. Although the RAMF conceptualizes conflict as a standard component of relationships, ruptures must be addressed and repaired, especially attending to feelings of disempowerment (Jordan, 2010). To address this concern, the RAMF encourages professors to model broaching, which is defined as an ongoing commitment and openness to exploring diversity and cultural issues with clients and students (Day-Vines et al., 2018). Because research has shown that broaching early on in counseling can reduce attrition and strengthen therapeutic relationships with racial and ethnic minority clients (Jones et al., 2019), CITs must have the opportunity to practice broaching within the classroom setting. Central to this practice is creating a safe space, whereby professors actively encourage students to practice vulnerability and cultural humility by leaning into challenging conversations and providing feedback to enhance both self and relational awareness.
Active Engagement
The RAMF posits that active engagement is necessary to multicultural education and effective diversity training of CITs. Ikonomopoulos et al. (2016) conducted a study that demonstrated that practicum-level CITs developed their self-efficacy by actively engaging in direct client contact and peer-group interactions. We define active engagement as the process of encouraging students to learn in a deeper context, engage in activities, and reflect upon the material in a meaningful way. Depending on the course, there is no one “correct” way to attain or measure active engagement, yet active engagement should be seen in student questions, writings, and participation. Fundamental to Adlerian theory and RCT is the belief that individuals and groups are best understood in their relationships. Using the RAMF, CITs are required to actively engage in cultural immersion experiences and service-learning projects to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences and unique challenges of marginalized group members.
Research has demonstrated the utility of service-learning experiences for CITs to develop clinical competencies (Dari et al., 2019), enhance a sense of preparedness to apply learned clinical skills (Havlik et al., 2016), deepen their understanding of human development from a social justice perspective (K. A. Lee & Kelley-Petersen, 2018), and promote social justice advocacy competency and cognitive development (K. A. Lee & McAdams, 2019). Following these experiences, scholars have noted that open dialogue about cultural and diversity matters is needed to bolster CITs’ clinical knowledge and attitudes (Celinska & Swazo, 2016; Wagner, 2015). For instance, in a study conducted by Villalba and Redmond (2008), an experiential learning exercise was incorporated in which students were exposed to a film to help facilitate multicultural competence through self-reflection. This study’s findings revealed the essentiality of open discussion on relevant social justice issues to process the experience fully. Further, Ratts et al. (2016) indicated that counselors who embody multicultural and social justice competence demonstrate cross-cultural communication skills. In using the RAMF, we emphasize classroom dialogue, such as open processing and role-plays, as a crucial part of developing these competencies in CITs. Counseling programs are tasked with preparing CITs to be future leaders and allies within the profession. This endeavor requires the exposure of CITs within culturally diverse groups by actively engaging with the community at large. In doing so, CITs stand a greater chance of developing essential multicultural and social justice competencies needed to effectively treat and conceptualize diverse client populations. The MSJCC endorses the implementation of counseling and advocacy interventions crucial to holistic diversity training; specifically, CITs must actively engage beyond intrapersonal self-reflection by considering relational, community, societal, and global interventions (Ratts et al., 2016).
Inherent to the RAMF is its focus on active engagement in social justice and advocacy initiatives to facilitate multicultural competence. Some strategies include engaging trainees in open conversations about current sociopolitical challenges and the subsequent impact on marginalized group members, promoting attendance and engagement in presentations at professional conferences, and collaborating on professional journal articles related to multicultural competence. Ultimately, the RAMF is intended to be the vehicle that translates applied multicultural knowledge and skills into active engagement. The fundamental links between RCT and Adlerian theory are social equality and relational connections. These factors are crucial not only to the active engagement component of the RAMF but also to the framework as a whole. An integrative application outlining strategy relevant to the RAMF components is illustrated in Figure 2.
Considerations and Implications for Using the RAMF in Pedagogy
The RAMF poses several implications in the realm of CE, namely enhanced clinical competency and self-efficacy with multicultural concepts. This is particularly important as graduates of counseling programs have often indicated feeling unprepared to work with culturally diverse clients (Barden et al., 2017; Bidell, 2012; Schmidt et al., 2011). They have also reported a lack of self-efficacy in key multicultural competencies when first engaging in counseling work (Flasch et al., 2011). This competency deficit among trainees may be attributed to the historical overcrowding of multicultural competencies and skills into a single-course format, which is insufficient considering multiculturalism’s depth and scope (Celinska & Swazo, 2016). The RAMF’s multimodal approach to infusing multicultural and social justice competencies across the curriculum may help bridge this gap.
Given the rise in diverse client demographics and cultural pluralism (C. C. Lee, 2019), it has become the professional responsibility of all counselors to develop essential multicultural competencies needed to provide culturally competent counseling (ACA, 2014). This need is addressed through the RAMF, which serves as an integrative vehicle to effectively transmit this knowledge to CITs. CE programs are tasked with engaging in culturally responsive gatekeeping practices to maintain professional standards, namely protecting clients from culturally incompetent trainees. Counselor educators have noted the critical importance of seeing trainees’ multicultural competence development beyond the classroom and throughout the program within their gatekeeping role (Ziomek-Daigle et al., 2016).
Directions for Future Research
The RAMF may be used to bridge the gap in multicultural competency and self-efficacy among CITs in CE programs. Currently, there is no evidence regarding the efficacy of this integrative framework as a pedagogical model. Therefore, directions for future research may include a quantitative study measuring the RAMF’s effectiveness using a pretest-posttest design. For example, pre-post of the RAMF in a course may illustrate its overall effectiveness from the beginning to the end of the semester. The RAMF can be incorporated in CITs’ practicum and internship courses, after which a posttest can be administered to measure confidence and competence upon graduating. This method will serve to address the current deficit in CITs’ multicultural competence following graduation. Future research may also include developing an instrument that measures the constructs illustrated in the RAMF. Hays (2020) noted the importance of moving beyond traditional counseling research and integrating decolonizing methodologies, such as qualitative designs, that allow for triangulation with CITs and program faculty. Thus, we suggest collecting qualitative data to learn about the individual lived experiences of CITs following their course.
Further research on implementing the RAMF into CE programs is also needed to validate its evidence base. Regarding the evaluation of multicultural competence utilizing the RAMF, we recommend that CITs take Holcomb-McCoy and Myers’ (1999) Multicultural Counseling Competence and Training Survey-Revised (MCCTS-R), which will provide insight into CITs’ perceived level of multicultural competence. This 32-item measure is grounded in the MSJCC (Barden et al., 2017) and assesses competency in three domains—multicultural knowledge, multicultural awareness, and multicultural terminology—using self-report, Likert-type questions ranging from 1 (not competent) to 4 (extremely competent; Holcomb-McCoy & Myers, 1999). To evaluate the effectiveness of the RAMF and facilitate formative feedback, we recommend administering the MCCTS-R to all CITs at the beginning and end of a course. The successful implementation of the RAMF is evidenced by CITs’ growth in the following MSJCC domains: attitudes and beliefs, knowledge, skills, and action (Ratts et al., 2016). These domains must be routinely evaluated as part of an ongoing CE program evaluation to enhance multicultural and social justice competency among CITs (Hays, 2020).
Conclusion
CE programs may use the RAMF to address challenges to CITs’ self-efficacy and ability in treating culturally diverse clients, thereby potentially reducing gatekeeping concerns that stem from lack of multicultural competence. Overall, implementation of the RAMF could pose several benefits to CE programs. A limitation of this framework includes possible compassion fatigue because of its emphasis on authentic interactions and contact with difficult conversations (e.g., power and oppression, unique challenges faced by marginalized group members). However, the RAMF’s integrative approach to addressing multicultural and social justice competence throughout the curriculum may allow for CITs to develop knowledge and skills proactively rather than retroactively engaging in future remediation strategies.
Conflict of Interest and Funding Disclosure
The authors reported no conflict of interest
or funding contributions for the development
of this manuscript.
References
Adler, A. (1946). Understanding human nature. Permabooks.
American Counseling Association. (2014). ACA code of ethics.
Baker, C. A., Gaulke, K., & Smith, K. (2015). Counselor education cultural climate: Underrepresented master’s students’ experiences. Journal for Multicultural Education, 9(2), 85–97.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JME-07-2014-0032
Barden, S. M., & Greene, J. H. (2015). An investigation of multicultural counseling competence and multicultural counseling self-efficacy for counselors-in-training. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling, 37(1), 41–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-014-9224-1
Barden, S. M., Sherrell, R. S., & Matthews, J. J. (2017). A national survey on multicultural competence for professional counselors: A replication study. Journal of Counseling & Development, 95(2), 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12132
Bidell, M. P. (2012). Examining school counseling students’ multicultural and sexual orientation competencies through a cross-specialization comparison. Journal of Counseling & Development, 90(2), 200–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-6676.2012.00025.x
Bitter, J. R., Robertson, P. E., Healey, A. C., & Cole, L. K. J. (2009). Reclaiming a pro-feminist orientation in Adlerian therapy. Journal of Individual Psychology, 65(1), 13–33.
Bornsheuer-Boswell, J. N., Polonyi, M. M., & Watts, R. E. (2013). Integrating Adlerian and integrated developmental model approaches to supervision of counseling trainees. The Journal of Individual Psychology, 69(4), 328–343.
Bradley, N., Stargell, N., Craigen, L., Whisenhunt, J., Campbell, E., & Kress, V. (2019). Creative approaches for promoting vulnerability in supervision: A relational-cultural approach. Journal of Creativity in Mental Health, 14(3), 391–404. https://doi.org/10.1080/15401383.2018.1562395
Byers, L. G., Bragg, J., & Munoz, R. (2020). Increasing diversity and oppression scale scores through Relational Cultural Theory. Journal of Teaching in Social Work, 40(1), 18–30.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08841233.2019.1685625
Celinska, D., & Swazo, R. (2016). Multicultural curriculum designs in counselor education programs: Enhancing counselors-in-training openness to diversity. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 8(3). https://doi.org/10.7729/83.1124
Chang, C. Y., & Rabess, A. (2020). Response to signature pedagogies: A framework for pedagogical foundations in counselor education: Through a multicultural and social justice competencies lens. Teaching and Supervision in Counseling, 2(2), 3. https://doi.org/10.7290/tsc020203
Chouari, A. (2016). Cultural diversity and the challenges of teaching multicultural classes in the twenty-first century. Arab World English Journal, 7(3), 3–17. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2859237
Comstock, D. L., Hammer, T. R., Strentzsch, J., Cannon, K., Parsons, J., & Salazar, G., II. (2008). Relational-cultural theory: A framework for bridging relational, multicultural, and social justice competencies. Journal of Counseling & Development, 86(3), 279–287. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2008.tb00510.x
Cottone, R. R. (2012). Paradigms of counseling and psychotherapy. Smashwords.
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs. (2015). 2016 CACREP standards. http://www.cacrep.org/forprograms/2016-cacrep-standards
Crenshaw, K. (1989). Demarginalizing the intersection of race and sex: A Black feminist critique of antidiscrimination doctrine, feminist theory and anti-racist politics. University of Chicago Legal Forum, 1989(1), 139–167.
Dari, T., Laux, J. M., Liu, Y., & Reynolds, J. (2019). Development of community-based participatory research competencies: A Delphi study identifying best practices in the collaborative process. The Professional Counselor, 9(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.15241/td.9.1.1
Davis, E. S., Norton, A., & Chapman, R. (2019). Using music for case conceptualization: Looking through an Adlerian lens. The Journal of Individual Psychology, 75(2), 156–170. https://doi.org/10.1353/jip.2019.0013
Day-Vines, N. L., Booker Ammah, B., Steen, S., & Arnold, K. M. (2018). Getting comfortable with discomfort: Preparing counselor trainees to broach racial, ethnic, and cultural factors with clients during counseling. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling, 40(2), 89–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10447-017-9308-9
Dipre, K. A., & Luke, M. (2020). Relational cultural theory–informed advising in counselor education. The Professional Counselor, 10(4), 517–531. https://doi.org/10.15241/kad.10.4.517
Flasch, P., Bloom, Z. D., & Holladay, K. (2011). Self-efficacy of counselor trainees in pre-practicum: A phenomenological study. Journal of Counselor Practice, 7(1), 1–20. https://www.journalofcounselorpractice.com/uploads/6/8/9/4/68949193/flasch_et_al_vol7_iss1.pdf
Goodman, R. D., & Gorski, P. C. (Eds.). (2015). Decolonizing “multicultural” counseling through social justice. Springer.
Gorski, P. C. (2016). Making better multicultural and social justice teacher educators: A qualitative analysis of the professional learning and support needs of multicultural teacher education faculty. Multicultural Education Review, 8(3), 139–159. https://doi.org/10.1080/2005615X.2016.1164378
Gorski, P. C., & Swalwell, K. (2015). Equity literacy for all. Educational Leadership, 72(6), 34–40. http://edchange.org/publications/Equity-Literacy-for-All.pdf
Hall, B. S., Harper, I., & Korcuska, J. (2018). Exploring a relational cultural group trainee model for master’s level counseling students. Journal for Specialists in Group Work, 43(1), 81–104.
https://doi.org/10.1080/01933922.2017.1411410
Hall, K. G., Barden, S., & Conley, A. (2014). A relational-cultural framework: Emphasizing relational dynamics and multicultural skill development. The Professional Counselor, 4(1), 71–83. https://doi.org/10.15241/kgh.4.1.71
Havlik, S. A., Bialka, C., & Schneider, K. (2016). Theory to practice: Integrating service-learning into a pre-practicum introduction to school counseling course. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.7729/82.1168
Hays, D. G. (2020). Multicultural and social justice counseling competency research: Opportunities for innovation. Journal of Counseling & Development, 98(3), 331–344. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12327
Henfield, M. S., Woo, H., & Washington, A. (2013). A phenomenological investigation of African American counselor education students’ challenging experiences. Counselor Education and Supervision, 52(2), 122–136. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2013.00033.x
Hernández-Wolfe, P. (2011). Decolonization and “mental” health: A mestiza’s journey in the borderlands. Women & Therapy, 34(3), 293–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/02703149.2011.580687
Holcomb-McCoy, C. C., & Myers, J. E. (1999). Multicultural competence and counselor training: A national survey. Journal of Counseling & Development, 77(3), 294–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6676.1999.tb02452.x
Hook, J. N., Davis, D. E., Owen, J., Worthington, E. L., Jr., & Utsey, S. O. (2013). Cultural humility: Measuring openness to culturally diverse clients. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 60(3), 353–366. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032595
Ikonomopoulos, J., Cavazos Vela, J., Smith, W. D., & Dell’Aquila, J. (2016). Examining the practicum experience to increase counseling students’ self-efficacy. The Professional Counselor, 6(2), 161–173. https://doi.org/10.15241/ji.6.2.161
Jones, C. T., Welfare, L. E., Melchior, S., & Cash, R. M. (2019). Broaching as a strategy for intercultural understanding in clinical supervision. The Clinical Supervisor, 38(1), 1–16.
https://doi.org/10.1080/07325223.2018.1560384
Jordan, J. V. (2010). Relational-cultural therapy (1st ed.). American Psychological Association.
Jordan, J. V. (2018). Relational-cultural therapy (2nd ed.). American Psychological Association.
Killian, T., & Floren, M. (2020). Exploring the relationship between pedagogy and counselor trainees’ multicultural and social justice competence. Journal of Counseling & Development, 98(3), 295–307. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12324
Kim, B. S. K. (2011). Client motivation and multicultural counseling. The Counseling Psychologist, 39(2), 267–275. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011000010375310
Lee, C. C. (2019). Multicultural issues in counseling: New approaches to diversity (5th ed.). American Counseling Association.
Lee, K. A., & Kelley-Petersen, D. J. (2018). Service learning in human development: Promoting social justice perspectives in counseling. The Professional Counselor, 8(2), 146–158. https://doi.org/10.15241/kal.8.2.146
Lee, K. A., & McAdams, C. R., III. (2019). Using service-learning to promote social justice advocacy and cognitive development during internship. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 12(1). https://repository.wcsu.edu/jcps/vol12/iss1/8
Lertora, I. M., Croffie, A., Dorn-Medeiros, C., & Christensen, J. (2020). Using relational cultural theory as a pedagogical approach for counselor education. Journal of Creativity in Mental Health, 15(2), 265–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/15401383.2019.1687059
Lewis, C., & Olshansky, E. (2016). Relational-cultural theory as a framework for mentoring in academia: Toward diversity and growth-fostering collaborative scholarly relationships. Mentoring & Tutoring: Partnership in Learning, 24(5), 383–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/13611267.2016.1275390
McGee Banks, C. A., & Banks, J. A. (1995). Equity pedagogy: An essential component of multicultural education. Theory Into Practice, 34(3), 152–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405849509543674
Miller, J. B. (1976). Toward a new psychology of women. Beacon Press.
Miller, J. B., & Stiver, I. P. (1997). The healing connection: How women form relationships in therapy and in life. Beacon Press.
Miller, R., & Taylor, D. D. (2016). Does Adlerian theory stand the test of time?: Examining individual psychology from a neuroscience perspective. The Journal of Humanistic Counseling, 55(2), 111–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/johc.12028
Morgan Consoli, M. L., & Marin, P. (2016). Teaching diversity in the graduate classroom: The instructor, the students, the classroom, or all of the above? Journal of Diversity in Higher Education, 9(2), 143–157. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039716
Pedersen, P. B., Crethar, H. C., & Carlson, J. (2008). Inclusive cultural empathy: Making relationships central in counseling and psychotherapy. American Psychological Association.
Pieterse, A. L., Evans, S. A., Risner-Butner, A., Collins, N. M., & Mason, L. B. (2009). Multicultural competence and social justice training in counseling psychology and counselor education: A review and analysis of a sample of multicultural course syllabi. Counseling Psychologist, 37(1), 93–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011000008319986
Priester, P. E., Jones, J. E., Jackson-Bailey, C. M., Jana-Masri, A., Jordan, E. X., & Metz, A. J. (2008). An analysis of content and instructional strategies in multicultural counseling courses. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 36(1), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-1912.2008.tb00067.x
Pryor, D. B., & Tollerud, T. R. (1999). Applications of Adlerian principles in school settings. Professional School Counseling, 2(4), 299–304.
Ratts, M. J., Singh, A. A., Nassar-McMillan, S., Butler, S. K., & McCullough, J. R. (2016). Multicultural and Social Justice Counseling Competencies: Guidelines for the counseling profession. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 44(1), 28–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmcd.12035
Sanchez Bengoa, D., Ganassali, S., Kaufmann, H. R., Rajala, A., Trevisan, I., van Berkel, J., Zulauf, K., & Wagner, R. (2018). Shared experiences and awareness from learning in a student multicultural environment: Measuring skills’ development in intercultural intensive programs. Journal of International Education in Business, 11(1), 27–42.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JIEB-01-2017-0006
Schmidt, S. W., Glass, J. S., & Wooten, P. (2011). School counselor preparedness: Examining cultural competence regarding gay, lesbian, and bisexual issues. Journal of School Counseling, 9(11). https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ933177.pdf
Schwartz, H. L. (2019). Connected teaching: Relationship, power, and mattering in higher education. Stylus.
Seward, D. X. (2014). Multicultural course pedagogy: Experiences of master’s-level students of color. Counselor Education and Supervision, 53(1), 62–79.
https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2014.00049.x
Shelton, R. (2020). A qualitative study on understanding entry-level professional counselors experience developing and implementing multicultural and social justice advocacy competencies in professional practice (Publication No. 28259670) [Doctoral dissertation, Capella University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
Sheperis, D. S., Coker, J. K., Haag, E., & Salem-Pease, F. (2020). Online counselor education: A student–faculty collaboration. The Professional Counselor, 10(1), 133–143. https://doi.org/10.15241/dss.10.1.133
Singh, A. A., Appling, B., & Trepal, H. (2020). Using the Multicultural and Social Justice Counseling Competencies to decolonize counseling practice: The important roles of theory, power, and action. Journal of Counseling & Development, 98(3), 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12321
Soheili, F., Alizadeh, H., Murphy, J. M., Bajestani, H. S., & Ferguson, E. D. (2015). Teachers as leaders: The impact of Adler-Dreikurs classroom management techniques on students’ perceptions of the classroom environment and on academic achievement. The Journal of Individual Psychology, 71(4), 440–461. https://doi.org/10.1353/jip.2015.0037
Sue, D. W., Arredondo, P., & McDavis, R. J. (1992). Multicultural counseling competencies and standards: A call to the profession. Journal of Multicultural Counseling and Development, 20(2), 64–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-1912.1992.tb00563.x
Swank, J. M., & Houseknecht, A. (2019). Teaching competencies in counselor education: A Delphi study. Counselor Education and Supervision, 58(3), 162–176. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceas.12148
Trahan, D. P., Jr., & Keim, J. (2019). Counselor educators’ teaching practices in contemporary society. The Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 12(3). https://repository.wcsu.edu/jcps/vol12/iss3/1
Uzunboylu, H., & Altay, O. (2021). State of affairs in multicultural education research: A content analysis. Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education, 51(2), 1–20.
https://doi.org/10.1080/03057925.2019.1622408
Villalba, J. A., & Redmond, R. E. (2008). Crash: Using a popular film as an experiential learning activity in a multicultural counseling course. Counselor Education and Supervision, 47(4), 264–276. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6978.2008.tb00056.x
Wagner, T. M. (2015). Addressing multicultural issues in the counselor education classroom: A phenomenological analysis [Doctoral dissertation, University of North Texas]. https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc822760
Walker, S. (2015). Relationship-based teaching: A relational ethics led approach to teaching social work. Ethics and Social Welfare, 9(4), 394–402. https://doi.org/10.1080/17496535.2015.1088703
Watts, R. E. (2003). Adlerian therapy as a relational constructivist approach. The Family Journal: Counseling and Therapy for Couples and Families, 11(2), 139–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066480702250169
Watts, R. E. (2013). Adlerian Counseling. In B. J. Irby, G. Brown, R. Lara-Alecio, & S. Jackson (Eds.), The handbook of educational theories (pp. 459–472). IAP: Information Age Publishing.
Yee, T. T. L., Stevens, C. R., & Schulz, L. L. (2016). Exploring master’s students’ social justice consciousness through experiential group: An Adlerian approach. The Journal of Individual Psychology, 72(2), 90–103. https://doi.org/10.1353/jip.2016.0008
Ziomek-Daigle, J., Goodman-Scott, E., Cavin, J., & Donohue, P. (2016). Integrating a multi-tiered system of supports with comprehensive school counseling programs. The Professional Counselor, 6(3), 220–232. https://doi.org/10.15241/jzd.6.3.220
Taylor Irvine, MEd, EdS, LMHC, is a doctoral candidate at Florida Atlantic University. Adriana Labarta, MEd, EdS, LMHC, is a doctoral candidate at Florida Atlantic University. Kelly Emelianchik-Key, PhD, NCC, ACS, LMHC, LMFT, is an associate professor at Florida Atlantic University. Correspondence may be addressed to Taylor Irvine, Florida Atlantic University, 777 Glades Rd. [ED 47], Rm. 271, Boca Raton, FL 33431, tirvine1@fau.edu.






